BIOS 1140 Exam 2 SCC Anatomy
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
cerebrum
controls higher mental functions, divided in to left and right cerebral hemispheres
cerebellum
coordinates repetitive body movements and skeletal activity
where is the insula located?
deep to lateral sulcus
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
- voluntary muscle action
- concentration
- verbal communication
- decision making
- personality
what is the function of the temporal lobe?
- hearing
- smelling
what is the function of the occipital lobe?
- vision
- visual memories
what is the function of the parietal lobe?
- interpretation of touch
- pressure
- pain
- and temperature
what is the function of the insula?
- taste
- memory
what does the central sulcus do?
separates posterior frontal lobe from anterior parietal lobe (splits the brain in half the hamburger way until lateral sulcus)
what does the lateral sulcus do?
separates frontal lobe from temporal lobe
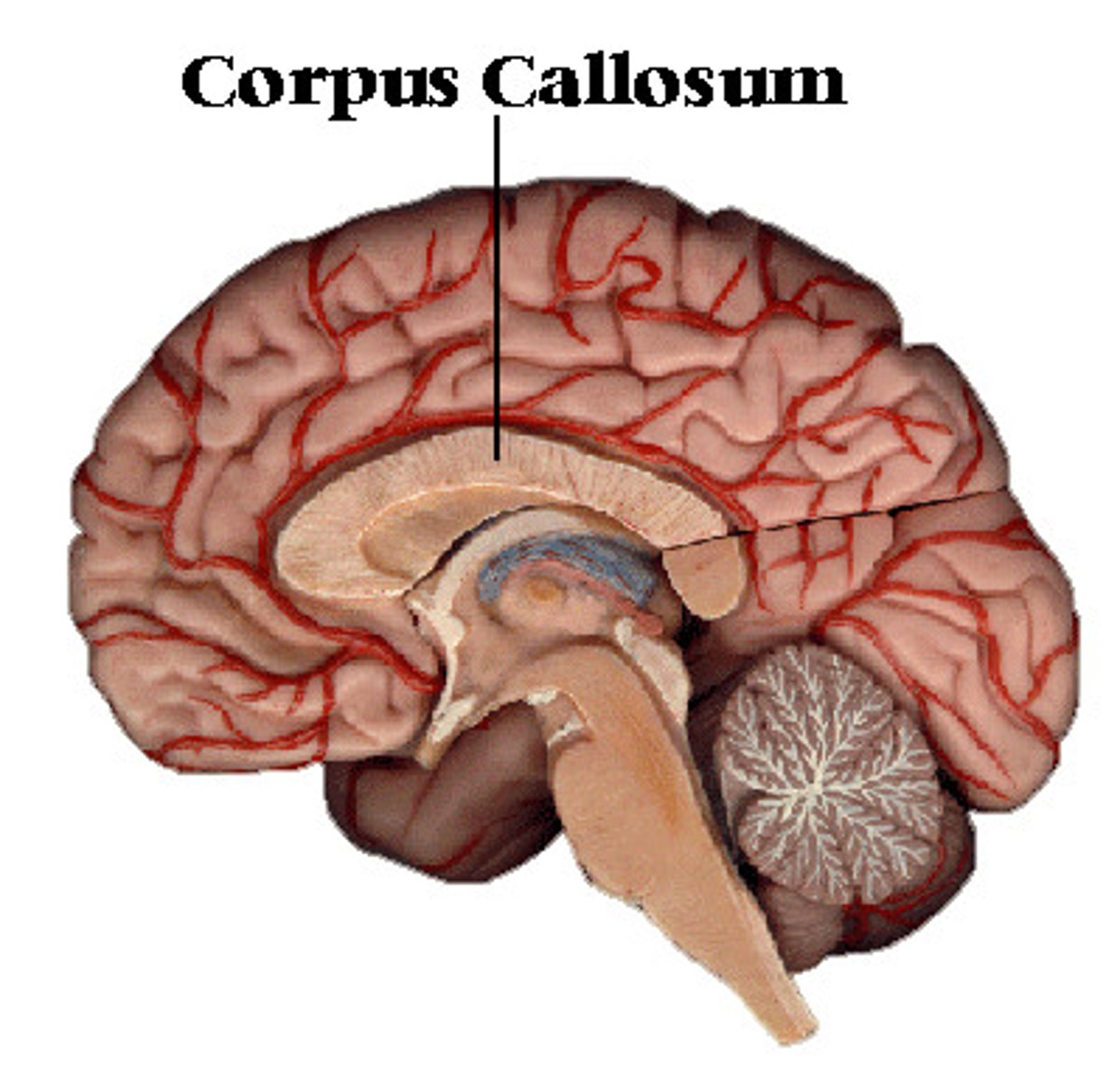
corpus callosum
bundle of nerves that connects the LEFT and RIGHT hemispheres
what are the components of the limbic system?
-cingulate gyrus
-hippocampus
-parahippocampal gyrus
-fornix
-amygdaloid
what is the function of the limbic system?
long term memory
where is the diencephalon located?
inferior to the cerebrum
what does the diencephalon link the cerebrum with?
the brain stem
what are the three divisions of the diencephalon?
