Neoplasia #2: Classifications of Cancer, Tumor Spread, and Grading vs. Staging
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
4 major classifications of cancer
Carcinoma, sarcoma, melanoma, and lymphoma/leukemia
What are carcinomas?
Carcinomas are malignant tumors of
epithelial surfaces
organs with epithelial-lined ducts/glands
Endocrine glands (I.e. thyroid)
Carcinomas are positive for
cytokeratin immunostains!!!!!
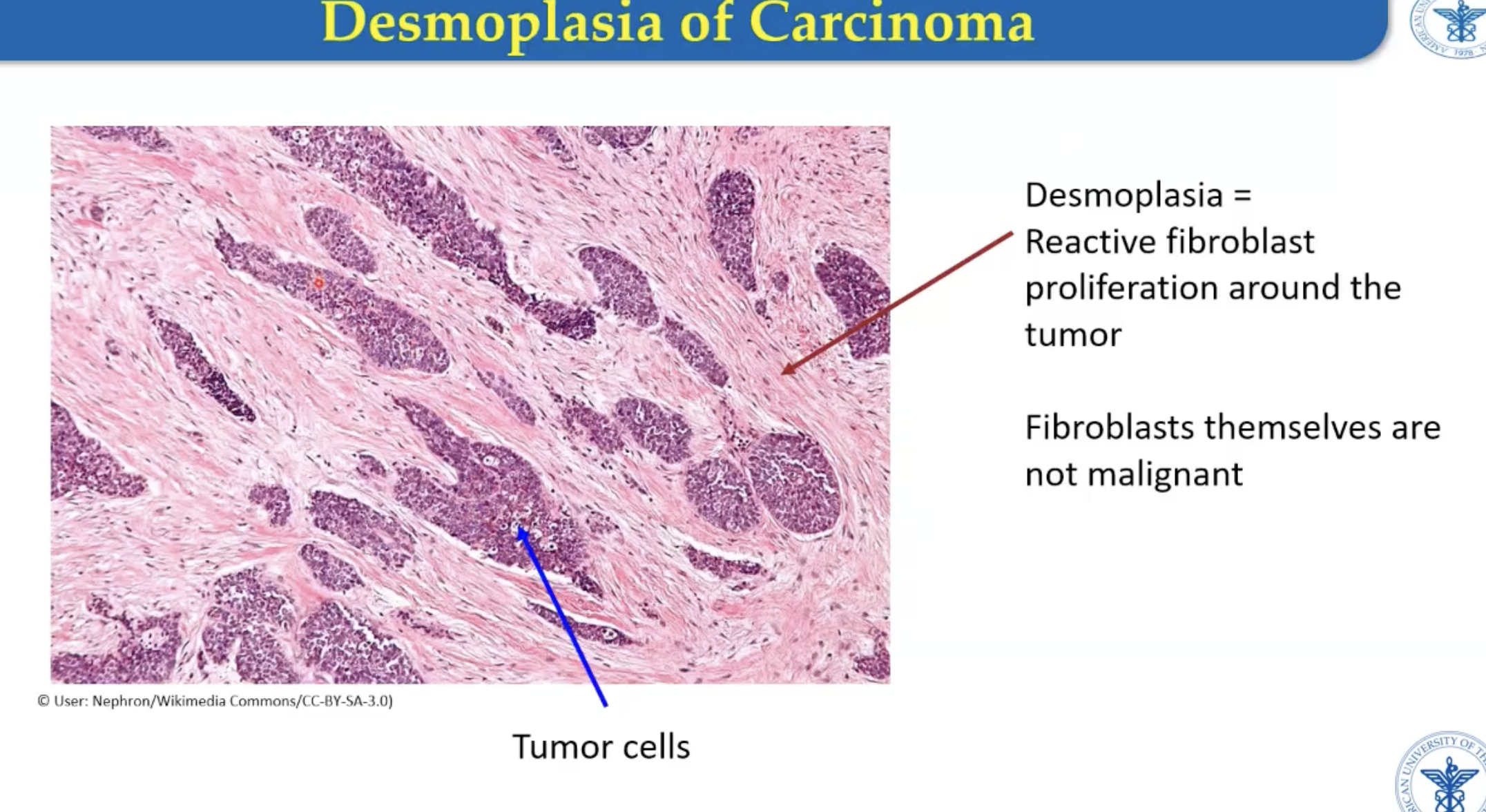
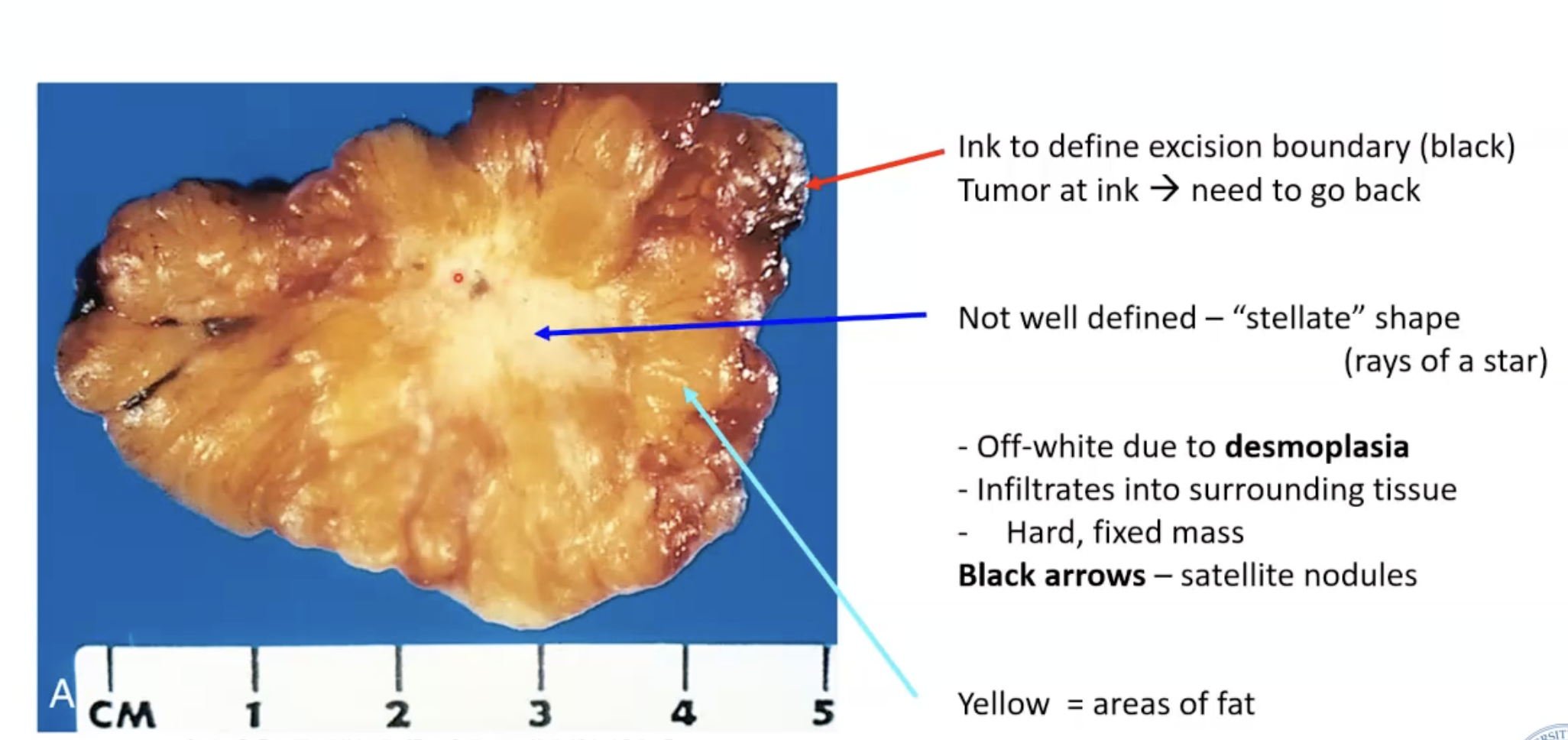
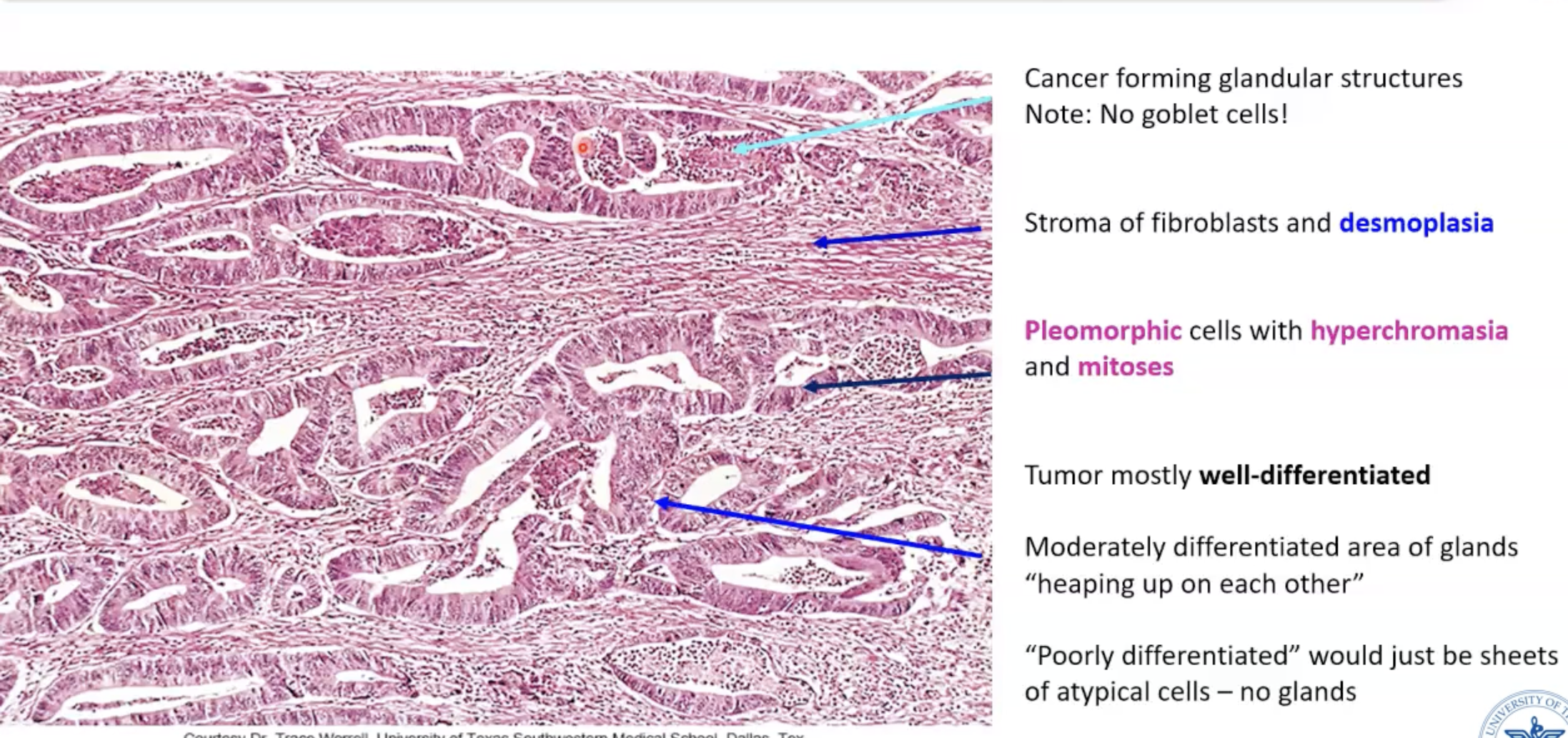
What is desmoplasia?
