IX. Anemias
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pg: 269-277
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Anemia
dec. in RBCs and Hgb, resulting in dec. oxygen delivery to the tissues.
How are anemias classified?
morphologically using RBC indices
etiology/cause: Hgb: <12 g/dL in men or <11 g/dL in women
Relative (pseudo) anemia
plasma vol. is inc
Reticulocyte count normal
normocytic/normochromic anemia
Ex: Pregnancy
Absolute anemia
RBC mass is decreased
Mechanisms:
DECREASED delivery → reticulocytopenia
INCREASED loss of red cells → reticulocytosis
Iron-deficiency anemia
Most common type of anemia
Laboratory: Microcytic/hypochromic anemia
LOW: serum iron, ferritin, Hgb/HCT, RBC indices, & retic
RDW and TIBC high
show ovalocytes/pencil forms
Clinical symptoms: Fatigue, dizziness, pica, stomatitis (cracks in the corners of the mouth), glossitis (sore tongue), and koilonychia (spooning of the nails)
Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD)
2nd most common type of anemia
Inability to use available iron
Impaired release of storage iron w/ inc. hepcidin lvls
Liver hormone; + acute-phase reactant
Levels inc.; dec. iron release from stores
Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD) Lab
Lab: Normo/normo, or slightly micro/hypo
inc. ESR; N to inc. ferritin; low serum iron and TIBC
Persistent infections, chronic inflammatory disorders (SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, Hodgkin lymphoma, cancer)
Sideroblastic anemia
caused by blocks in the protoporphyrin pathway
defective Hgb synthesis and iron overload.
Characterized by ringed sideroblasts (Pappenheimer bodies on Wright stained smears)
1° (irreversible) dimorphic
2° (reversible)
Siderocytes are best demonstrated using what stain?
Prussian Blue
Sideroblastic Anemia Lab
Microcytic/hypochromic anemia
increased ferritin and serum iron
Total iron binding capacity (TIBC) dec.
Lead poisoning
Normocytic/normochromic anemia w/ basophilic stippling
MULTIPLE blocks in protoporphyrin pathway
gum lead line from blue/black deposits of lead sulfate
Lead Poisoning Lab
Normocytic/normochromic anemia w/ basophilic stippling
Porphyrias
group of INHERITED disorders characterized by A block in protoporphyrin pathway of heme synthesis.
Clinical symptoms: Photosensitivity, abdominal pain, CNS disorders
Megaloblastic anemias
Defective DNA synthesis
Megaloblastic
either a vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency
Megaloblastic Anemias’ Lab
macrocytic/normochromic anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency (cobalamin)
Pernicious anemia
deficiency of intrinsic factor
achlorhydria (stomach does not produce enough HCl acid)
Clinical symptoms: CNS problems
Pernicious
having a harmful effect, especially in a gradual or subtle way
ex: Pernicious anemia → body's immune system attacks cells in the stomach that produce intrinsic factor, a protein needed for vitamin B12 absorption → Vitamin B12 deficiency
Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 Deficiency both cause Megaloblastic anemia…
How do they differ?
Vit. B12 defic.
CNS involvement
pernicious anemia (intrinsic factor defic.)
achlorhydria
Folic Acid defic.
no CNS involvement
methotrexate (anti-folic drug)
Non-megaloblastic macrocytic anemias
anemias include alcoholism, liver disease, and cause accelerated erythropoiesis.
Non-megaloblastic macrocytic vs megaloblastic macrocytic anemias
round RBCs vs oval RBCs
Aplastic anemia
BM failure → pancytopenia
Lab: dec. in Hgb/HCT and retics
normocytic/normochromic anemia
Treatment: BM or SC transplant and immunosuppression
Can be genetic, acquired, or idiopathic
Genetic aplastic anemia (Fanconi anemia)
Autosomal RECESSIVE
inc. risk of malignancy (especially acute lymphoblastic leukemia).
Acquired aplastic anemia (secondary)
~30% from drug exposure.
