Molecules - BIO
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
alanine (ala, a)
nonpolar
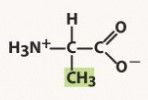
arginine (arg, r)
polar basic, positive charged R group
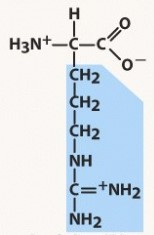
asparagine (asn, n)
polar, neutral (uncharged) R group
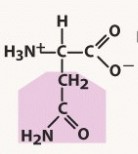
aspartate (asp, d)
polar acidic, negative charged R group
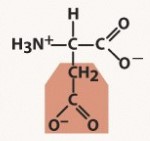
cysteine (cys, c)
polar, neutral (uncharged) R group
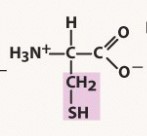
glutamate (glu, e)
polar acidic, negatively charged R group
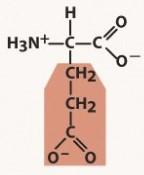
glutamine (gln, q)
polar, neutral (uncharged) R group
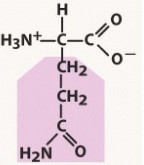
glycine (gly, g)
nonpolar
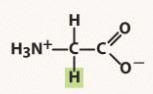
histidine (his, h)
polar basic, positive charged R group
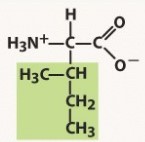
isoleucine (ile, i)
nonpolar
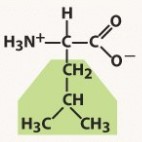
leucine (leu, l)
nonpolar
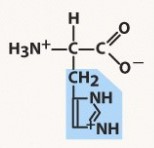
lysine (lys, k)
polar basic, positive charged R group
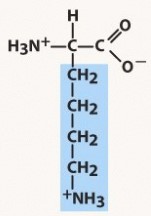
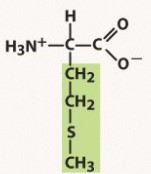
methionine (met, m)
nonpolar
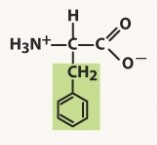
phenylalanine (phe, f)
nonpolar, aromatic R group
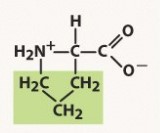
proline (pro, p)
nonpolar
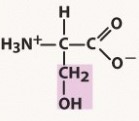
