NURS 333 OB clinical
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Edwards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
acetaminophen
Brands: Tylenol, Abenol, Panadol
Classification- Analgesic (nonopioid), antipyretic; not an NSAID bc it lacks anti-inflammatory action
Indications- Tx of pain and fever
Contraindications / Precautions- allergy to acetaminophen; severe hepatic impairment or chronic alcoholism
Adverse Reactions / Side Effects- Hepatic toxicity, nephrotoxicity; GI upset; anaphylaxis
Nursing Considerations- Check allergies, assess pain/fever, evaluate liver/renal function. Regularly evaluate pain relief and fever control; monitor liver enzymes (AST/ALT), BUN/creatinine in at-risk patients; monitor CBC if prolonged use
Patient/Family Teaching: Avoid taking multiple acetaminophen- containing products; adhere to maximum daily dose; avoid alcohol; report symptoms like jaundice, rash, bleeding; measure dose accurately
Overdose Management: Antidote: N‑acetylcysteine (NAC)
aldomet
(Methyldopa)
Indication: Chronic hypertension in pregnancy.
Contraindications: Liver disease; MAOIs.
Side effects: Sedation, depression, hemolytic anemia, liver dysfunction.
Nursing: Monitor BPs, LFTs, mental status.
Teaching: May cause drowsiness; avoid alcohol; report jaundice or unusual fatigue.
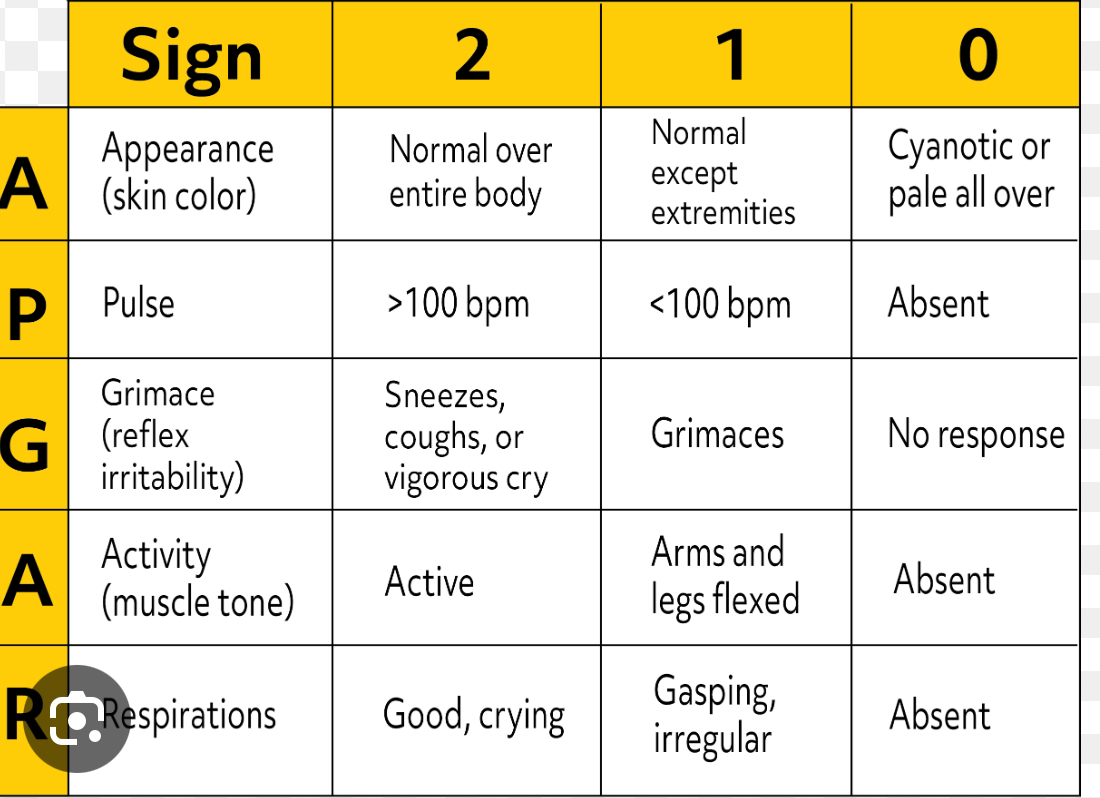
APGAR scoring
Done at 1 min and 5 mins
0-3= severe distress
4-6= moderate difficulty adjusting
7-10= good adjustment
focused assessment for MOTHER
BUBBLE-REEDAH
(get vitals first!)
