EKG pctc
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
where does deoxygenated blood enter the heart?
the inferior and superior vena cava
what two major spaces does deoxygenated blood travel through in the heart?
the right atrium and right ventricle
where does deoxygenated blood travel out from in the heart?
the right and left pulmonary arteries
where does oxygenated blood flow into the heart?
the right and left pulmonary veins
what two major spaces does oxygenated blood flow through?
the left atrium and left ventricle
where does oxygenated blood flow out of the heart?
the aorta
how does deoxygenated blood turn into oxygenated blood?
it travels through the heart’s right ventricle and atrium, leaves through the left and right pulmonary arteries and goes to the lungs. here, the lungs replace the CO2 with O2, and the blood travels through the pulmonary veins back to the heart as oxygenated blood.
what is the network called that replaces CO2 in blood with O2?
the pulmonary alveolar capillary network
what system is responsible for the pumping action of the heart
the electrical conduction sysstem
what cells control the rate and rhythm of the heart
pacemaker cells
where does the conduction system begin?
sinoatrial (SA) node
where does the impulse travel after the SA node?
intermodel pathway
where does the impulse in the heart end?
the purkinje fibers in the ventricular myocardium.
referring to an obstruction to the myocardial tissue.
myocardial infarction
lack of oxygen-rich blood int he heart
myocardial ischemia (angina)
a term used to refer to any disorder of the heart rate or rhythm
arrhythmia
a tool used to record the electrical activity of the heart
EKG
a device that amplifies electrical impulses and prints a record
electrocardiograph
each lead is marked with a different ___
color and lead number
the right arm lead is ___
white and marked RA
the left arm lead is ____
black and marked LA
the right leg lead is ___
green and marked RL
the left leg lead is ___
red and marked LL
chest leads are normally what color
brown
the V1 chest lead
fourth intercostal space to the right of the sternum
the V2 chest lead
the fourth intercostal space, left of sternum
the V3 chest lead
midway over fourth and fifth intercostal space, halfway between base and sternum
V4
fifth intercostal space, in line with nipple
V5
midway between the nipple and midpoint of axilla
V6
over intercostal space at axilla midpoint
Limb Lead - Lead 1
records electrical activity from right arm to left arm
Limb lead - Lead II
records electrical activity from right arm to left leg
Limb Lead - Lead III
records electrical activity from left arm to left leg
augmented lead - aVR
across heart to right shoulder
augmented lead - aVL
across heart to left shoulder
augmented lead - aVF
across heart towards feet
the V chest leads record what?
activity between the center of the heart and the chest wall where the V lead is placed
the horizontal line on the electrocardiogram measures what
time
the vertical line on the electrocardiogram measures what
amplitude or voltage
a straight line on the ECG that illustrates resting state of myocardial cells, also shows the beginning and ending point of waves
the isoelectric line
the firing of what represents the “P” wave
the SA node
what kind of polarization does the p wave represent?
the depolarization of the right and left atria
what does a P wave look like?
a smooth, upward deflection around .1 second in length
the PR interval represents _
the time the impulse travels from the SA node, through the atria, to the ventricles
the “Q” of the QRS complex
deflects down from the baseline
the “R” of the QRS complex
an upward deflection after the Q wave that depicts a patient’s heart rate
the “S” of the QRS wave
a downward deflection following R
how long is the QRS complex time-wise?
under 0.12 seconds
what occurs during the ST segment, polarity-wise?
the ventricles are depolarized and repolarization begins
the T wave looks like
a slightly asymmetrical rounded wave
what does the T wave indicate?
repolarization or recovery phase of ventricles
what is known as the resting phase of the cardiac cycle?
the T wave
the five steps in analyzing an ECG
heart rate, regularity, P-waves, QRS complex, P-R interval
normal heart rate
60-100 bpm
tachycardic heart rate
over 100 bpm
bradycardic heart rate
under 60 bpm
what is the only heart rate method that can be used on an irregular rhythm?
