BIO 181 Exam 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Nucleotides are composed of
- Deoxyribose (sugar backbone) and nucleic acids (bases)
Nucleic Acid bases
- A
- T
- C
- G
DNA
- a molecule (can be different amounts)
Gene
- segment of DNA that codes for a protein
- one gene = one protein
- = a trait
Chromosome
- one whole strand of DNA
How do genes impact structure and function
- Genes (DNA) code for proteins (=traits)
- each chromosomes has 100s - 1000s of genes
Amino Acid
- each codon (set of three bases)
- 4 bases of DNA
- 20 of them
20,000 proteins in humans
- used at different times (in development or due to environmental/phycological triggers)
- used alone or with others in different combinations
Gene -> protein
- copied in nucleus (into RNA 0
- transported to ribosome
- reads copy and builds protein
mutation
- change in DNA sequence
- from external influences (radiation, chemicals) or from replication errors
substitution (type of mutation)
- exchange one base
deletion or insertion (type of mutation)
- remove or add 1+ base
- frame shift
allele
- different combinations of nucleotides within a gene segment
- different forms of a trait
what can a mutation do?
- nothing
- small change
- large change
sexual recombination
- genes shuffle during gametogenesis
- genes combine during fertilization
- meiosis is random
- fertilization is random
Evolution
- variation + selection
- changes over time (generations)
- exponential, not linear
heritability
- traits pass down to offspring
selection
- cause by environment, mates, humans, and random events
over-reproduction
- too many offspring produced to survive
Variation: Step 1
- mutations and recombination
- mutations can create new traits
- mutations are random (non purposeful)
- traits may be helpful or harmful
Variation: Step 2
- Selection by selective pressures
- some traits harm or kill the organism
- some traits reduce energy needed to survive or reproduce
- some traits result in more offspring than others
Selective pressure
lowers diversity
microevolution
- change in traits over time within a species (still interbreed)
macroevolution
- change in traits over time above the species level (no interbreeding)
Genetic Variation Impacts
- external traits (coloration, size, forms)
- physiological traits (functions such as transports, immunity, metabolic pathways, senses, behaviors)
- growth and development (sequence, regulation, transitions)
Gene flow
- spreads mutation within a species
- movement of genes among populations
- = migration
Variation builds up
- inherit DNA (changes build up over time)
- build up of changes in proteins
- Build up diversity = up range/niches = more populations = higher chance of divergence (NEW SPECIES)
speciation
- higher chance of divergence
Using genes to see evolution
- use DNA sequences
- use protein sequences
duplicate gene
- mutations can occur without hurting organism
molecular clock
- for DNA segments without selective pressure (pseudogenes), mutations occur at a relatively constant rate
Hemoglobin
- protein divergence
- transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
modern synthesis
- Malthusian competition
- Variation
- mutation
- natural selection
- genetic variation
- mendelian inheritance
Malthusian competition