Fibroblast reactive proliferation to create collagen (non-neoplastic)
Fibroblasts themselves are not malignant
On cut section, tumor fibrosis appears white/gray
** Characteristic of carcinomas
Remember: not the same as capsules (which is a feature of benign tumors)
Carcinomas are described as
polygonal
What is adenocarcinoma?
Invasive carcinomas that form glandular configuration
Example: ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) - adenocarcinoma that has NOT breeched the basement membrane of the glandular epithelium
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
Carcinomas that form solid nests of cells with: distinct borders, intercellular bridges, and pink keratinized cytoplasm
Characteristic feature of squamous cell carcinoma
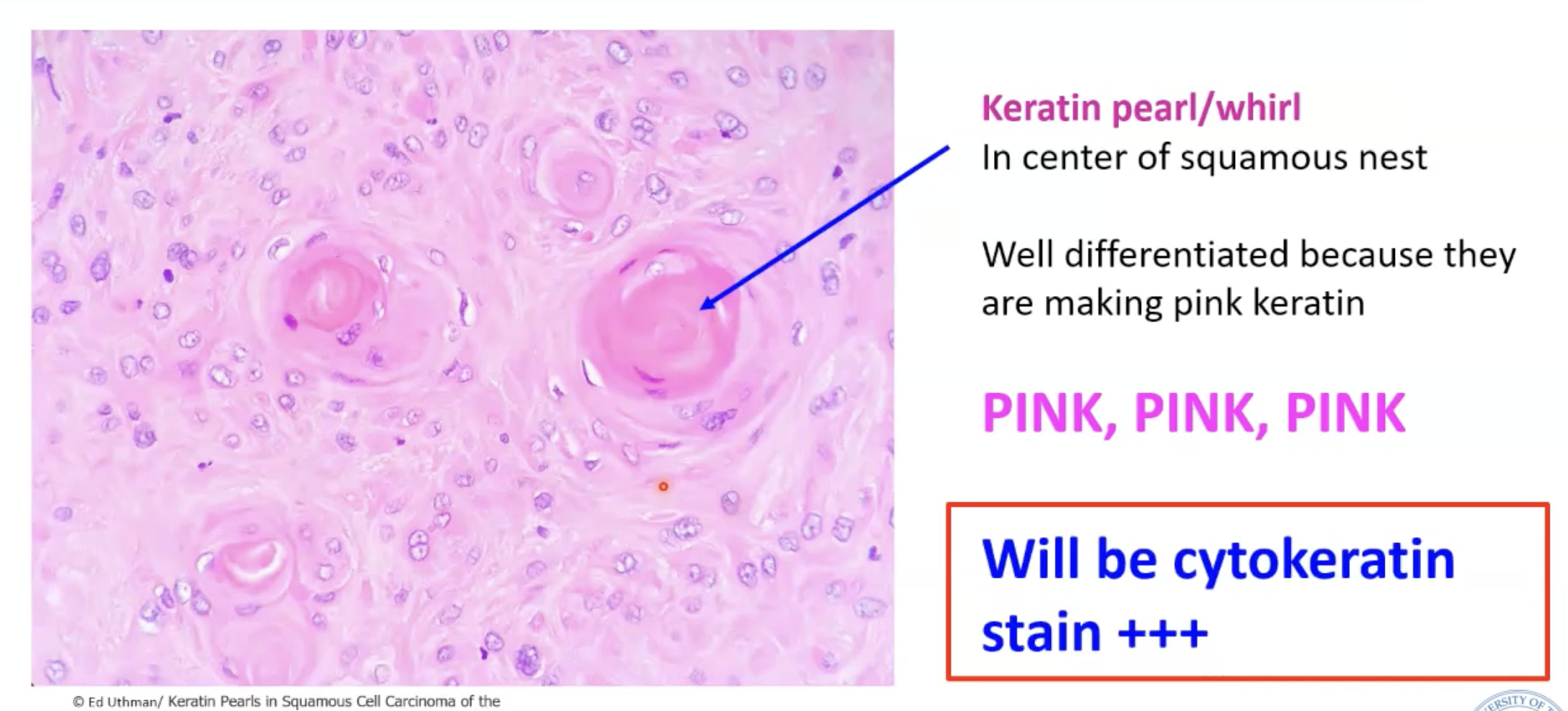
Create keratin pearls/whirls
Cytokeratin positive stain
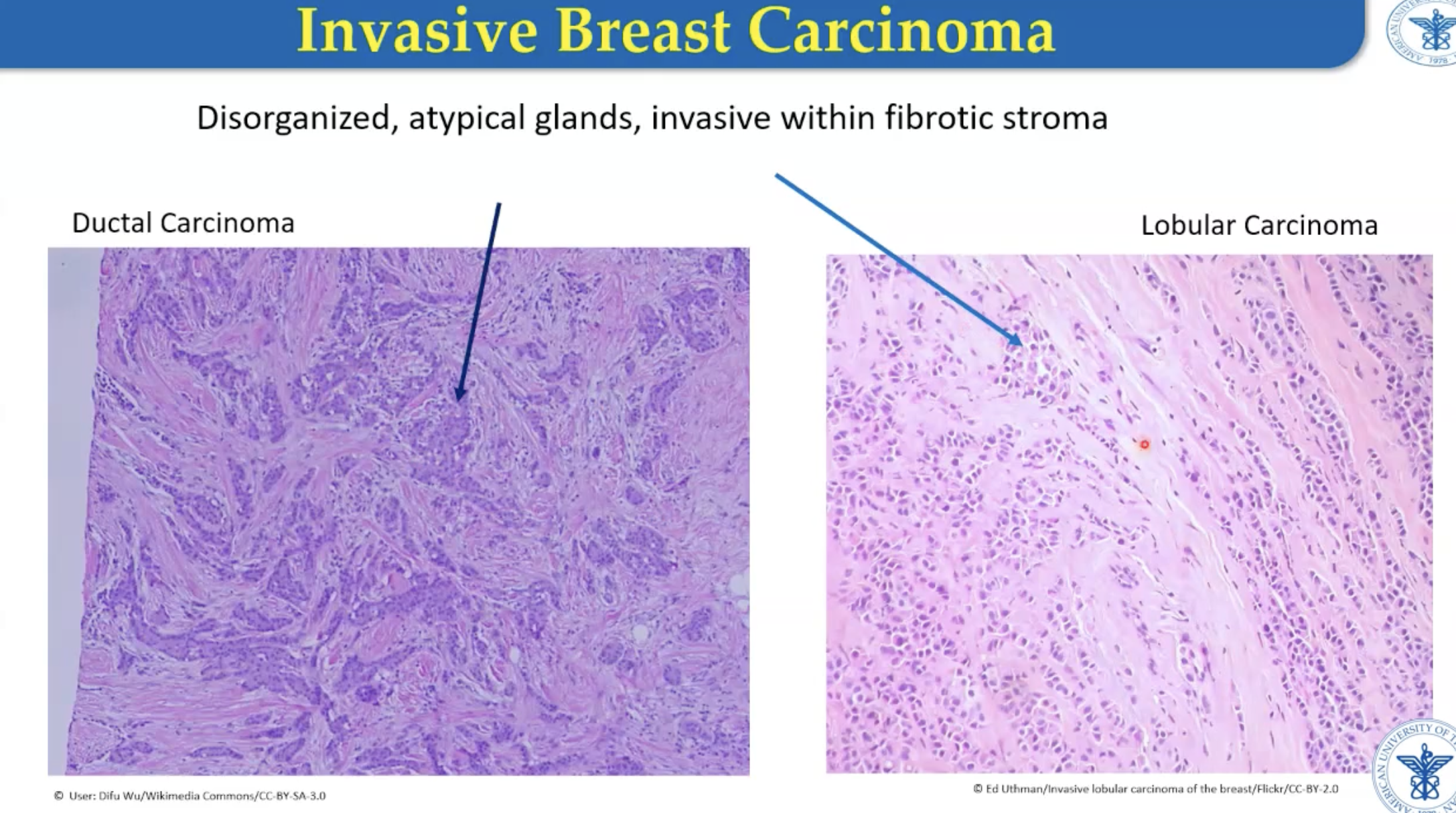
What is ductal breast cancer?
