DRRR2 CONCEPTS WW2 pt.1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
NDRRMC
National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council
PHIVOLCS
Dedicated to provide information on the activities of volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
Specialized information and services primarily for the protection of life and property and in support of economic, productivity, and sustainable development.
Earthquake
Shaking of the Earth caused by waves on and below the Earth’s surface causing surface faulting, aftershocks, tsunamis, tremors, vibrations, liquefaction, and landslides.
Epicenter
The point on the Earth’s surface above the point at depth in the Earth’s crust.
Where do earthquakes begin?
Earth’s crust
Focus
The point at which the earthquake rupture begins, usually deep within the Earth.
Magnitude
Is a measure of energy released by an earthquake.
Intensity
Measures the strength of shaking produced by the earthquake at a certain location.
Determined from the effects on people, human structures, and the natural environment.
Ground Shaking
The primary cause of an earthquake damage to man-made structures.
Ground Shaking: The damage depends on…
Topography
Geologic Conditions
Bedrock
Location of Fault
Distance to Epicenter
Ground Shaking: How is it measured?
It is determined from the logarithm of the amplitude of waves recorded by seismographs.
Ground Shaking: Impacts
Damaged structures and infrastructures, injuries, loss of lives.
Ground Shaking: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Understanding how damage from strong shaking occurs.
Evaluating and improving earthquake-resistant design strategies and also methods for predicting the seismic performance of structures.
Ground Subsidence
The lowering of land surface.
Rapidly occurring caused by a sinkhole or underground mine collapse, or during a major earthquake.
Ground Subsidence: Impacts
Cracked infrastructures, changes in elevation and gradient of channels, broken pipes and utility lines, disrupted drainage, injury, death.
Ground Subsidence: How is it measured?
Elevation change, interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), continuous GPS (CGPS) measurements, campaign global positioning system (GPS) surveying, spirit-leveling surveying.
Ground Subsidence: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Public Information Programs
Maps
Land-use Management
Landslide
Involves the movement of Earth, rock, or debris on a downslope under the influence of gravity (UNDP).
Landslide: Impacts
Damage to properties, disruption of transportation, loss of agricultural sources, death.
Landslide: How is it measured?
Is usually measured by the movement of land mass. It is usually monitored by a GPS.
Landslide: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Identify landslide-prone areas.
Engineering solutions
Vegetation and landscaping.
Water Management
Regulation and Zoning
Liquefaction
“Quicksand”
Causes the sinking and/or tilting of building and structures and formation of sand boils.
Liquefaction: How is it measured?
There are no direct methods in determining a liquefaction’s potential in a particular location.
Liquefaction: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Ground improvement engineering.
Select locations where the soil is not predominantly sand.
Tsunami
“Harbor Wave”
Originates from the undersea or coastal seismic activity, landslides, and volcanic eruptions.
Where sea water is displaced with a violent motion and swells up, ultimately surging over land with great destructive power.
Tsunami: Signs
Strong ground shaking from an earthquake, unusual sea-level fluctuations, abnormally huge waves, and loud ocean roars.
Tsunami: How is it measured?
It is measured in the sea using tsunami buoys that collect data on changes in water levels through underwater pressure gauges.
Tsunami: Causes of damage…
High velocity impact of incoming waves, inland distance of wave runup, vertical height of wave runup, inadequate resistance of buildings, flooding inadequate horizontal and vertical evacuation, and proximity to source of tsunami.
Tsunami: Impacts
Damage to properties, damage to infrastructures, death by drowning.
Tsunami: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Land use management, planting and environmental preservation, structural designs, hazard awareness, tsunami warnings.
Faulting/Ground Rupture
The movement of the ground along one side of a fault relative to the other side, caused by an earthquake.
Faulting/Ground Rupture: How is it measured?
It is measured in distance/area.
Generally, the area of the fault that rupture increases with magnitude.
Faulting/Ground Rupture: Impacts
Damage to existing structures, damage to infrastructures, broken pipes and utility lines, injuries, death.
