1 The Market
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
• characteristics
• market size and market share
• brands.
b) Dynamic markets:
• online retailing
• how markets change
• innovation and market growth
• adapting to change.
c) How competition affects the market.
d) The difference between risk and uncertainty.
What are markets?
Known for buyers and sellers to meet to exchange goods.
In today’s world, you can trade goods and serviced without buyers and seller meeting up due to advancement in technology
What are some example of the market?
Consumer goods market- products such as magazines, food, cosmetics are sold
Markets for services- these can include services for individuals (hairdressing, business services)
Housing market- where people sell and buy property
Commodity markets: raw materials such as oil, copper, wheat and coffee are traded
Financial markets: where currencies and financial products are traded
* Designing products to meet these needs
* Understanding threats posed by competitors
* Telling customers about the products
* Charing the right price
* Persuading customers to buy products
* Making products being available in convenient locations
What is marketing?
identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer needs
What is mass market?
when a business sells the same products to all consumers and markets in the same way
Things sold at mass market known as fast moving consumer goods such as drinks, chips and etc
Have large amount of customers
They can exploit economies if scale by producing large quantities leading to higher sales and higher profits
A lot of competition so companies usually spend a lot on advertising. Ex: Coca-Cola has high budget for advertising $4000million+
Advantages of mass markets:
Large Customer Base: Mass markets encompass a broad audience, providing access to a large and diverse customer base.
Economies of Scale: High production volumes often lead to lower per-unit production costs, allowing for competitive pricing.
Profit Potential: Selling to a large market can generate substantial revenue and profit if successful.
Brand Recognition: Mass market products have the potential to become widely recognized and establish strong brand identities.
Market Power: Dominating a mass market can provide a company with significant market power and influence.
Disadvantages of mass markets:
Intense Competition: Mass markets often attract numerous competitors, making it challenging to stand out.
Limited Product Customization: Mass-produced products may lack customization options, limiting appeal to niche markets.
Price Sensitivity: Customers in mass markets tend to be price-sensitive, which can lead to reduced profit margins.
Customer Loyalty: Building and maintaining customer loyalty can be challenging in a market where consumers have many choices.
Changing Trends: Mass markets are susceptible to changing consumer trends, which can affect demand unpredictably.
Market Saturation: Over time, mass markets may become saturated, leaving little room for growth.
What is a niche market?
small market segment which are usually not used by large businesses
Involved in selling it small customer base and sometimes meeting their specific needs
Small businesses benefit from niche market as they can avoid competitions from large rivals
Easier to focus on the needs of the customers
If there is no competitions, businesses can charge premium prices
Advantages of niche markets:
Targeted Customer Base: Niche markets cater to a specific, well-defined audience with unique needs and preferences.
Reduced Competition: Niche markets often have fewer competitors, making it easier to establish a strong market presence.
Loyalty and Engagement: Niche customers tend to be more loyal and engaged with a brand that meets their specialised needs.
Higher Profit Margins: Businesses in niche markets can often charge premium prices due to the specialised nature of their products or services.
Personalisation: Niche businesses can focus on customising products or services to better suit the unique requirements of their customers.
Expertise and Reputation: Specialisation allows niche businesses to become experts in their field, building a strong reputation.
Market Resilience: Niche markets may be less affected by economic downturns or external factors because of their specialized focus.
Disadvantages of niche markets:
Limited Customer Base: Niche markets are inherently smaller, which can limit the potential for revenue and growth.
Economies of Scale: Smaller production volumes can result in higher per-unit production costs, affecting pricing.
Marketing Challenges: Targeting and reaching a niche audience can be challenging, and marketing costs can be relatively high.
Risk of Dependency: Relying solely on a niche market can be risky if it becomes saturated or if customer demand shifts.
Competition from Larger Players: Larger companies may enter niche markets, intensifying competition.
Limited Diversification: Diversifying product offerings can be difficult within a narrow niche.
What happenes if a business exploits niche markets?