Cancer from glands that carry milk to nipple
** BRCA1 and BRCA 2 are associated with hereditary cases.
What is lobular breast cancer?
Cancer from lobules that produce milk (connects to ducts)
70-80% are invasive ductal
** BRCA1 and BRCA 2 are associated with hereditary cases.
Breast adenocarcinoma
Invasive breast carcinoma
Lobular - cells like to line up one behind the other
Disordered and atypical
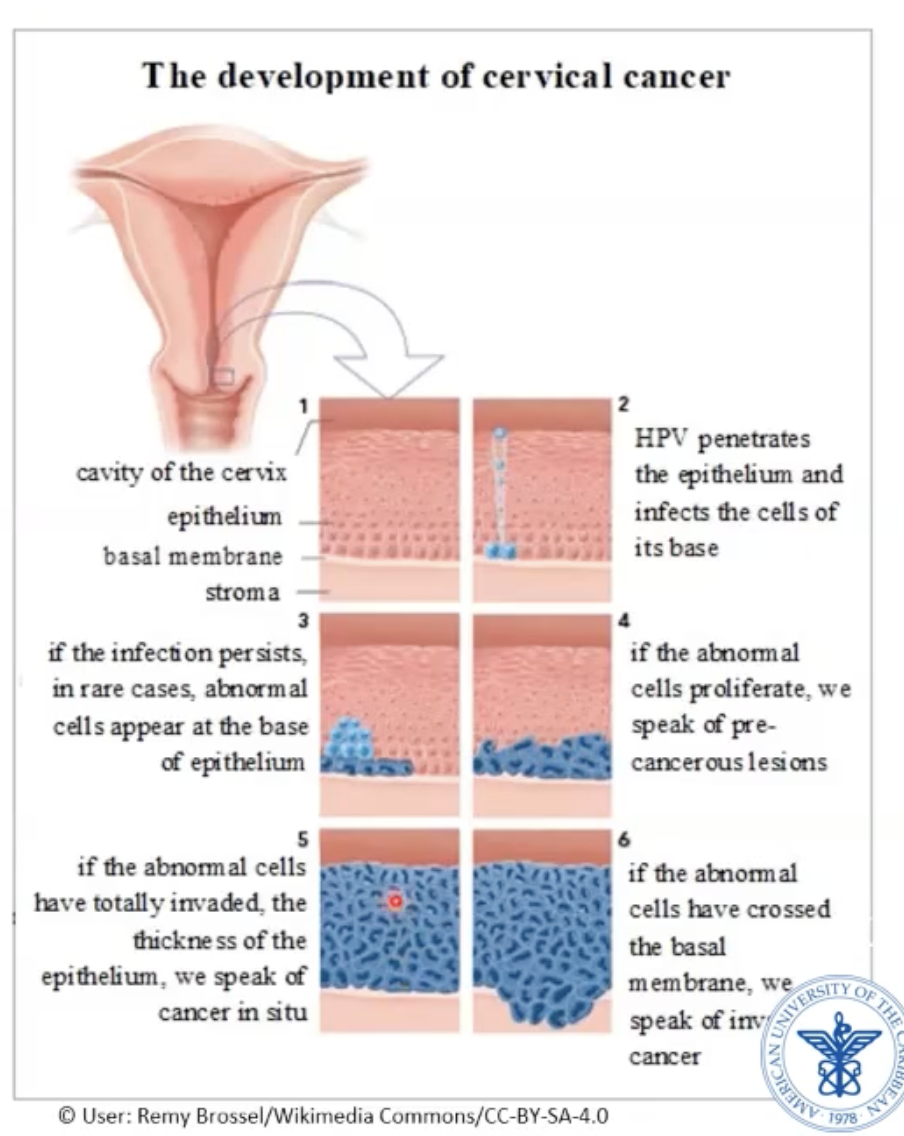
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma
Starts in transition zone - transition from endocervix to exocervix
Columnar → squamous
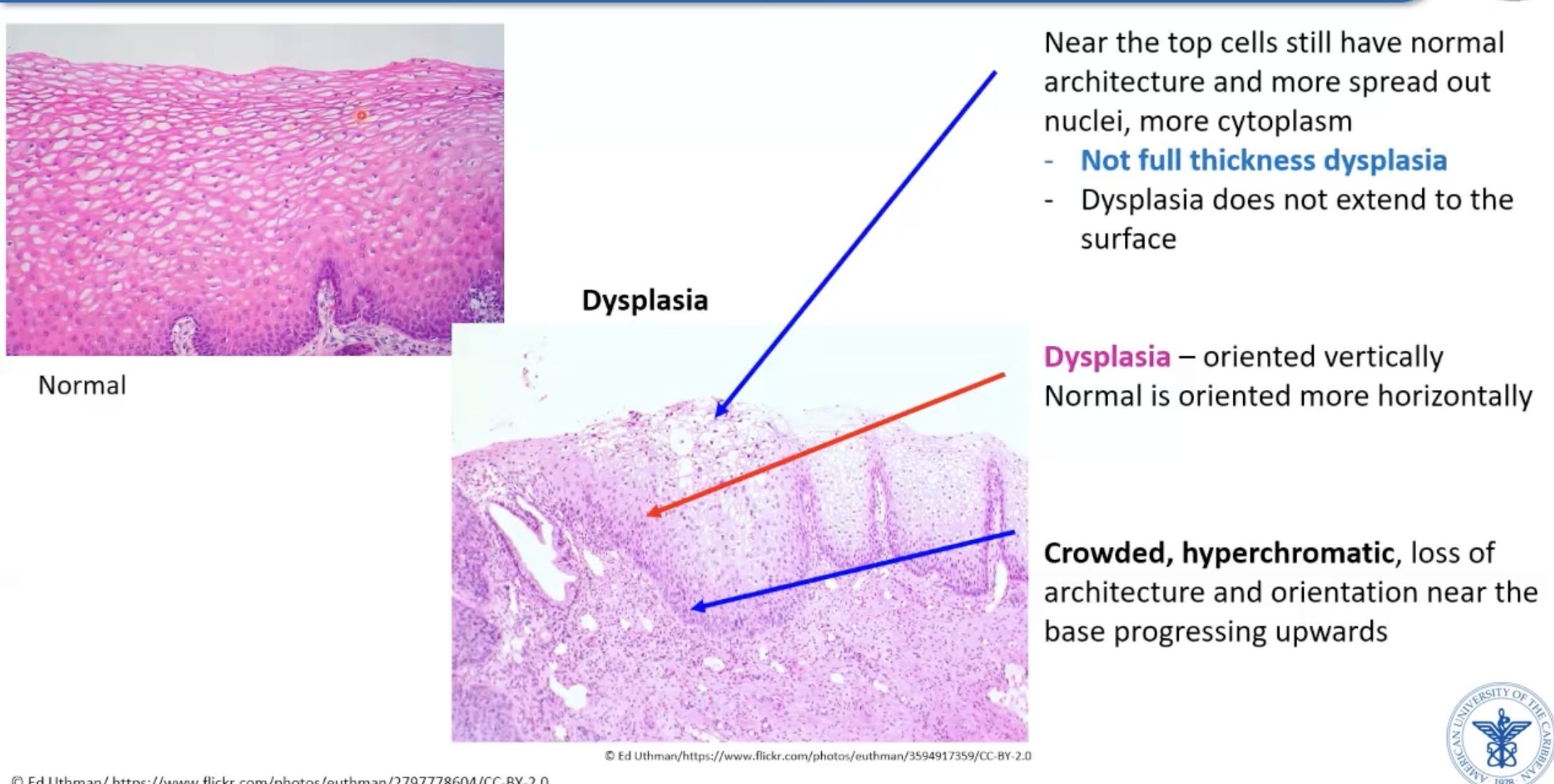
Starts as dysplasia (not full thickness atypic)
