GCSE Physics- P5 Forces (uncomplete- missing pressure)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
scalar
values with a magnitude only
Vectors
values with a magnitude and directioni
scalar examples
speed, temperature, distance, energy
vector examples
velocity, displacement, force, acceleration
displacement
overall distance from A to B in the direction A to B
distance
actual length travelled
acceleration
rate of change of velocity, is a vector
acceleration unit
m/s²
acceleration equation
(v-u)/t or Δv/Δt
v being final velocity or velocity
u being initial velocity
acceleration
if Δv is positive
deceleration
if Δt is negative
velocity
distance per second with a direction
acceleration equation from velocity and displacement
a= (v²-u²)/2s
v being final velocity
u being initial velocity
s being displacement
Distance-time graphs (DT)
gradient of DT graph= speed

velocity-time graphs / speed-time graphs (VT)
gradient of VT graph= acceleration
area of VT graph= distance travelled
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
mass units
Kilograms (Kg)
weight
force on a mass as a result of gravity
weight units
Newtons (N)
Weight equation
W=mg
Free body diagrams
shows forces acting upon an object
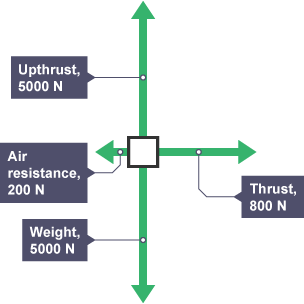
Resultant force
overall force on an object, sum of all the forces acting, accounting for their directions
resultant force equation
F=ma
F being the resultant force
Gravitational field strength unit
N/Kg or m/s²- because acceleration due to gravity
they are equal units
terminal velocity
the maximum speed of which an object falls, there is no more acceleration because the upwards and downwards forces are balanced
Newton’s first law
if the resultant force on an object is zero, the object will stay at rest or continue moving at a constant velocity
ΣF=0 - sum of all forces=0 ∴ acceleration=0
Newton’s second law
resultant force of an object is equal to its mass multiplied by its acceleration
ΣF≠0 - sum of all forces≠0 ∴ acceleration≠0
F=ma
Newton’s third law
when object A exerts a force on object B, object B exerts an equal and opposite force back on object A
always 2 objects with the same line of action
acting on 2 different bodies
Inertia
tendency to do nothing or remain unchanged
inertia mass
measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object, ratio of force over acceleration
inertia mass equation
m= F/a
Momentum equation
P=mv
momentum units
Kilogram metres per second (Kgm/s)
momentum conservation
total momentum before a collision equals the total momentum after a collision
Pbefore = Pafter
Momentum-force equation
F=ΔP/t
F being resultant force
stopping distance
thinking distance + braking distance
thinking distance to speed
proportional
thinking distance factors
tiredness, drugs/alcohol, visibility, tyres/brake conditions, mass passengers and car, speed, age
braking distance factors
speed, brake/tyre condition, road conditions (wet, icy, dry), vehicle+passenger weight
deformation
takes more than one force acting on the same object to cause it do deform (eg. extension, compression, bending), different to action-reaction- both forces act on same object
Hooke’s law practical variables
independent: Force (N)
dependent: extension of spring (cm)
controls: spring constant (N/m), type of spring, position of measurement
Hooke’s law
extension of a spring ‘e’ is directly proportional to the force applied ‘F’
Hooke’s law equation
F=ke
k is the spring constant- force constant/spring constant measuring stiffness of spring
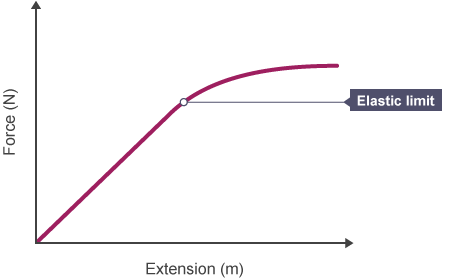
Limits of proportionality / elastic limit
point in which force is not proportional to length
elastic deformation
temporary deformation, bonds between atoms extended, but not broken
plastic deformation
permanent deformation, bonds between atoms broken
Elastic potential energy (Ee)
energy stored in a object caused by a force that deforms elastically, Ee of a spring that obeys Hooke’s law is equal to the work done by the force to stretch (or squash) the spring
Elastic potential energy (Ee) equation
Ee= ½ke²
k being spring constant
e being extension
Work done
energy transferred (J)
Work done equation
W=Fs
W being work done
s being distance moved (in the direction of the force)
work done units
Joules (J)- same as enegy
pivot
the point around which something rotates
Moment
the turning effect of a force- a force that is further from the pivot which depends on size of force and the distance from pivot
Moment equation
M=fd
M being moment
d being distance from pivot
Moments units
Newton-metres (Nm)- 1 Nm is equal to 1 Joule (J)
Lever
rigid bar pivoted on a fixed point (used to transmit force)
Load
force provided by the object you are trying to move
effort
force applied to move the load (work done)
gears
rotating wheel with teeth (cogs) that interlock with another wheel
multiplying force
bigger wheel transmits a smaller force than a smaller wheel, a bigger wheel rotates slower than a smaller wheel