6 X 10
the most accurate way of measuring heart rate that can only be used on regular rhythm
the 1500 method
describe the 1500 method
count the number of squares between R-waves and divide number by 1500
counting the QRS complexes gives you what measurement?
the ventricular rate
counting the P waves determines what measurement?
the atrial rate
how to measure regularity?
measure distance between all R waves. if they are the same, then the rhythm is regular.
what is total irregularity?
no consistency inbetween R waves
what condition may show as total irregularity?
a-fib
what is partial irregularity?
where the irregularity repeats over and over
what condition may present as patterned irregularity?
AV-heart blocks
if you have more P waves than QRS complexes…
AV heart block
normal QRS complexes should be….
0.6-0.12 seconds
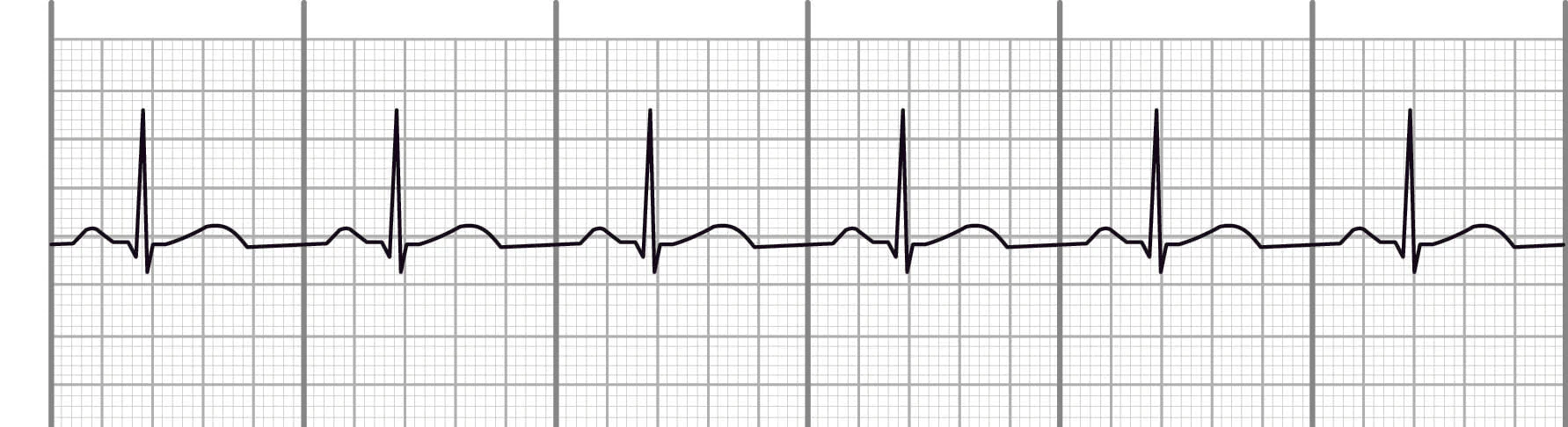
what is this
normal sinus rhythm
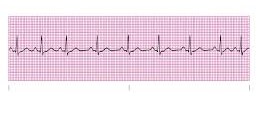
what is this
sinus dysrhythmia
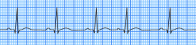
what is this
premature atrial complexes
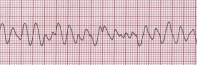
what is this
wandering atrial pacemaker
describe sinus dysrhythmia
comes from an irregular heart rate
describe premature atrial complexes
p waves will appear different than those of underlying rhythm
describe wandering atrial pacemaker
slightly irregular, p waves continuously changing
describe supraventricular tachycardia
p waves cannot be identified, PR interval is absent
pulseless electrical activity
sinus rhyhm EKG but no pulse
any electrical activity that is non-cardiac in origin and represents unwanted marks
artifact