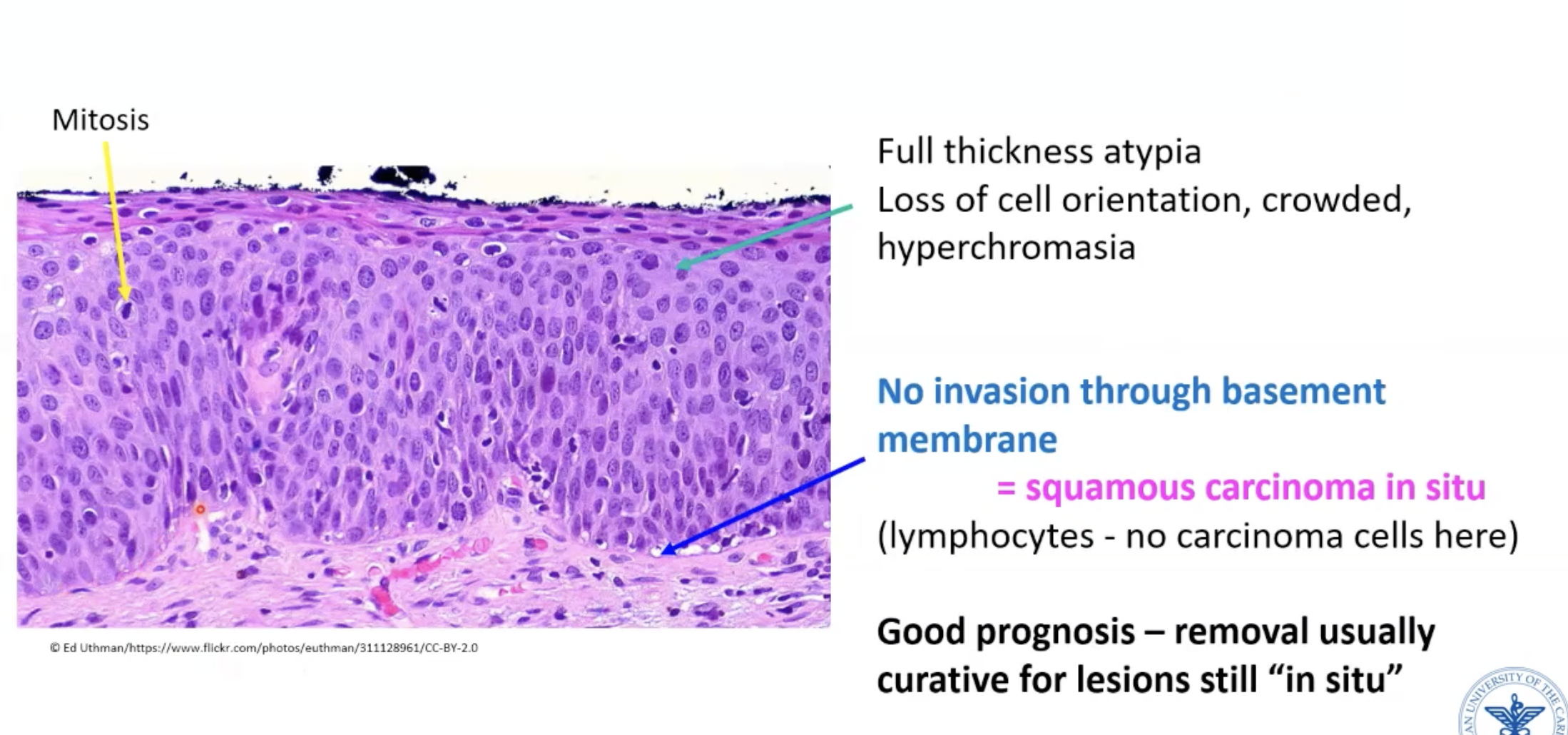
Progresses to squamous cell carcinoma in situ
Progresses to invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Cervical dysplasia histology
Cervical carcinoma in-situ histology
Fully atypical cells from base to apical surface
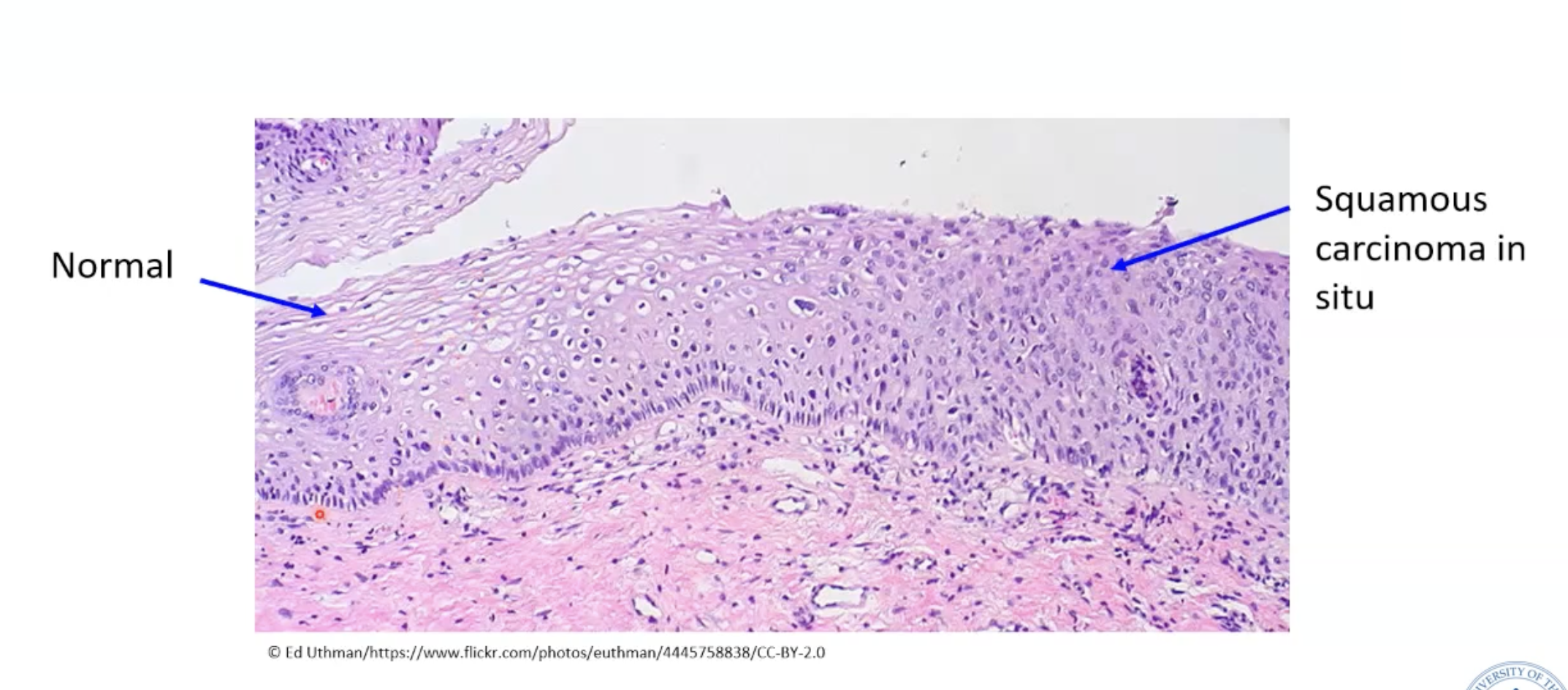
Cervix normal vs squamous carcinoma in situ histology
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma
KERATIN PEARLS!
Keratin is really bright pink
“Round nests” usually indicates invasive
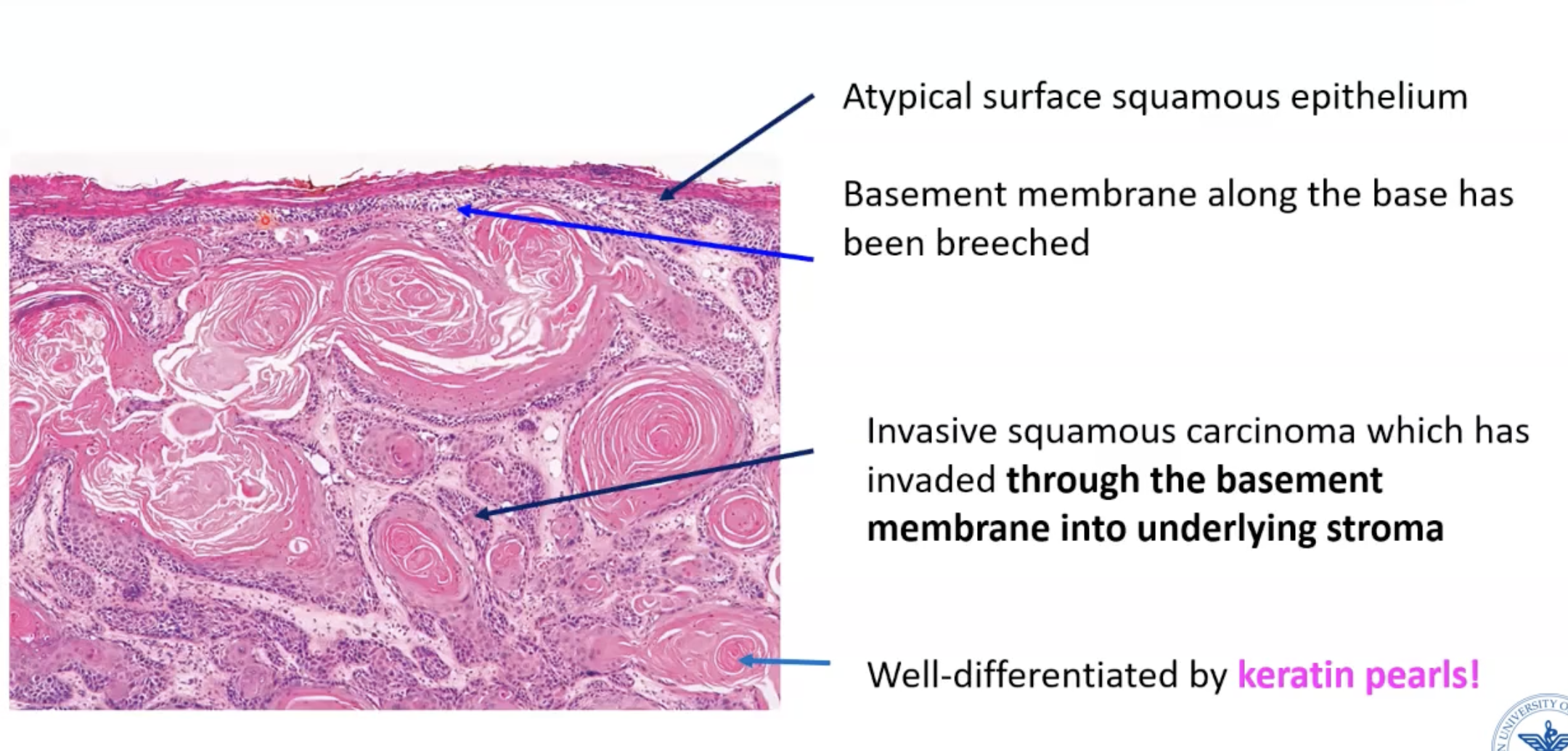
Well-differentiated invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Should be able to to identify this easily!!!!
