Chapter 9 - Blood Vessels of the Lower Limb
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What comprises the Cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and all blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
Artery - any vessel that carries blood away from the heart
–Arteries supply any structure that they go past
Arterial patterns are moderately variable between different individuals
–Muscles can be supplied by more than one artery
Large or long muscles usually supplied by several arteries
Know location of artery within body and surrounding structures that could be supplied by that artery*
Vein - any vessel that carries blood toward heart
–Veins have thinner walls compared to arteries - due to lower venous blood pressure
Blood flows down pressure gradient - higher blood pressure in arteries
–Movement of blood in veins aided by contraction of adjacent muscles
Bulging of contracted muscle squeezes veins; moves blood
Particularly important in lower limb, where is blood must move against gravity
–Veins have one-way valves - prevent backflow of blood
Varicose veins - due to weak valves that allow backflow; leads to pooling of blood, inflammation, and pain
–Venous patterns are highly variable between individuals
–Vein running with an artery has same name as artery
Capillary - microscopic vessels connecting arteries and veins
Very thin walled
Capillaries are the only vessels that allow for the exchange of nutrients and metabolic waste products between blood and cells of body
Describe the blood supply to limbs
Blood is pumped to body by left ventricle of heart
Blood pumped into aorta (largest artery of body)
Aorta - divided into 3 regions:
–Ascending aorta - 1st region
Exits left ventricle and passes superiorly
Located at mid-line of thorax, directly behind upper sternum
–Arch of aorta (aortic arch) - 2nd region
Makes U-turn - curves posteriorly and to left
Gives off 3 arteries that supply head, neck, & upper limbs
–Descending aorta - 3rd region
Passes posterior to heart and runs inferiorly through thorax and abdomen
–Located against posterior body wall (immediately anterior to vertebral column)
Subdivided into thoracic aorta and abdominal aorta
Terminates in lower abdomen (at level of your umbilicus) - divides into right & left common iliac arteries
–Common iliac arteries supply the pelvis and lower limbs*
Describe blood supply to hip and thigh
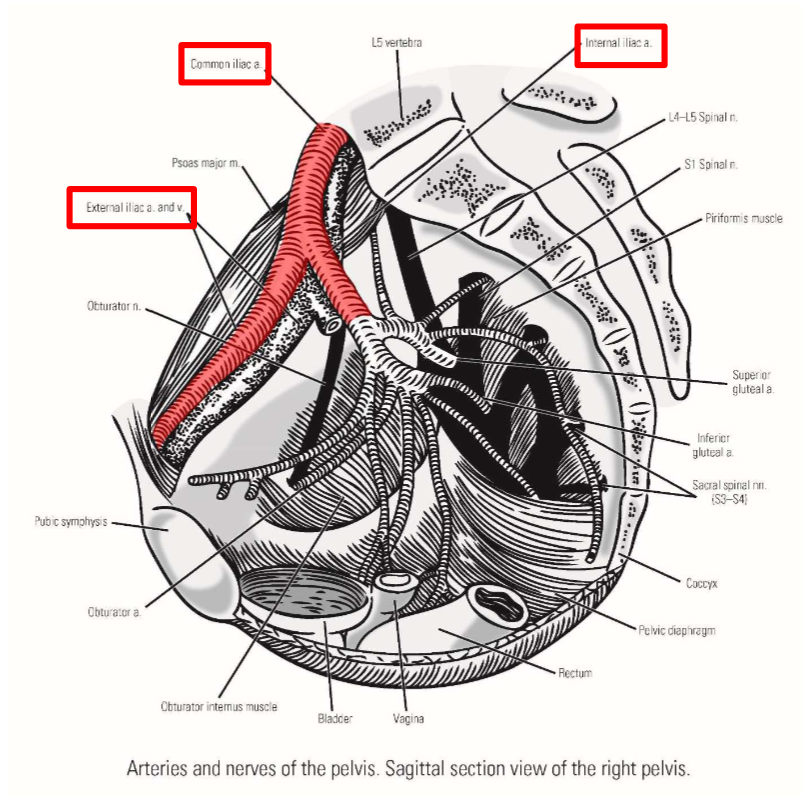
Common iliac artery
–Terminal branch from abdominal aorta
Runs inferiorly and laterally - descends into pelvic region
–Terminates by dividing into:
External iliac artery
Internal iliac artery
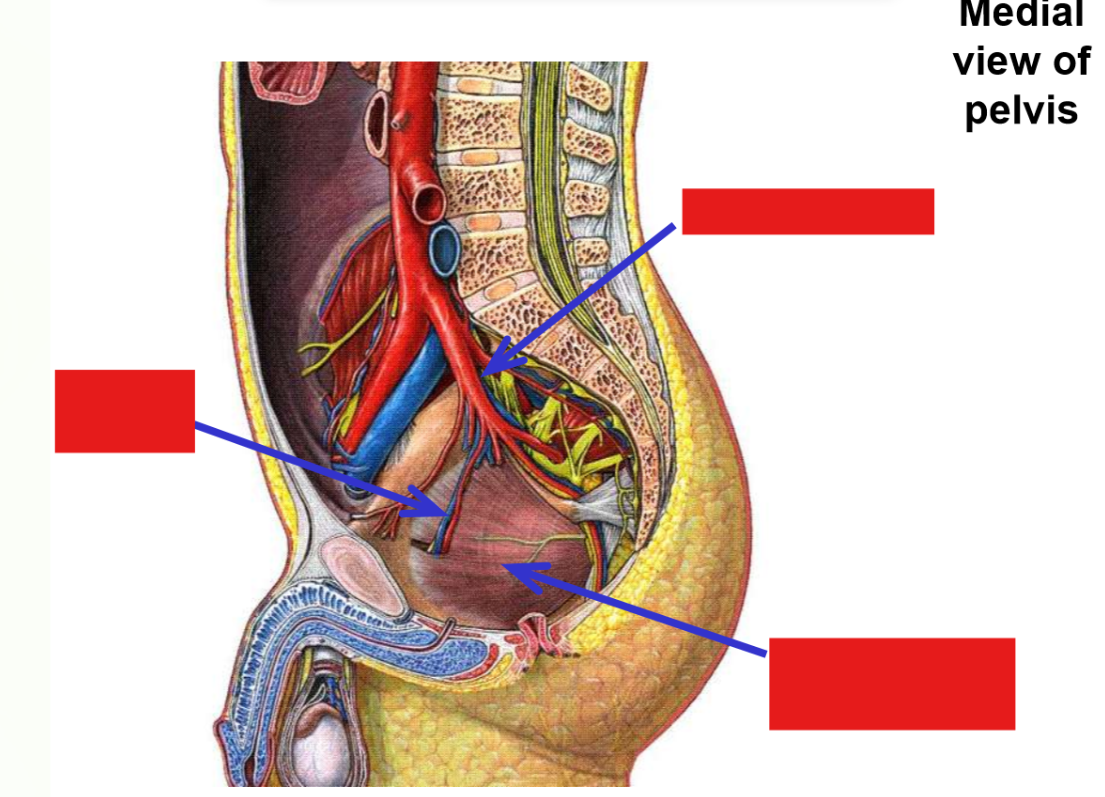
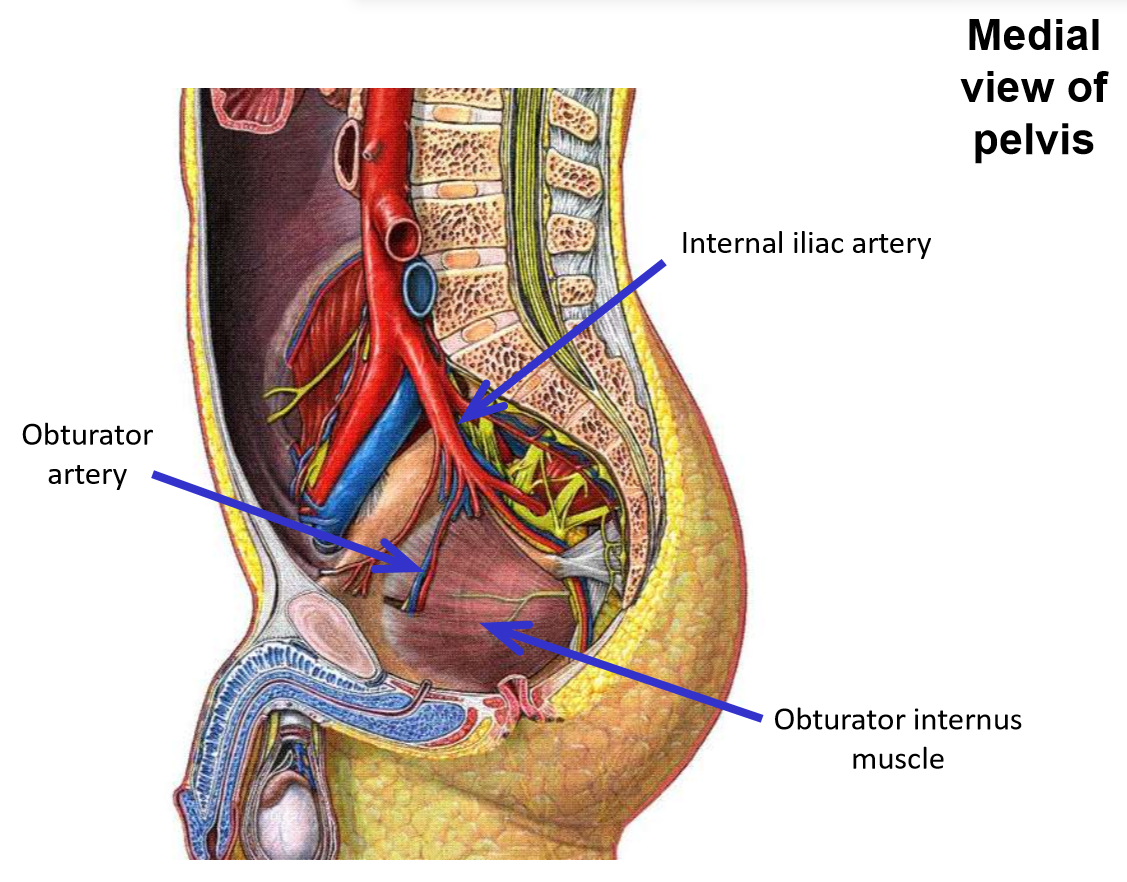
Internal iliac artery. Branches, exits, emerges, supplies
–Passes into true (lesser) pelvic cavity
–Gives off branches that supply pelvic organs
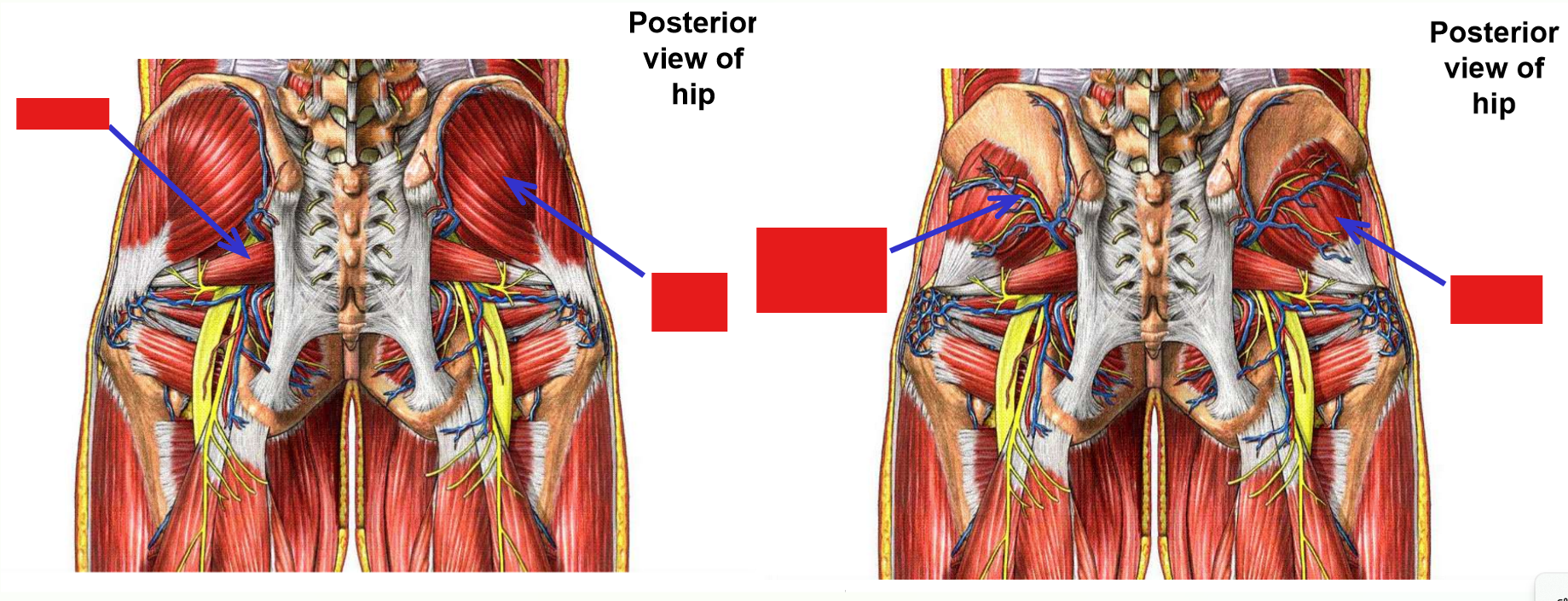
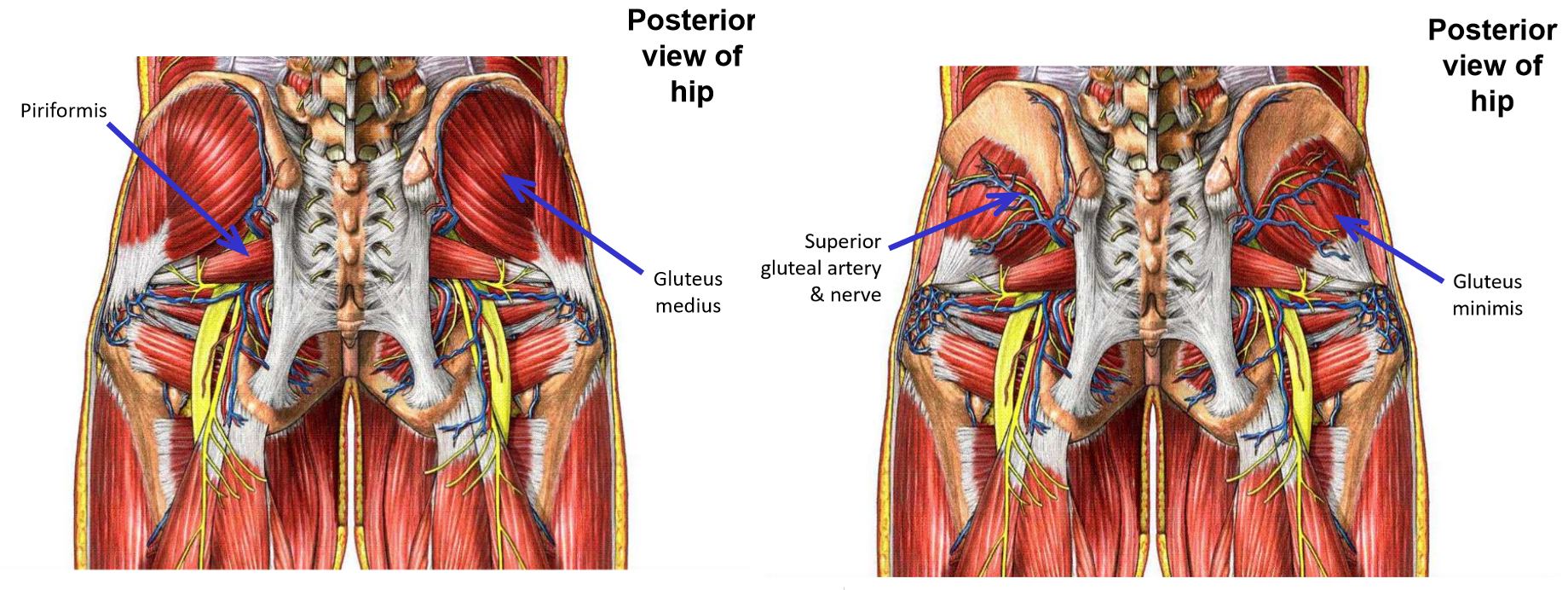
–Branches to posterior hip that exit pelvis:
Superior gluteal artery (runs with superior gluteal n.)