Idiopathic (primary) aplastic anemia
50–70% have no known cause
Diamond-Blackfan anemia
True red cell aplasia (WBCs and PLTS normal)
Autosomal inheritance
Myelophthisic (marrow replacement) anemia
Hypoproliferative anemia caused by replacement BM hematopoietic cells
Lab: Normocytic/normochromic anemia
Hemochromatosis
A genetic disorder causing excessive iron absorption and accumulation in the body, leading to tissue damage.
Acute blood loss anemia vs. Chronic blood loss anemia
SUDDEN loss of blood vs GRADUAL, long-term loss of blood
Acute blood loss anemia
sudden blood loss
Clinical symptoms: Hypovolemia, rapid pulse, low blood pressure, pallor
Lab: Normocytic/normochromic anemia
inc. in PLT, leukocytosis w/ left shift
dec. in Hgb/HCT and RBC
Chronic blood loss anemia
gradual, long-term loss of blood
Lab: Initially normo/normo anemia
gradual loss of iron →
micro/hypo anemia
Hgb/HCT dec.
Hemolytic Anemias Due to Intrinsic Defects all cause…?
normocytic/normochromic anemia
Types of Hemolytic Anemias Due to Intrinsic Defects
Hereditary..
spherocytosis
elliptocytosis/ovalocytosis
stomatocytosis
acanthocytosis (abetalipoproteinemia)
GP6D deficiency
Pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Hereditary spherocytosis
Most common membrane defect
Spherocytes on PBS
Dec. surface area-to-vol ratio
MCHC > 37 g/dL (hyperchromia)
Hereditary elliptocytosis (ovalocytosis)
Autosomal DOMINANT
>25% ovalocytes
Hereditary stomatocytosis
Autosomal DOMINANT
up to 50% stomatocytes
Hereditary acanthocytosis (abetalipoproteinemia)
Autosomal RECESSIVE
50-100% acanthocytes
G6PD Deficiency
Sex-linked (X) enzyme defect
most common enzyme deficiency in the hexose monophosphate shunt
results: Hgb to methemoglobin (Fe3+ = Ferric) → unable for RBCs to bind to O2
forms Heinz bodies
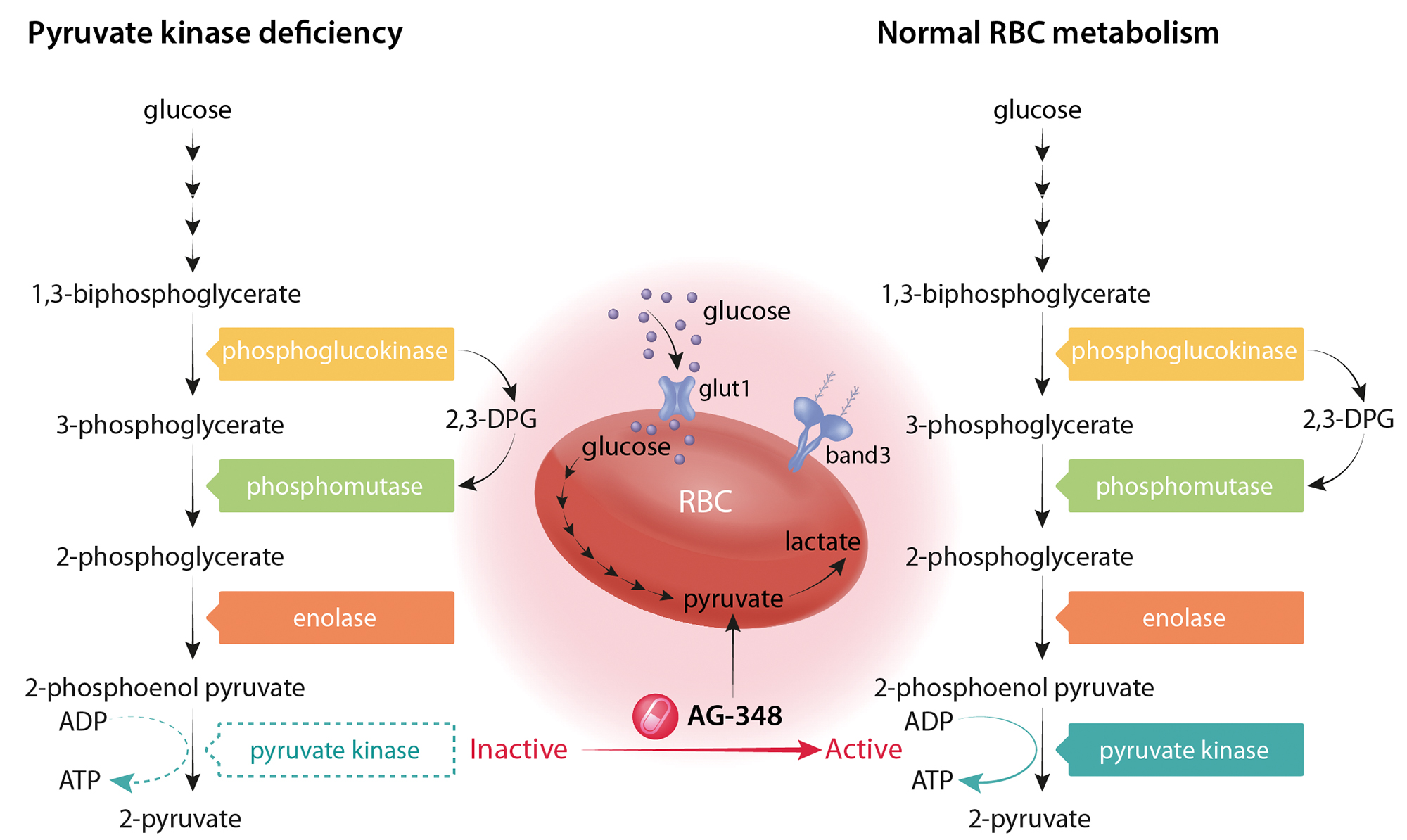
Pyruvate Kinase (PK) deficiency
Autosomal RECESSIVE
Embden-Meyerhof pathway defect → reduced life span of RBC (deformed, severe)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
ACQUIRED membrane defect