serine (ser, s)
polar, neutral (uncharged) R group
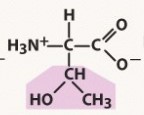
threonine (thr, t)
polar, neutral (uncharged) R group
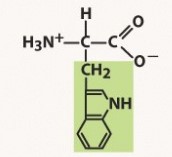
tryptophan (trp, w)
nonpolar, aromatic R group
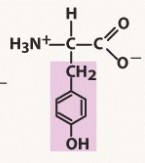
tyrosine (tyr, y)
polar, aromatic R group
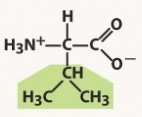
valine (val, v)
nonpolar
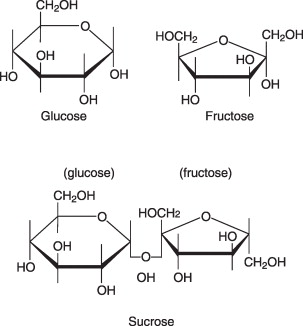
Glucose
CHO, Carbohydrate
(6 ring)
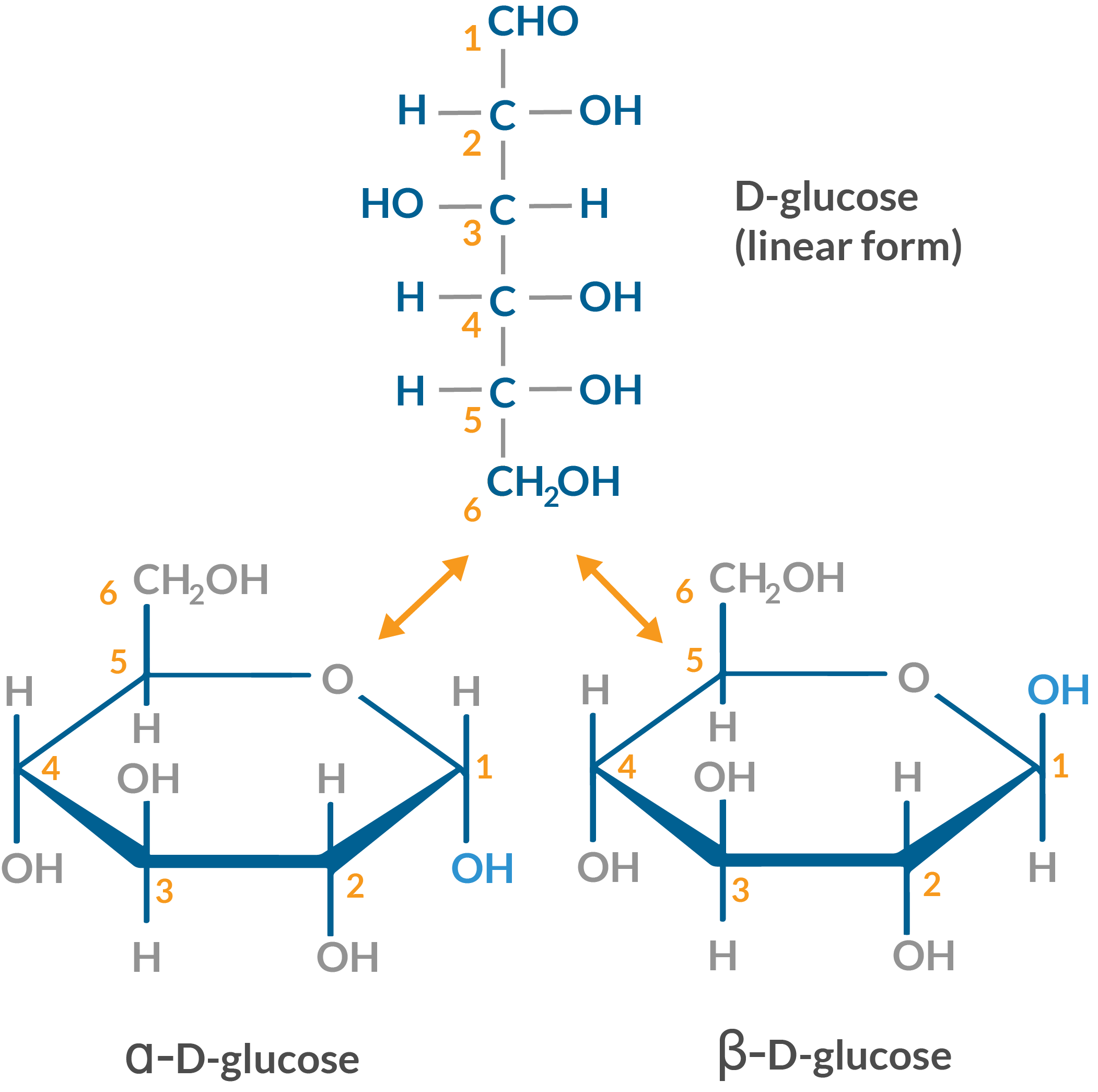
Ribose
Used in RNA
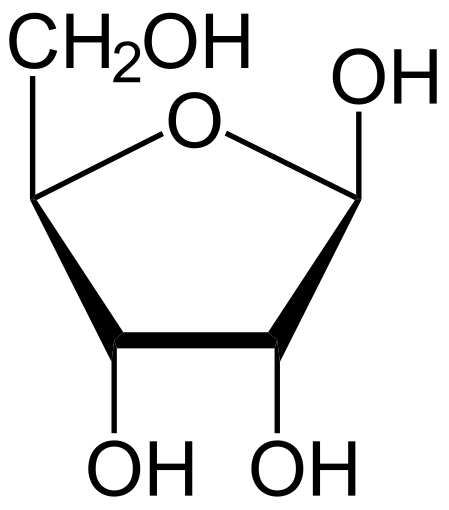
Deoxyribose
Used in DNA
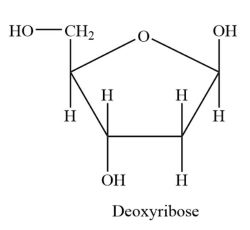
Fructose
5 ring
Sucrose
Fructose + Glucose
