IMED1004 - Microbial Control (L7)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

Practice Qs Lecture 1 ANSWERS
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 2


Practice Qs Lecture 2 ANSWERS
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 3


Practice Qs Lecture 3
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 4

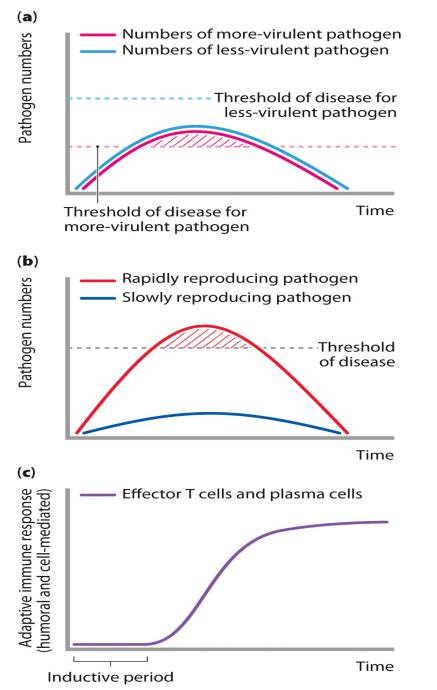
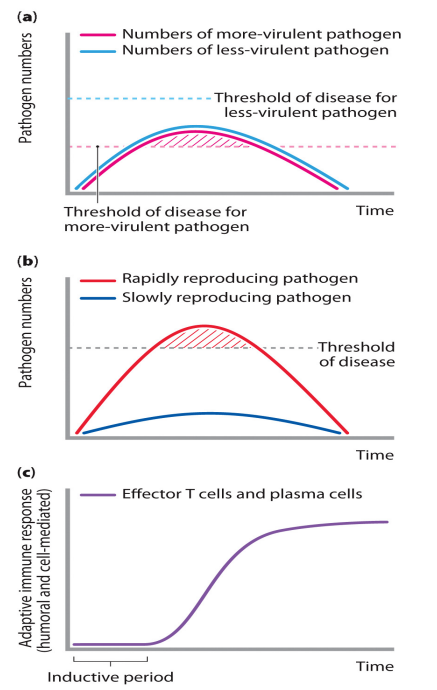
Likelihood of disease
- first one (part a) shows that they replicate at the same rate
- but what if our immune system fails or it is not enough
Nosocomial infections = hospital acquired
- "Hot beds" for infection
- sick people - damaged barriers, weakened immunity
- medical staff movement
- Preventable with basic control measures
- handwashing
- instrument sterilisation
- antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
- once curable infections no longer respond
- Learning outcome: nosocomial infections are hospital acquired which are associated with immunocompromised individuals, poor hand hygiene and sterilisation and antimicrobial resistance

Factors to consider when selecting a method to control microorganisms
- where, what and how much we want to control