Inc. sens. to complement-mediated lysis of RBCs,
Pancytopenia and chronic intravascular hemolysis
Diagnosed via Ham’s and sugar water tests; inc. leukemia risk.
leads to hemolysis & hemoglobinuria
Types of Hemolytic Anemias Due to Extrinsic/Immune Defects
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (WAIHA)
Cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia (CAIHA or cold hemagglutinin disease)
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
Hemolytic transfusion reaction
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN/HDFN)
Hemolytic Anemias Due to Extrinsic/Immune Defects all cause…?
normocytic/normochromic anemia
acquired disorder
accelerated destruction w/ reticulocytosis
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (WAIHA)
RBCs coated w/ IgG and/or complement
Macrophages phagocytize these
Lab: Spherocytes, MCHC >37 g/dL, increased osmotic fragility, bilirubin, reticulocyte count, occasional nRBCs (DAT).
Cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia (CAIHA or cold hemagglutinin disease)
RBCs coated w/ IgM and complement at temps BELOW 37C
Can be idiopathic or secondary to M. pneumoniae
MCHC >37 g/dL
Inc. bilirubin & retic count
Positive DAT (complement-coated RBCs)
Warm sample to 37°C for accurate results if high antibody titer
CAIHA vs WAIHA (Antibody Type and Cause)
IgG ± complement; reacts at 37°C, 60% idiopathic
vs.
IgM + complement; reacts below 37°C, Idiopathic, Secondary to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
CAIHA vs WAIHA (Laboratory)
Laboratory Finding | Warm AIHA (WAIHA) | Cold AIHA (CAIHA/CAD) |
|---|---|---|
DAT | IgG ± complement (C3d) | complement only (C3d) |
Peripheral smear | Spherocytes | RBC clumping (macro/microscopic) |
MCHC | Increased | Increased |
Sample handling | Normal processing | Must warm to 37°C if high cold agglutinin titer |
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
IgG biphasic Donath-Landsteiner Ab w/ P specificity fixes complement to RBCs in cold (< 20°C); the complement-coated
RBCs lyse when warmed to 37°C.