Can attract completion
Niche markets are usually for smaller firms and unable to support competing firms, so large businesses enter niche markets to overrun smaller rivals
What happens to businesses that rely on single niche markets?
Can be vulnerable because they are no spreading risk
If they lose grip on the market chooses it might collapse because they do not have other products or markets as a back up
How is market size estimated By the total sales of all businesses in the market?
Value
total amount spent by customers buying goods
Volume
quantity of products that are produced and sold
Example: In China, domestic air travel market size is measured by the number of passengers, which was 487,960 million in 2016.
Some volume estimates are based on users, subscribers, or viewers, especially in service markets.
Examples include the number of mobile phone users, television viewers, or households with digital television.
- Market sizes vary by industry; for instance, the market for savory snacks is typically smaller than the market for footwear in a given year in a country.
What is market share?
Market share refers to the percentage or portion of the total market for a specific product, service, or company's offerings that is controlled or captured by that particular product, service, or company.
It is a measure of a business's relative size or presence in a given market compared to its competitors.
Market share can be calculated based on factors such as sales revenue, units sold, or customer base, and it is used to assess a company's competitive position and its ability to influence and impact the market.
How can you calculate market share of a business?

Why is measuring market share important?
Indicates if a business is a market leader, influencing others to follow or maintain their position.
Influences a business's strategy and objectives; a small market share business may aim to increase it.
Can indicate the success or failure of a business or its strategy.
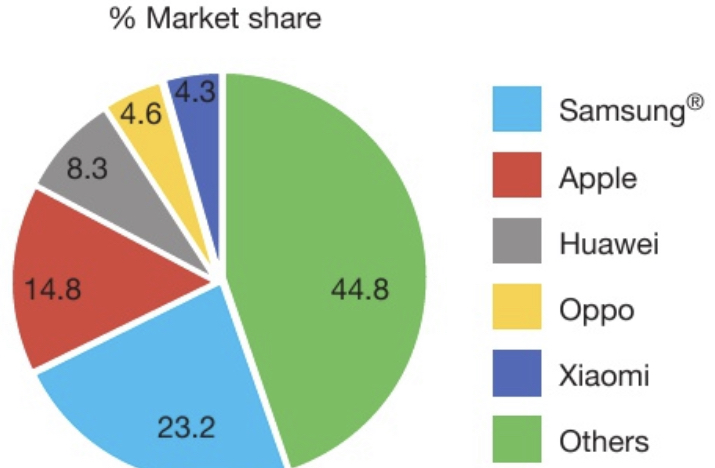
- Example: Figure 2 displays global market shares of smartphone suppliers, Samsung as the leader and with the top five producers collectively holding over half of the market.
Why do businesses use branding?
Distinguish their products from others in competitive markets.
Foster customer loyalty.
Enhance product recognition.
Develop a specific brand image.
Can charge premium prices when the brand becomes strong
Crucial for mass markets where rivals are competing with each other for market share
Examples of common brand names include Google®, Coca-Cola, Toyota, Nike®, and Apple®.
What are dynamic markets?
Markets are typically dynamic, constantly changing over time.
Changes in markets can include growth, shrinkage, fragmentation, emergence, or disappearance.
- Example: The market for cassettes largely disappeared as digital downloads became the norm for music.
Dynamic markets have significant impacts on businesses; failure to adapt can lead to business collapse.
Businesses that can adapt to dynamic market changes are more likely to survive in the long term
- For instance, Kodak® didn't adapt to digital photography, focusing on film cameras, leading to its eventual liquidation..
What is online retailing?
Online retailing, or e-tailing, is a significant development in product marketing.
It's a branch of e-commerce that has grown with the Internet, involving ordering goods online and home delivery.
Prominent e-tailers include Amazon® and Alibaba®, offering a wide range of products online.
Both large and small retailers now offer online services.
Online retailing is rapidly growing and expected to continue to do so.
Is online retailing ideal?
Online retailing offers convenience and variety but may not suit everyone’s preferences or needs. The choice between online and offline shopping depends on individual preferences and the nature of the products being purchased.