Faulting/Ground Rupture: How do we reduce its vulnerability?
Selection location far from a fault line.
Government should provide zones where structures may be built.
Proper structural and geotechnical engineering designs.
Local Strategies
Be aware of earthquakes risk.
Live in houses safe from seismic waves.
Sources of open flame and appliances must be made stable and safe.
Sources of open flame and appliances must be made stable and safe.
Earthquake and disaster drill.
First-aid training groups.
General Strategies
Construction (building codes and higher standards of construction quality).
Implement location planning to reduce urban densities on geological areas known to amplify ground vibrations.
What are possible ways to prepare for the “Big One”?
Water
Food
‘Go Bag’
Evacuation Plan
Lifesaving Skills
Infrastructures Audit
Static Water Tank
Fuels Supply
Basic Life Support
Communication Services
Barangay Census
Seismology
Study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the Earth.
Seismic Waves
Vibrations generated by a sudden impulse in the Earth.
Seismograph
Is the complex system/device that records ground movement using the seismometer.
Seismometer
Is the main component of a seismograph that records ground motion caused by seismic waves.
Types of Surface Waves
Rayleigh Waves
Love Waves
Types of Body Waves
P-Waves
S-Waves
Body Waves
Travels through the interior of the Earth.
Primary/Compressional Waves
Travels the fastest (~6 km/s in the upper crust)
They cause the matter to oscillate forward and backward, parallel to the motion of the seismic wave front.
Pushes to compress and pulls to dilate.
Secondary/Shear Waves
Travel slower (~3.5 km/s in the upper crust)
They cause the matter to oscillate side-to-side, perpendicular to the motion of the seismic wave front.
Shears the rock that they pass through.
Surface Waves
They are slower than body waves.
They do the damage in Earthquakes.
Love Waves
Shakes the ground side-to-side like an S Wave.
Rayleigh Waves
Displace the ground like rolling ocean waves.
Seismograph (Parts of a Seismic Wave)
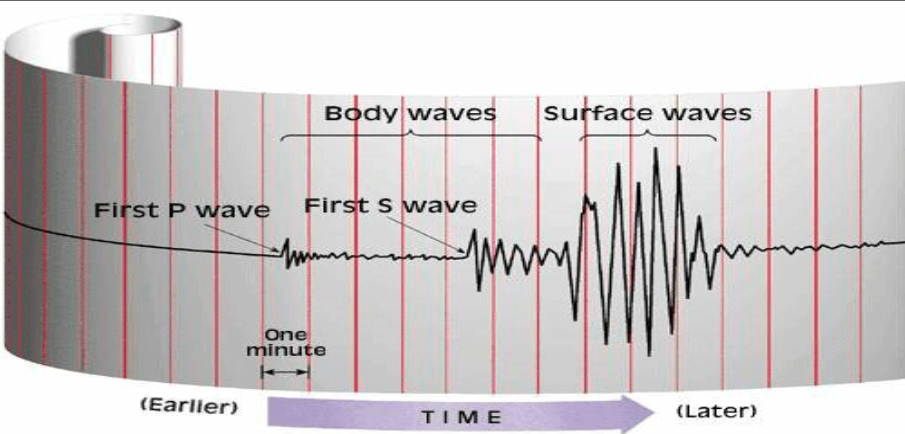
Richter Scale (Magnitude)
A measurement of earthquake magnitude, based on seismic wave size.
Mercalli Scale (Intensity)
Measure the intensity of an earthquake based on its observed effects on people, building, and the Earth’s surface.
Provides a qualitative assessment of the earthquake’s impact ranging from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
Before an Earthquake
Create an emergency plan.
Prepare an emergency kit.
Secure heavy objects.
Reinforce the Structure.
During an Earthquake
Drop, Cover, and Hold On.
Stay Indoors
Stay away from hazards.
If outdoors, move to an open area.
After an Earthquake
Check for injuries.
Be prepared for aftershocks.
Evacuate if necessary.
Listen to official instructions.
Check utilities
Document damages