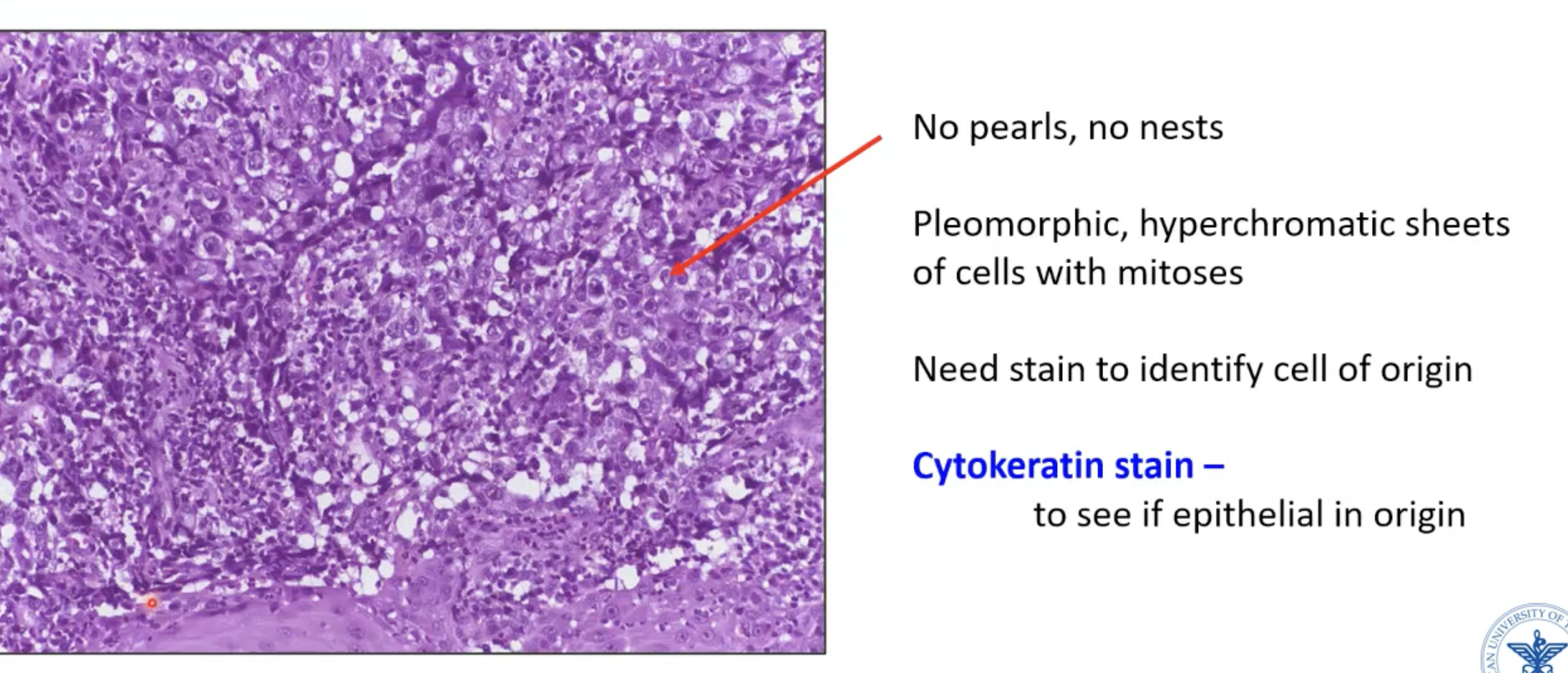
Poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
Cell sizes are very different
No pearls/nests
Cytokeratin stain would prove whether it is a carcinoma or not
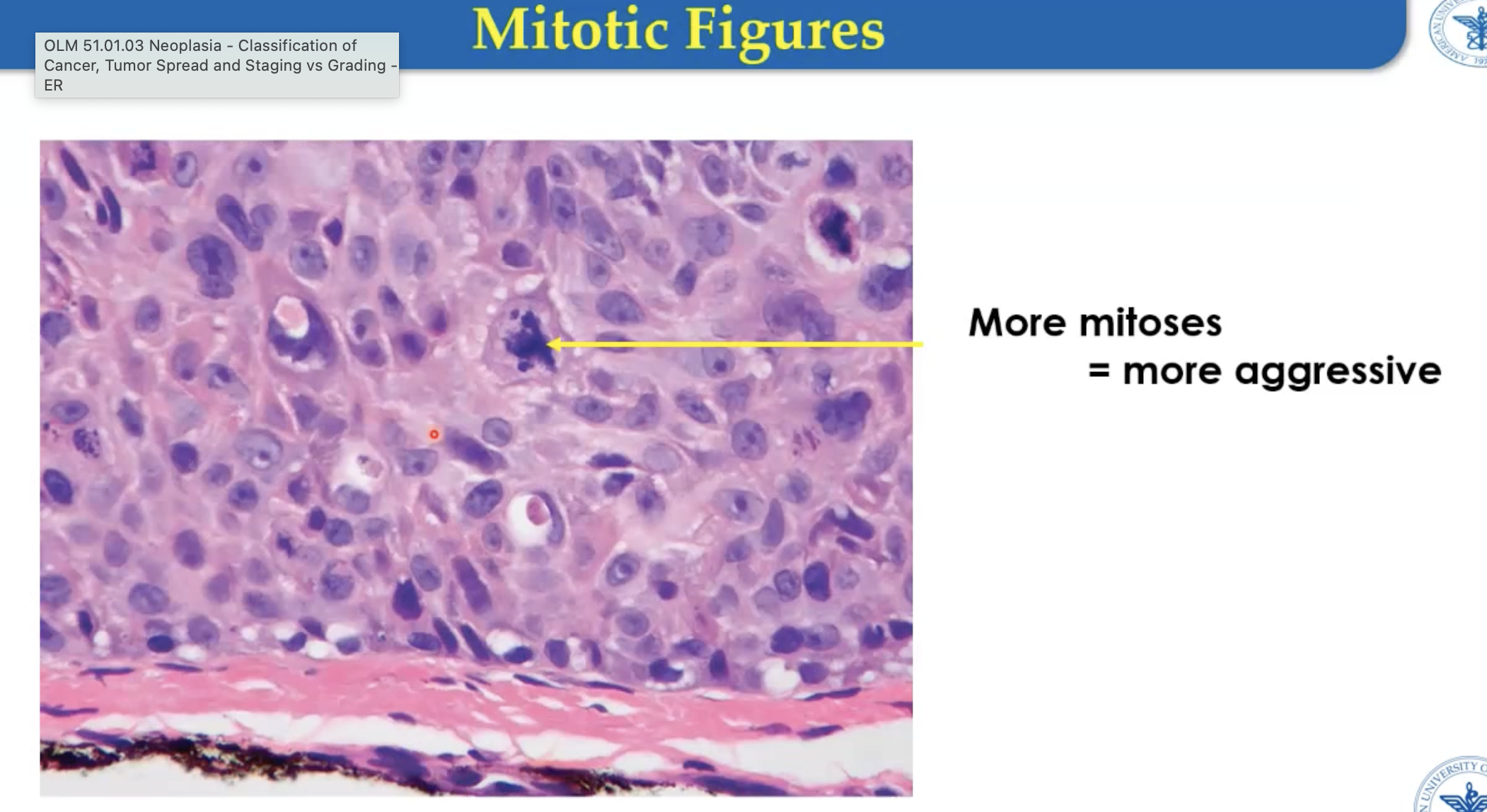
Mitotic figures
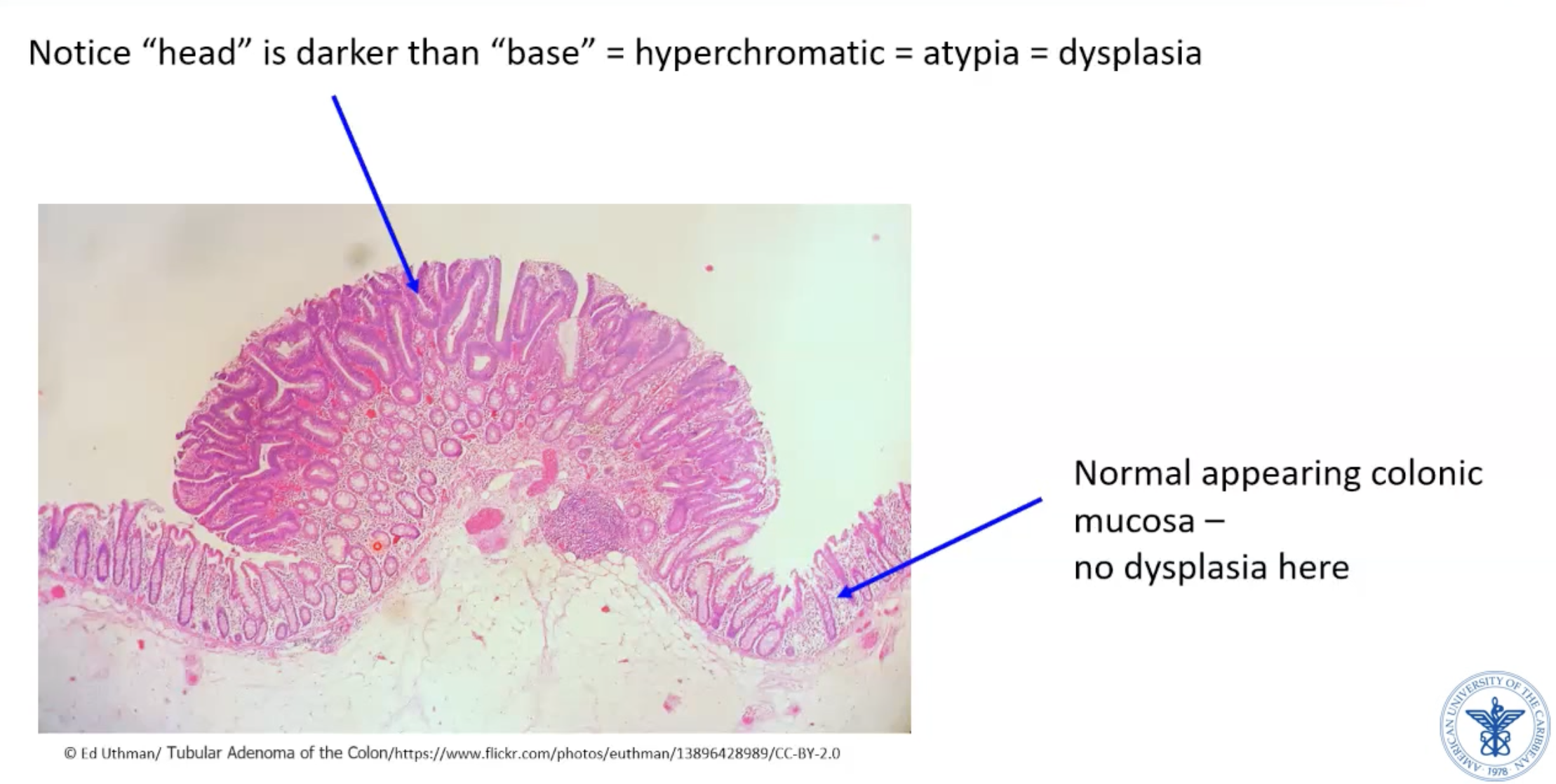
Colonic polyp
Growth above epithelium
Can be benign or precursor to malignancy
** Tubular adenoma - usually benign polyp
Colonic polyp - tubular adenoma histology
Colonic adenocarcinoma