- left thalamus
- right thalamus
- hypothalamus
where is the thalamus located?
inferior to the fornix, circular area
what happens in the thalamus?
all sensory information arrives and is stores here
where does sensory information arrive and get stored?
the thalamus
where is the hypothalamus located?
anterior from the inferior edge of the thalamus
what are the six functions of the hypothalamus?
- controls the autonomic nerves
- regulates body temperature
- coordinates activities of endocrine system
- controls emotions
- produces emotions and behavioral drives (feeding and thirst center)
- controls circadian rhythms
what is the pituitary gland connected to?
the hypothalamus via the infundibulum (stalk)
what does the pituitary gland do?
interfaces nervous and endocrine systems, is the major endocrine gland
the brain stem processes information between...
the spinal cord and cerebrum or cerebellum
what components make up the brain stem?
- midbrain
- pons
- medulla oblongata
what is the function of the midbrain?
- maintains involuntary muscle tone
- maintains consciousness
what is the pons made of?
nerve tissue
the pons connects what two structures?
the cerebellum to brain stem
what is the function of the pons?
regulates rate and depth of breathing
what does the medulla oblongata do?
- regulates rhythmic breathing
- regulates BP
- involuntary coughing
- sneezing
- vomiting
where is the corpora quadrigemina located?
the posterior edge of the midbrain
what does the superior colliculus allow us to do?
turn our head towards a visual stimulus
what does the inferior colliculus allow us to do?
turn our head towards an auditory stimulus
where is the pineal gland located?
superior to the corpora quadrigemina
what does the pineal gland do?
secrete melatonin which regulates the circadian rhythms
where is the mammillary body located?
the posterior edge of the hypothalamus
what does the mammillary body do?
- involved in the feeding reflexes of licking
- swallowing
- and chewing.
each cerebral hemisphere contains one...
large lateral ventricle
lateral ventricles are separated by...
a thin medial partition called the septum pellucidum
where is the third ventricle located?
a cavity within the thalamus
lateral ventricles communicate with the..
third ventricle
where is the fourth ventricle located?
between the pons area and the cerebellum
the fourth ventricle becomes continuous with...
the central canal of the spinal cord
the fourth ventricle connects with the...
third ventricle
what makes cerebrospinal fluid?
the choroid plexus
what are the 5 embyonic divisions of the brain?
1. telencephalon
2. diencephalon
3. mesencephalon
4. metencephalon
5. myelencephalon
the cerebral nuclei are embedded in the...
cerebrum
what do the cerebral nuclei do?
direct subconscious activities
what make up the cerebral nuclei?
1. caudate nucleus
2. putamen
3. globus pallidus
4. amygdaloid body
what is the substantia nigra?
mass of NERVES at the superior edge of the pons
what three things are responsible for the physical protection of the brain?
- the bones of the cranium
- cranial meninges
- cerebrospinal fluid
what are the three layers of the cranial meninges?
1. dura mater
2. arachnoid mater
3. pia mater
what is the most superficial layer of the cranial meninges?
the dura mater
what cranial meninges covers the brain?
arachnoid mater
what cranial meninges is attached to the brain surface by astrocytes?
pia mater
what surrounds all exposed surfaces of the CNS?
cerebrospinal fluid
what are the three functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
- cushions delicate neural structures
- supports the brain
- transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products
the most anterior cranial nerve is...
CN1
cranial nerves are a part of the...
PNS, peripheral nervous system
what are the cranial nerves in order?
I. Olfactory
II. Optic
III. Oculomotor
IV. Trochlear
V. Trigeminal
VI. Abducens
VII. Facial
VIII. Vestibulocochlear
IX. Glossopharyngeal
X. Vagus
XI. Accessory
XII. Hypoglossal
what does CN1 (olfactory) do?
- senses smell
what does CNII (optic) do?
- detects vision
what does CNIII (oculomotor) do?
- controls eye muscles for eye movement
- controls focusing of the lens
- pupil constriction
what does CNIV (trochlear) do?
- controls superior oblique muscle of the eye
what does CNV (trigeminal) do?
- detects head and face sensations
- controls chewing movements
what does CNVI (abducens) do?
- controls lateral rectus muscle of the eye
what does CNVII (facial) do?
- detects taste
- allows facial expressions
what does CNVIII (vestibulocochlear) do?
- senses balance
- senses sound
what does CNIX (glossopharyngeal) do?
- controls muscles for swallowing
- detects tongue sensations
what does CNX (vagus) do?
- detects thoracic and abdominal organ sensations
- controls thoracic and abdominal movements
what does CNXI (spinal accessory) do?
- controls trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
what does CNXII (hypoglossal) do?
- controls tongue movement
cranial nerves can be... (/3)
1. sensory nerves
2. motor nerves
3. mixed nerves
sensory nerves (afferent nerves) can...
transmit impulses from the periphery to the CNS (TO BRAIN)
motor nerves (efferent nerves) can...
transmit impulses from the CNS to periphery (FROM BRAIN TO REAL LIFE)
mixed nerves can...
transmit impulses in BOTH directions
what are the SENSORY (afferent) nerves?
- olfactory
- optic
- vestibulocochlear
what are the MOTOR (efferent) cranial nerves?
- oculomotor
- trochlear
- abducens
- spinal accessory
- hypoglossal
what are the MIXED cranial nerves?