Physical Control - manipulation of environment
- microbes have optimal growth temperature (range)
- direct and inexpensive
- Heat, Cold, Sterilisation, Pasteurisation, Filtration, Radiation, Gamma, UV, Drying
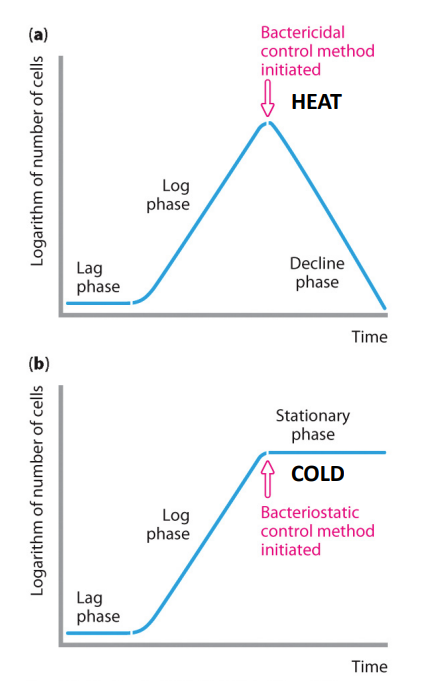
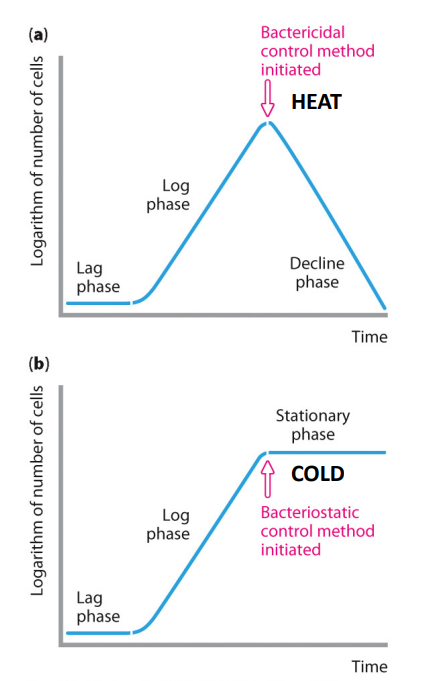
Physical control: Cold
Cold generally doesn't kill, it inhibits growth
- "static" e.g bacteriostatic, fungistatic
- inhibits microbial replication
- Those that can grow, slowly, at room temp are usually low disease risk, except Listeria monocytogenes
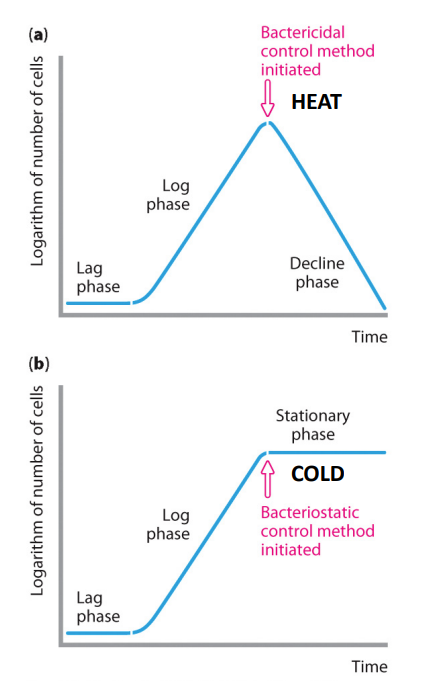
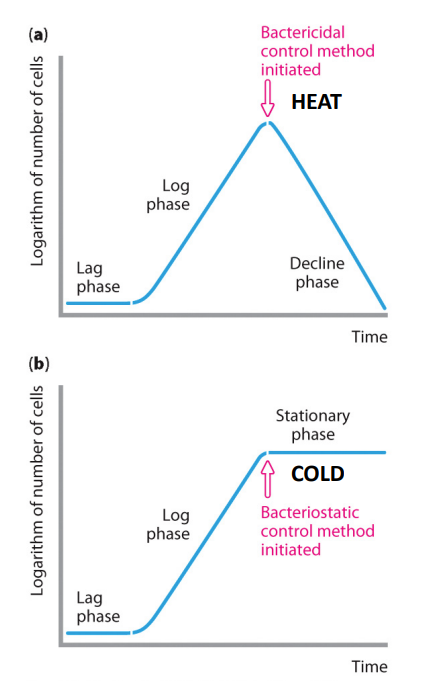
Physical Control: heat
heat is effective means of killing:
- "cidal" e.g bacterial, fungicidal
- penetrates an object and kill organisms throughout
- denatures proteins - not suitable for all substances
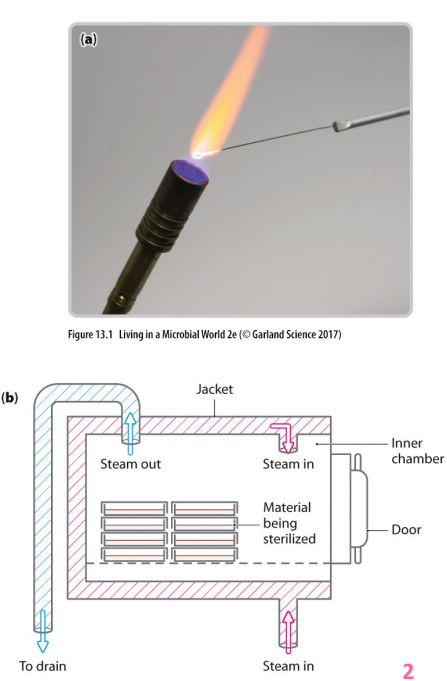
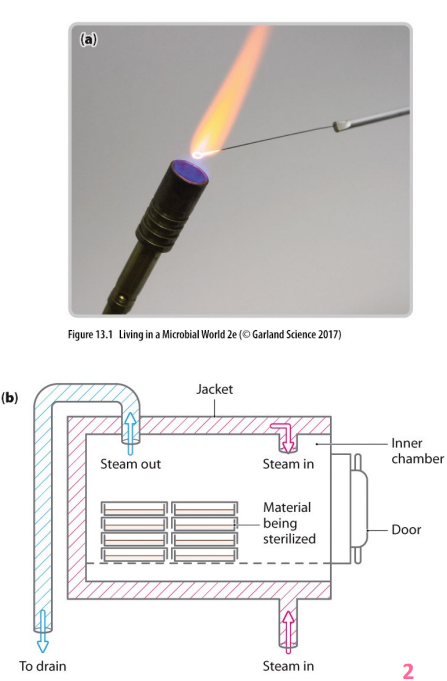
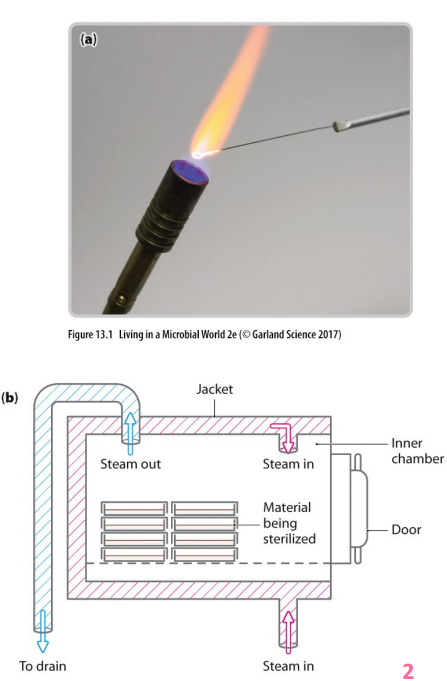
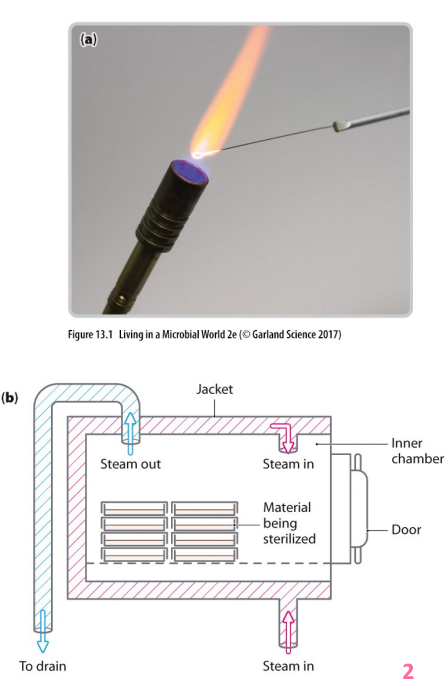
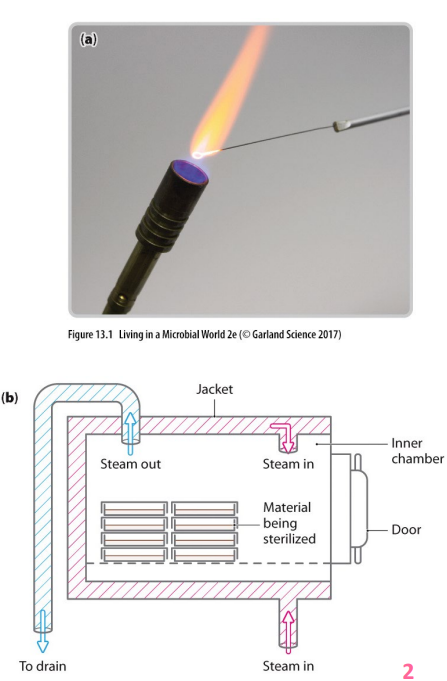
Physical control: sterilisation
- complete elimination of all organisms
- dry heat (flame or hot oven) - requires considerable time and higher temps for heat resistant organisms/endospores