Can be idiopathic, or secondary to viral infections
Laboratory: inc. bilirubin and plasma HgB, dec. haptoglobin, Donath-Landsteiner test positive
Hemolytic transfusion Rxn
Recipient has Abs to Ags on donor RBCs → donor cells are destroyed.
ABO incompatibility:
Usually IgM Abs
Can trigger DIC
Lab: + DAT, inc. plasma HgB
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN/HDFN)
Rh (ABO) incompatibility (erythroblastosis fetalis)
Rh(-) woman (group O) exposed to Rh(+) fetal blood → forms IgG Abs
IgG crosses placenta in subsequent pregnancies → coated RBCs are phagocytized
Lab
Severe anemia
nRBCs
(+) DAT
High bilirubin → risk of kernicterus (brain damage)
Use of Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGam) for prevention
Types of Hemolytic Anemias Due to Extrinsic/Nonimmune Defects
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemias (MAHAs)
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
March hemoglobinuria
Other causes: Infectious agents, mechanical trauma, thermal burners
Hemolytic Anemias Due to Extrinsic/NONimmune Defects all…?
All cause a normocytic/normochromic anemia
caused by trauma to the RBC.
All are acquired disorders that cause intravascular hemolysis
schistocytes and thrombocytopenia.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Systemic clotting due to toxins triggers coagulation, causing organ failure and RBC fragmentation.
Fibrin is deposited in small vessels, causing RBC fragmentation.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
Occurs most often in children following a gastrointestinal infection (e.g., E. coli)
Clots form, causing renal damage
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
occurs most often in adults.
deficiency of the enzyme ADAMTS-13 (breaks down vWF → dec.)
von Willebrand factor
Mediates platelet adhesion & stabilizes factor VIII for clotting.
Uncleaved multimers: microthrombi → leads to:
RBC damage (→ schistocytes/MAHA)
Neurologic symptoms (→ CNS involvement in TTP)
March hemoglobinuria
Transient hemolytic anemia that occurs after forceful contact of the body with hard surfaces (e.g., marathon runners and tennis players)
Other causes of Hemolytic Anemias Due to Extrinsic/Nonimmune Defects
Infectious agents (e.g., Plasmodium falciparum, Clostridium perfringens)
Mechanical trauma (e.g., prosthetic heart valves/"Waring blender syndrome")
Thermal burns (especially third-degree)
Cause direct RBC membrane damage → acute hemolysis
Aplasia meaning and significance
the failure of an organ or tissue to develop or to function normally → dec. in RBCS due to failure of the BM to produce them
Pyruvate Kinase (PK) Deficiency Lab
Normocytic anemia
Reticulocytosis
↑ unconjugated bilirubin
Echinocytes/Burr
Negative DAT (non-immune hemolysis)
Positive DAT vs Positive IAT
+ DAT = Abs are attached to the RBCs → suggesting autoimmune hemolytic anemia
+ IAT = Abs in the serum that may react with RBCs → used for blood typing or crossmatching
Donath-Landsteiner test
detects the presence of the Donath-Landsteiner Ab
→ IgG Ab that binds to RBCs at low temp and then triggers their destruction when warmed
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria (PCH).
Paroxysmal
Sudden onset or sudden recurrence of symptoms; a sudden attack or burst of activity
→ hemolytic episodes can happen suddenly
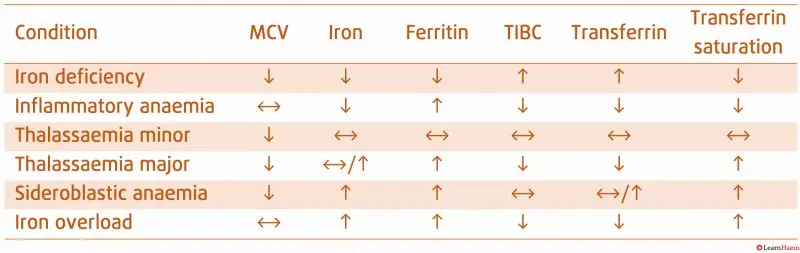
Iron Studies Chart
Serum iron reflects the amount of iron circulating in the blood, TIBC measures the blood's capacity to transport iron, and ferritin indicates the body's iron storage levels