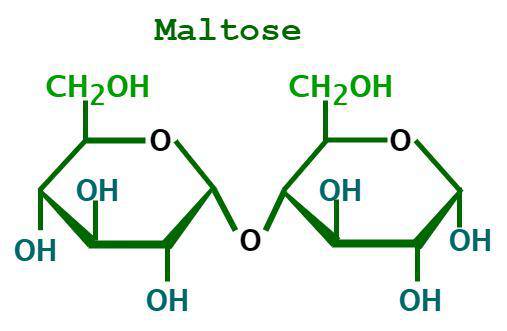
Maltose
2 Glucoses
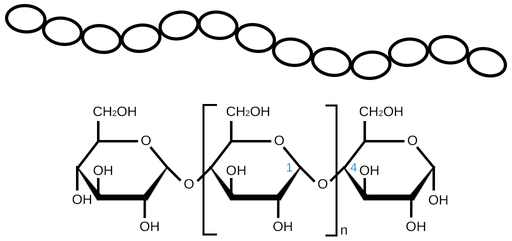
Glycogen
found in human liver and muscles
A Type of Starch

Starch
Long links of monomers
Alpha glucose
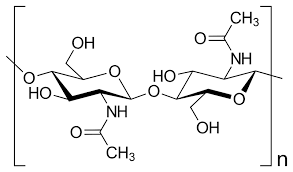
Chitin
has amino group (amide)
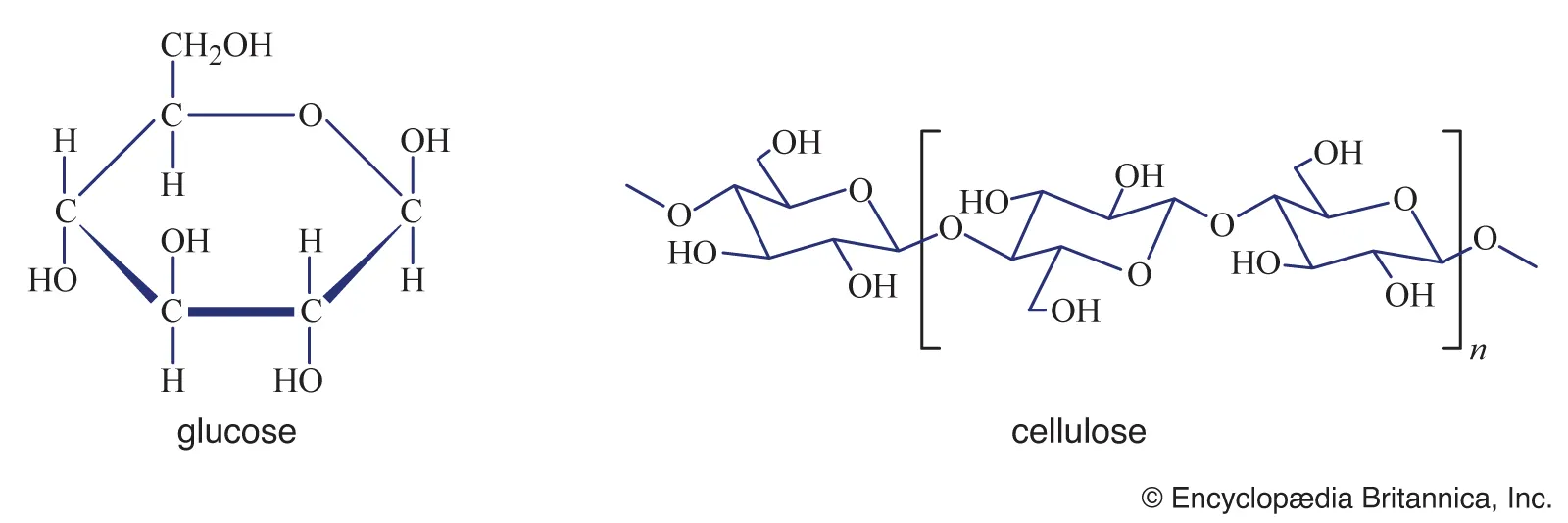
Cellulose
beta Glucose
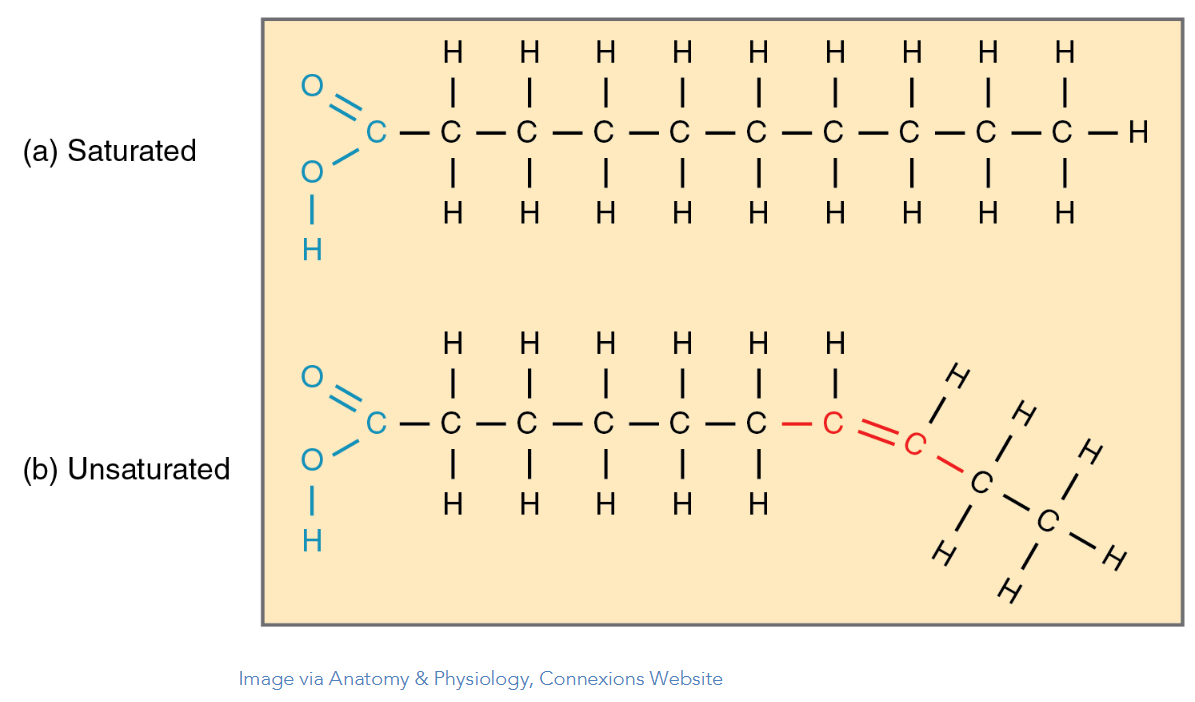
Saturated Vs. Unsaturated Fat
Saturated = No Alkenes, Unsaturated = Alkenes
The warmer something is the less alkene(saturated)it is, the colder something is, the more alkenes it has (unsaturated).
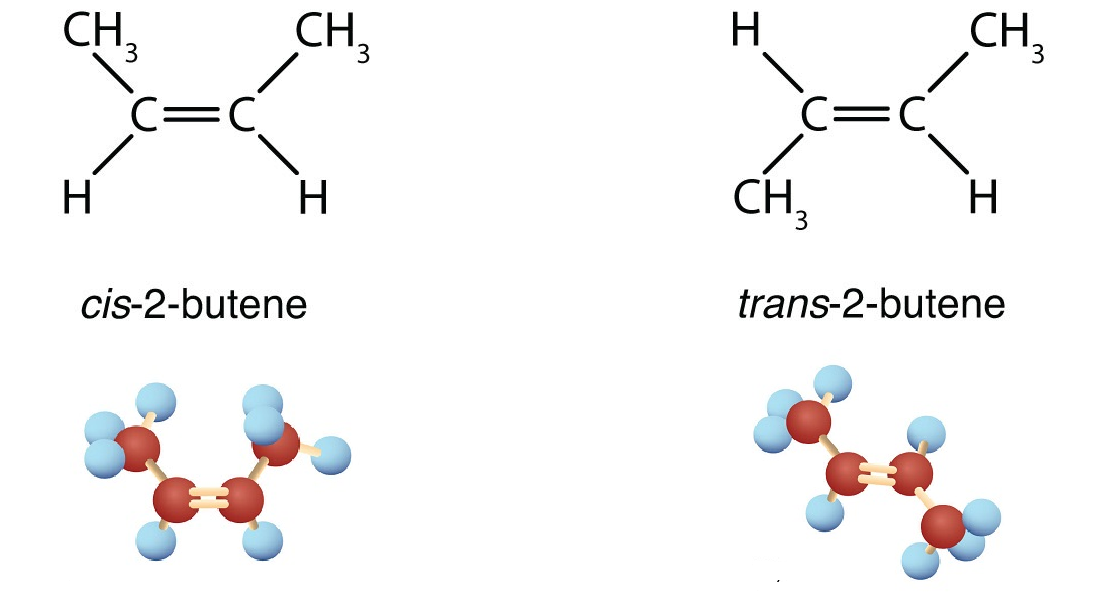
Fatty Acid: trans vs cis
Alkene
Steroids
special shape - fat