- moist heat (pressurised steam in autoclaves) - penetrates more quickly at lower temps, achieves temps above boiling point required to kill heat resistant organisms/endospores
- boiling (15-20minutes for food/water) - may not kill heat resistant organisms/endospores
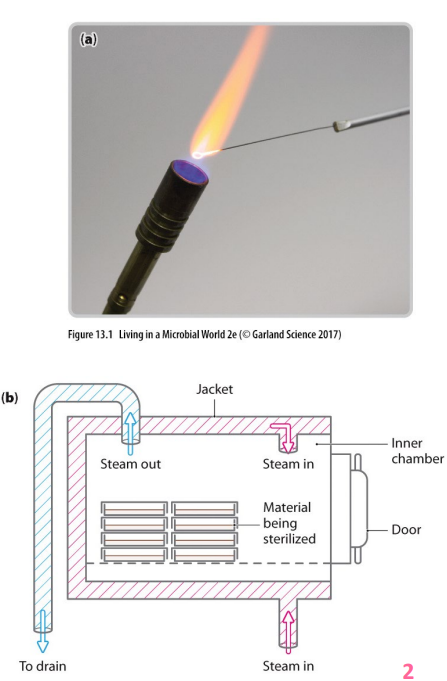
Physical control: Pasteurisation
- temporary heating of liquids sensitive to prolonged heat (without losing flavour)
- may not kill heat resistant organisms, but these organisms will struggle to thrive at body temp
Physical Control: filtration
- liquids that can't tolerate high temps passed through membrane with pores of size to exclude bacteria (0.45 micrometres), but not all viruses
Physical Control: Radiation
- can be used to kill microorganisms in some situations.
- causes thymine dimers in DNA that inhibit replication
Physical Control: Gamma Radiation
- widely used to sterilise medical equipment and to treat vaccine preparations, some transplant tissues, and some food products
Physical Control: UV
- rarely sterilises, but can significantly reduce numbers on surfaces and in the air