Benefits online retailing
Convenience: Shoppers can browse and purchase products from the comfort of their homes or anywhere with an internet connection.
Accessibility: Online stores are accessible 24/7, allowing customers to shop at their convenience, even outside regular store hours.
Reach more customers
Decrease in costs: marketing costs decrease as it is cheaper to send a message on email rather than on post, sales staff, rent and other costs can be avoided
Charge lower prices: costs are low
Variety and Selection: Online retailers often offer a vast array of products and brands, providing shoppers with more choices than physical stores.
Online retailers can use data to personalize product recommendations and offers, enhancing the shopping experience.
Drawbacks of online retailing
Lack of Physical Interaction: Online shopping lacks the in-person experience, making it challenging to physically examine products before purchase.
Shipping Costs and Delays: Shipping fees can add to the overall cost, and delivery times may vary, potentially causing delays.
Security Concerns: Online transactions involve sharing personal and financial information, raising security and privacy concerns.
Returns and Refunds: Returning products purchased online can be difficult than returning items to physical stores, involving shipping and restocking fees.
Technology Dependence: Shoppers need internet access and technical proficiency to navigate online stores effectively.
Risk of Scams: Online shoppers may encounter fraudulent websites or sellers, risking their financial information.
How do markets change:
Market Size:
Some markets remain stable over time, like the milk market in the UK as consumption is constant
Most markets tend to grow, such as the global packaging market, which increased from US 799 billion in 2012, with projected sales exceeding US $1 trillion.
Some markets decline due to changing needs; for instance, dial-up Internet services are being replaced by broadband.
Nature of Markets:
Many markets are constantly changing (in flux), including consumer spending patterns.
Ex: In Indian markets, shopping has become more social, frequent, and focused on immediate gratification.
Social media influences consumer behavior and brand choices. Make consumers desire to buy more. People attempt to match spending patterns on who they see on media
New Markets:
possible for markets to completely disappear but new markets are always constantly changing
Emerging economies like BRIC nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China) and others like Mexico, Thailand, and Indonesia create new markets.
New markets also emerge with the introduction of entirely new products, such as mobile phones, smartphones, flat-screen televisions, and e-books in past decades.
different factors of why market growth increases/decreases over time:
Economic growth
Innovation
Social changes
Changes in legislation
Demographic changes
economic growth
Global living standards tend to rise over time, increasing people’s spending power
Businesses can expand their output to meet growing global markets.
As people become wealthier, their demand shifts toward different types of goods, such as holidays, electronics, cars, air travel, cosmetics, furniture, and luxury items.
Innovation
Innovation is a driver of market growth, creating new products, spotting market gaps and addressing emerging needs and wants
Technological research and development lead to breakthroughs like smartphones, tablets, the Internet, 3D printing, and driverless cars which did not exist before, providing an opportunity of opening up new markets.
innovation can come in different forms such as new marketing strategies to develop more Wats, supply in new locations
the 2008 financial crisis, new companies emerged to compete with traditional banks. Platforms like crowdfunding and peer-to-peer lending started offering unsecured loans, have relatively small market shares. However, if these new innovations prove successful, established banks may need to adapt and incorporate similar approaches to stay competitive.
Social changes
changes in society can have big impacts on markets
Societal shifts like declining marriages, more working women, and one-parent families can reshape markets.
These changes increase demand for services such as childcare and housing.
Changes in legislation
New laws and regulations can significantly impact markets.
ex: environmental legislation promotes growth in renewable energies and green products.
tighter laws on payday lending may reduce the size of the lending market. Bans on tobacco advertising can shrink the market for cigarettes in some countries.
Demographic changes
Population structure changes, with most countries experiencing an aging population which can affect the size.
This aging population leads to growth in markets for specialist elderly services, healthcare, care homes, and mobility aids.