Exits via greater sciatic foramen
Emerges at superior margin of piriformis muscle
Supplies mm. gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae
Inferior gluteal artery (runs with inferior gluteal n.)
Exits via greater sciatic foramen
Emerges at inferior margin of piriformis muscle
Supplies m. gluteus maximus
–Internal iliac artery sends one branch to the thigh:
Obturator artery (runs with obturator n.)
Exits via obturator foramen
Passes into medial thigh
Supplies obturator externus and proximal ends of medial thigh muscles
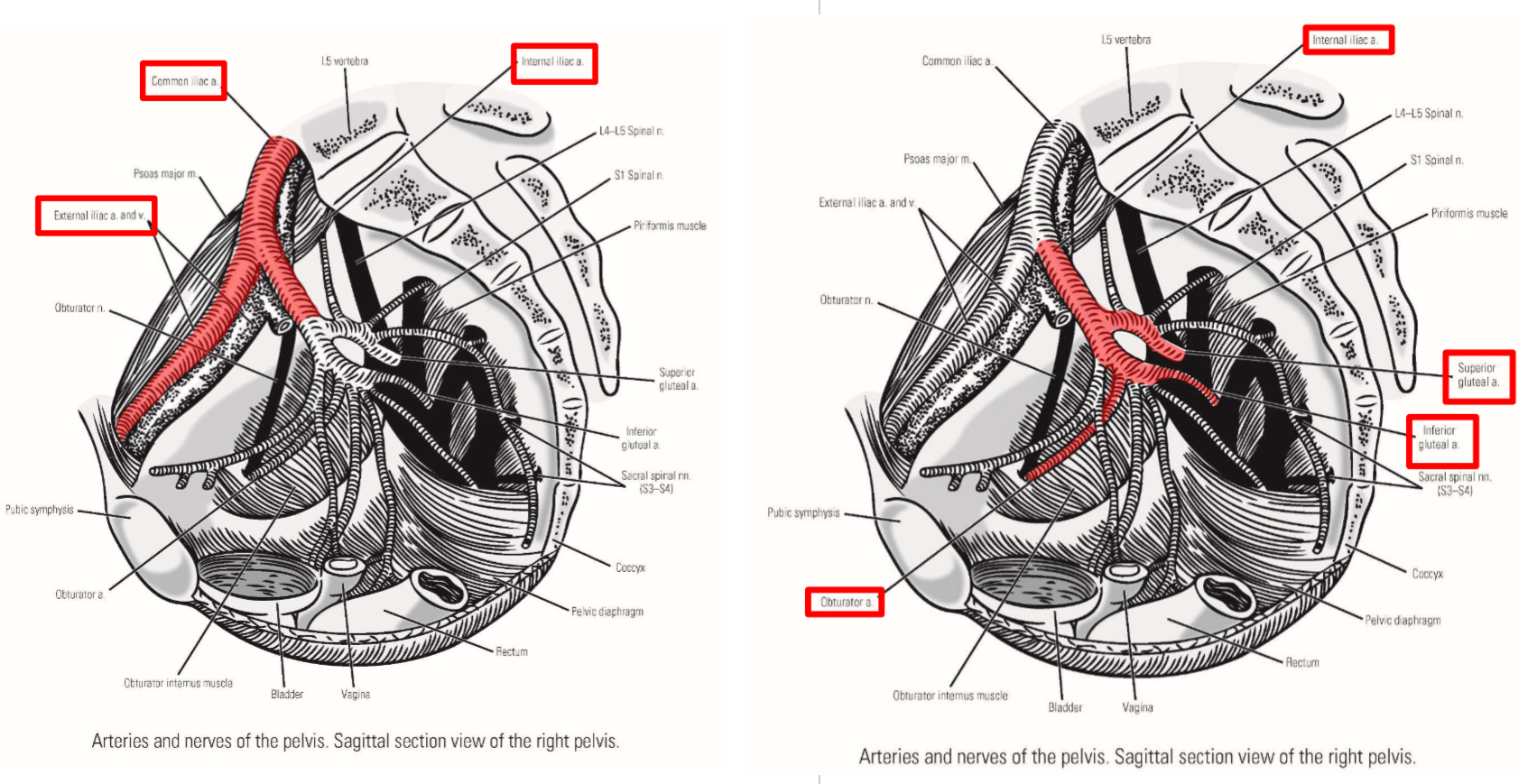
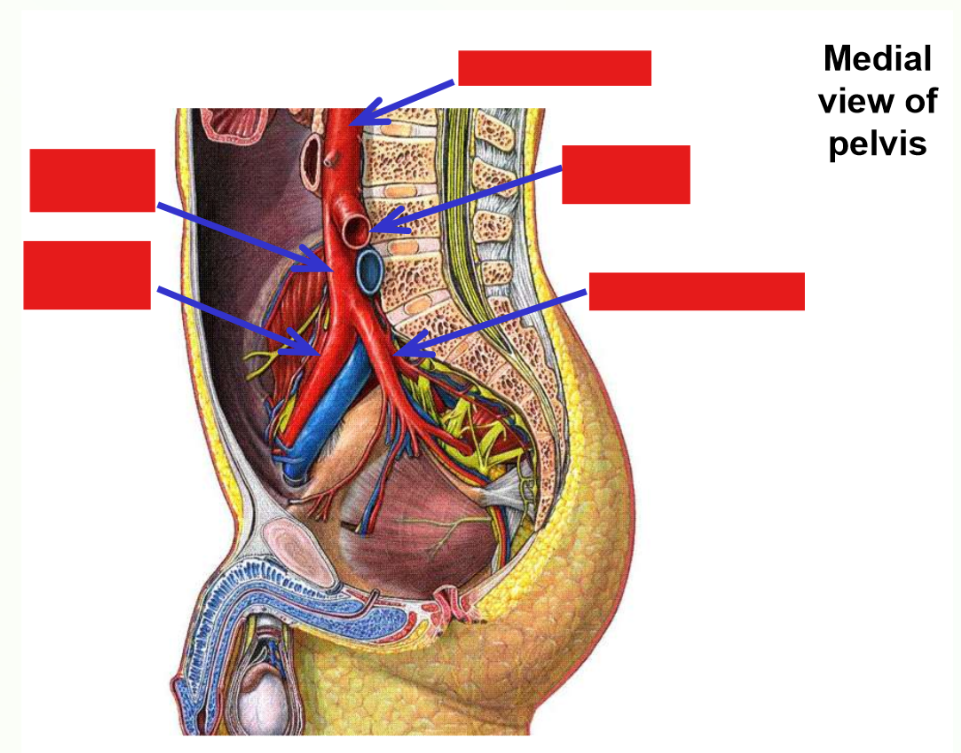
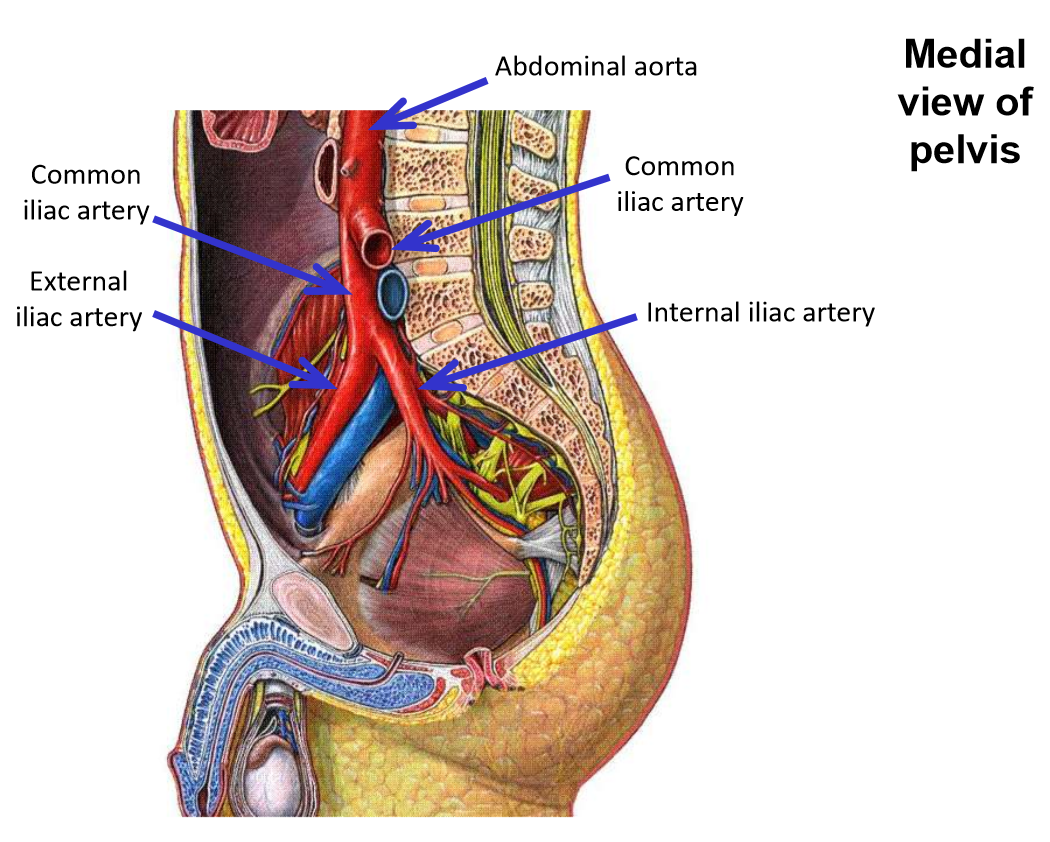
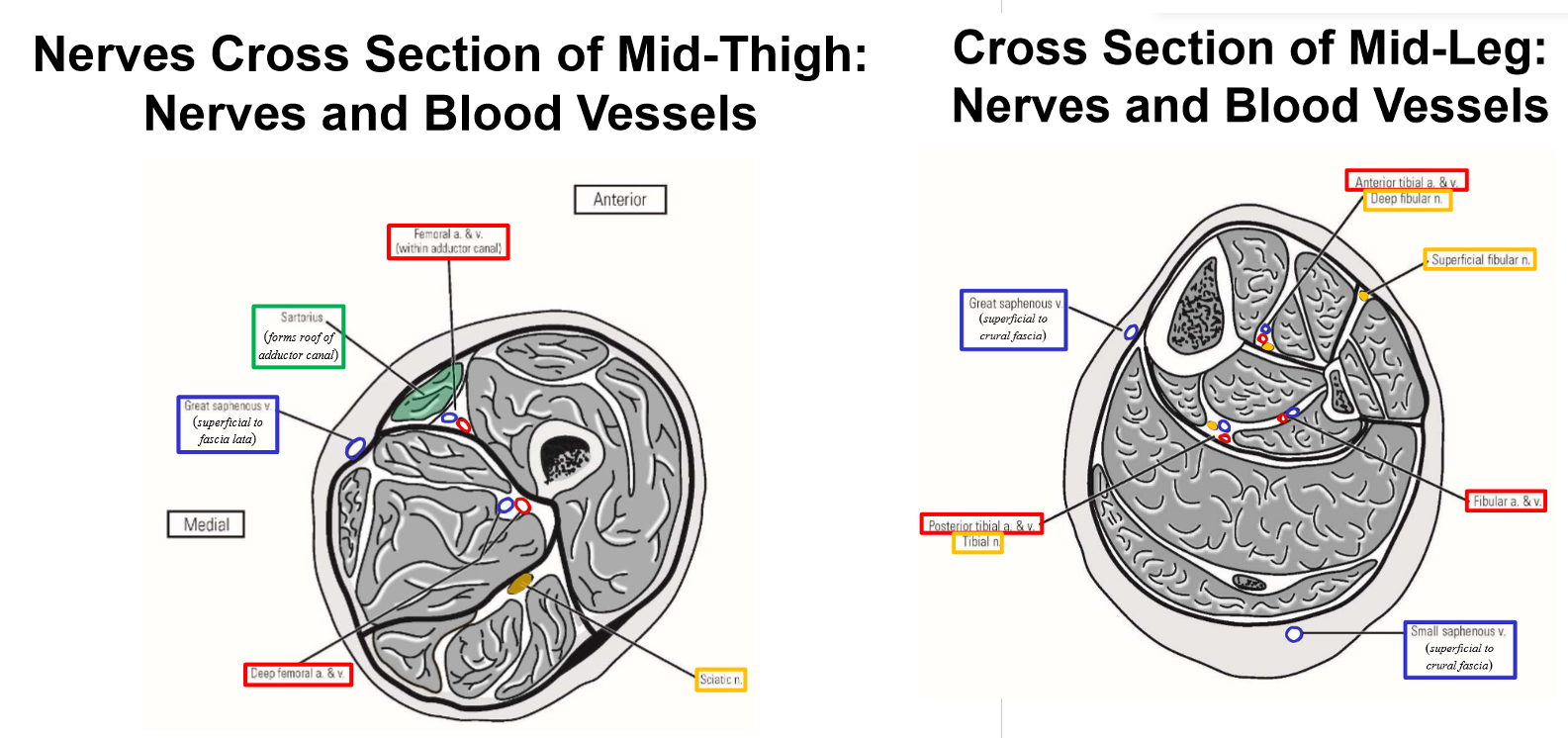
External iliac artery
–Runs along pelvic brim