- used in hospital operating rooms, nursing homes, prisons, childcare centres, food prep areas (not when people in the room)
Physical Control: Drying
- age old way of preserving fish and meat products
- coupled with water removal by salt/sugar, does not kill organisms but creates environment not conducive to reproduction
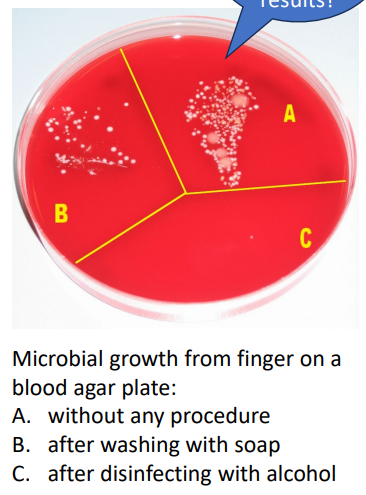
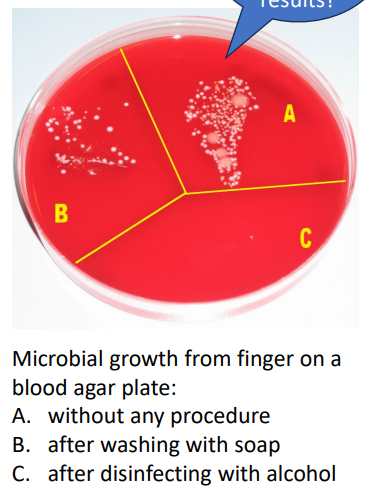
Chemical Control on living and non-living materials
FOR NON-LIVING MATERIALS: DISINFECTANTS:
- Bleach (chlorine) - bactericidal, forms an acid when added to water, surface cleaner and swimming pool and drinking water treatment
- alcohol - kills by denaturing proteins and disrupting microbial cell membranes (bacteria, fungi, enveloped viruses) on surfaces
FOR LIVING TISSUE: ANTISEPTICS: (basically this is for when u wanna clean on skin)
- Iodine - binds amino acids of enzymes to inhibit activity, also binds fatty acids in microbial cell membranes
- Phenol - denatures proteins, listerine named after Joseph Lister who first applied phenol to bandages to control infection
- Alcohol - also effective on skin, but not open wounds as it congeals host proteins
- soaps, detergents disrupt microbial adherence, can kill through disruption