- trigeminal
- facial
- glossopharyngeal
- vagus
sensory (afferent) nerves pass through various...
foramina of the skull
what foramina does the olfactory nerve pass through?
olfactory foramina
what canals does the optic nerve pass through?
optic canals
what canal does the vestibulocochlear nerve pass through?
internal acoustic canal
what fissure does the oculomotor nerve pass through?
superior orbital fissure
what fissure does the trochlear nerve pass through?
superior orbital fissure
what fissure does the abducens nerve travel through?
superior orbital fissure
what foramen does the spinal accessory nerve pass through?
jugular foramen
what canal does the hypoglossal nerve pass through?
hypoglossal canal
what does the glossopharyngeal nerve pass through?
jugular foramen for BOTH sensory and motor
what does the vagus nerve pass through?
jugular foramen for BOTH sensory and motor
what does the facial nerve pass through?
internal acoustic canal and the stylomastoid foramen for BOTH sensory and motor
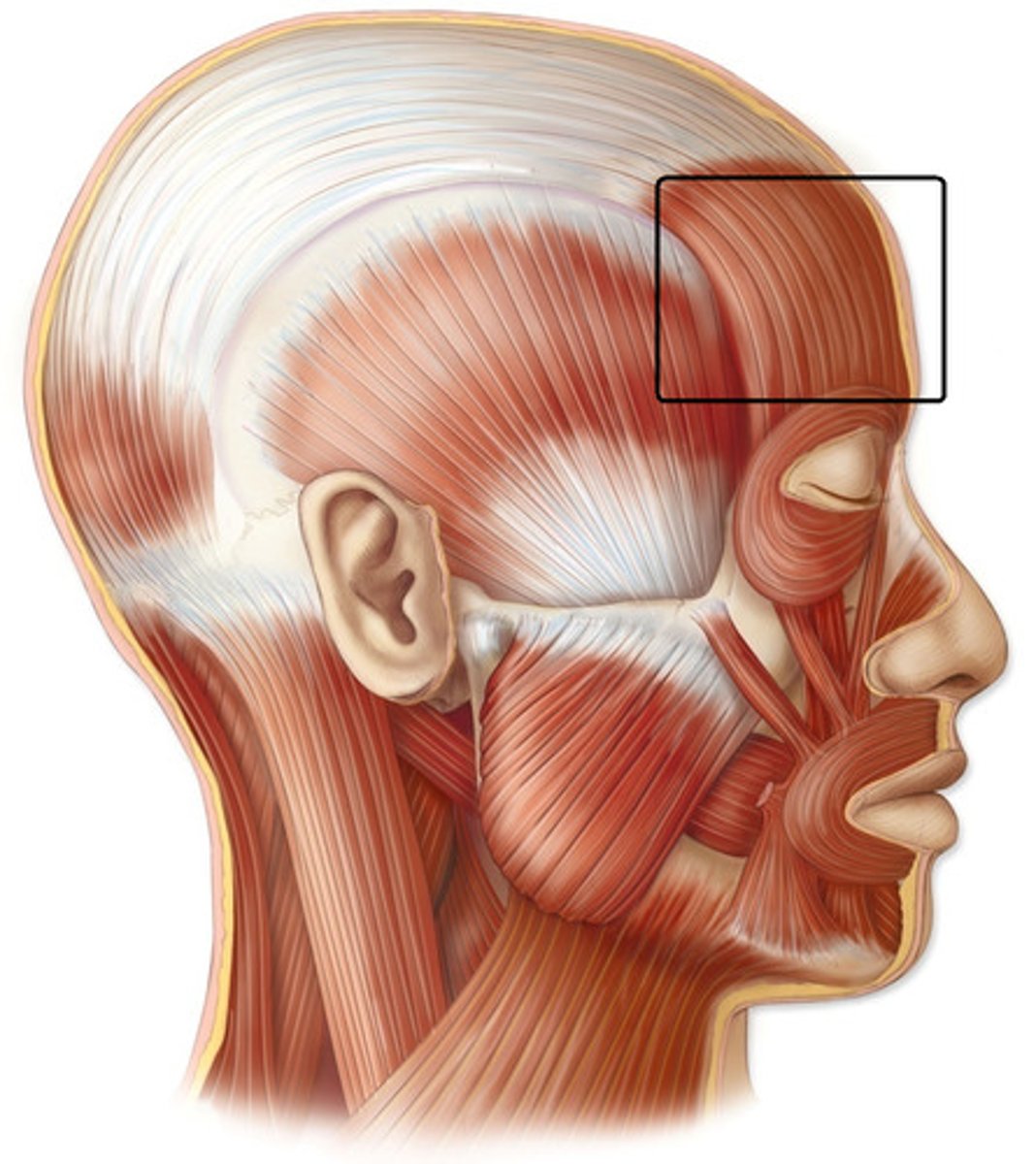
frontalis
muscles that covers the frons area
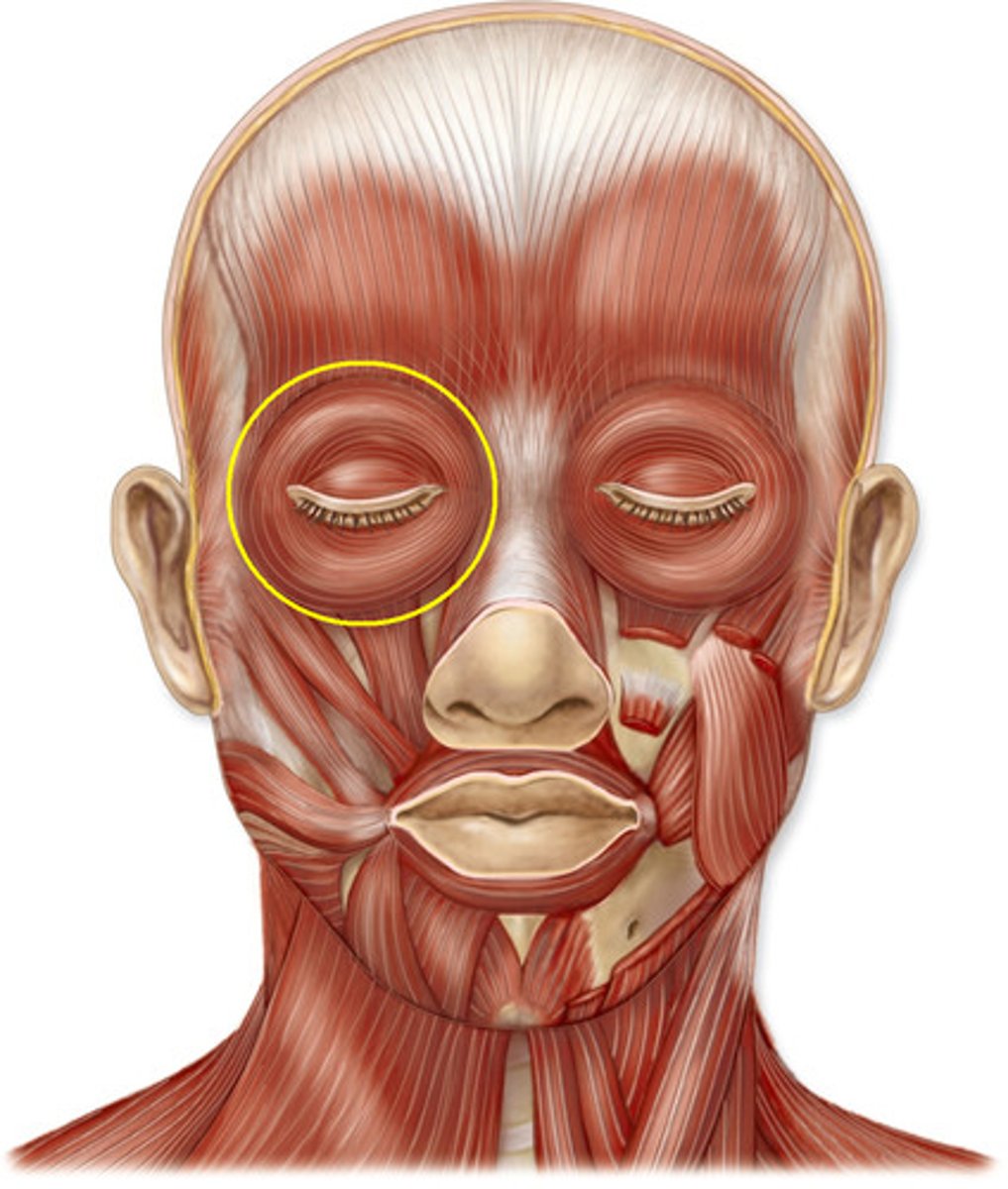
orbicularis oculi
muscle that encircles the orbit of the eye
nasalis
muscle that covers the bridge of the nose
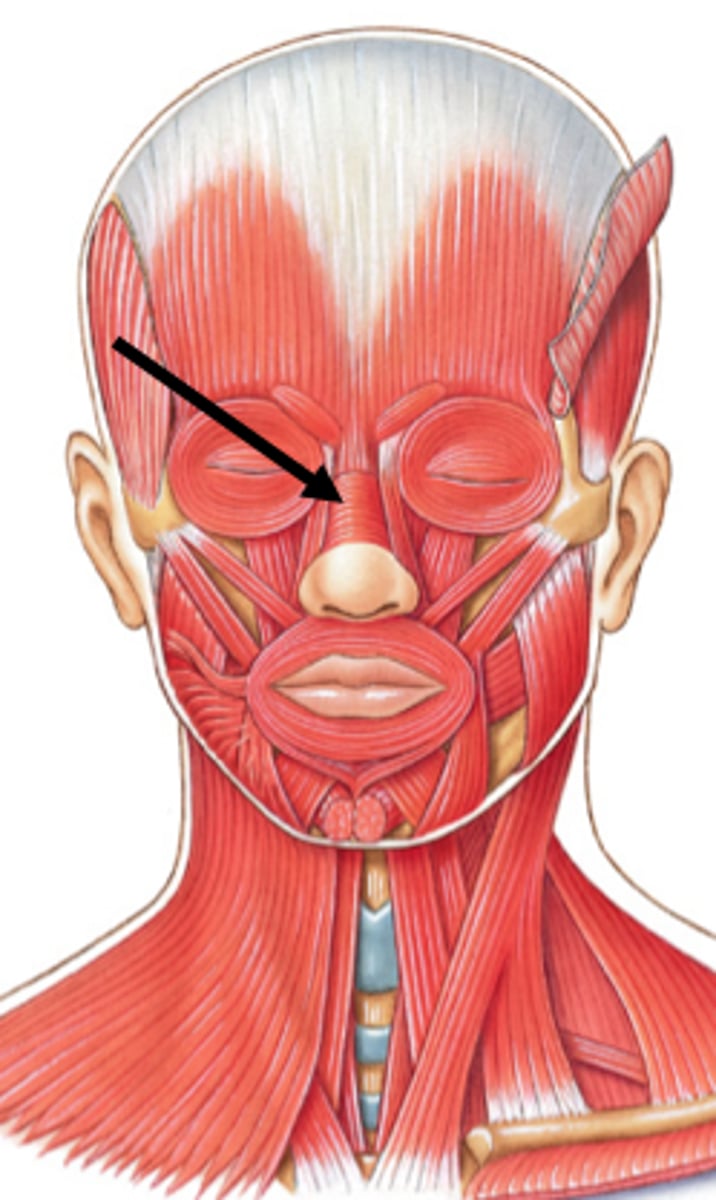
orbicularis oris
muscle that encircles the mouth