B- breasts- firmness (soft, filling, or engorged); condition of nipples; breast or bottle feeding
U- uterus- with HOB flat & empty bladder, palpate the fundus (top of uterus). It should be firm & midline, right above umbilicus. If it’s “boggy” (soft), perform a gentle fundal massage
B- bladder- assess voiding patterns, look for retention/distention. Foley for 6-8 hrs after birth. Should void minimum 30ml / hr
B- bowels- Patterns/flatus/ bowel sounds. Colace= common stool softener; Symproic= helps relieve gas
L= Lochia = Normal discharge from vagina after delivery (blood, mucus, tissue). If the pt fills a peri pad every hour, that is too much! (scant, minimal, moderate, heavy). Document color, amt, odor (normal fleshy), clots
E= episiotomy = During a vaginal delivery, the doctor may cut the perineum (bottom of the vagina) if the baby is too large to exit the birth canal
REEDAH assesses episiotomy/ C-section incision
R- redness
E- edema- may see initially, should decrease daily
E- ecchymosis- bruising
D- discharge from episiotomy- should be NONE (can signify infection, esp. if odor is present)
A- approximation= all skin edges should be together
H- Homan’s sign- checks for deep vein thrombosis / DVT / blood clot in leg! Mothers are at high risk after delivery. Dorsiflex pt’s foot (bend toes up & back) - if they have calf pain, they may have a DVT in that leg. Also check for unilateral pain, warmth, swelling, tenderness)
normal vital signs for full term newborn
(40 weeks gestation)
Heart Rate- 110-160 bpm
Respirations- 40-60 breaths per min
bp- 80-60 s / 60-40 d mm Hg
Temp- 97.7 ͦF - 99.6 ͦF (36.5 ͦC- 37.5 ͦC)
SpO2- > 95% in right hand. with 3% or less difference in O2 sat between the right hand and r/l foot.
Head Circumference- 13-15 inches (33 to 37 cm)
Length- 19-21 in (48 to 53 cm)
Weight
Females= 2.8 - 4.0 kg (6lb, 3 oz to 8 lb, 14 oz)
Males= 2.9 - 4.2 kg (6 lb, 7 oz to 9 lb, 5 oz)
LBW = <2500g
ankyloglossia
assess for this in a newborn
when a short frenulum attaches the tongue to the floor of the mouth, limiting its mobility
interferes with breastfeeding
Ballard assessment
determines a newborn’s gestational age - if it was preterm or unknown
length, weight, & head circumference can then be placed on Growth Chart
Placenta complications: previa, abruptio, accreta
Previa- placenta covers the cervix
Painless vaginal bleeding
C section is required
no vaginal exams
Abruptio- placenta detaches from uterus
Abrupt painful bleeding
Baby is deprived of oxygen and nutrients
Third trimester
Accreta- placenta grows too deeply in the uterine wall
Does not spontaneously separate & deliver after birth
Moro
“Startle reflex”
Newborn moves symmetrically in response to loud noise or sudden movement
Disappears at 3-4 months
Babinski reflex
Stroking sole of infant’s foot upward in a J shape elicits a hyper extension of toes
disappears at 1 year
Rooting
When cheek or mouth of newborn is stroked, they turn toward that side
usually disappears at 3-4 months but can last up to 1 year
Tonic neck
“Fencing position”
newborn reflex
Neck turns sharply to that side, arm and leg on that side extend while arm and leg on opposite side are flexed
Disappears in 3-4 months
Lochia
Normal discharge after childbirth
blood, mucus, uterine tissue
Can “gush” out when standing up bc it pools while sitting or lying down
Continues for 4-6 weeks after birth
How body temp changes during menstrual cycle
Basal Body Temp (BBT) rises slightly after ovulation
can prevent conception
Why do newborns bleed after birth?
Absence of intestinal bacteria & LACKING VITAMIN K.
viramin K is produced by bacteria in the stomach which haven’t grown yet
Newborn gets a Vit K shot
Jaundice
Newborns sometimes have immature hepatic function (liver not functioning properly). It can’t break down Bilirubin in the bloodstream- causes yellow appearance
Colposcopy
Magnifies vagina and cervix for examination
looks for precancerous lesions
Biopsy taken
Light bleeding may occur after
Culdoscopy
Views structures in the pelvic cavity
after the procedure, lay client on stomach with pillow underneath to expel air that entered the abd.
Checking Under Lady parts thru the CUL De sac of Douglas
Primigravida
A woman pregnant for the first time
after delivery, they’re a primipara
Rh incompatibility
Occurs when the mother is Rh negative and is carrying a Rh positive fetus.
Mom’s body doesn’t recognize Rh positive cells and attacks the baby’s cells
Firstborn babies are not affected usually bc the mom’s body takes time to build antibodies (unless mom had a previous miscarriage)
If mom and dad are Rh positive, incompatibility is not possible
Moms/babies at risk need given RhoD immune globin
Depressed fontanels in newborns
Indicate fluid volume deficit
Preeclampsia
Pregnant mother’s arteries constrict, causing increased bp
report decreased fetal movement, urine output, or persistent and severe Headache
Vernix caseosa
Cheesy substance covering a full-term newborn
Characteristics of a preterm newborn
bright pink / translucent skin
Lanugo present (fine hair on body)
Soft ear cartilage
Meconium stool
Treating/ preventing heartburn
when the lower esophageal sphincter is weak and stomach acid back flows into throat
sit up after meals
Eat small, frequent meals
avoid gassy, fatty, spicy, fried food
Myth: drink milk (this can temporarily reduce burning but later causes reflux again bc of fat)