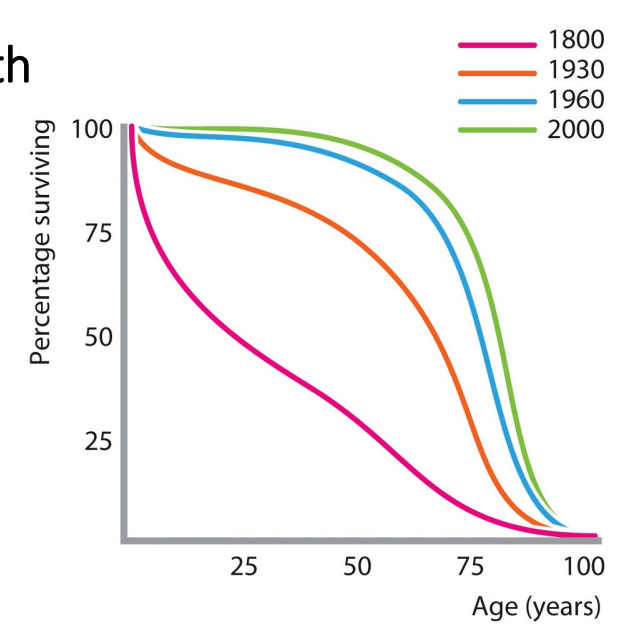
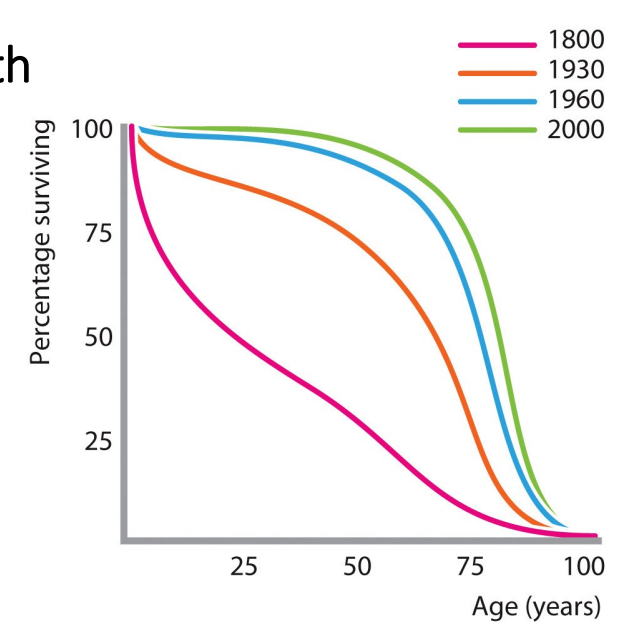
Sanitation and antibiotics > major improvements in health
Human survival increased thanks to (1800-1930):
- germ theory of disease
- aseptic techniques
- Improvements in sanitation
1930-1960:
- development of antibiotics
- procedures considered routine today were life-threatening pre-antibiotics
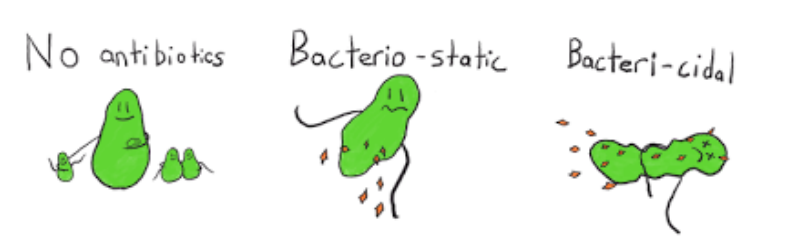
Antibiotics are anti-bacterial agents
- Bactericidal antibiotics KILL - e.g penicillin prevents bacterial cell wall synthesis causing rupture
- more direct effect; essential in immunocompromised patients
- Bacteriostatic antibiotics Inhibit replication - hold numbers in check allowing the immune response a greater chance of clearance
- effect relies on continual presence of the drug until infection is cleared
First antibiotics
initially produced by microorganisms
- penicillin from mold
- streptomycin from soil bacterium streptomyces
- ideally inhibits microorganisms without harming host = selective toxicity
SELECTION OF MOST APPROPRIATE ANTIBIOTIC DEPENDS ON:
- known drug allergies
- identification of infecting organism and antibiotic sensitvity