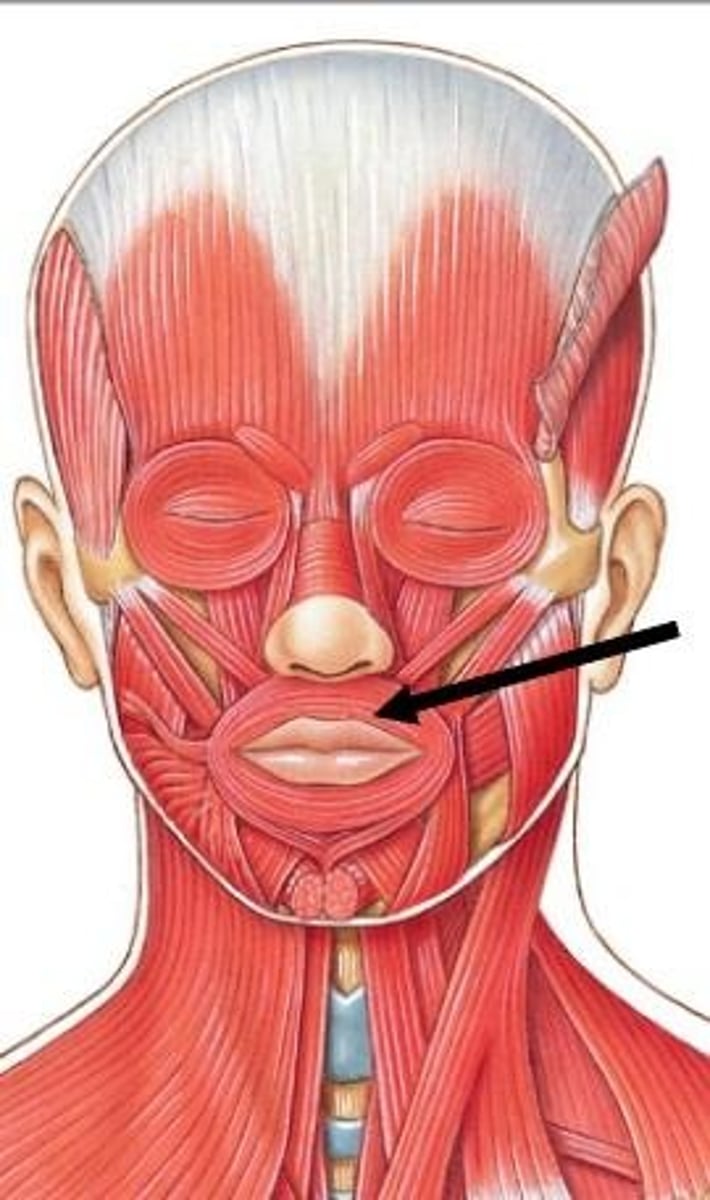
mentalis
muscle that is in the center of the chin
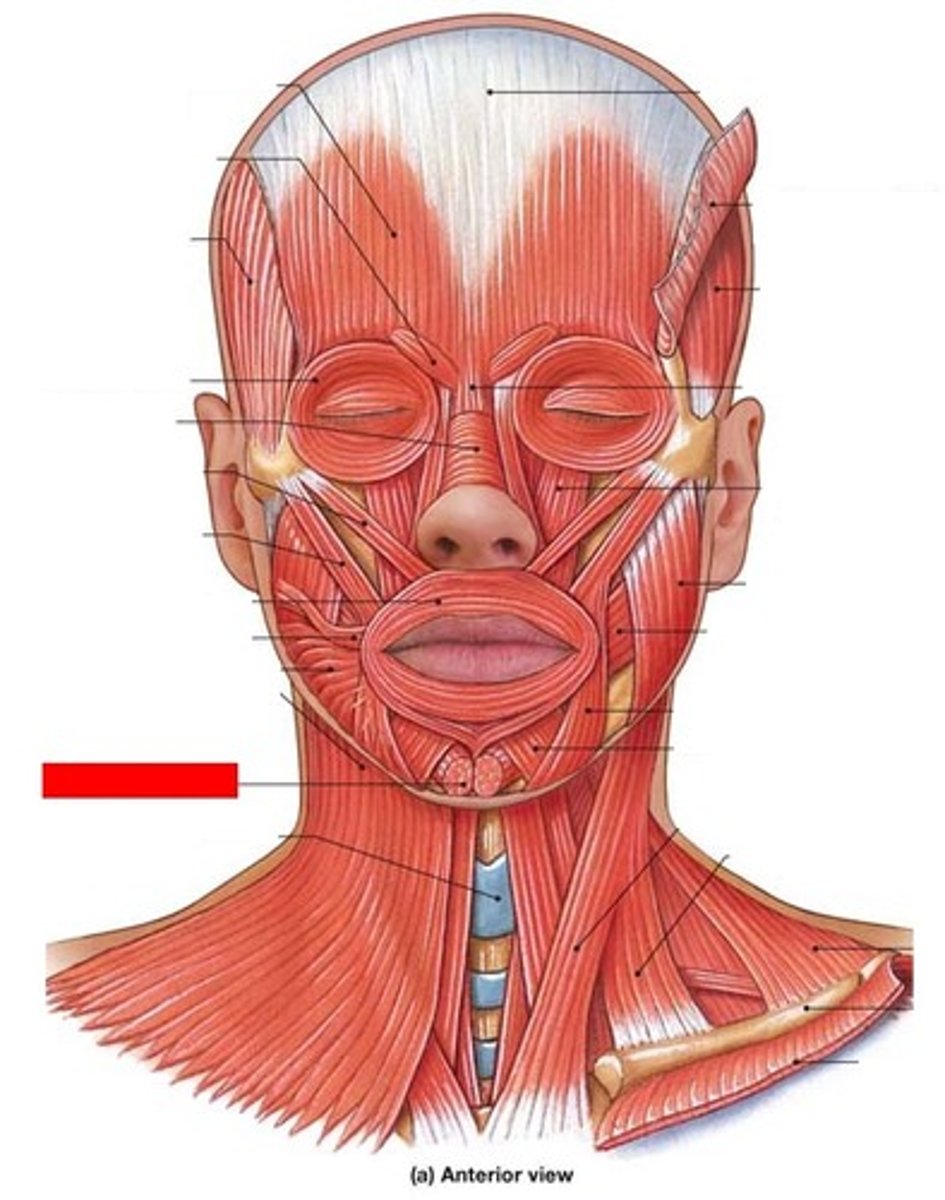
depressor labii inferioris
muscle that is lateral to the mentalis
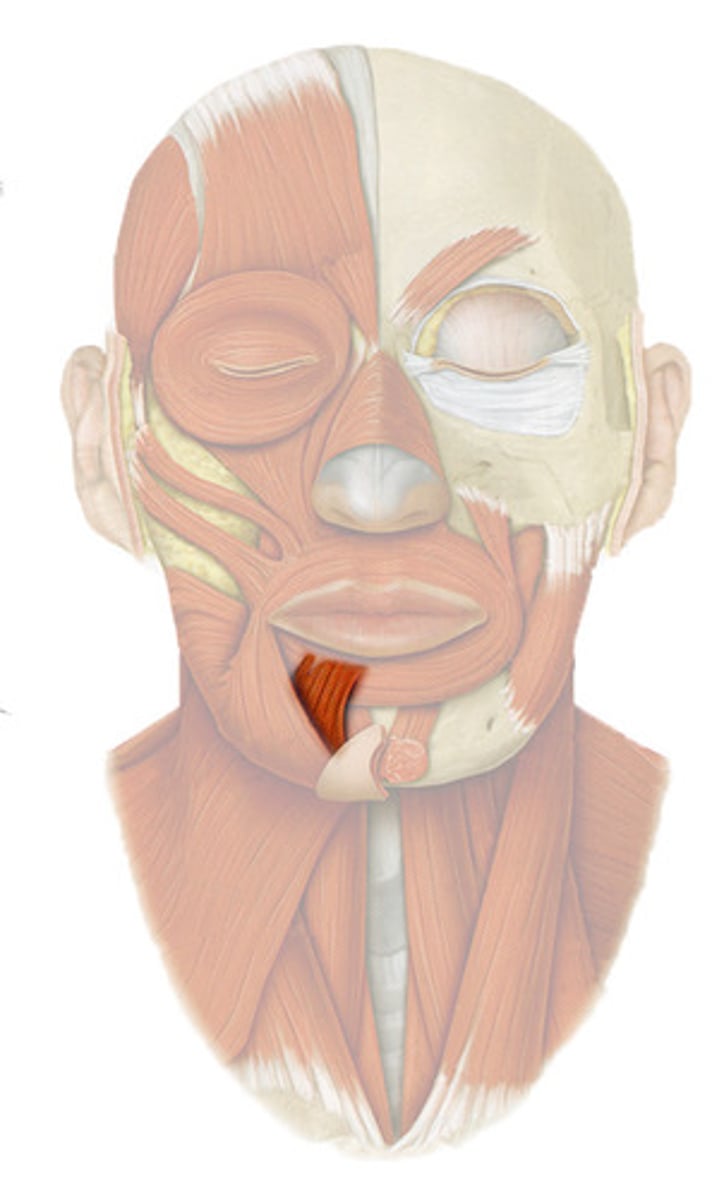
depressor anguli oris
muscle that is lateral to the depressor labii inferioris
