Physio Renal 1
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are the functions of the kidneys
Regulation of: electrolyte, osmolarity, acid-base balance
Excretion of foreign substances and metabolism
Produces hormones (Eg. Erythropoietin)
Renal functional anatomy
Cortex (outer portion)
Medulla (inner portion)
Renal Corpuscle (Glomerus and Bowman’s capsule)
Loop pf henle
Collecting duct
Nephron (Functional unit)
Blood vessels
Lymphatics
Nerves
This tubule reaches up to medullary portion and is impiortant for concentrating and diluting ability of the kidney
Juxtamedullary nephrons
This is the site where urine formation occurs
Nephron
Glomerular capillaries enclosed within the Bowman’s capsule
Renal corpuscle
Proximal to bowman’s capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Appears as hairpin loop consisting of ascending and descending loop
Loop of henle
What are the two ascending loop
Thin ascending loop
Thick ascending loop
Responsible for filtering out toxic substances, secreting substances back into urine, and reabsoring substances back into the blood
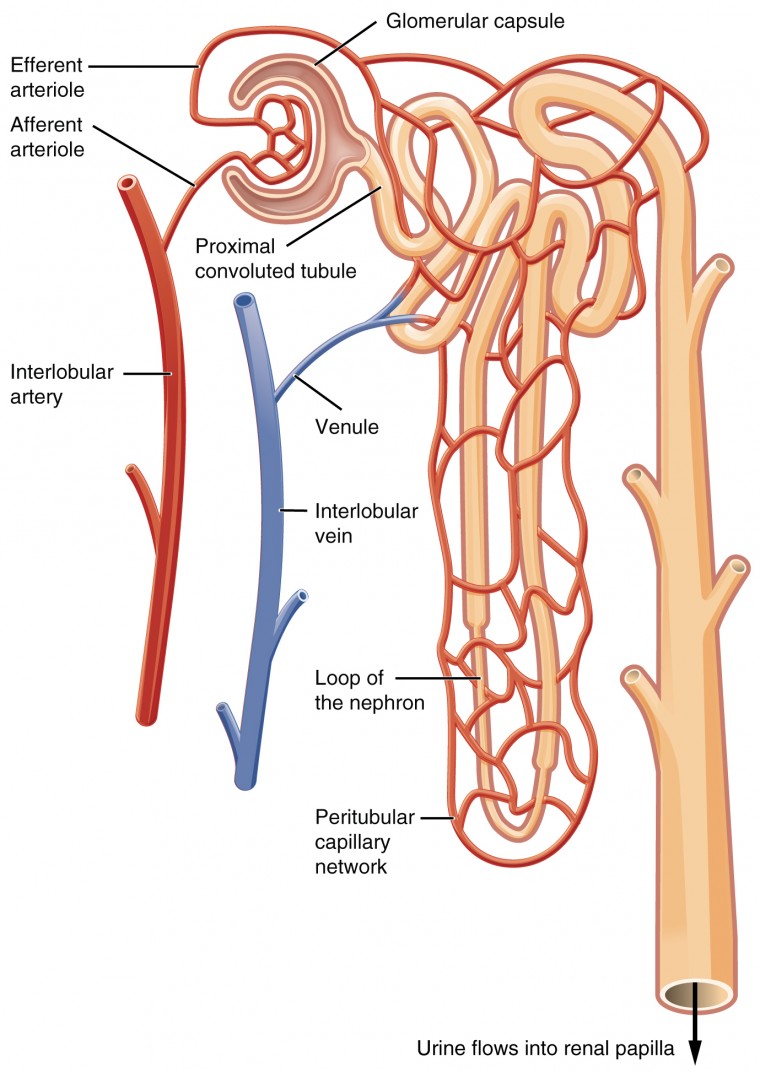
Blood flow
Cardiac output:
Cortex
Medulla
Cortex > Medulla
Blood flow pathway
Aorta - Renal artery - afferent arteriole - glomerular capillaries - efferent arteriole - peritubular capillaries
Surrounds the tubules and is the second capillary system. Important for tubular reabsorption and secretion processes
S
Glomerular capillariesn enclosed within the Bowman’s capsule
Renal Corpuscle
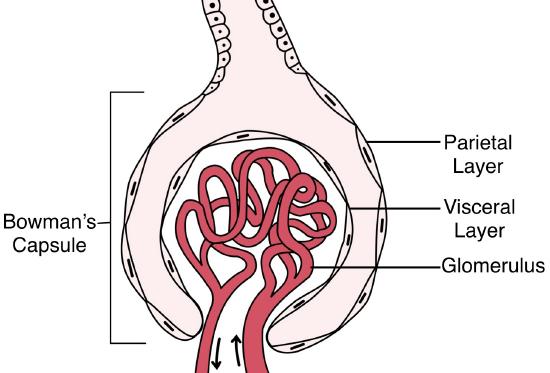
Visceral layer ofn the Bowman’s capsule
Podocytes
Space between visceral and parietal layers
Bowman’s space
Filtration
Large surface area
smaller surface area
Large surface area (Dilated) > small surface area (constricted)
Function of mesangial cells
Structural support for capillaries
Secrete extracellular matrix
Secrete prostaglandins, cytokines
Phagocytic activity
Filtration barrier is composed of
Podocyte foot processes
Glomerular basement membrane
Capillary endothelium
Fenestrated and Contains negatively charged glycoproteins
Capillary endothelium
Identify one’s that are permeable to capillary endothelium
RBC
WBC
Platelets
Sodium
Urea
Glucose
anions
cations
RBC (unpermeable)
WBC (unpermeable)
Platelets (unpermeable)
Sodium (permeable)
Urea (permeable)
Glucose (permeable)
anions (unpermeable)
cations (permeable)
Porous matrix of njegatively charged glycoproteins and is MAIN CHARGE-SELECTIVE FILTER
Glomerular Basement membrane
Long-fingerlike processes that interdigitate to coverthe GBM. It is size-selective filter
foot processes of the podocytes
Fluid found within Bowman’s space that contains substances which have passed through kidney’s filtration process
Ultrafiltrate
Filterability
> 42A
18-42 A
< 18 A
> 42A (not filtered)
18-42 A (Varying filterability)
