Neuro Physiology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Receptors
Input: sensory
Special sensory receptors: monitor smell, taste, vision, hearing
visceral sensory receptors: monitor internal organs
somatic sensory receptors: monitor skeletal muscles, joints, and skin surface
Effectors
output: causing change
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
glands
adipose tissue
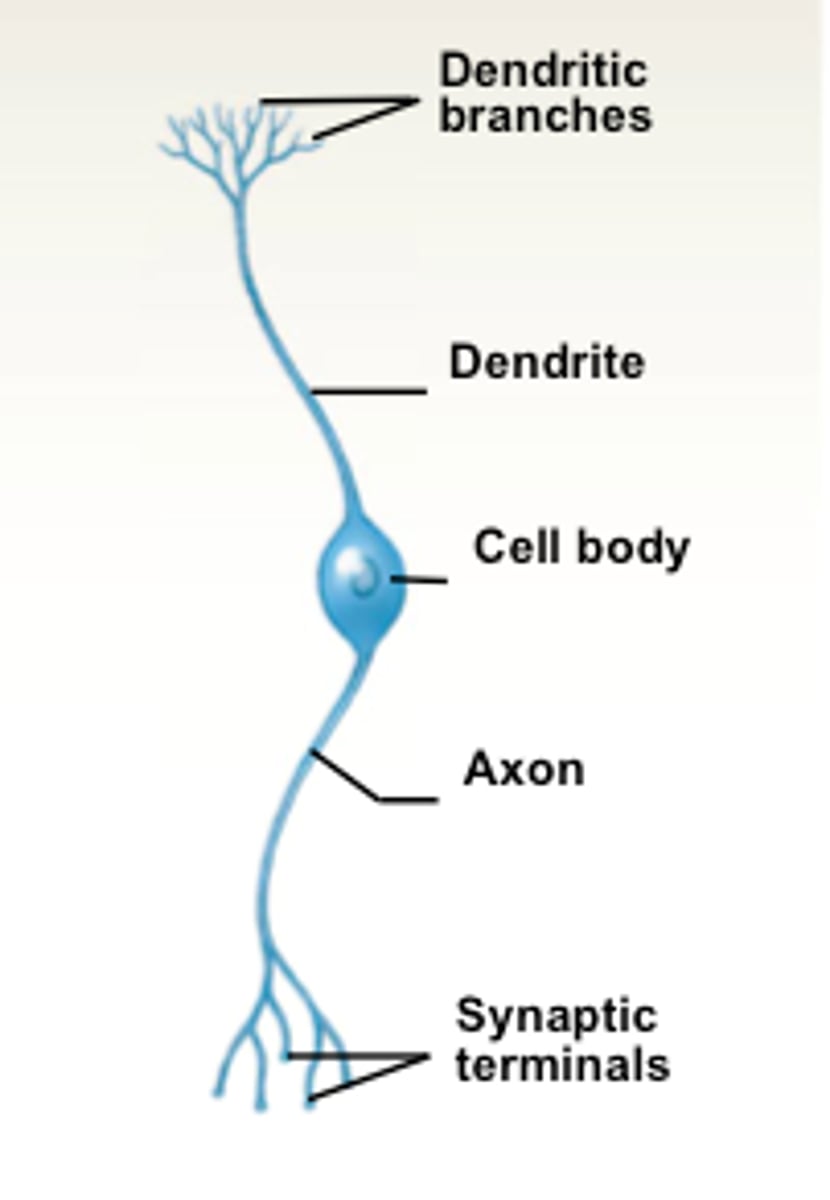
Dendrites
branches of a neuron that increase surface area and reach out to other areas
Axon terminals
connect to another cell and creates a pathway
Anaxonic Neuron
Doesn't have axons
integrating cell
takes in a bunch of info and decides where it goes
Bipolar Neuron
Special senses: taste, smell, sight
Two processes separated by the cell body
Unipolar neuron
Sensory neurons in spinal cord
quick signal bypasses cell body
single elongated process
cell body located off to the side
Multipolar neuron
Effectors
found in muscles
single axon and multiple dendrites
Ependymal cells
Line ventricles and central canal
assist in producing, circulating, and monitoring cerebrospinal fluid
Astrocytes
Maintain blood- brain barrier
provide structural support
regulate ion, nutrient, and dissolved gas concentrations
Absorb and recycle neurotransmitters
form scar tissue after injury
Oligodendriocytes
myelinate CNS axons
provide structural framework
Microglia
Remove cell debris, wastes and pathogens by phagocytosis
Satellite cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia
regulate O2, CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons in ganglia
Schwann cells
surround all axons in PNS
responsible for myelination of peripheral axons
participate in repair process after injury
Sodium
depolarizes via entering cell through Na channels
Calcium
depolarizes via entering cell through Ca channels
Potassium
hyperpolarizes via exiting cell through K channels
Chloride
Hyperpolarizes via entering cell through Cl channels
Continuous Propagation
Nonmyelinated axons
Saltatory Propagation
large sensory neurons
Myelinated axons
Glutamate
Main Actions: excitatory neurotransmission
Modulation of synaptic plasticity
Activation of second messenger system
GABA
Main Action: Inhibitory neurotransmission
Acetylcholine
Main Actions: Muscle contraction
Autonomic functions
Parasympathetic functions
Neuromodulation
Norepinephrine
Main Action: Sympathetic functions
Neuromodulation
Dopamine
Main Action: Neuromodulation
Serotonin
Main Action: Neuromodulation
Histamine
Main Action: mainly excitatory neuromodulation
Glycine
Main Action: Inhibitory neurotransmission
Peptides
Main Action: Neuromodulation
Direct effects
Binds to chemically gated channel> produces action
Indirect effects
attaches to different types of receptor and cascading effects within cell
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
Leads to quick graded depolarization
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
leads to quick graded hyperpolarization
Neuromodulation
slow secondary cellular signal cascades that either facilitates or inhibits signal transmission
Temporal summation
two or more stimuli arriving at different times creating an action potential
Spatial summation
two stimuli arriving at the same time creating an action potential
Segmental level
lowest level
reflexes
spinal cord
Projection level
Middle level
voluntary control
can over ride some reflexes
motor cortex and brain stem nuclei
Precommand level
highest level
Preprogrammed response
cerebellum and basal nuclei