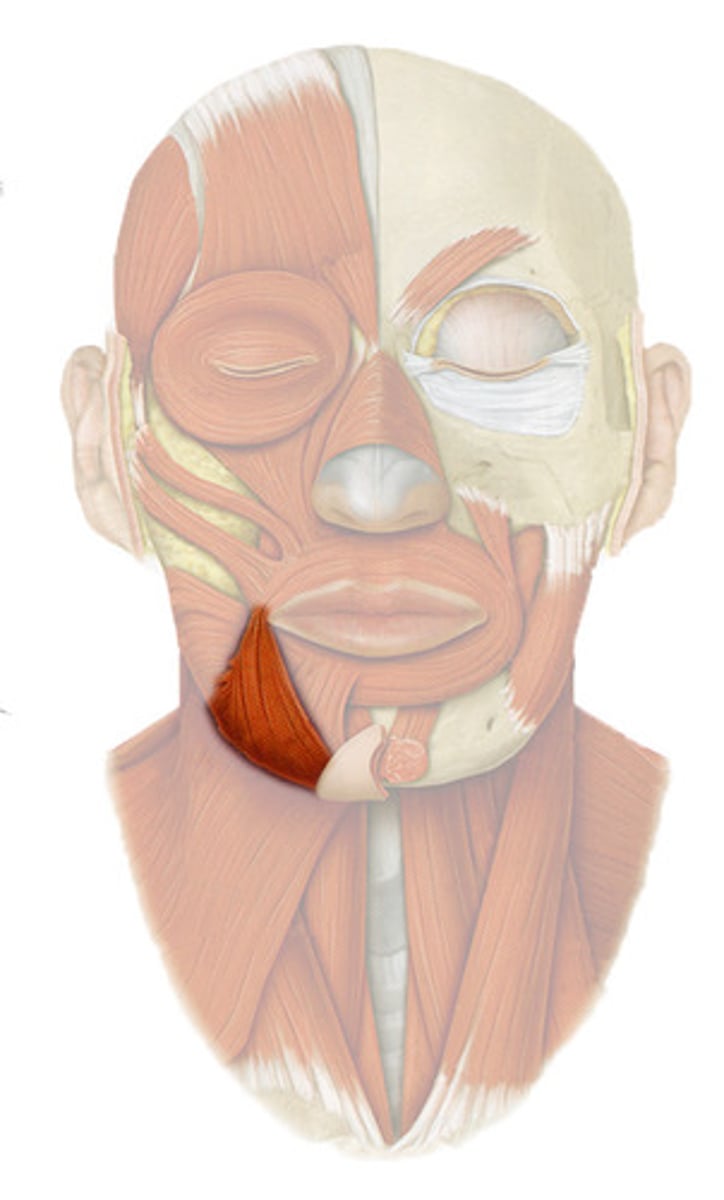
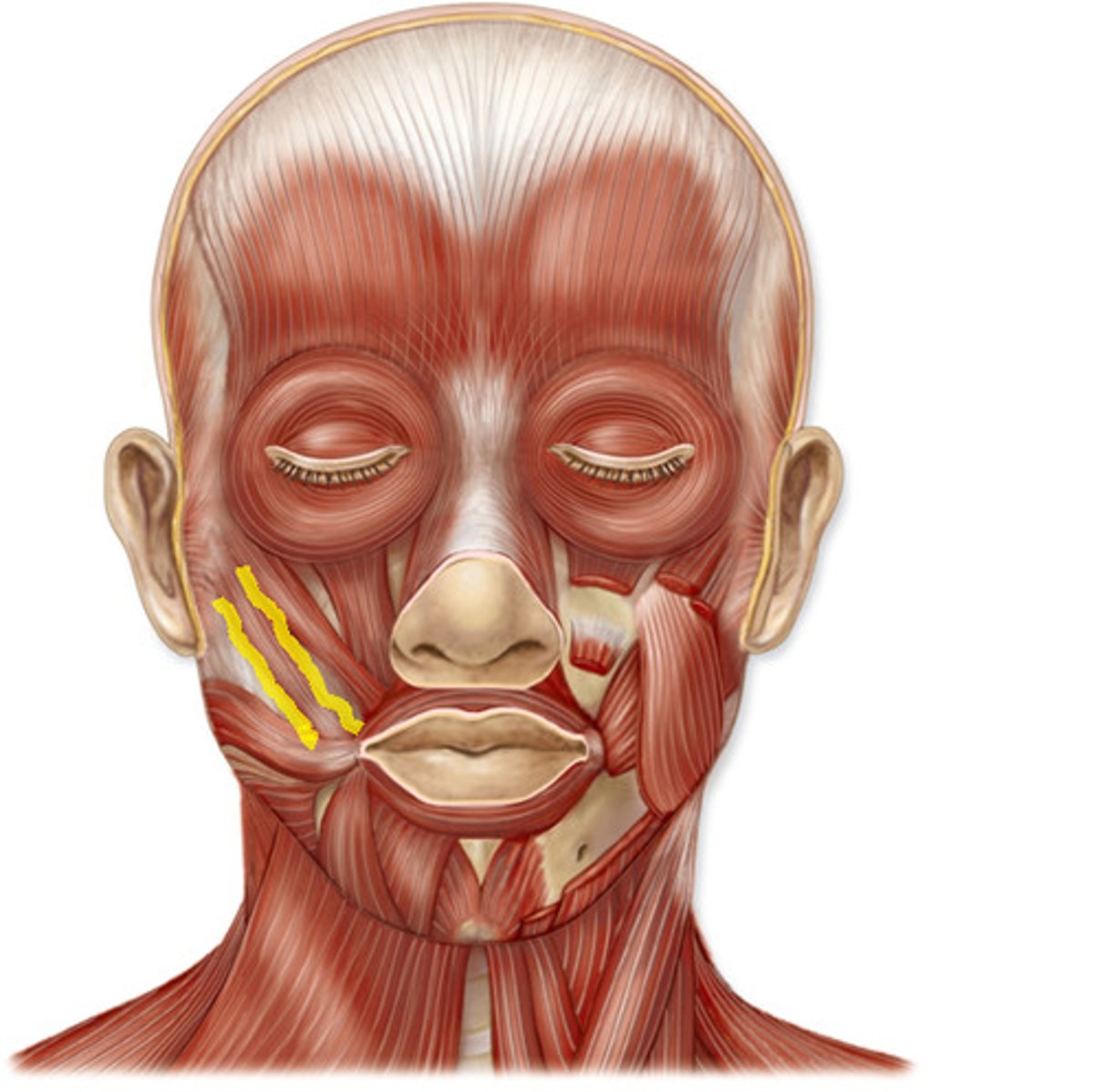
zygomaticus minor
muscle that extends from the orbicularis oris to the zygomatic bone
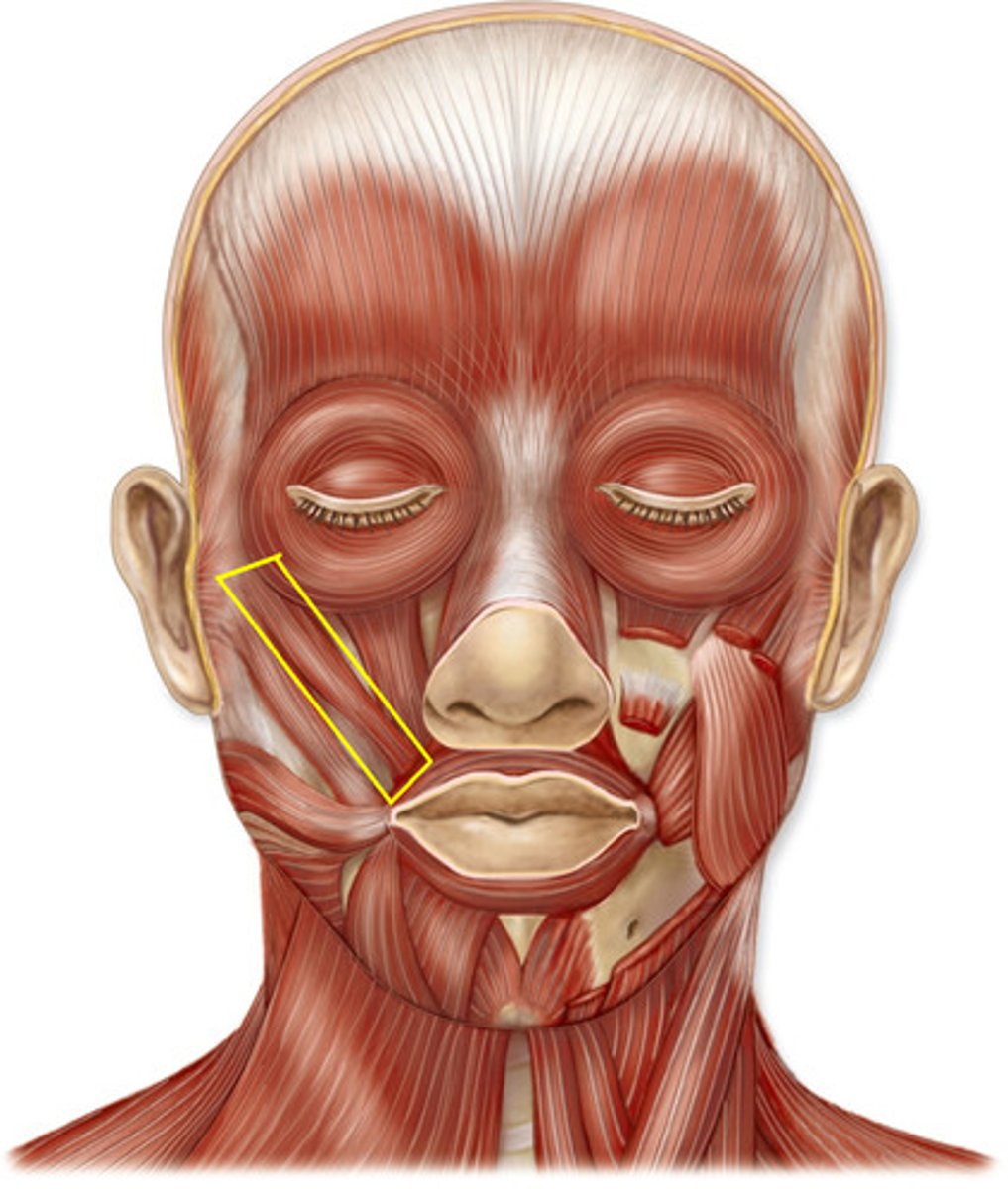
zygomaticus major
muscle that extends from the corner of the mouth to the zygomaticus bone (it is inferior to the zygomaticus minor)