What happened if businesses do not adapt to changes:
Loss of market share: failing to adapt consumer references and rivals will take over
Decline in revenue and profit: shift in demand, businesses fail to adjust to customer presences, therefore leads to losing consumers
Customers dissatisfaction: not meeting consumer expectations
Reputation damage: business seen as unresponsive, outdated, damage its image and trustworthiness
Missed opportunities: market changes allow opportunities, growth, innovation and expansion
How do businesses adapt to change:
Flexibility
Market research
Investment
Continuous improving in the competitive environment
Develop a niche
Flexibility
Businesses should introduce a culture of flexibility, which includes flexible working practices, equipment, pricing, and staff roles to adapt to changes.
Staff should be trained in various skills and be willing to switch tasks when necessary to better serve customers when changes occur.
Market research
Regular market research is crucial to stay updated on customer needs, change in trends and market developments.
Consistent communication with customers and potential customers is vital to remain current in the market.
Investment
Investing in research and development, product innovation, and training can lead to long-term survival and increase market share growth.
Research and development can be expensive, failure to innovate can be even more costly to the business
New version of product (product development), brand can increase sales and win larger shares of market
Continuous improve the in the competitive environment
Businesses must strive for continuous improvement in all aspects of operation; efficiency, cost reduction, customer service, and product innovation to stay competitive.
Helps business to adapt to the market
Develop a niche
In declining markets, businesses can survive by serving profitable niches or loyal customer groups.
Firms that cannot adjust quickly to changing customer needs risk losing out to more adaptable competitors.
How does competition affect the market?
competition is the rivalry that exists between in a market
Rare for businesses to operate in a market with no competition
Existence of competition has an impact on businesses and consumers
Impact from competitions to businesses:
Businesses face pressure so they try to attract customers into buying their products and making them stay away from rivals and some of these strategies are:
Lowering prices
Creating product differentiation from rivals
Offering higher-quality products
Utilizing powerful advertising and promotions
Providing high customer service
These competition strategies can reduce a business's profitability as they entail expenses. However despite the cost, businesses must employ these methods to survive in a competitive market.
Owners and managers may seek to reduce competition in the market by:
Taking over rival companies by purchasing them
Making it difficult to enter the market, such as through high budget advertising, which new entrants may find challenging to match.
Typically, larger businesses have more resources to reduce competition.
Laws exist to prevent businesses from engaging in unfair practices that restrict competition.
Impact from competitions to consumers:
Benefits of Competition for Consumers:
More choices in the market as there are lots of businesses in the market
Variety in products, styles, colors, and specifications
Potential for better-quality products and prices due to competition
Drawbacks of No Competition for Consumers:
Risk of exploitation by businesses
Possible price increases and limited choice
Lack of incentive for innovation and new products
Government's Role in Ensuring Competition:
Government's responsibility to promote competition in markets
Preventing monopolies (when a single business dominates the whole market) or businesses with little competition
Ensuring fair pricing, choice, and innovation for consumers
How does risk pose threats to businesses?
Risk for Business Owners:
Business owners face risks and take actions with unknown outcomes.
They invest their own resources, including money, to start and run a business.
There’s a chance of losing all invested money if the business fails.
Many new businesses, up to 90%, may not survive beyond 5 years.
Continued Risks for Established Businesses:
Established businesses continue to take risks, such as investing in new products that might fail.
Investments in unsuccessful ventures can result in significant financial losses.
Example of Risk:
In 2014, Amazon launched the Amazon Fire Phone, which failed in the market. The price of the phone was quickly reduced, resulting in a reported loss of US$170 million for Amazon.
How does uncertainty pose threats to businesses?
External influences beyond a business’s control impact markets.
Influences include:
new competitors entering with superior products
changing consumer tastes,
government policies
technology advancements
natural disasters
economic recessions (decline in economy)
These influences are difficult to predict, creating an environment of uncertainty for businesses.
Positive Aspects of Uncertainty:
New technologies and changes can create opportunities for businesses.
The Internet, for instance, has opened up numerous business opportunities.
Generally, businesses prefer stability for easier decision-making, especially in long-term investments.