Histiogenesis of sarcomas
Arise from soft tissue (CT - components of mesoderm)
Examples: nerves, muscle, fat, bone, cartilage, fibroblasts, blood vessels
Generally big and “fleshy fish”, soft → no desmoplasia
What are the boards description for sarcomas?
Cells are very pleomorphic and spindle-shaped
Sarcoma histology
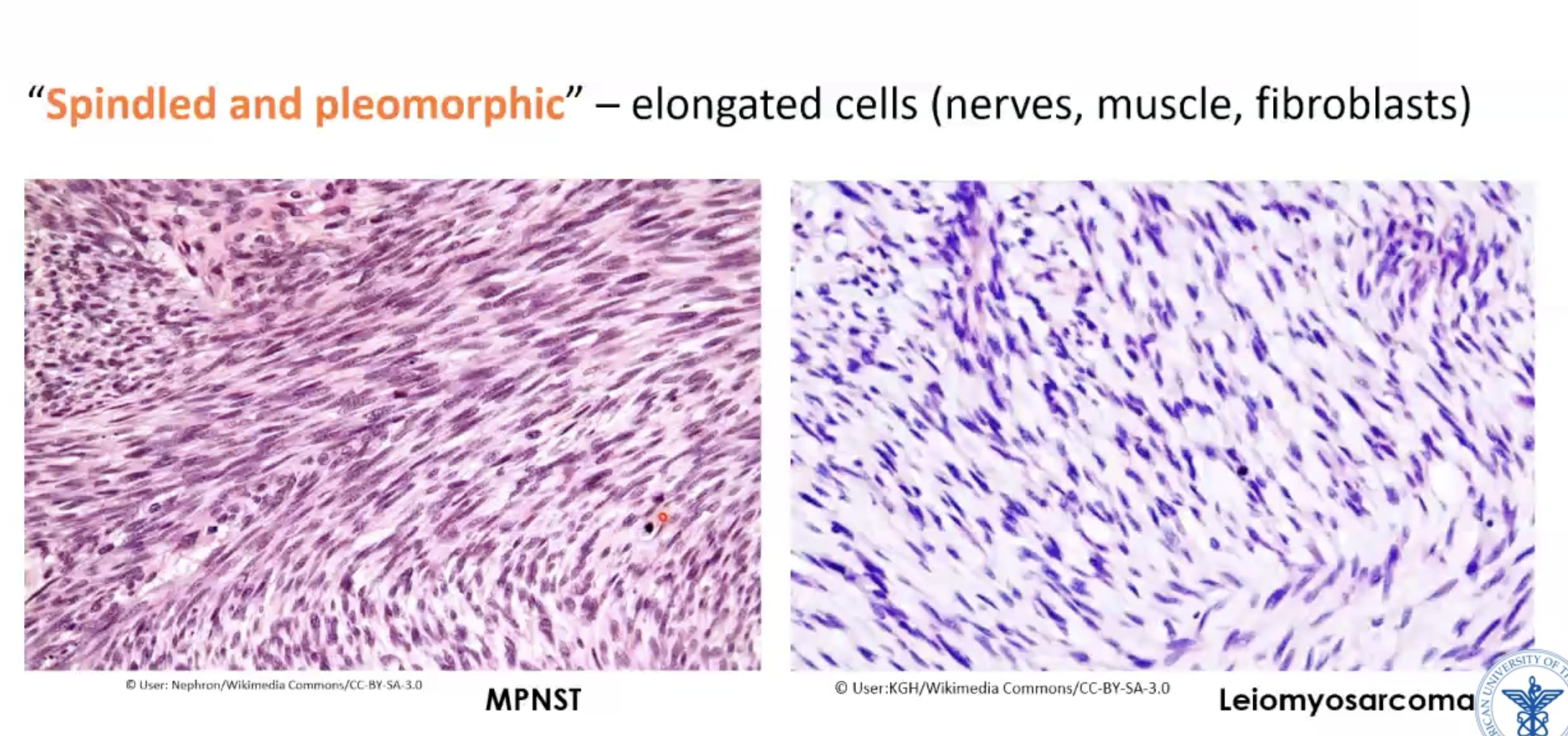
Leiomyosarcoma histology
Smooth muscle tumor
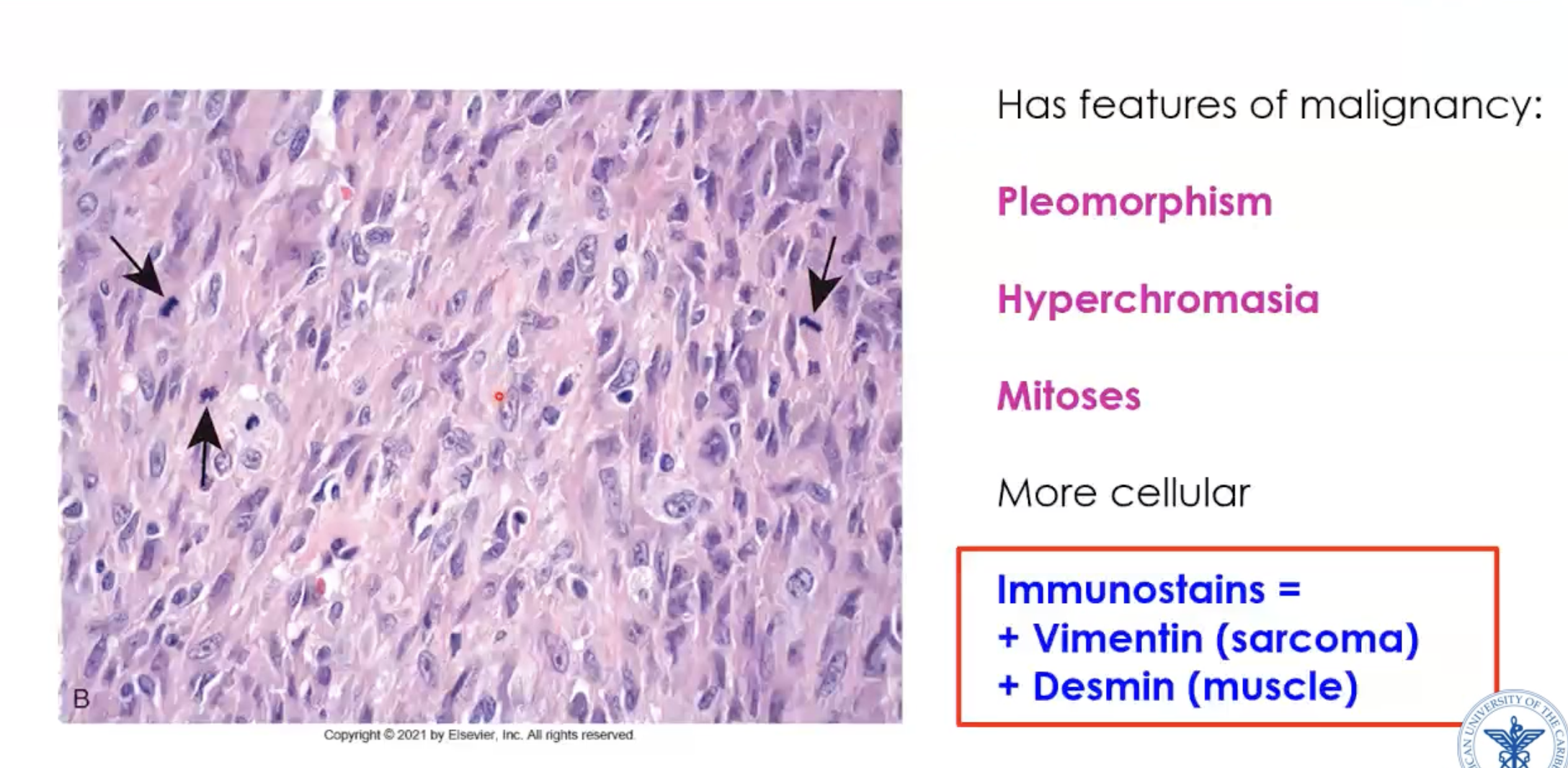
What stains are positive in leiomyosarcoma?