–Exits pelvis by passing under inguinal ligament - enters anterior thigh
–At inguinal ligament, name of artery changes to femoral artery
External iliac artery terminates at the inguinal ligament
Femoral artery begins at inguinal ligamen
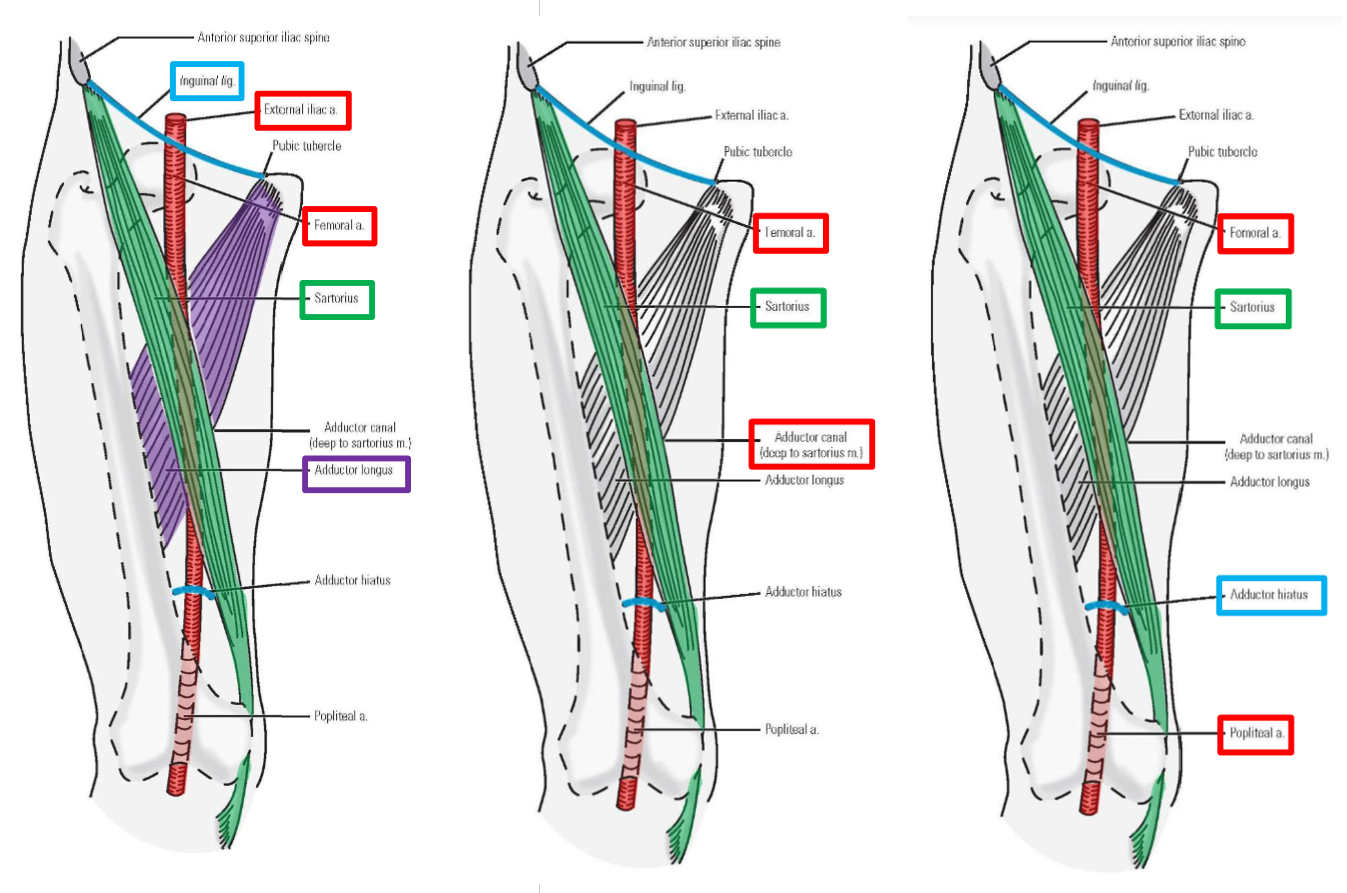
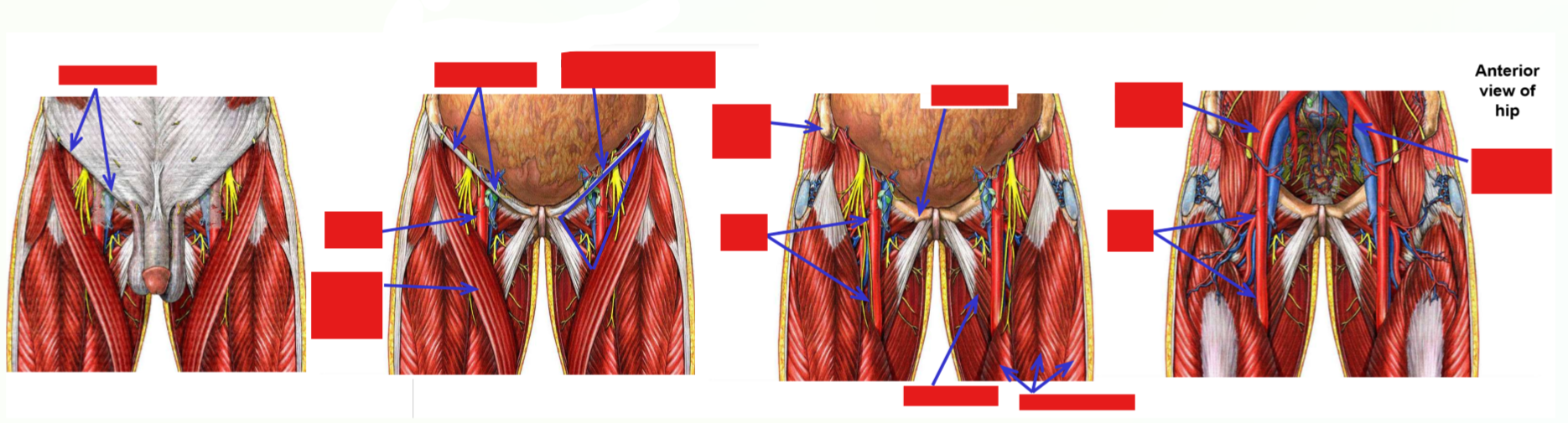
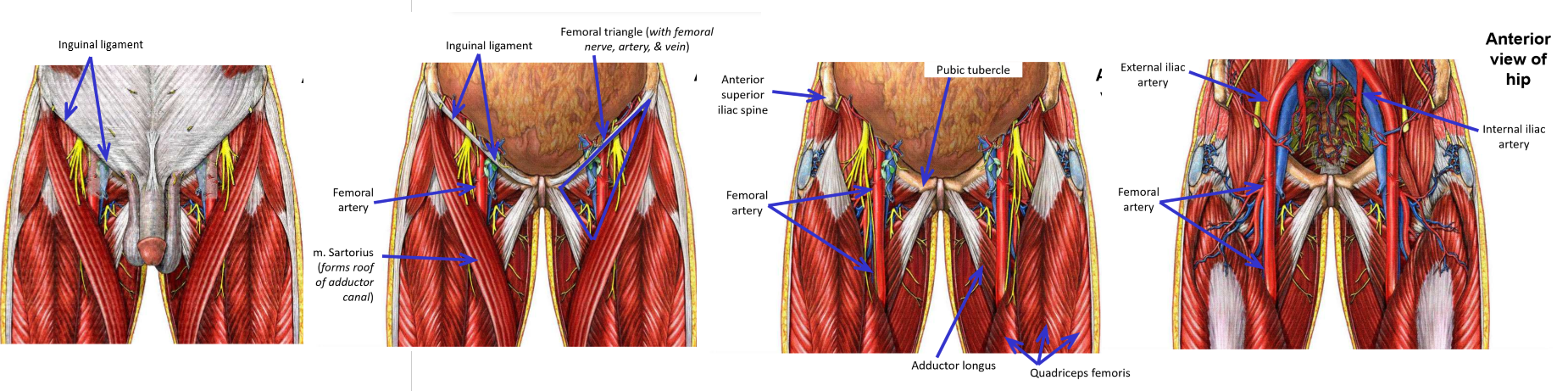
Femoral artery
–Femoral artery begins at inguinal ligament, then descends through thigh
–Proximal ⅓ of thigh - femoral artery is located within femoral triangle (with femoral nerve)
Femoral triangle: inguinal ligament, m. sartorius, m. adductor longus
–Middle ⅓ of thigh - femoral artery located within adductor canal
–Adductor canal - groove located between m. quadriceps femoris and adductor muscles of medial thigh
