bio msstate
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
how do plants affect humans?
oxygen, food, ecosytem
how do humans affect plants?
produce CO2, grow them, pollution
does not have vascular tissue
bryophytes (moss)
has vascular tissue
vascular plant
vascular plants that only use spores
fern and fern allies
vascular plants that use seeds
seed plant
if the seeds are found in cones
gymnosperms (conifers, gingko)
if the seeds are found in fruits
angiosperms (flowering plants)
the angiosperm has one seed leaf (cotyledon)
monocotyledon (monocots)
monocot
grass, corn, sugarcane
the angiosperm has two seed leaves (cotyledon)
dicotyledon (dicots)
dicots
roses, oak tree, peas
not plants
coral, mushroom, fungi
three basic parts of most plants
roots, leaves, stem
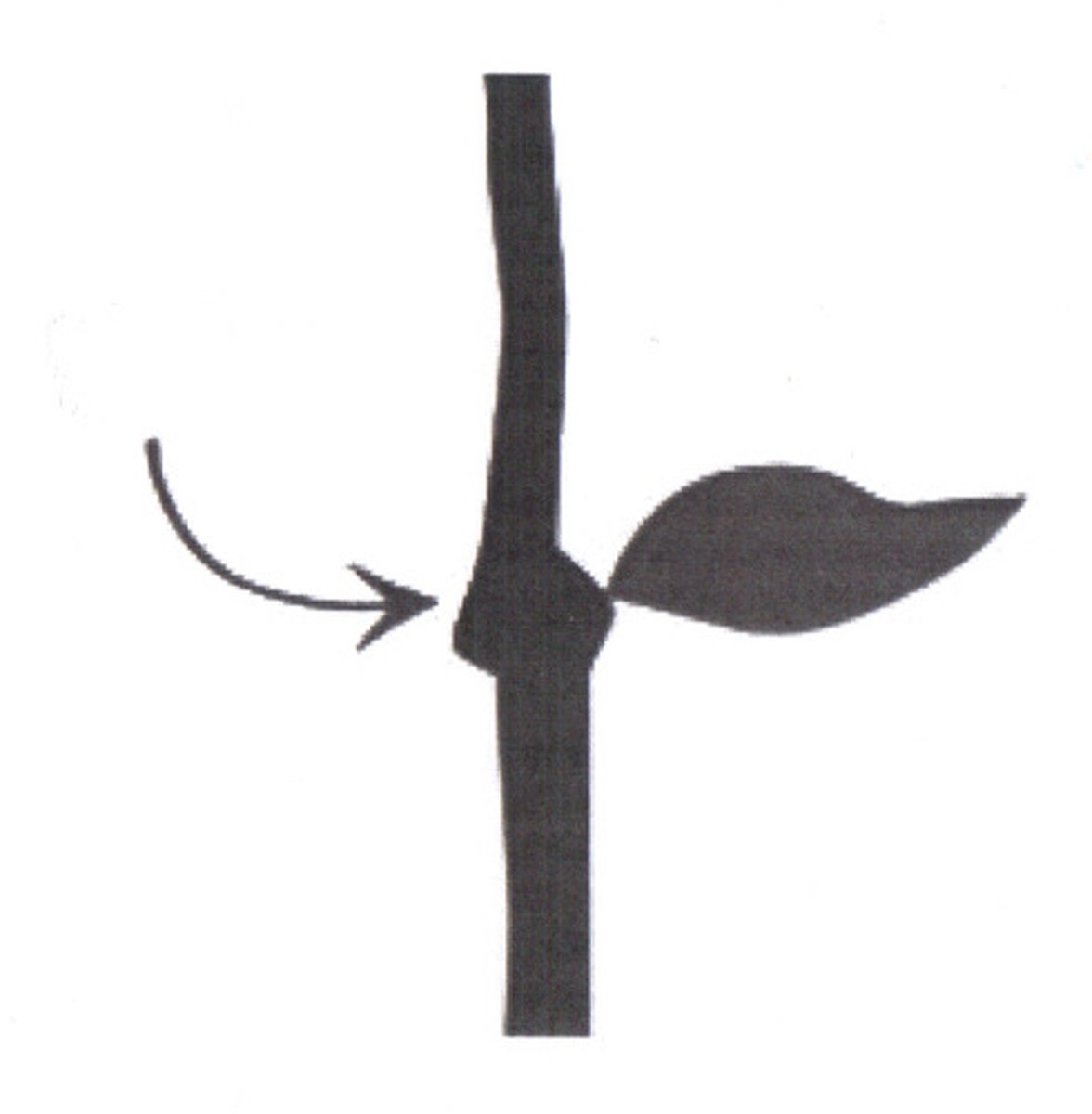
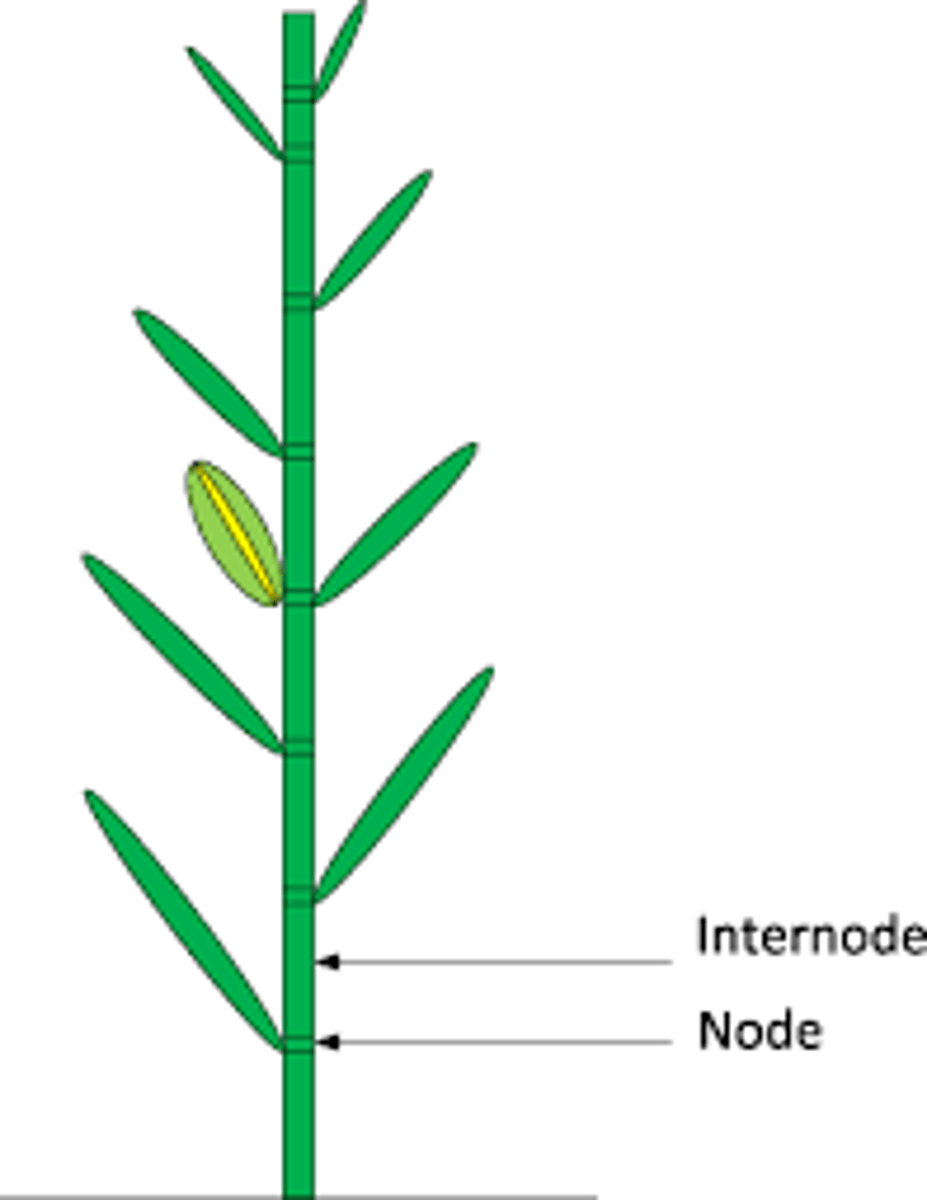
node
point of the stem where the leaf is attatched
internode
part of the stem between nodes
petiole
stalk that connects the leaf to the stem

shoot
leaves and stem together
tendril
type of shoot
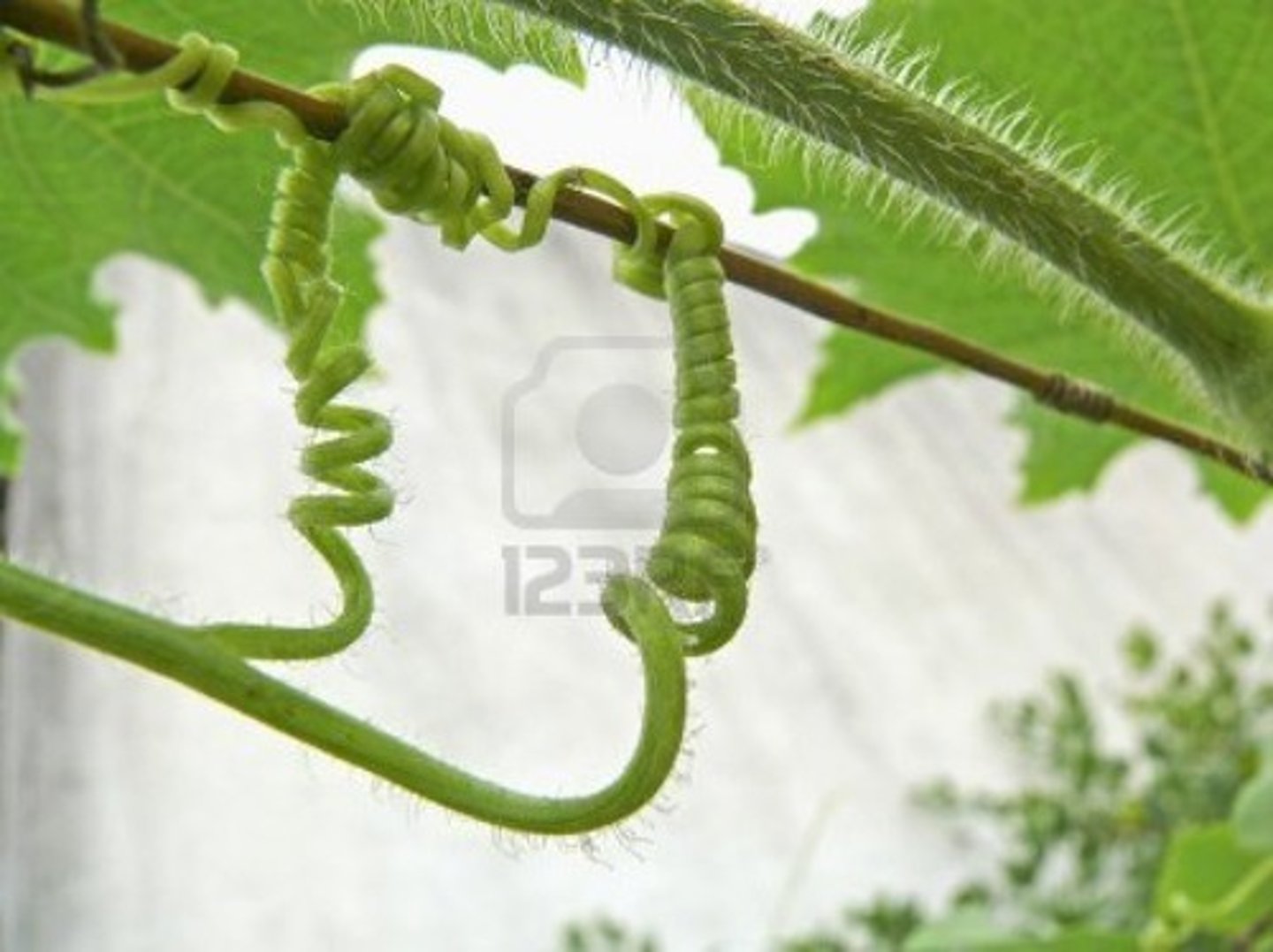

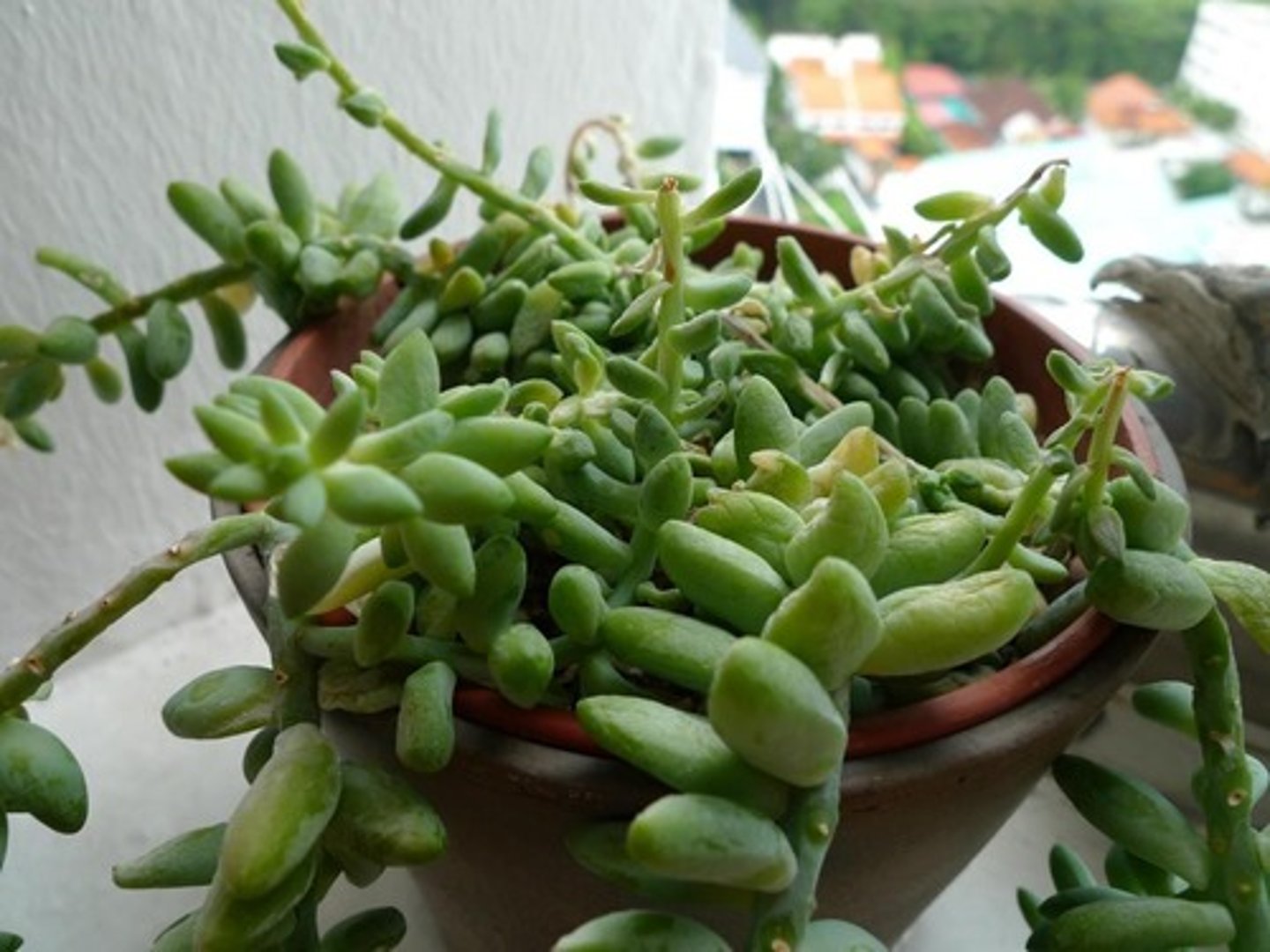
leaf succulent
type of shoot

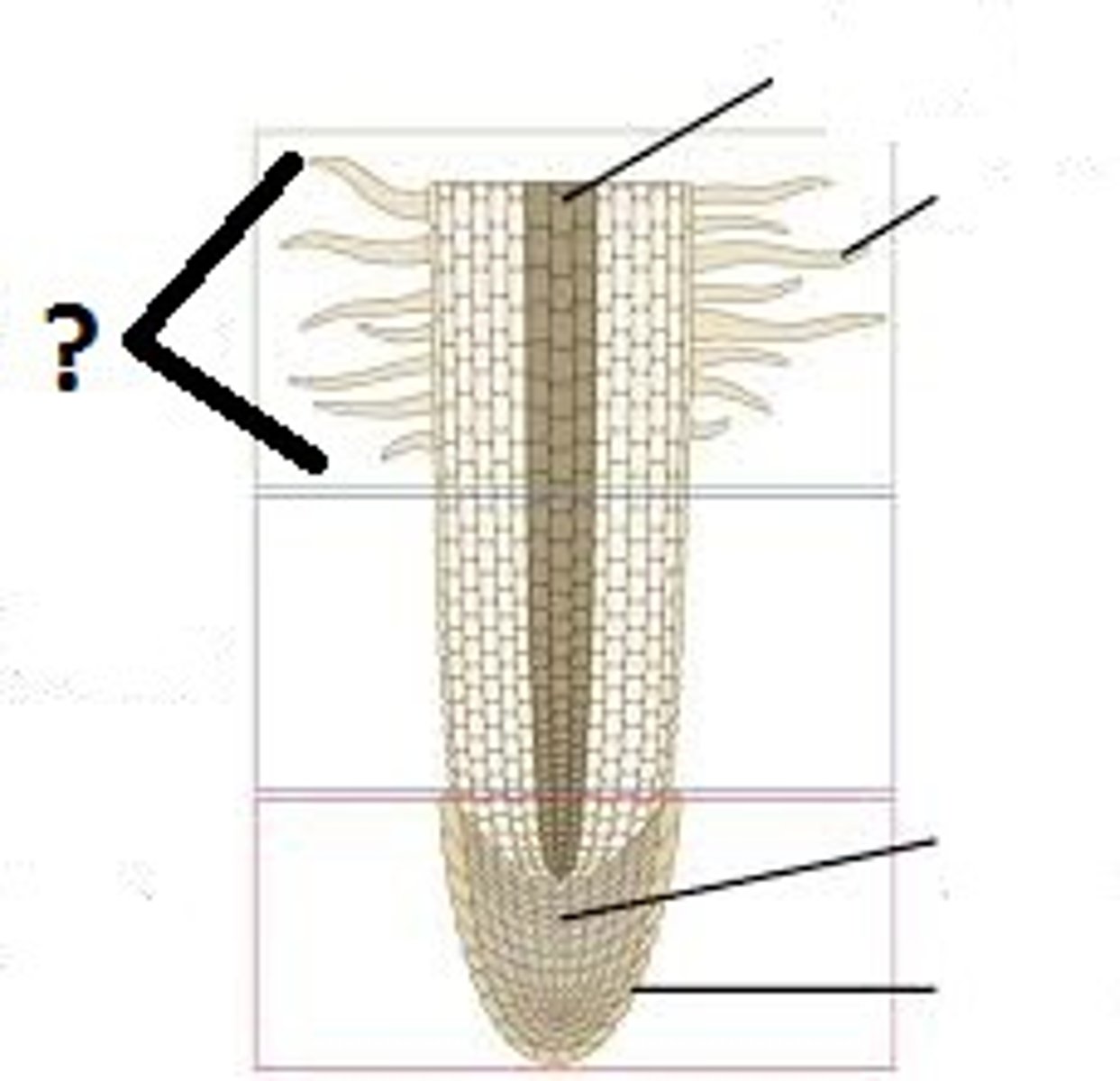
lowest point of the root
area of cell division / root cap
middle area of the root
area of elongation
top of the root
area of maturation / root hair
area of cell division
increase number of cells
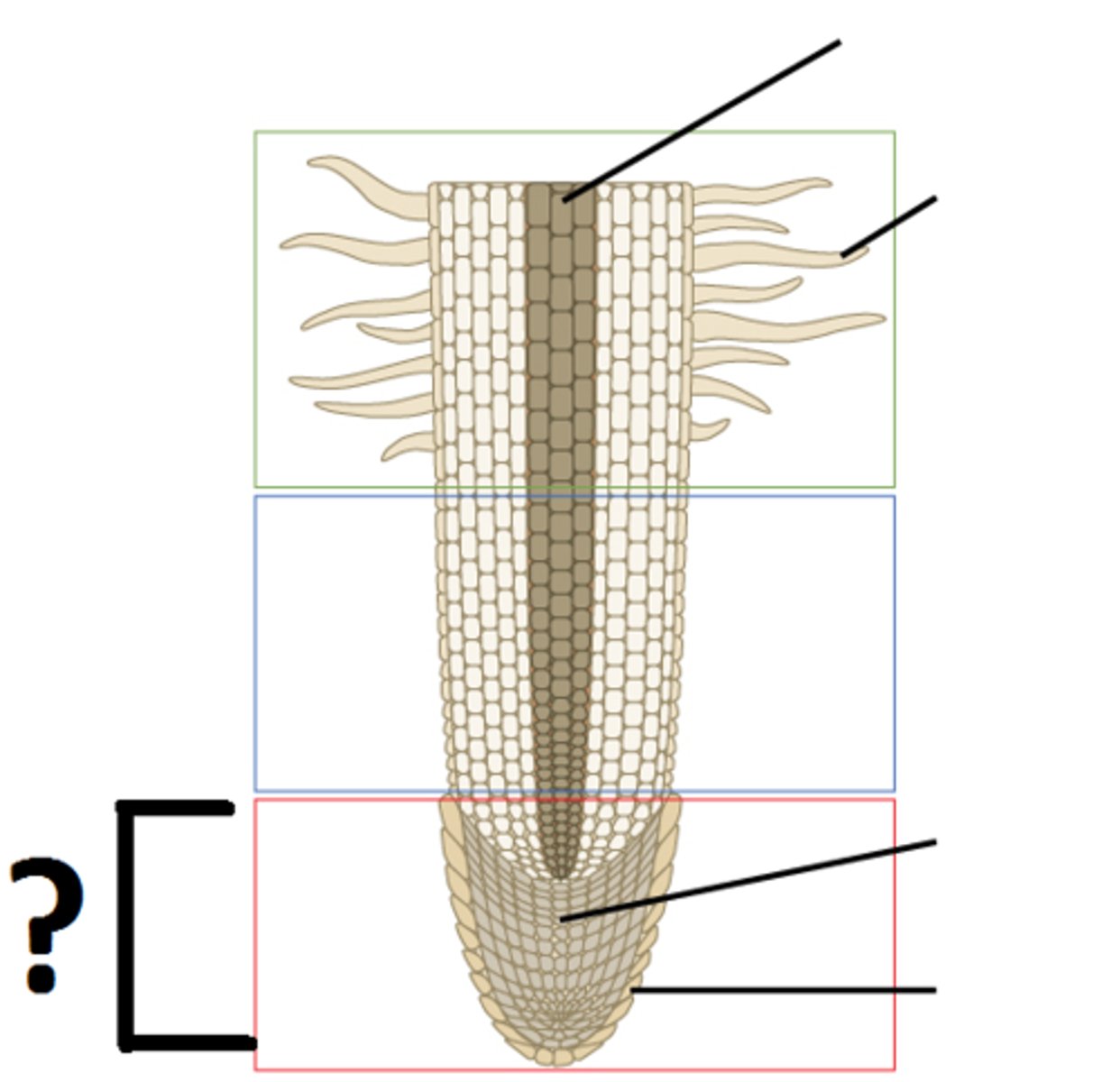
area of elongation
increase size of cells
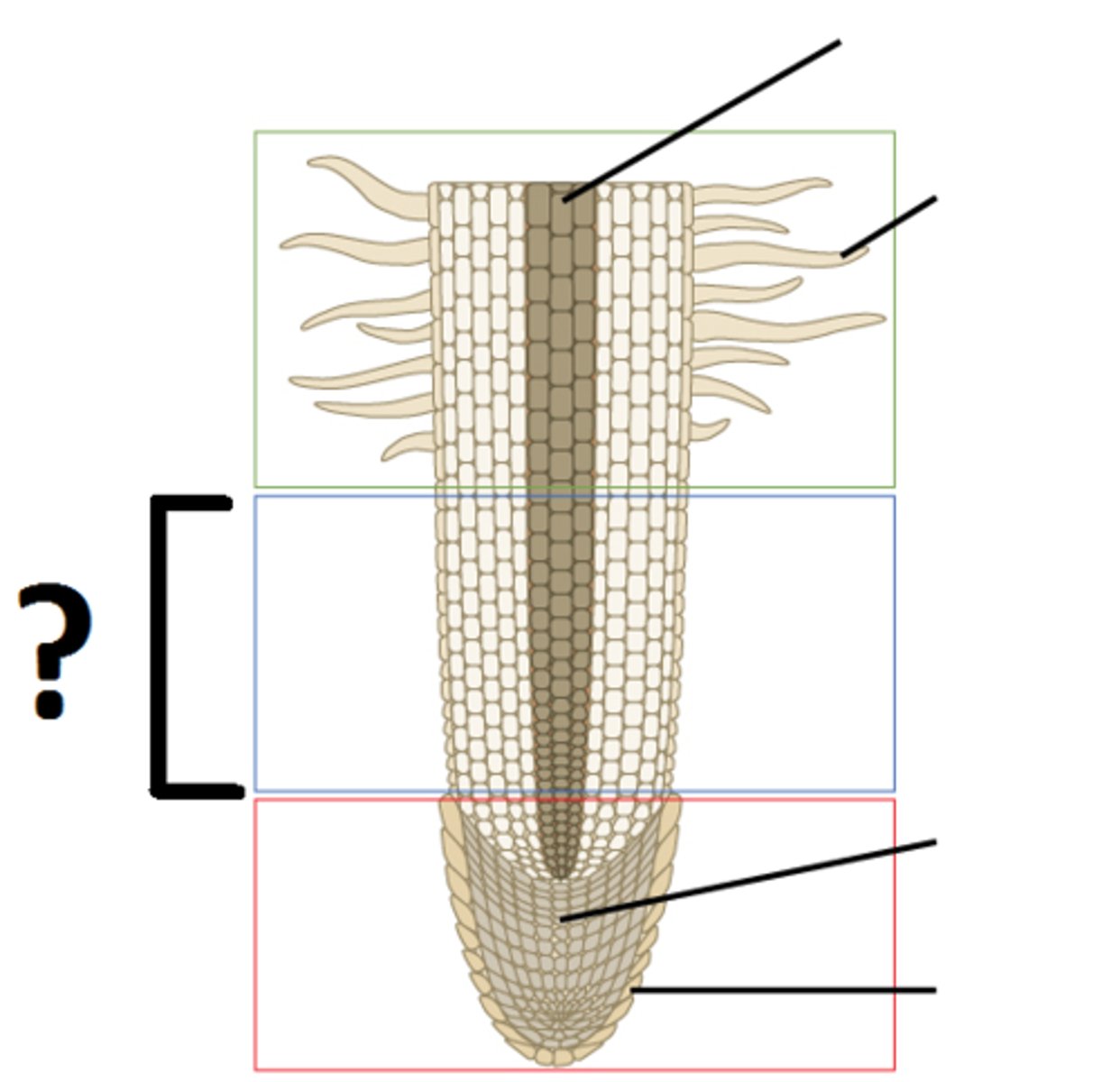
area of maturation
cells develop specialized functions