geometric population growth, limited resources
Variation
breeds, races, subspecies
mutation
small changes in individual characteristics
natural selection
survival of the fittest
genetic variation
alleles of individual genes, combing to give continuous variation
mendelian inheritance
2 copies of each gene, 1 from each parent
type of selective pressures
- by environment (natural)
- by humans (artificial)
- by mates (sexual)
- by random events (genetic drift)
natural selection
- successful traits due to survival, energy use, and reproduction
- acts on all traits over entire lifetime
- predictable (selects which traits are successful)
- =/ evolution
3 steps to natural selection
- 1. limited resources + overproduction = struggle for survival
- 2. variation of traits (gene) = some survive better
- 3. traits of inherited = over time, successful traits become more prevalent
artificial selection
- successful traits due to desirability to another species (humans)
- acts on few traits during growth and reproduction
- generally decreases survival via natural selection
sexual selection
- successful traits due to attractiveness to mate
- acts on sexual characteristics during courtship
- generally decreases survival via natural selection
genetic drift
- random selection, especially in small populations
- two tops: bottleneck effect, founder effect
bottleneck effect
- catastrophe decreases population to few
- surviving traits due to luck
founder effect
- new population form with few individuals
- traits due to luck
Trait shifts (selection)
- directional
- diversifying
- stabilizing
survival of the fittest
- fittest = best fit
- not strongest, biggest, fastest, smartest, etc
- best fit changes with different environments
adaptation
- surviving trait
- not purposeful traits for an environment
How do traits mix
- mix within species (gene flow)
- do not mis between species
allopatric (type of speciation)
- Separated by barrier
- geographic isolation
sympatric (Type of speciation)
- separated while sharing same range
- behavioral isolation
parapatric (types of speciation)
- separated due to distance in a large range
Clade (evolutionary trees)
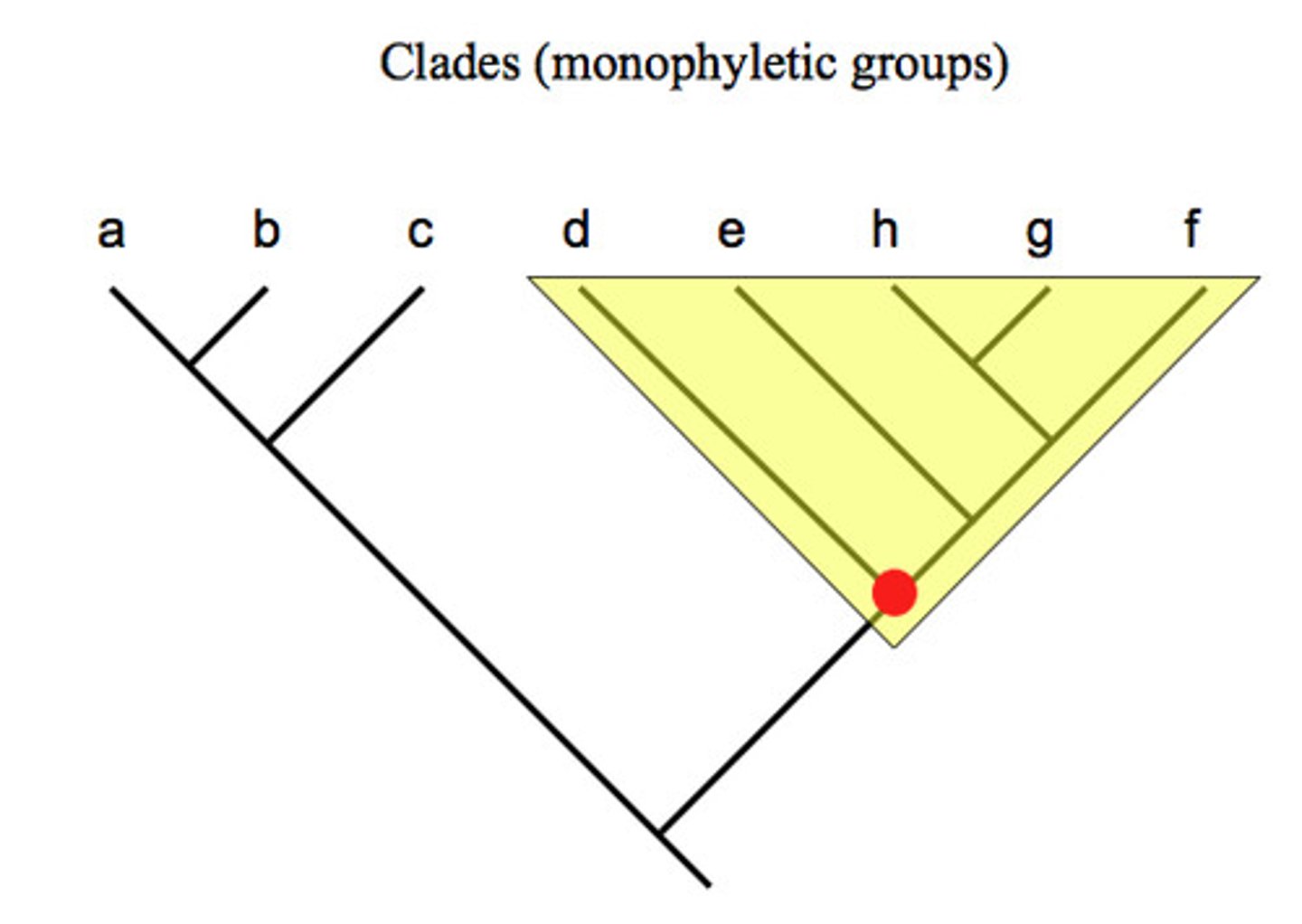
Clade
- a group of organisms with 1 ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor
4 billion years ago
- first life + prokaryotes
- fossil prokaryotes - stromatolites
- first land masses
3 billion years ago
- early photosynthesis = first O2
oxygen catastrophe
- Mass extinction due to photosynthesis waste product oxygen by bacteria
- 2.5 billion years ago
2.5 billion years ago
- success: eukaryotes (speciation)
1 billion years ago
- earliest multicellular organisms
- proto-plants, animals, fungi
500 million years ago
- Cambrian explosion
Cambrian explosion
- A burst of evolutionary origins when most of the major body plans of animals appeared in a relatively brief time in geologic history;
500 million years ago
- colonization of land
- plants (mosses), then arthropods (450 mya)
400 million years ago
- colonization of land by vertebrates
- due to high competition in water
- tiktaalik (375 mya)
300 million years ago
- first reptiles and conifers
250 million years ago
- Permian extinction
- great dying
Permian extinction (great dying)