Immunostains: vimentin positive (sarcoma - mesoderm origin) and desmin (muscle)
Vimentin (sarcoma) + desmin (muscle) =
Leiomyosarcoma
Vimentin (sarcoma) + S100 (nerve) =
Malignant nerve tumor
Vimentin (sarcoma) + CD31 (vessel) =
Angiosarcoma
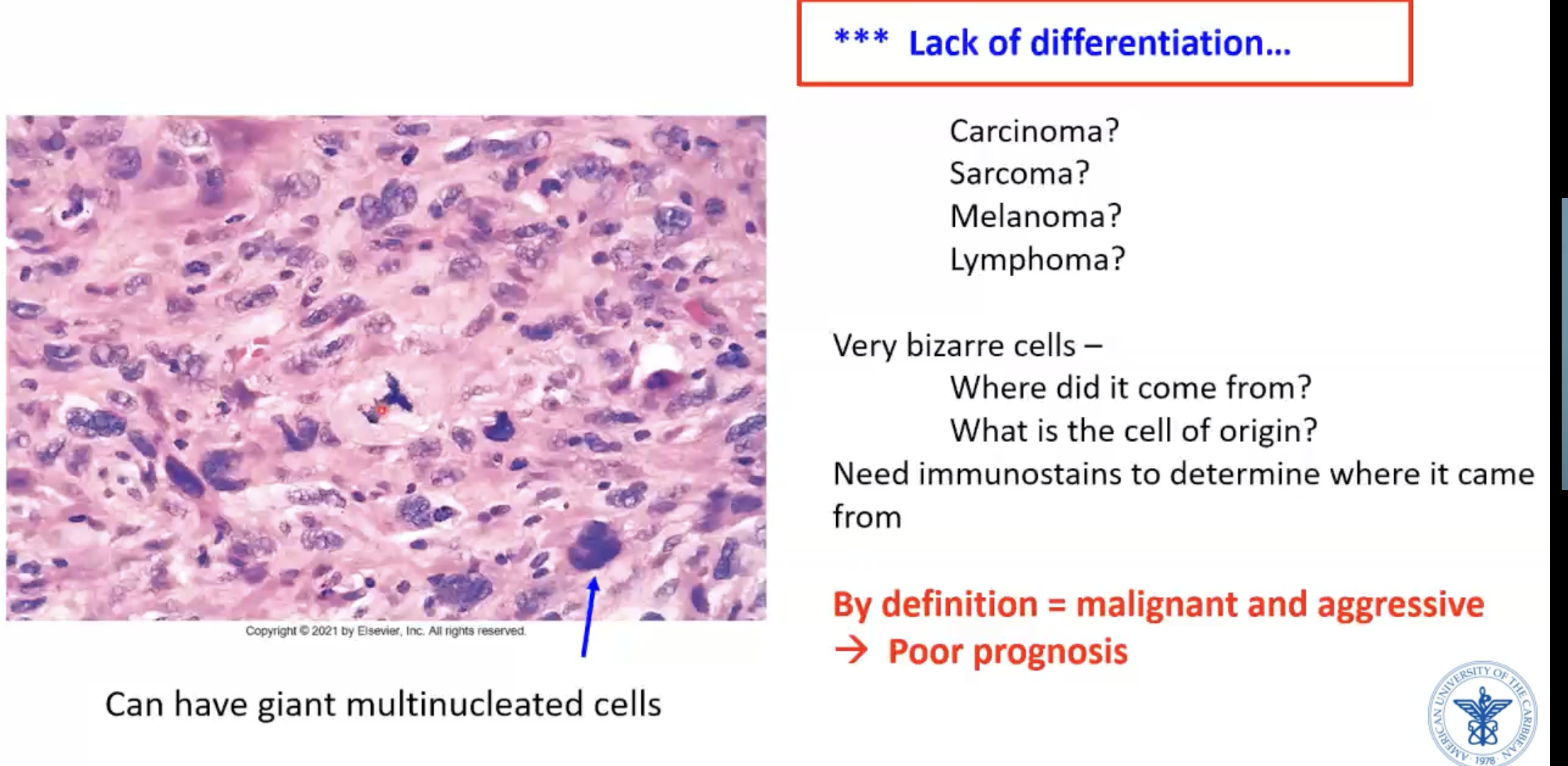
Anaplastic tumor
LACK OF DIFFERENTIATION
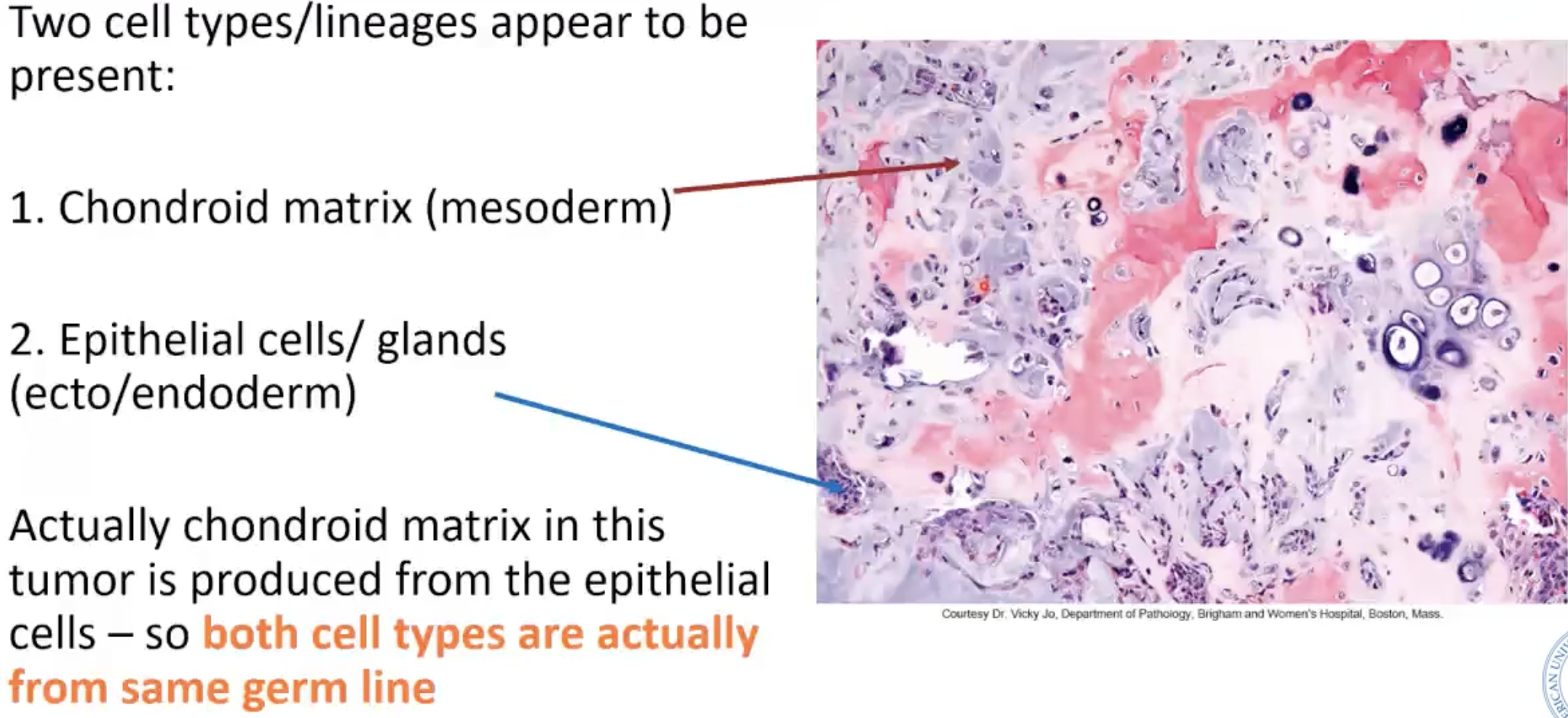
“Mixed tumor” of parotid gland
Also called = pleomorphic adenoma (benign)
Two cell types/lineages appear to be present
Teratoma of ovary has ___ tissue from ___ cell lines/germ layers
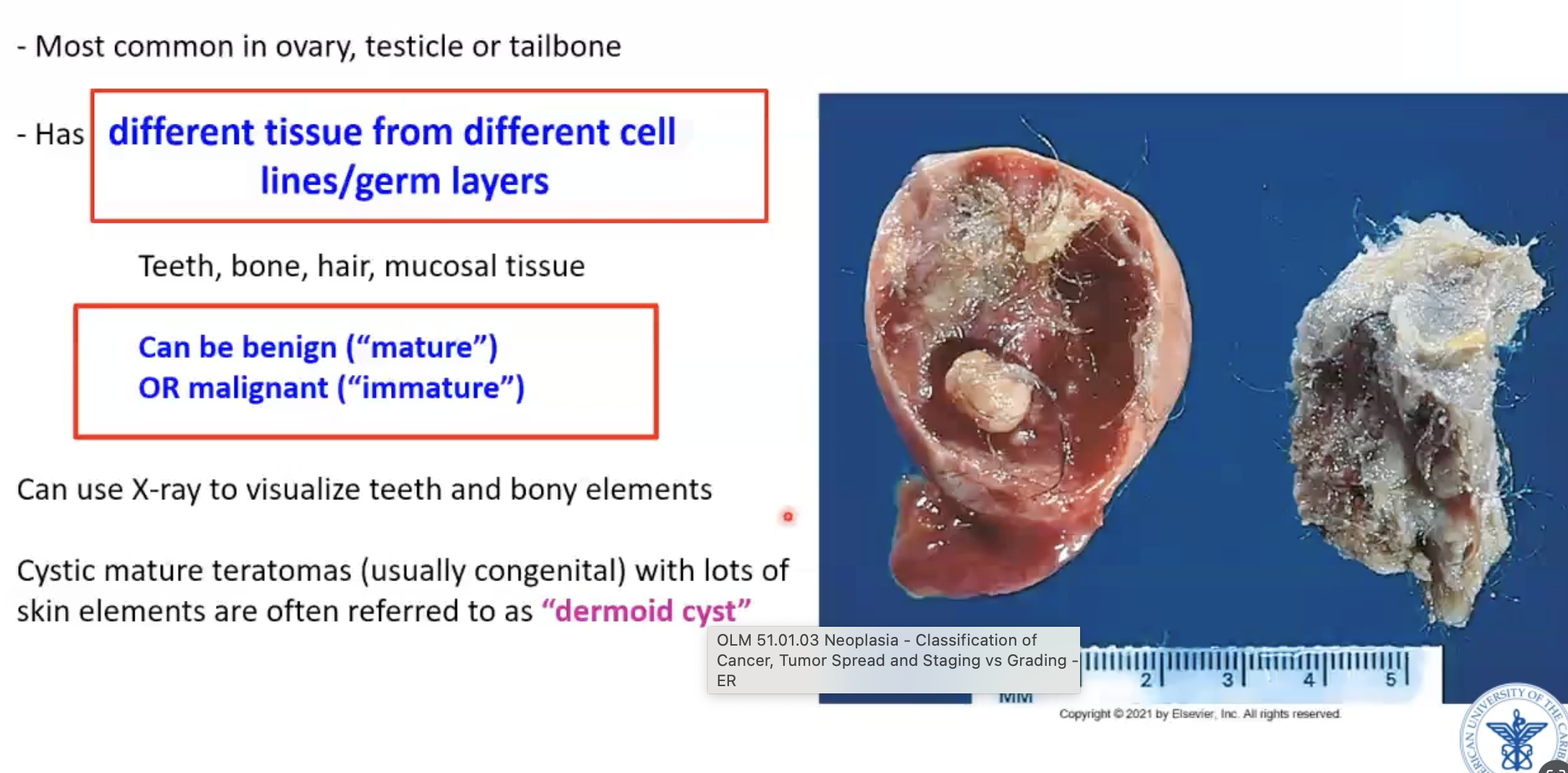
Teratoma of ovary histology
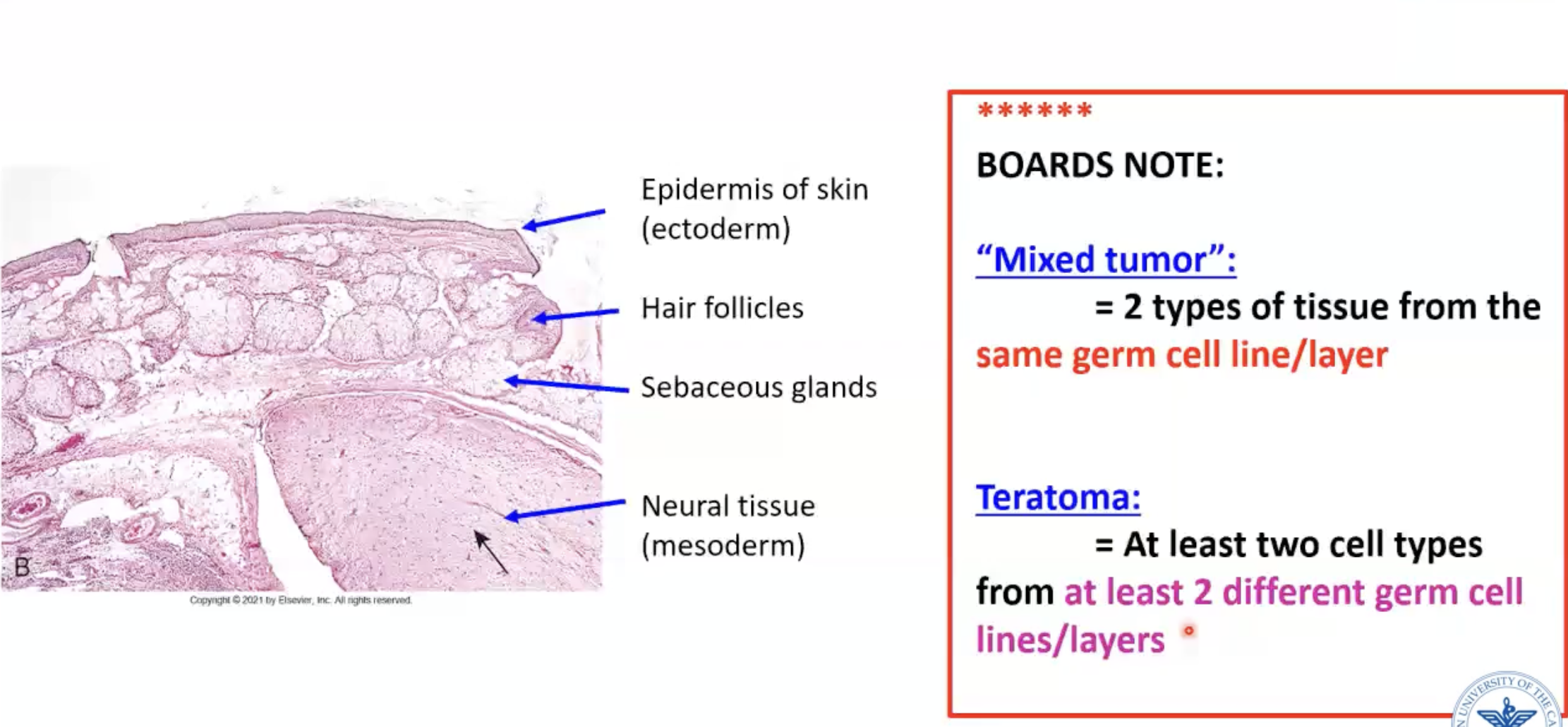
Define “mixed tumor”
2 types of tissue from the same germ cell line/layer
Define teratoma
At least two cell types from at least 2 different germ cell lines/layers
What are the four ways for tumors to spread?
Direct extension
Lymph channels to nodes (typical of carcinoma)
Exception: renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular like to spread via the venous system
Blood vessels (typical of sarcomas) → spread faster and farther
Seeding within body cavities
On the surface of organs, wherever fluid in the cavity touches
What happens with removal of all axillary nodes?
Can’t clear infection through lymphatics
** Never put IV on the same side of breast cancer because of this removal
GI carcinomas metastasize to the liver via
venous blood drainage d/t draining proximity to the liver

What is grading?
Histologic feature of a tumor that determine how differentiated a tumor is
How much does it resemble corresponding normal tissue?
Think: when grading papers, you compare to answer key and think how does it resemble it
What is staging?
How far has the tumor spread in the body
Requires entire patient
Think: staging a patient
Stage vs grade - which is more important?
Stage is more important than grade - important for prognosis/outcomes
** One exception: chondrosarcoma - grade of tumor is more important that stage
Tumor grade — progression
Well differentiated → moderately differentiated → poorly differentiated → anaplastic
Higher grade = worse prognosis!!
Basic criteria of staging
In situ→ micro-invasion → local invasion
TNM system
T - tumor
N - lymph node
M - metastases
DEPENDS ON SITE