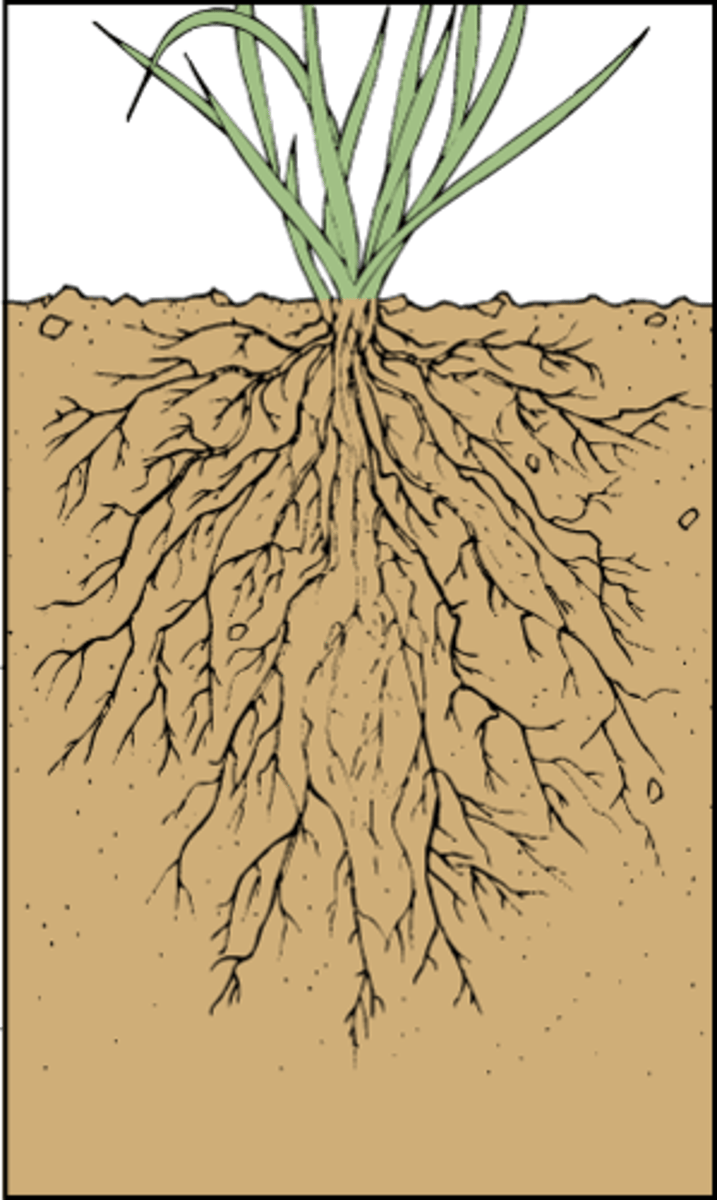
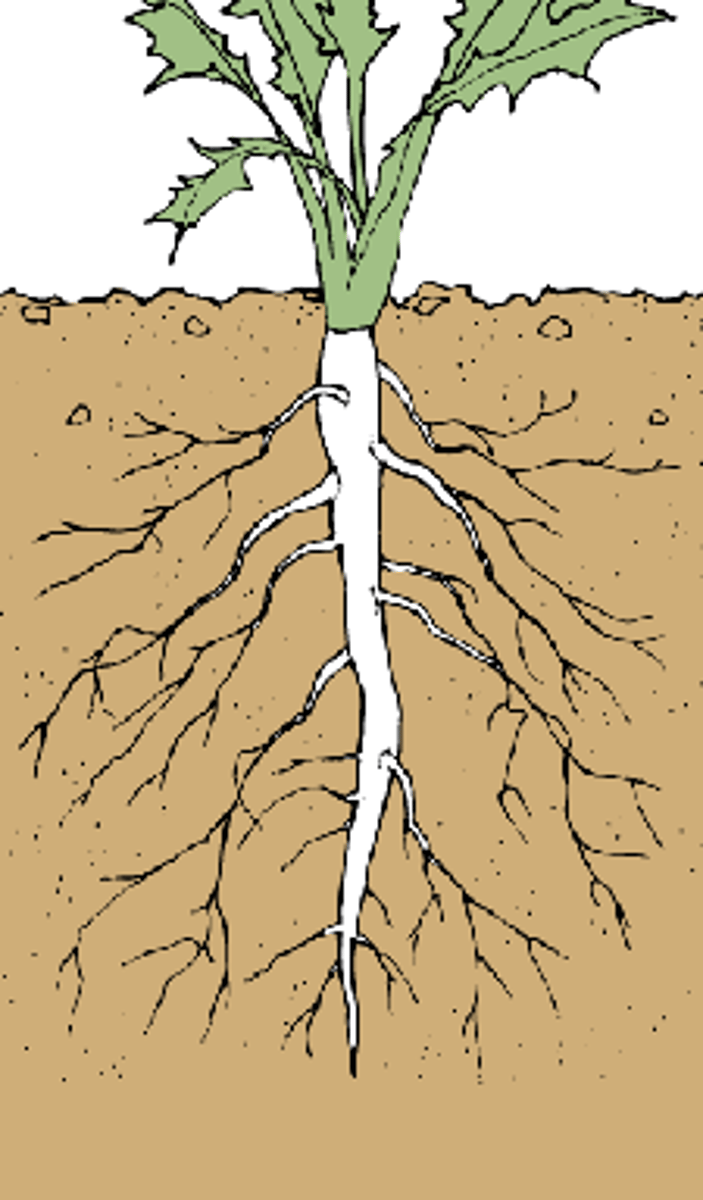
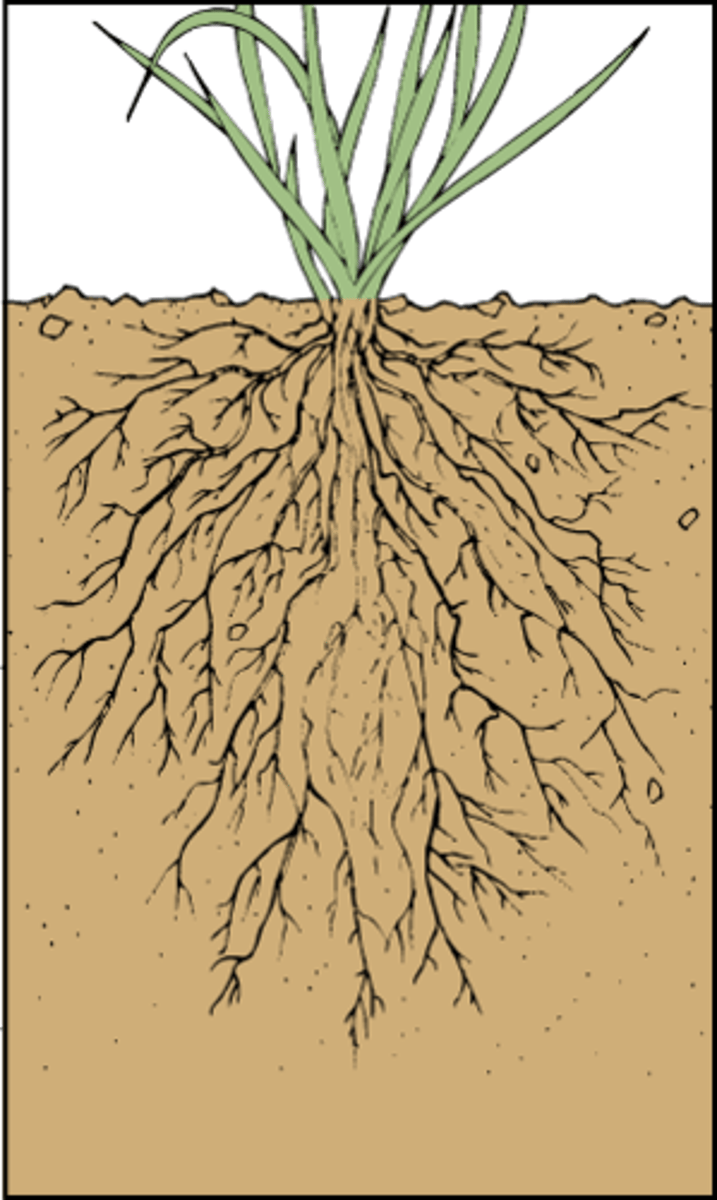
types of root systems
taproot and fibrous
taproot
primary root growing downward, extra from the side
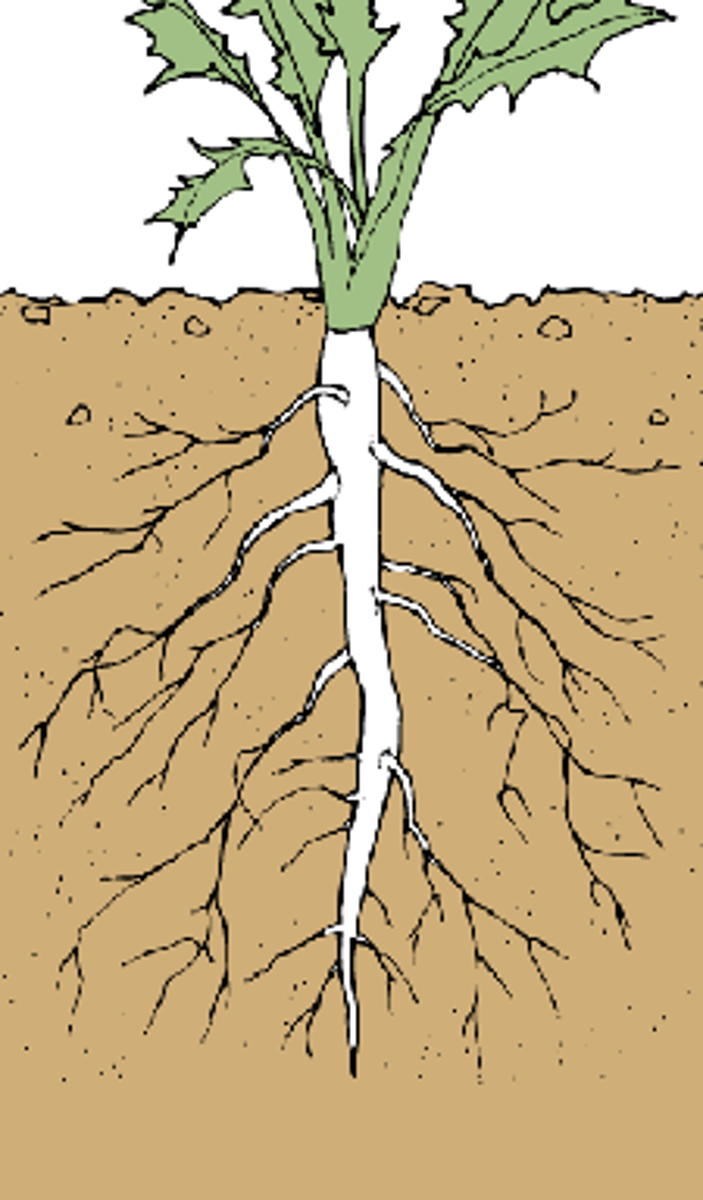
fibrous
no main root, always going down
4 basic parts of a flower
sepal, petal, stamen, carpel
sepal
usually green leaves that enclose a flower bud

petals
colorful, fragrant leaves attract pollinators

stamen
male reproductive plant part

parts of the stamen
anther and filament
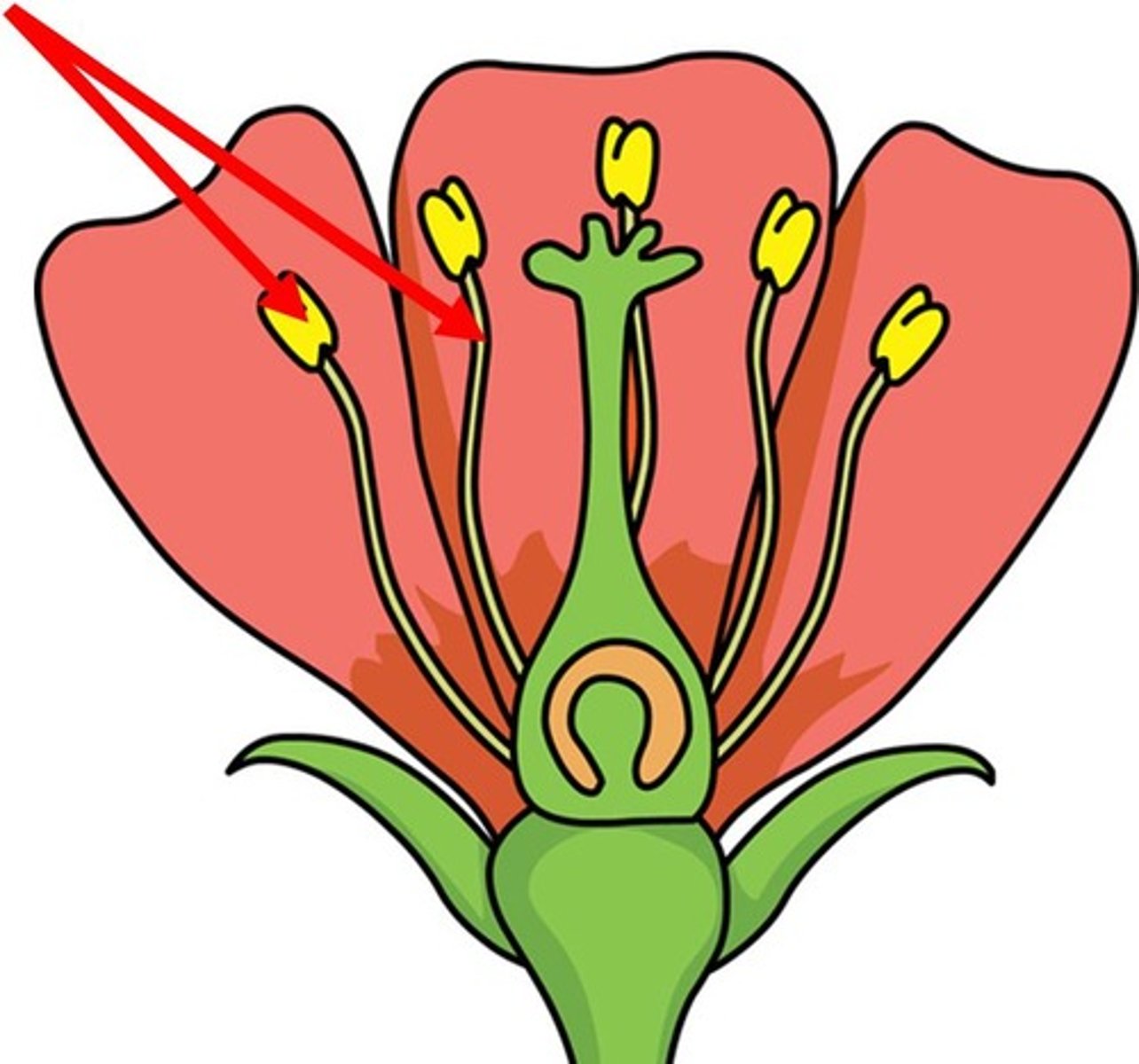
anther
has pollen pacs
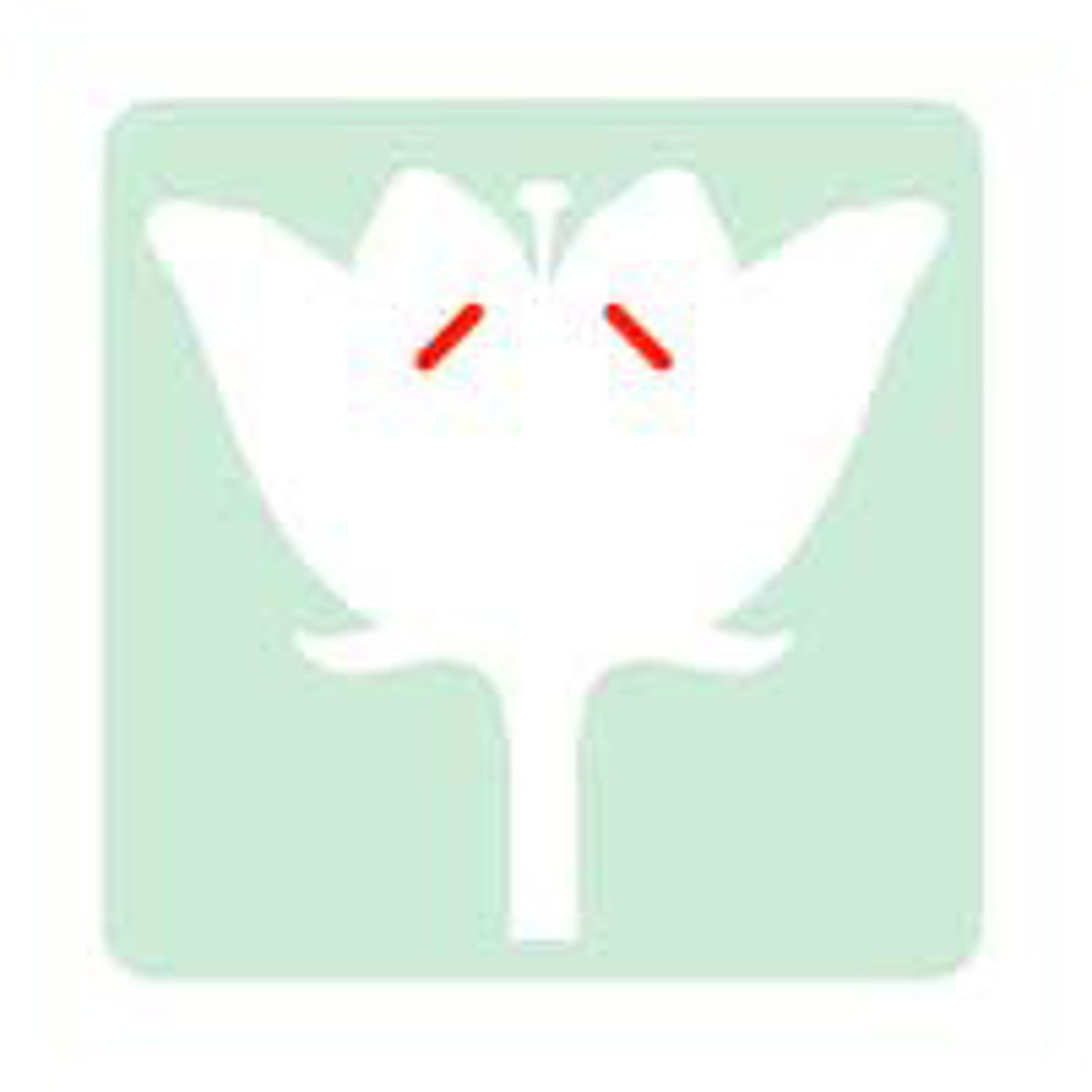

filament
upholds the anther

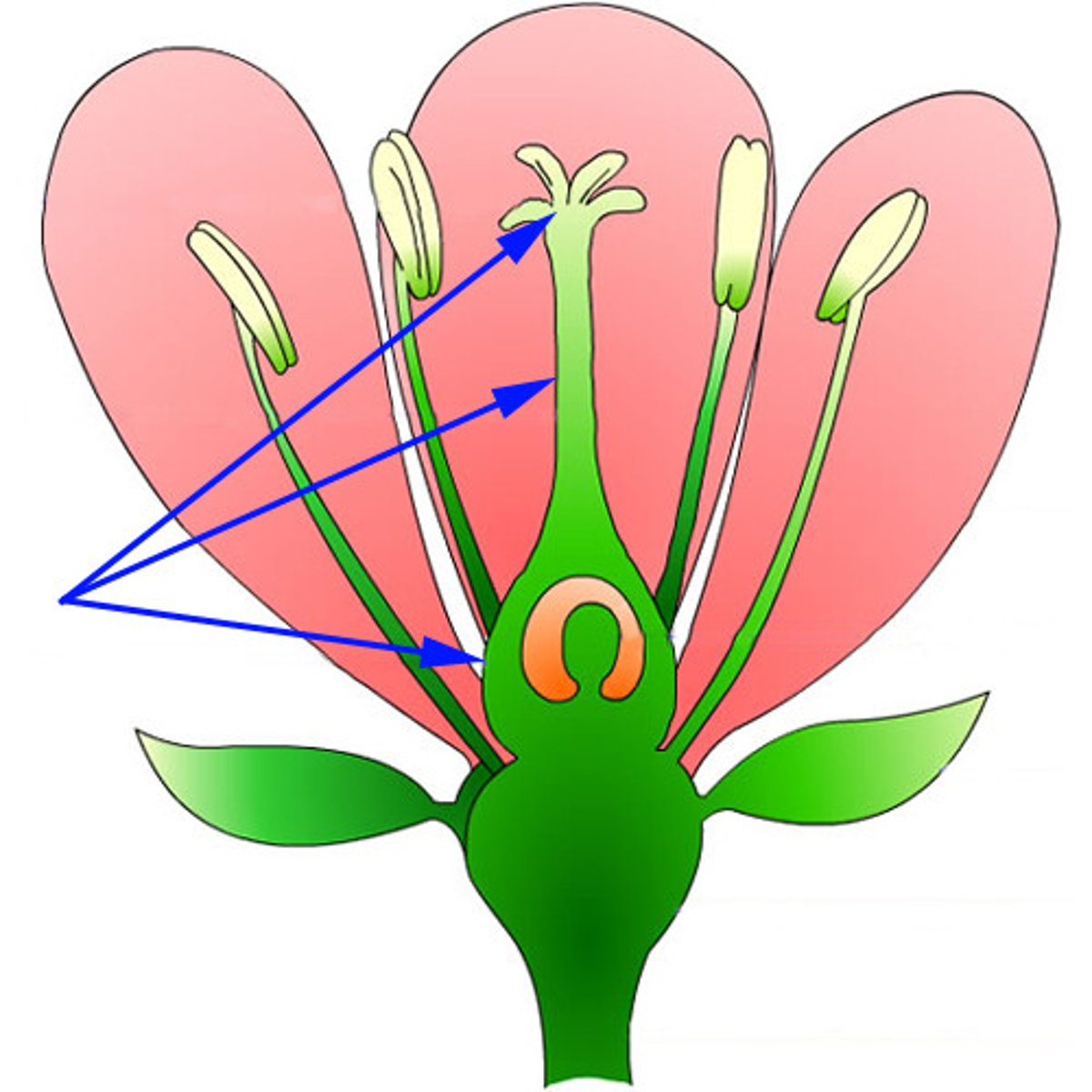
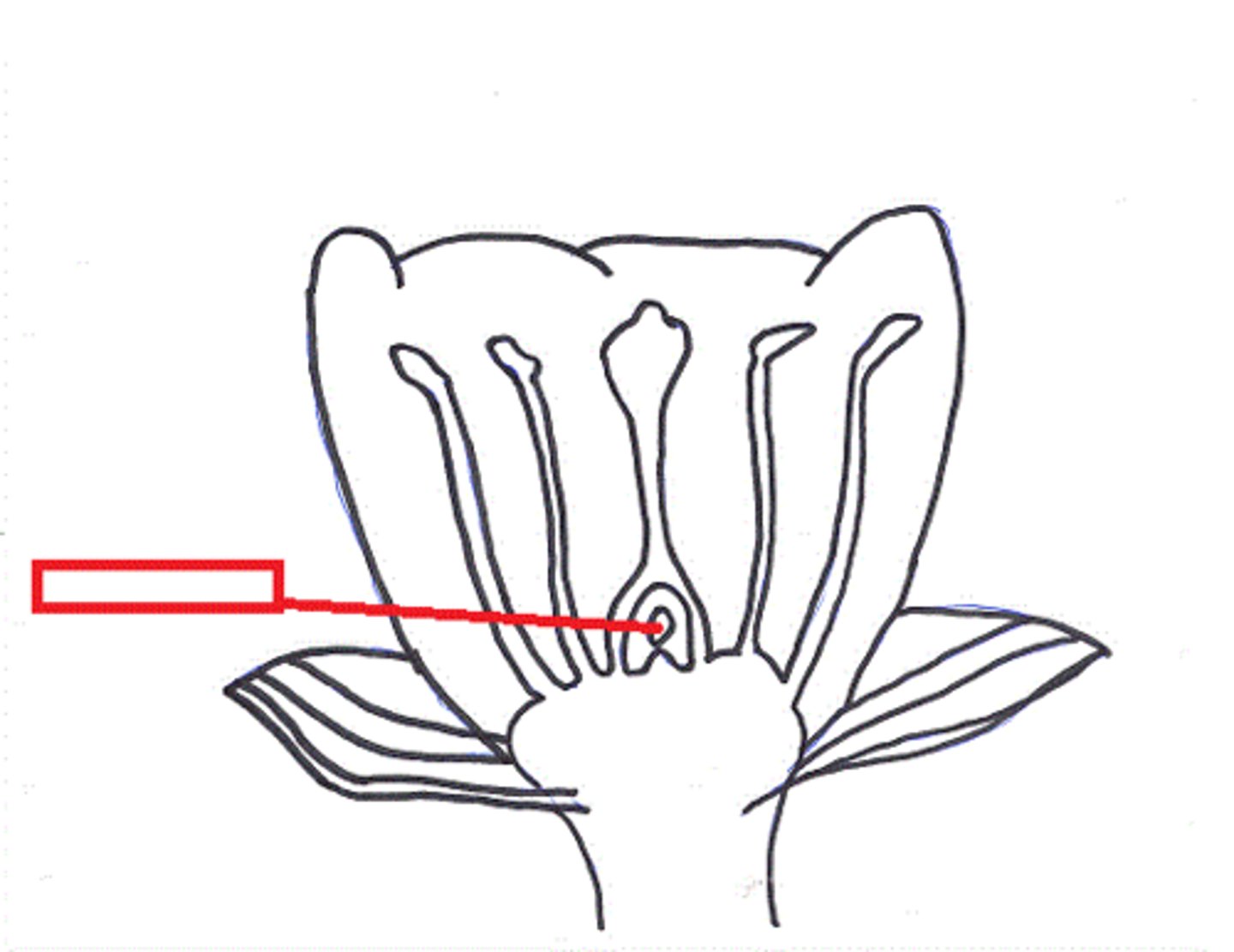
carpal (pistil)
female reproductive plant part