- site of infection
- cost
- speed of infection progression and/or antibiotic effectiveness
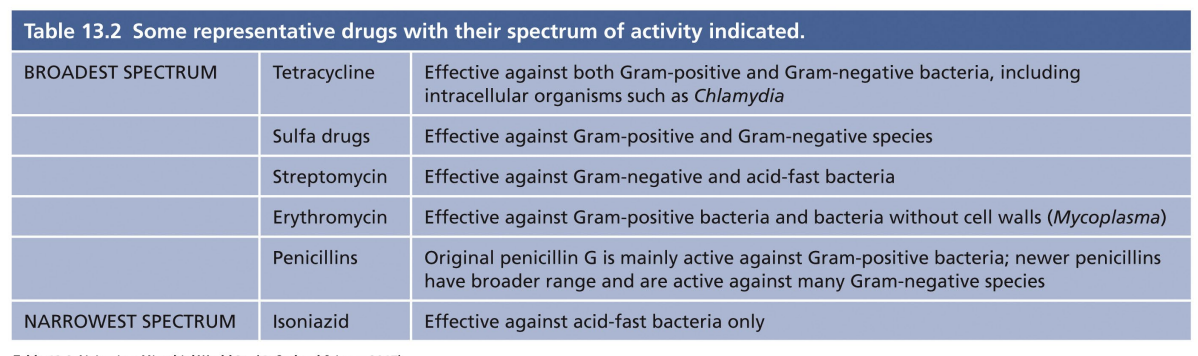
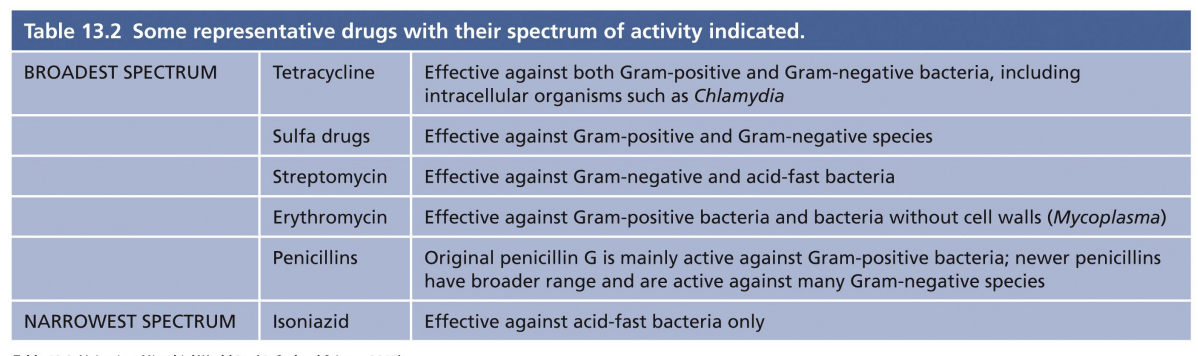
Broad vs Narrow Spectrum
- some combat a wide variety of microorganisms = broad spectrum
- used prophylactically - for immunocompromised patients - or if pathogen is not known
- Most likely to have off-target effects - disrupt normal microbiota
- narrow spectrum = highly targeted to specific types of infection/bacterial pathogens
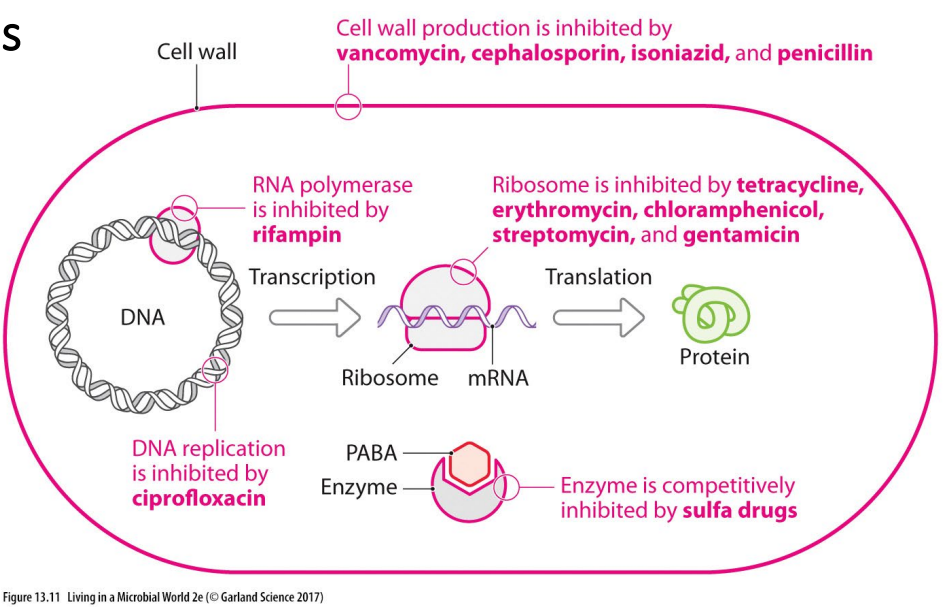
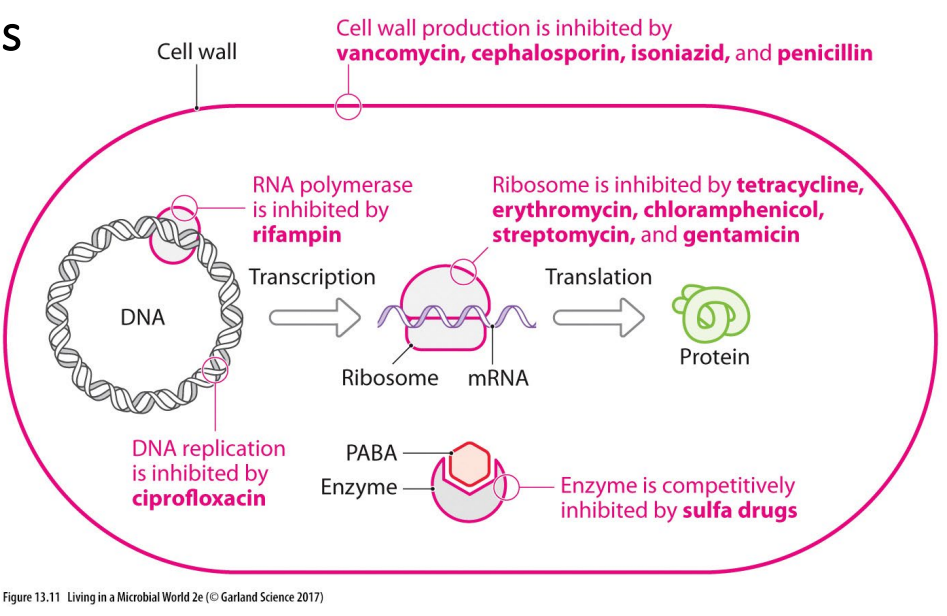
Antibiotics interfere with specific bacterial structures or enzymes
- it could stop cell wall production, which will make bacteria struggle to survive
- it could stop DNA replication, hence bacteria not able to replicate
- it could stop transcription or translation through an end product protein
Selective toxicity harder to achieve against eukaryotic pathogens
- limited drug options against protozoa and fungi
- similar to human cells - far fewer unique drug targets
- side effects common
- quinine - plant extract effective against malaria parasites