M. Sartorius forms roof of adductor canal (overlies femoral artery in middle ⅓ of thigh)
–Distal ⅓ of thigh - femoral artery passes through adductor hiatus (gap in insertion of adductor magnus muscle)
–Artery passes from thigh into popliteal fossa (behind knee)
Name of artery changes to become popliteal artery
–Femoral artery thus terminates at adductor hiatus
Popliteal artery begins at adductor hiatus
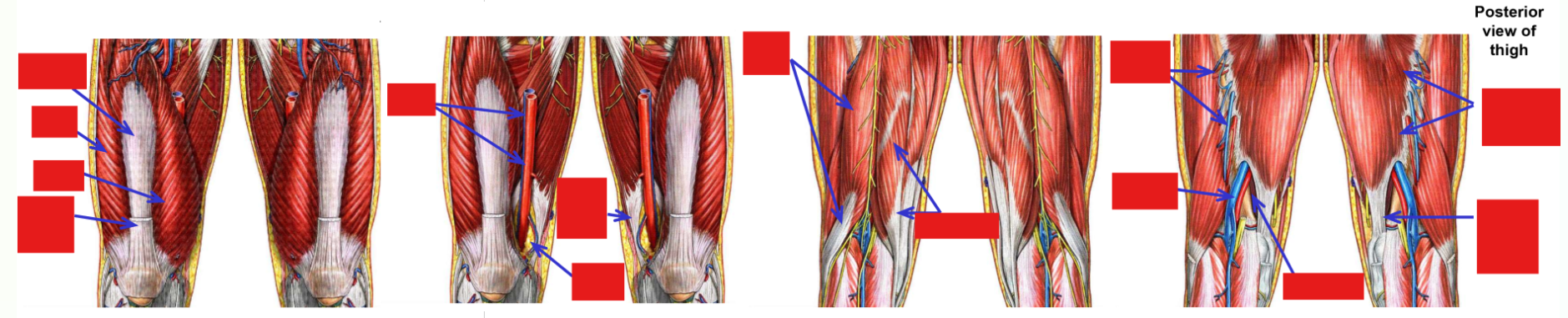
Describe and list the Branches of Femoral Artery
Only major branch given off by femoral artery within the thigh is the deep femoral artery
This branch provides majority of blood supply to muscles of thigh
Note: obturator artery supplies proximal ends of medial thigh muscles
Deep femoral artery
Perforating arteries
medial & lateral circumflex femoral arteries