parts of the carpel (pistil)
stigma, style, ovary
stigma
sticky surface where pollen lands

stye
long tube that connects stigma and ovary
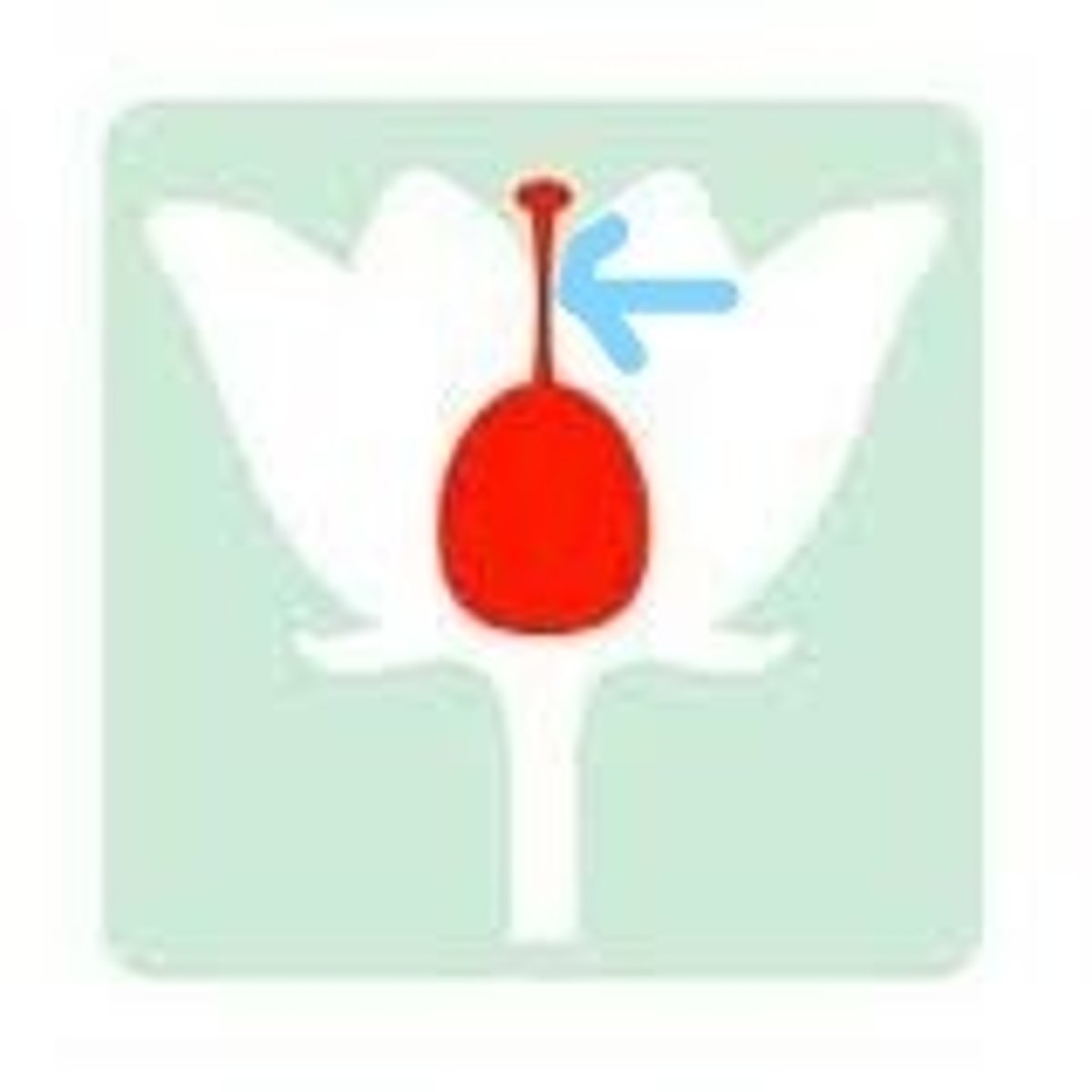

ovary
structure at bottom of carpel that contains ovules
fruits
have a core, have seeds, botanical
vegetables
no core, no seeds, culinary
plant bodies
less complex organs, growth at certain areas
animal bodies
more complex organs, entire body grows and certain amount of growth
lifespan of annuals
one year
lifespan of biennials
two years
lifespan of perennials
more than two years
first Lifestage
juvenile/childhood- developing, growing
second lifestage
adulthood- fully developed, able to reproduce
types of stems
herbaceous and woody
herbaceous
usually green, smooth, flexible, annuals, biennials, perennials