- synthetic chloroquine produced after global (WWII) shortage of quinine
- today, resistance is spreading and new drugs are needed
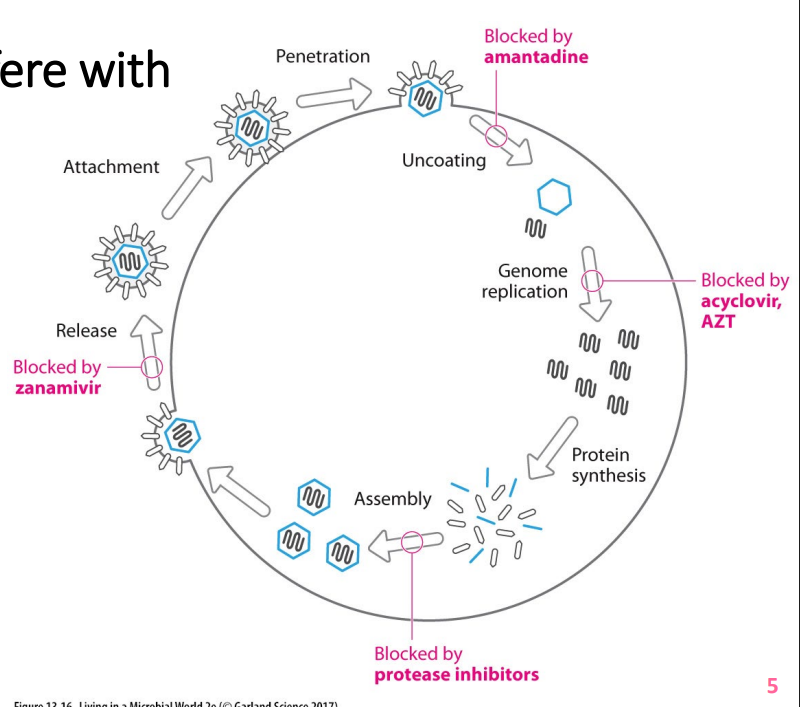
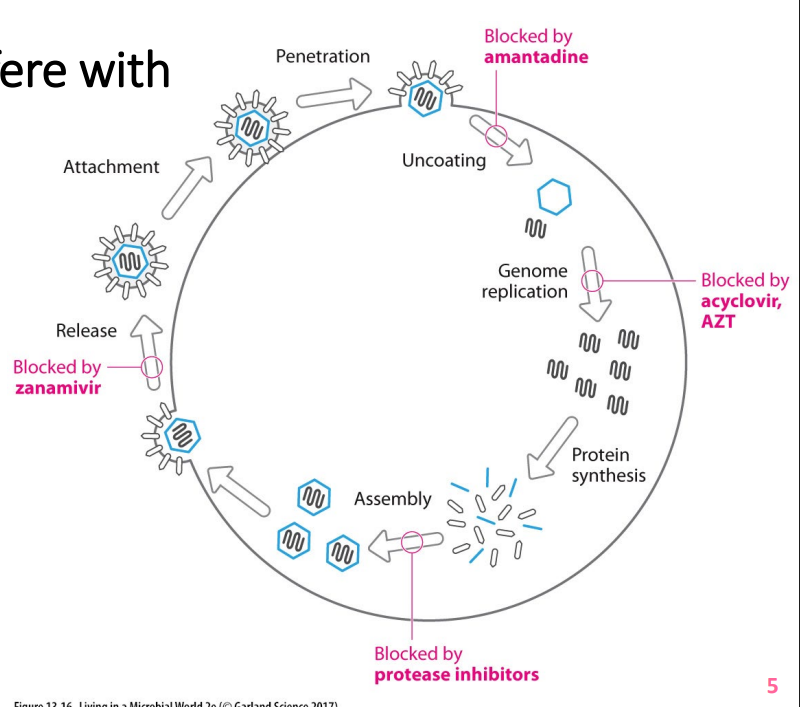
Antiviral drugs interfere with viral replication
- viral replication inside host cells
- viruses have some unique features - selective toxicity possible in theory
- newer, innovative anti-viral drugs on horizon
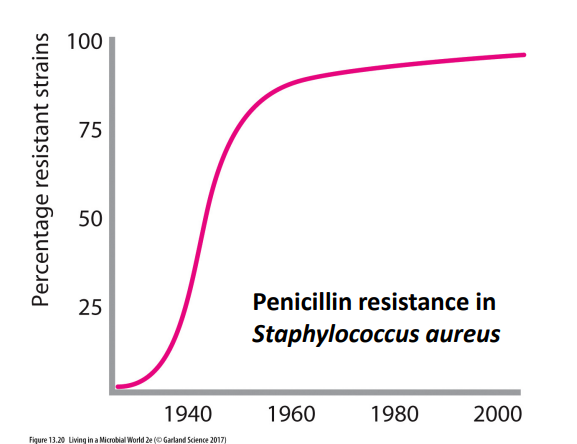
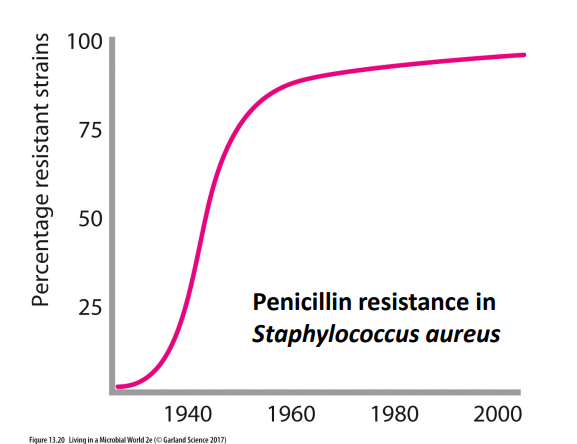
Antibiotic misuse has lead to drug resistance
- antibiotic resistance is not new, but is now a major public health threat
- Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance (R) are well understood
- tetracycline-R bacteria rapidly excrete the drug by protein pumps
- Erythromycin-R bacteria have modified ribosomes preventing drug binding
- Penicillin-R bacteria produce enzyme that cleaves the drug rendering it inactive
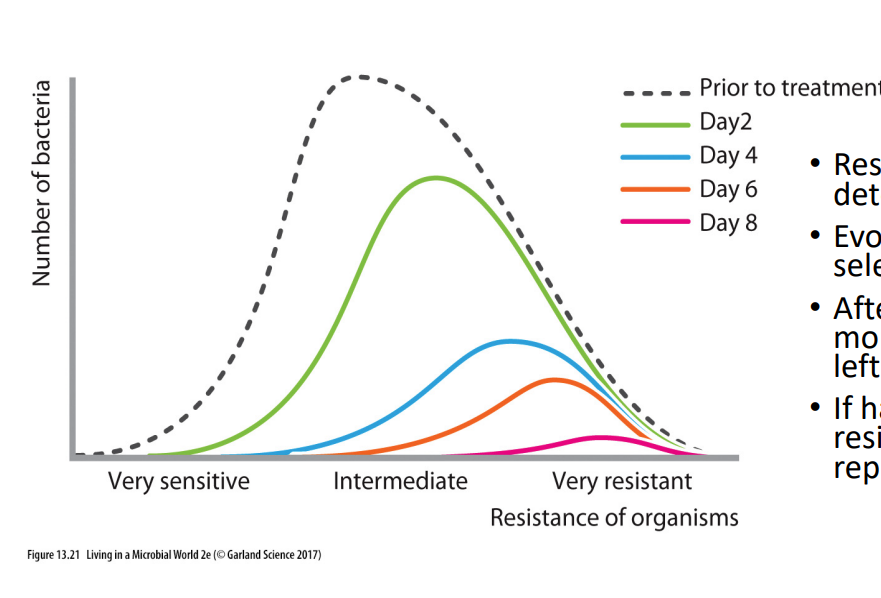
Antibiotics and selection pressure
- Resistance is genetically determined
- evolves through natural selection
- after each dose, increasingly more resistant bacteria are left behind
- if halted early, more resistant bacteria may reproduce
.