Deep femoral artery
–Branches from femoral artery within femoral triangle (in proximal thigh)
–Deep femoral artery dives deep and runs along medial side of femur
Terminates by dividing into four perforating arteries
Perforating arteries wrap around posterior, lateral, and anterior sides of femur
–Deep femoral artery (with perforating arteries) supply majority of blood for muscles of the thigh
Perforating arteries
Arteries must thus perforate (penetrate) through all muscles attaching to linea aspera of posterior femur:
•M. Vastus medialis
•M. Vastus lateralis
•M. Pectineus
•M. Adductor longus
•M. Adductor brevis
•Adductor part of m. adductor magnus
•Short head of m. biceps femoris
Perforating arteries also contribute to blood supply for mm. vastus intermedius & rectus femoris, plus all hamstring muscles of posterior thigh
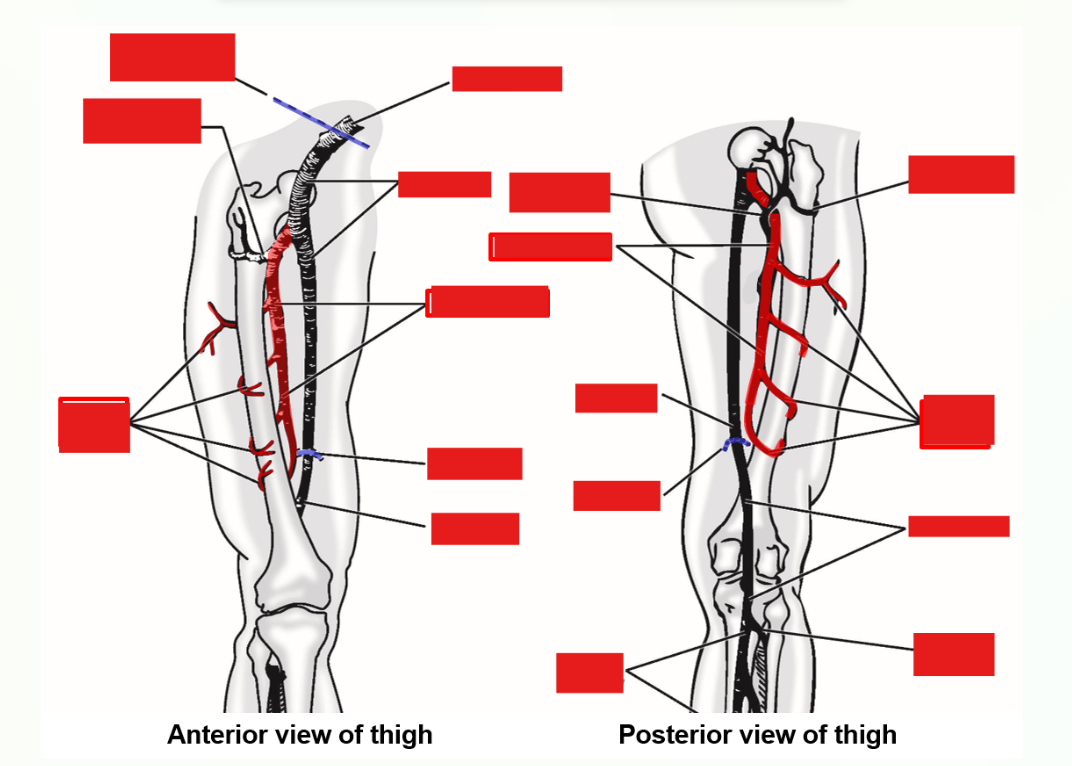
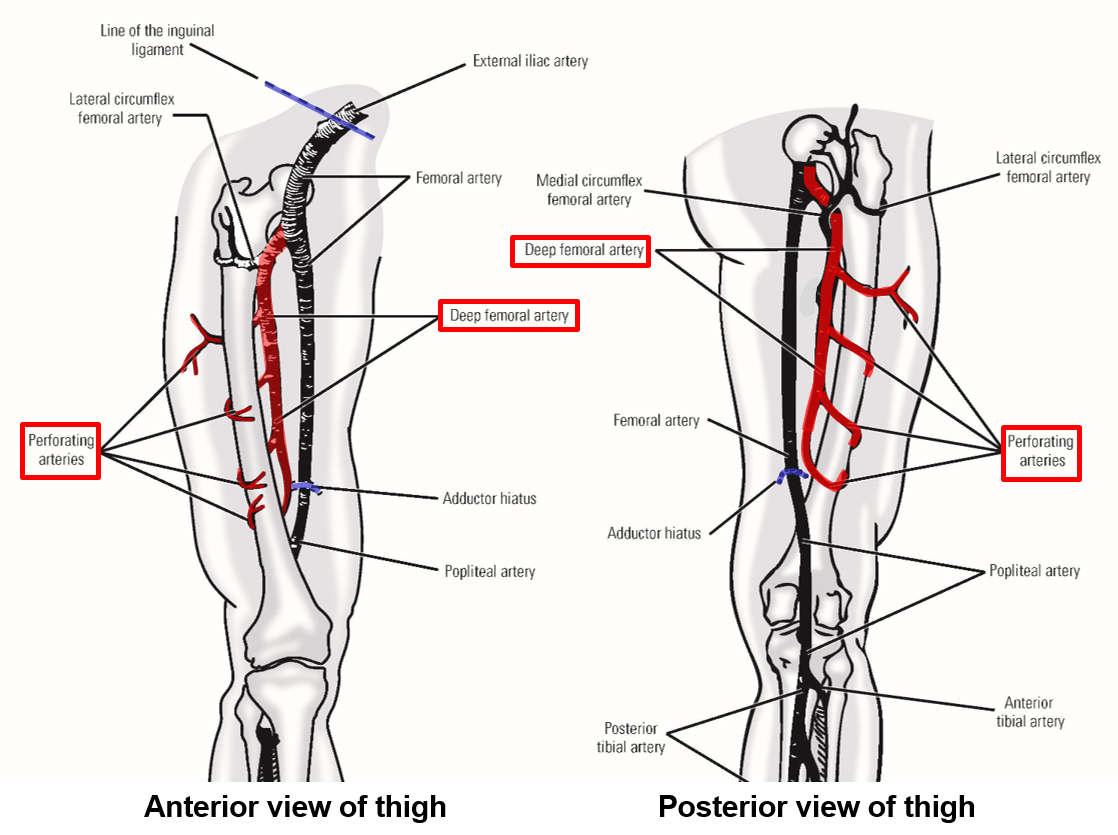
Medial & lateral circumflex femoral arteries
In proximal thigh, deep femoral artery also gives off medial & lateral circumflex femoral arteries
–These wrap around proximal end of femur (circumflex = “to bend around”)
Medial artery passes to medial side of proximal femur; lateral artery passes to anterior & lateral sides of femur
–Both supply muscles of the proximal thigh and muscles that attach to greater & lesser trochanters of femur
Also provide blood supply to head & neck of femur and to hip joint
“Broken hip” = fracture of femoral neck; damage to circumflex arteries can lead to poor healing or necrosis of femur
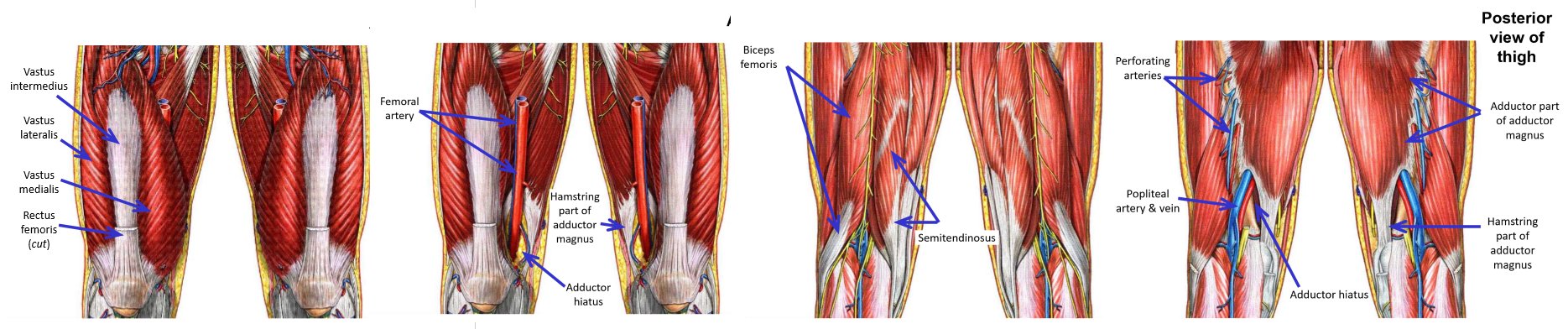