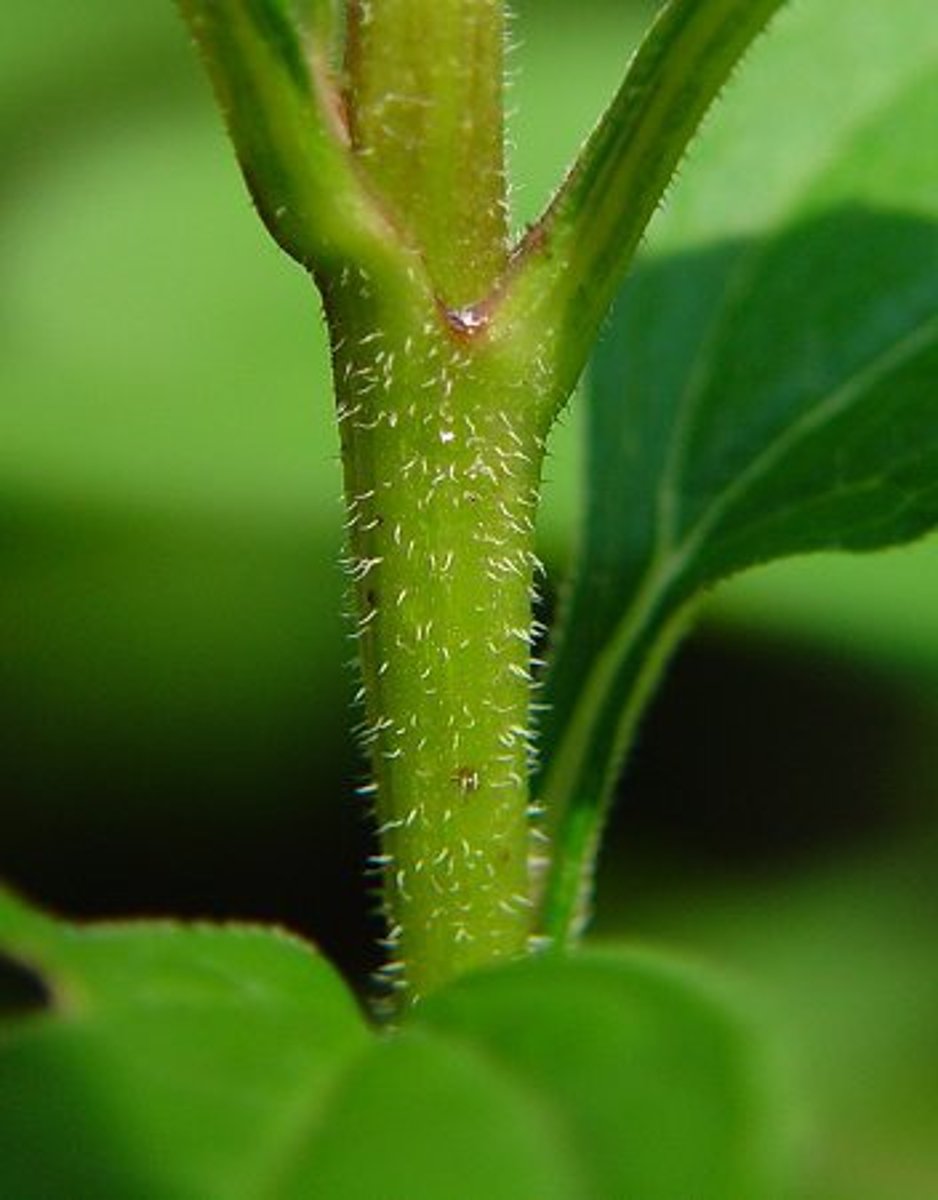

woody
bark, brown, rough, inflexible, perennials

levels of biological organization
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
hooke
coined the term "cell"
van leeuwenhoek
first person to see living cells under microscope
shleiden said
all plants are made of cells
schwann said
all animals are made of cells
virchow said
cells come from pre-existing cells/ father of pathology
cell theory
cell is the basic unit of life, all living things are made of cells, cells come from pre-existing cells
organelles
structures within cells that have specific function
cell wall
exterior most part of the plant cell, unique to plant cells, made of cellulose
plasma membrane
interior to cell wall, semi-permable
cytoplasm
jelly-like substance surrounding the organelles