- this is why doctors say to finish course of antibiotics so u dont give a chance to resistant bacteria to reproduce
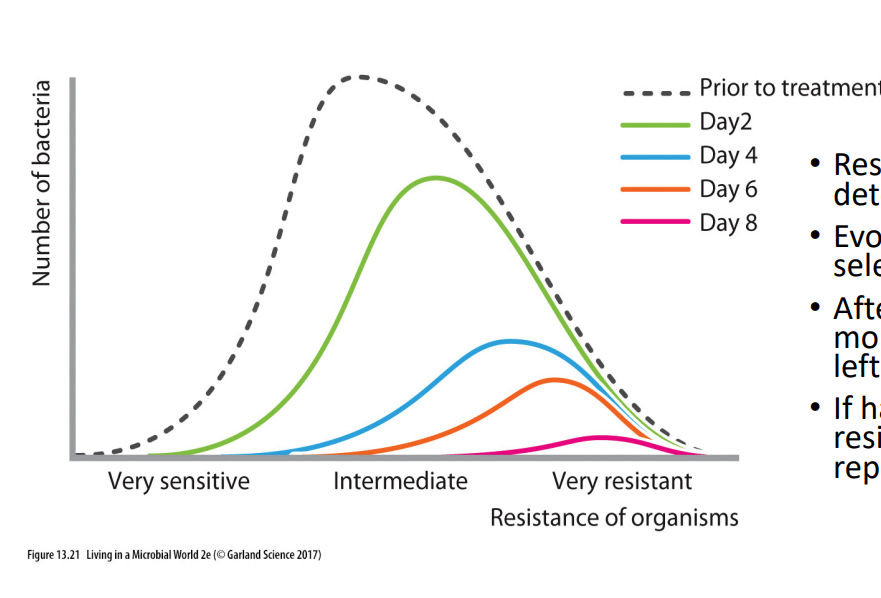
Antibiotic misuse has led to drug resistance
- when antibiotics used inappropriately to treat non-bacterial infections (no effect on viruses)
- Prophylactic use in animal feed results in exposure of humans to resistant organisms in contaminated food products
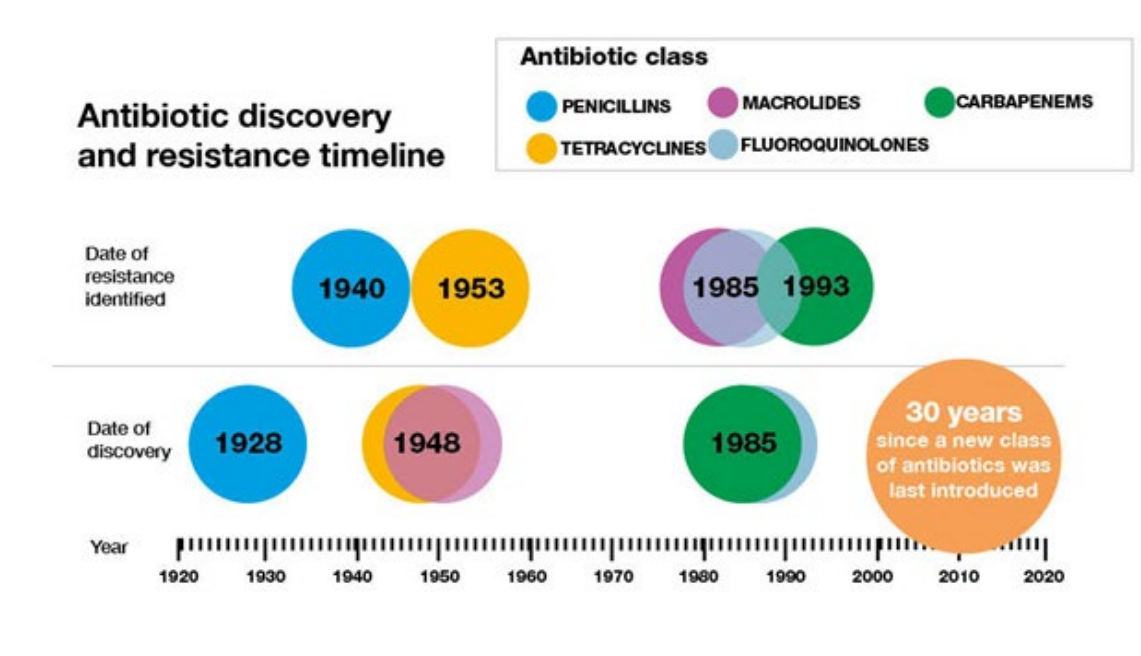
How quickly antibiotic resistance develops
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 27
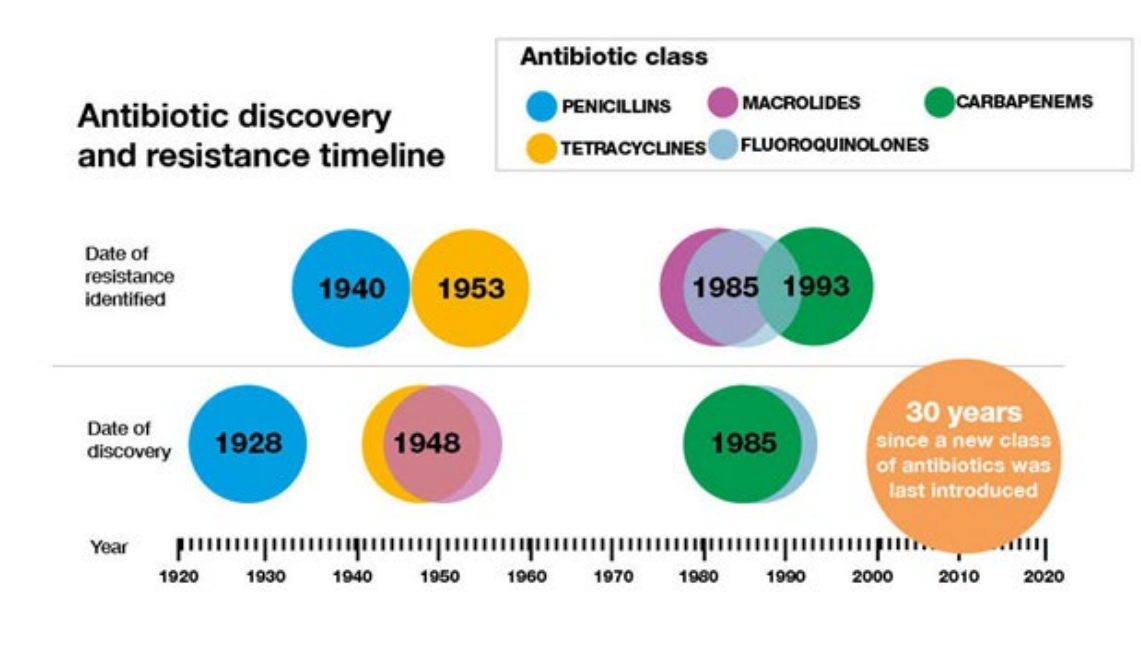

Summary
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 31
