B2 - Membranes and Compartmentalization
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Membrane Permeability
Membranes function as barriers between aqueous solutions so large molecules and hydrophilic particles do not pass easily.
Diffusion
Net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It is passive and only in liquids and gases.
Simple Diffusion Across cell Membranes
Small non-polar molecules diffuse easily
Rate of diffusion depends on the concentration. Higher concentration on one side = higher diffusion
If the concentration is equal particles will move in both directions evenly
Oxygen and Carbon are able to enter and leave cells
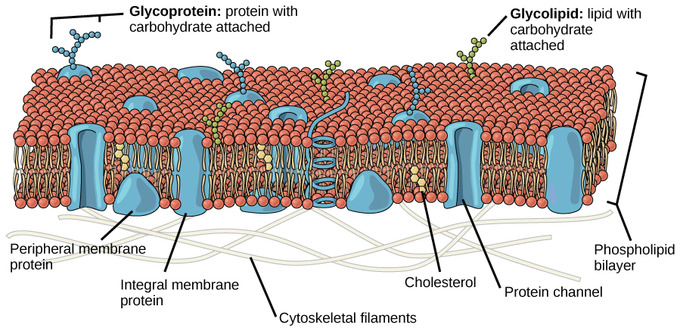
Integral proteins
Hydrophobic surface so are embedded in the bilayer. Includes transmembrane proteins which stretch from one side to the other.
Peripheral Proteins
Attached to the surface of the proteins or lipids of the membrane on just one sides
Facilitated diffusion through channel proteins
Include a pore allowing particles to pass through the membrane in either direction. Specific to one type of substance decided by size and charge or the pore. Passive movement, no ATP used.
Osmosis
The passive movement of water molecules from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration across a permeable membrane. Aquaporins increase permeability by allowing the movement of water molecules.
Active Transport
The movement of substances across the membranes using energy from ATP. Against the concentration gradient.
Pump Proteins
They carry out active transport. Work in one direction. Lower solute to higher solute,
Semi-Permeability/Partial Permeability
Allowing some substances through but not others.
Facilitated diffusion and active transport allows for control over particles. Net movement is always down the concentration gradient
Active transport can generate concentration gradients
Gycoproteins and Glycolipids
Polypeptide with carbohydrate attached.
Lipid with carbohydrate attached
Roles of Gycoproteins and Glycolipids
Cell adhesion: creating a carbohydrate rich layer on outer face of animal cells called glycocalyx. Can be fused together
Cell recognition: The differences in types allow cells to recognize other cells. Part of the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self cells
Fluid Mosaic Model
Advantages of Compartmentalization
Small volume of organelles allows enzymes and their substrates to be concentrated, speeding up enzyme activity
pH can be kept at an ideal level
Biochemical processes can be kept separated
Fertilization
The fusion of a male and female gamete to produce a zygote (single cell). In multicellular organisms this cel divides repeatedly to form an embryo. Early stage embryos are unspecialized.
Differentiation
The specialization of cells as they develop along different pathways
Morphogens
Signalling chemicals that indicate to a cell its position in the embryo and which pathway of differentiation it should follow. They are regulators of gene expression, determining which genes are transcribed.
Properties of Stem Cells
Self-replicating - can divide endlessly
Undifferentiated - has not developed specialized features so has the capacity to differentiate to different pathways
Types of Stem Cells
Totipotent: early stage, can differentiate into any cell type. Stem cell therapies
Pluripotent: Able to differentiate into many but not all cell types
Multipotent: found in bone marrow, differentiate into several cell types
Stem Cell Niches
The precise location of stem cells within a tissue with the proper microenvironment or conditions to stay undifferentiated for a long period or proliferate rapidly.
Bone Marrow - Stem Cell Niche
Soft, spongy tissue in large bones
Contains haematopoietic stem cells that produce red and white blood cells and platelets
Generous supply of blood carrying oxygen, amino acids, and nutrients through cardiac output
Hair Follicles - Stem Cell Niche
Stem Cells at the base of each hair divide repeatedly for hair growth. Blood capillaries supply nutrients
Specialization - Cell Size
Most efficient size for cell function:
Male Gametes - not wide but long for swimming to egg
Red Blood Cells - Small size with large surface-to-volume ratio for oxygen
White Blood Cells - Can grow to produce antibodies in bulk
Female Gametes - Very large volume of cytoplasm containing food to sustain embryo
Neurons - cell body + axon < 1m long! Allows for the carrying of signals
Striated Muscle Fibres - large cells that can exceed 10cm, large and powerful muscle contractions
Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio
Decreases with size of cell
Rate of materials entering or leaving the cell depends on surface area
Rate of materials used or produced depends on volume
Creates limits on max size of cells before division