- 96% all marine species
70% terrestrial vertebrates
many million year recovery
6 C warming average
extinctions create open ____
niches
250 million years ago
- early dinos
65 million years ago
- Late dinos
- Cretaceous extinction event
Cretaceous Extinction
- the extinction of more than half of all species on the planet, including the dinosaurs
- birds survive
- birds and mammals expand into open niches
Lilliput effect
- reduction of size of animals during an extinction event
50 million years ago
- miniscule picture
- animals similar to today
study of geology
- from coal mines
- industrial revolution (1750)
geologists noticed ...
- 1. different layers of earth with different fossils
- 2. deeper fossils were simpler
- 3. some species were no longer found (extinction)
how fossils are made
- 1. life form dies in/by water
- 2. covered by silt
- 3. if undisturbed, buried beneath additional layers
most likely to fossilize
- hard structure
- numerous organisms - higher chance that one will fossilize
- aquatic environments w/ fine mud deposits
- low decomposition rates
- no erosion
what can you learn from a fossil
- shape and movement
- function and form
- color and texture
- behaviors (food, fighting, care of young, etc)
- species interaction
- community and structure
- palynology and paleoecology
fossil dating
- rock layers (relative dating)
- radiometric dating
biogeography (fossils)
- 1. more similar individuals closer; less similar individuals further apart
- 2. when separated by natural barriers, species diverge
Biogeography of Islands and Speciation
- Near islands = higher immigration
- large islands = higher immigration
- same latitude = higher immigration
evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo)
- uses development of structures (embryology) to determine evolutionary origins
Divergent evolution
- most recent ancestry : same
- selective pressures : different
Convergent Evolution
- most recent ancestry : different
- selective pressures : same
divergent evolution -> homologous traits
- same ancestral trait in different environment = trait develops different function/appearance
convergent evolution -> analogous traits
- different ancestral trait in similar environment -> trait develops similar function/appearance
Vestigial organs
- organ that serves no useful function in an organism
- ie. wings in flightless birds, whale hips
- in humans: wisdom teeth, body hair, ear muscles
human evolution: 10000 ya
- agriculture, immune system, lactase and amylase
human evolution: 5000ya
- reduction of brain size
human evolution: 4000ya
- malaria and sickle cell anemia
human evolution: 1000 ya
- Sama-Bajau spleen size and deep-diving
Human evolution: 100s ya
- later menopause
how long have modern humans existed in a 24 hour clock?
-~ 4 seconds
primate groups
- prosimians (lemurs)
- new world monkeys (in Americas)
- old world monkeys (in Africa/Asia)
- apes (chips, gorillas, orangutans, and humans)
Human evolution
- humans did not 'descend from monkeys'
- we share a common primate ancestor
Hominid
- great ape (including human) ancestors
Hominin
- Human ancestors
- over 6,000 individuals
65 million years ago
- survival of small mammals through Cretaceous extinction
50 million years ago
- one population of insectivores
- primates