cytosol
liquid part of the cytoplasm
nucleus
contains DNA, double membranes
central vacuole
storage area(water, acid, waste), contains cell sap, surrounded by the tonoplast
types of plastids
pro plastid, chloroplast, chromoplast
pro plastid
most basic type of plastid, found in meristems
chloroplast
associated with photosynthesis, green chlorophyll
chromoplast
reddish-orange pigment
mitochondrion
energy generation, number varies by cell
types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
rough ER and smooth ER
rough ER
attached ribosomes
smooth ER
no ribosomes, makes lipids
ribosomes
makes proteins
microtubules and microfilaments
associated with cytoskeleton, transportation
intercellular spaces
spaces between cells, gas exchange, often found in mature plant parts
parenchyma cells
has primary cell wall, living at maturity, ass. with meristematic areas/ ex. apple
collenchyma cells
has primary cell wall, thickened at the corners, living at maturity/ ex. celery
sclerenchyma cells
has a primary cell wall and secondary cell wall, dead at maturity
types of sclerenchyma cells
fibers and sclereids
types of tissues
epidermis and vascular tissue
epidermis
outermost layer of plant parts
located in epidermis tissue
cuticle, stomata, guard cells, trichomes
cuticle
waxy coating on the epidermis
stomata
openings for gas exchange
guard cells
pair of cells surrounding stomata that controls its opening/closing
trichomes
hairlike projections on plant surfaces
located in vascular tissues
xylem and phloem
xylem
towards the back, transports water
phloem