< 18 A (freely filtered if polycationic or neutral)
Filterability
Water
Sodium
Glucose
Inulin
Myoglobin
Albumin
Water (1)
Sodium (1)
Glucose (1)
Inulin (1)
Myoglobin (0.75)
Albumin (0.005)
Rationale:
Filterability of 1: Substance is filtered as freely as water
As it approaches zero filterability decreases
Comes from muscle hence should not be seen in signifgseen n sigificant amounts in urine
Myoglobin
Its negative charge causes it to be repelled
Albumin
Glomerular filtration wherein antibodies attack GBM and loses its glomerular filtration barrier negative charges hence filtration of anionic proteins between 18 and 42 A increases
Proteinuria/Albuminuria
Marker of kidney disease
Usually glomerular disease
Strenous exercise
Endothelial problems
GBM problems
Foot processes
Characterizes by too much albumin in urine
Nephrotic syndrome
Measure kidney function and filtering ability of the glomerulus, and is the theoretical basis for measuring GFR and RPF
Renal clearance
True/False
A 24 hour urin sample and serum creatinine is used for clearance
True
A certain value that estimates how good your kidneys are in terms of filtration
Aggregate index of kidney function
Kidney health
High value of AIK
Low value of AIK
High value of AIK > Low value of AIK
Substance used for the GFR
Stable plasma concentration
Freely Filtered
Not reabsorbed
Not secretedn
Not metabolized or produced by the kidney
Does not alter GFR
Gold standard for the substance used for GFR
Inulin
Rationale:
Not readily available
Natural soluble fiber
Alternative and most used clinically substance
Creatinine
Formula of creatinine clearance to measure GFR
cuv/P
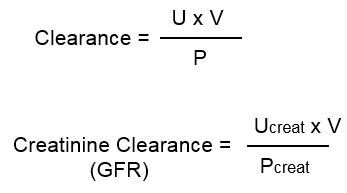
Creatinine
Higher muscle mass vs lower muscle mass
Male vs female
Younger vs older
Caucasians and africans vs asians
Higher muscle mass > lower muscle mass
Male > Female
Younger > older
Caucasians and africans > asians
Indication of very low GFR <60
decrease of filtration
Kidney disease or failure
Indication of very high GFR > 140
Hyperfiltrating kidney
Pressure within glomerulus is very high
Factors that increase GFR
PGC
πBS
Factors that decrease GFR
PBS
πGC
Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure, and is the main driving force of GFR
PGC
Bowman’s space oncotic pressure and is the pulling pressure exerted by albumin. It is equally zero in healthy in individuals
πBS
VR
KF
GFR
A.
Rationale:
Increase in KF increases GFR
Increase KF Increase permeability
Increase KF Increase SA
Increase KF Increase Kidney filtration
Afferent arteriolar Resistance Vasodilation
↓ Resistance
↑ PGC
↑ GFR
↑ RBF
Rationale:
Afferent arteriole is dilated
Efferent Arteriole is Constricted
Afferent favors filtration while efferent favors reabsorption
Afferent arteriolar Resistance Vasoconstriction
↑ Resistance
↓ PGC
↓ GFR
↓ RBF
Afferent vasoconstriction favors reabsorption