towards the inside, transports sugar/nutrients
stomata on leaves
more stomata on the lower leaf surface than the upper leaf surface
mesophyll
Interior leaf tissue containing chloroplasts.
palisade mesophyll
columns rich in chloroplast
spongy mesophyll
lots of open spaces for gas exchange
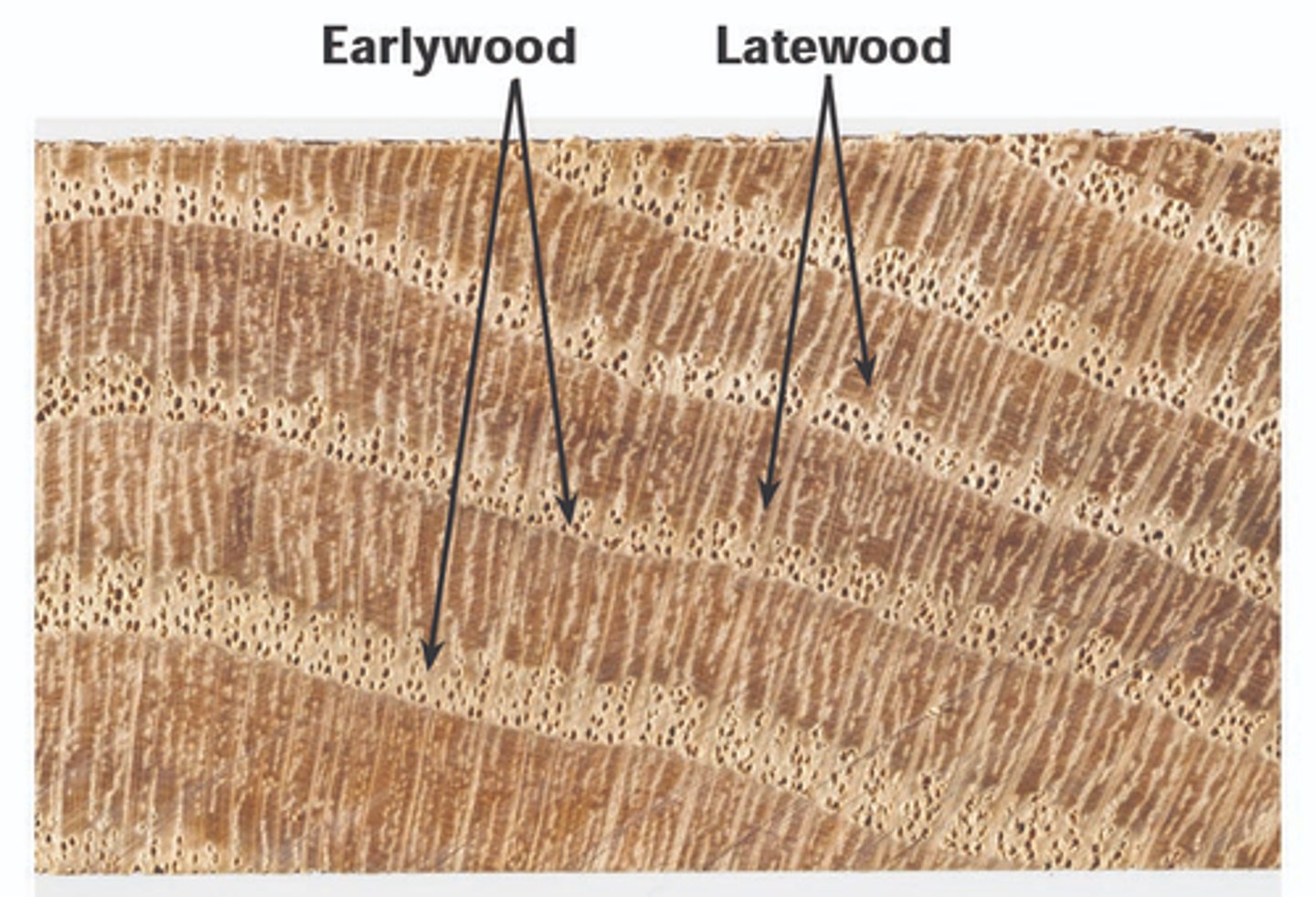
early/spring wood
more water, wider band, larger cells that aren't densely packed, lighter color
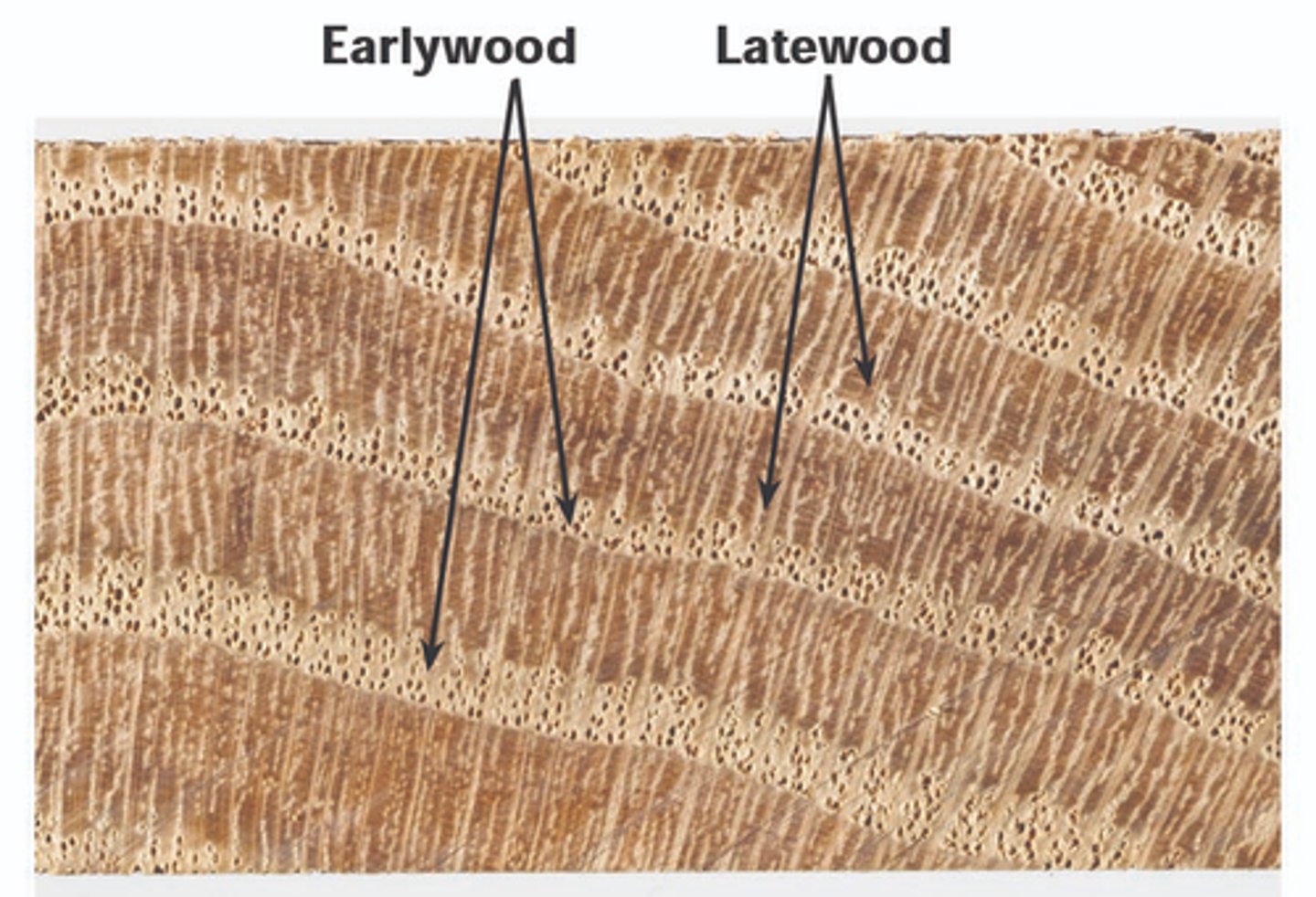
late/summer wood
less water, narrow band, smaller cells that are densely packed, darker color
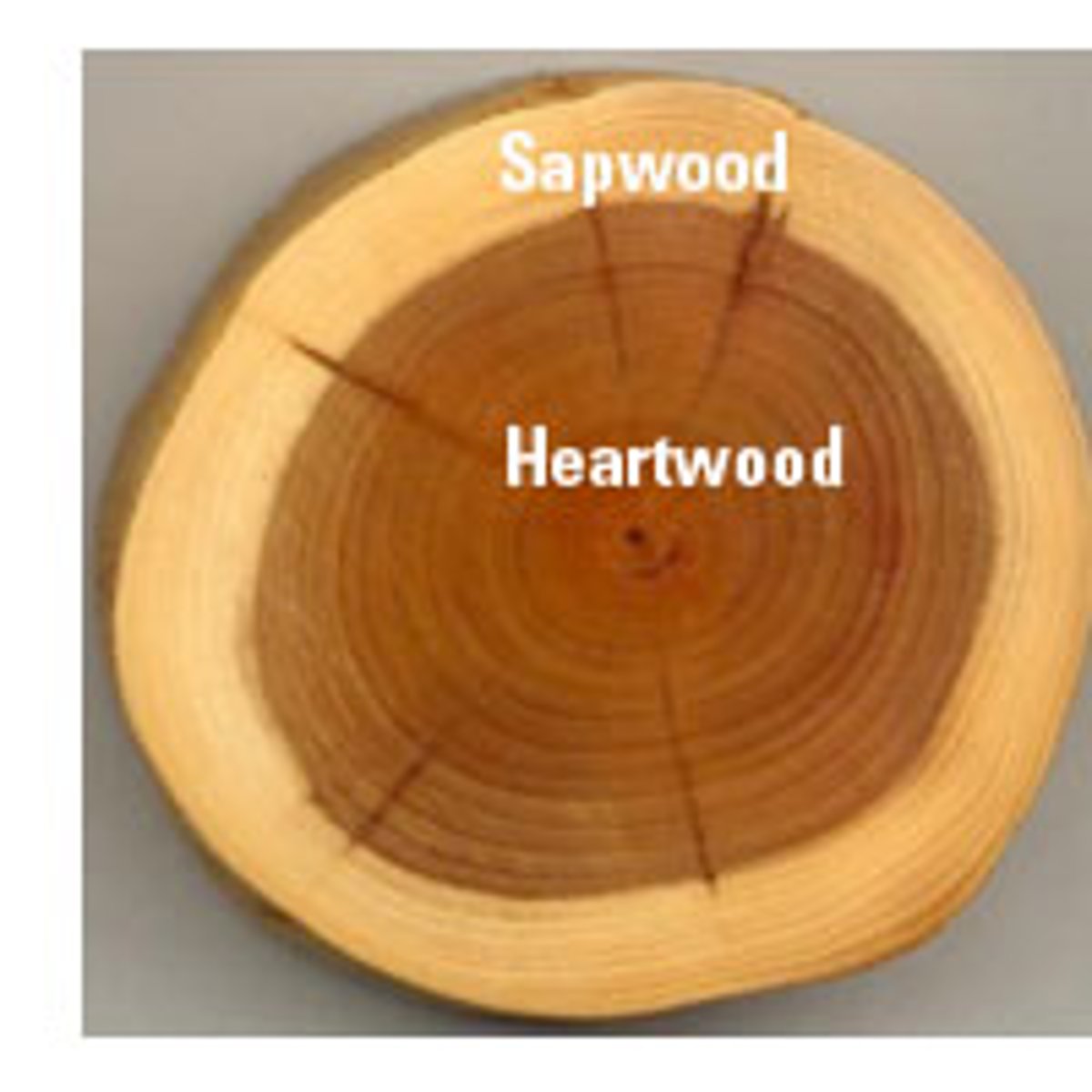
sapwood
outer portion, still conducts water, lighter in color
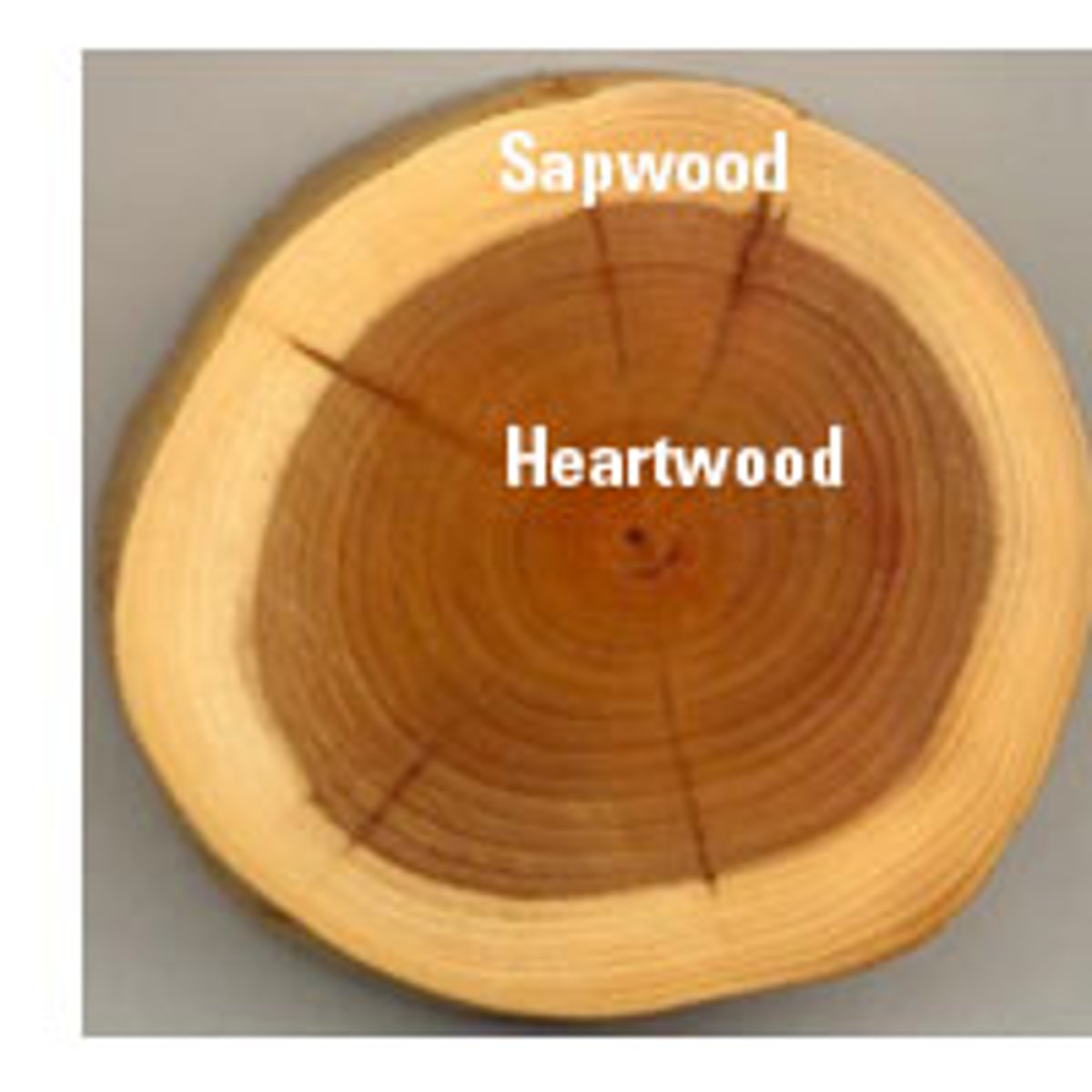

heartwood
darker in color, innermost portion does not conduct water, has antimicrobial compounds