Popliteal Artery
Popliteal artery
–Begins at adductor hiatus
Adductor hiatus - gap in attachment of adductor magnus muscle to femur
–Popliteal artery then descends through popliteal fossa
Popliteal artery is deepest structure within popliteal fossa
Tibial nerve is most superficial structure within popliteal fossa
–Begins at adductor hiatus - enters popliteal fossa
–Popliteal artery exits popliteal fossa and enters posterior leg
Passes between medial/lateral heads of m. gastrocnemius, then dives under m. soleus
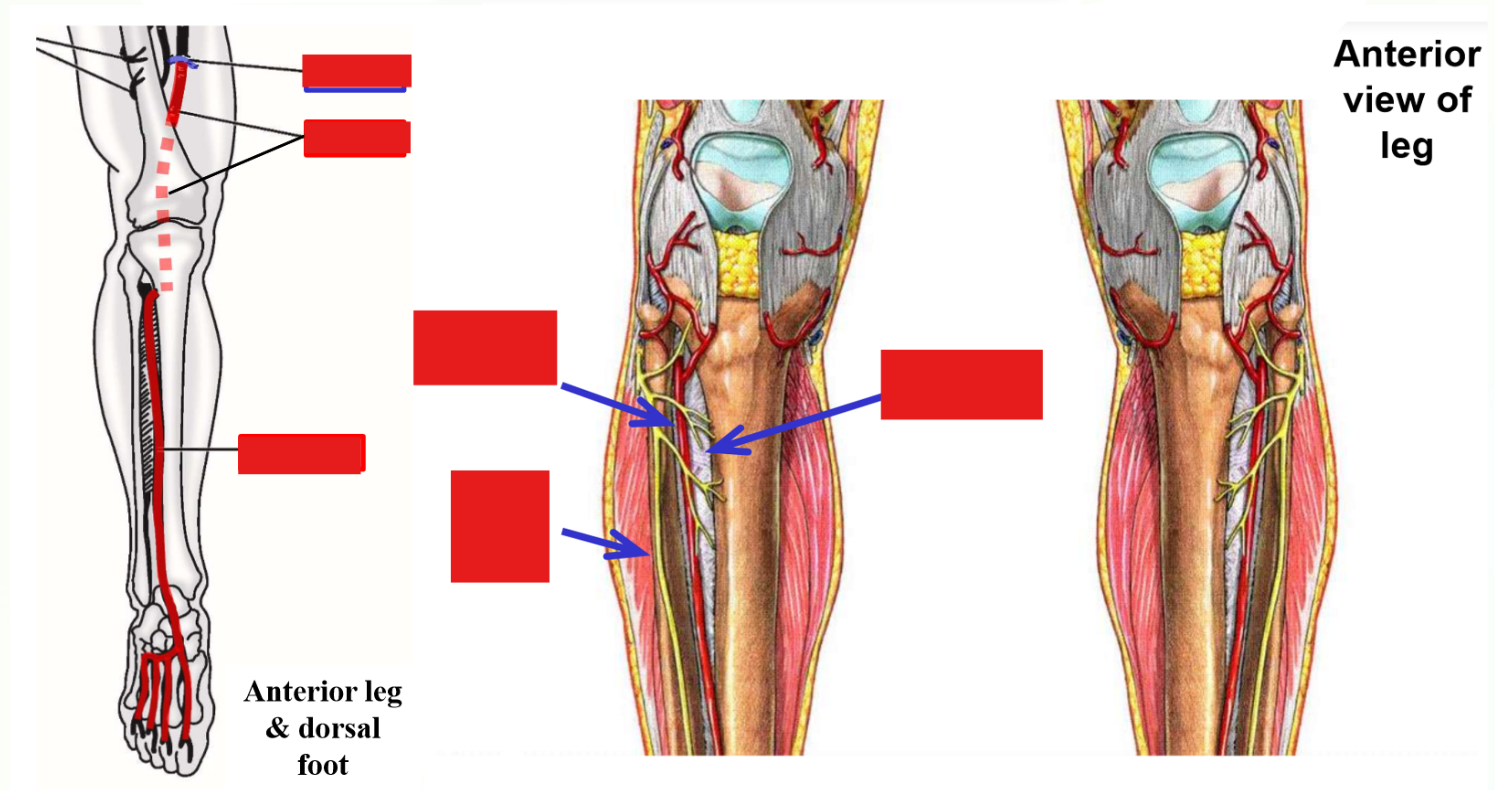
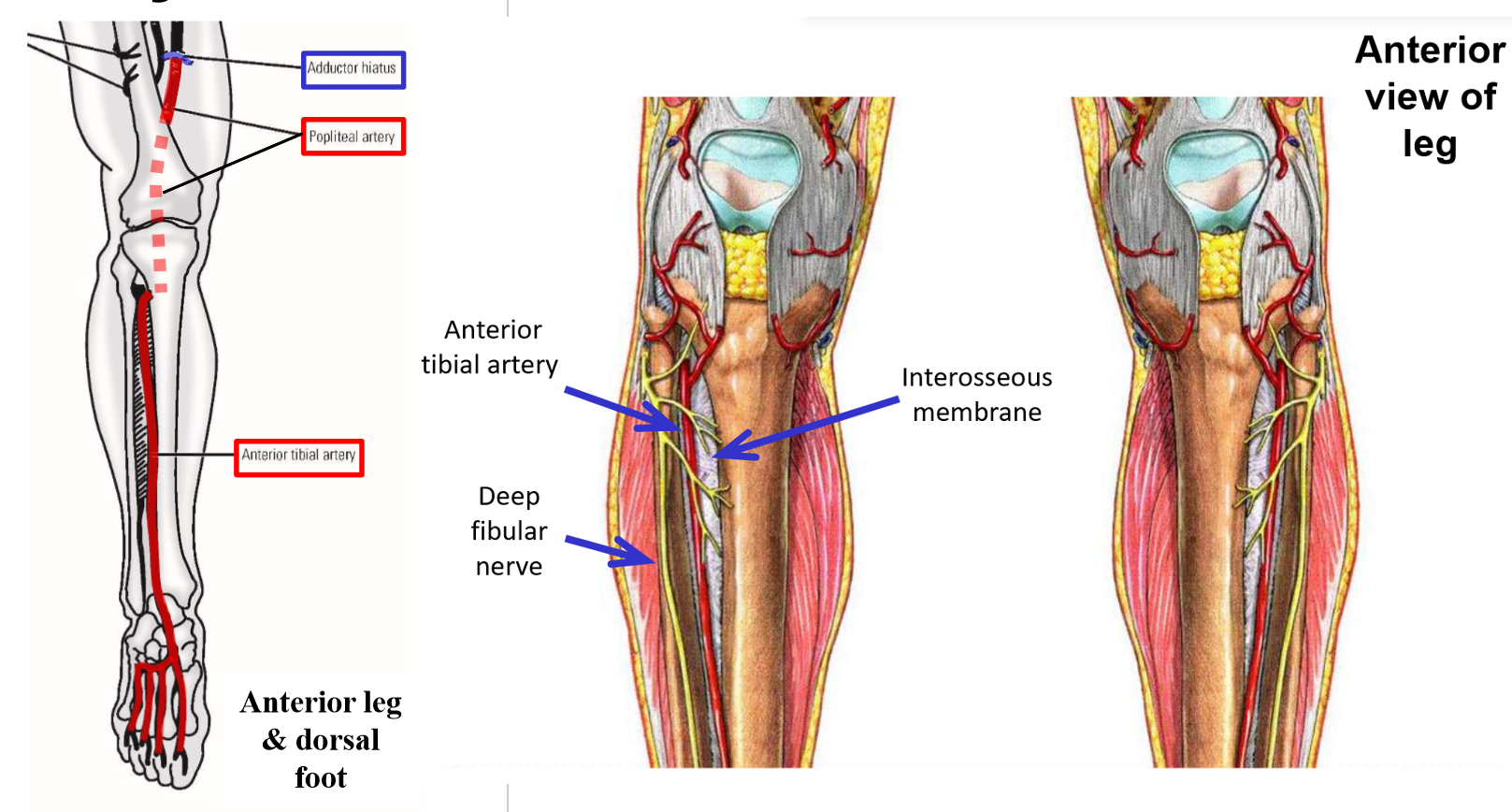
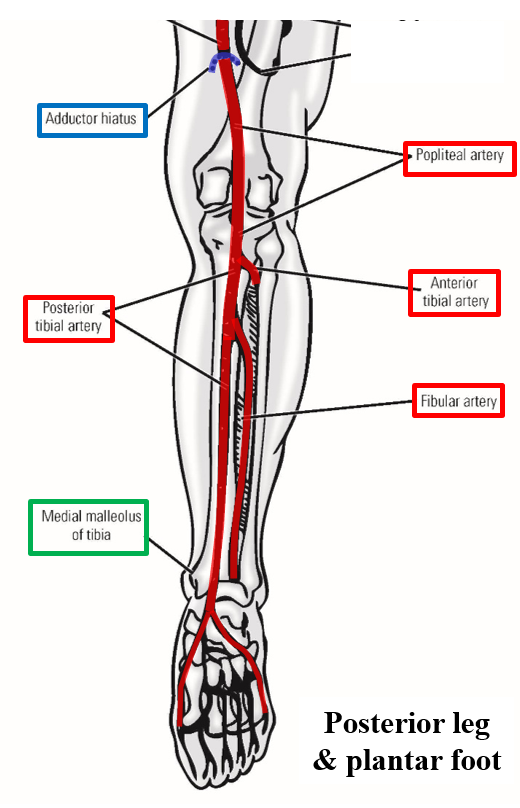
–Popliteal artery terminates in proximal leg by dividing into anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery
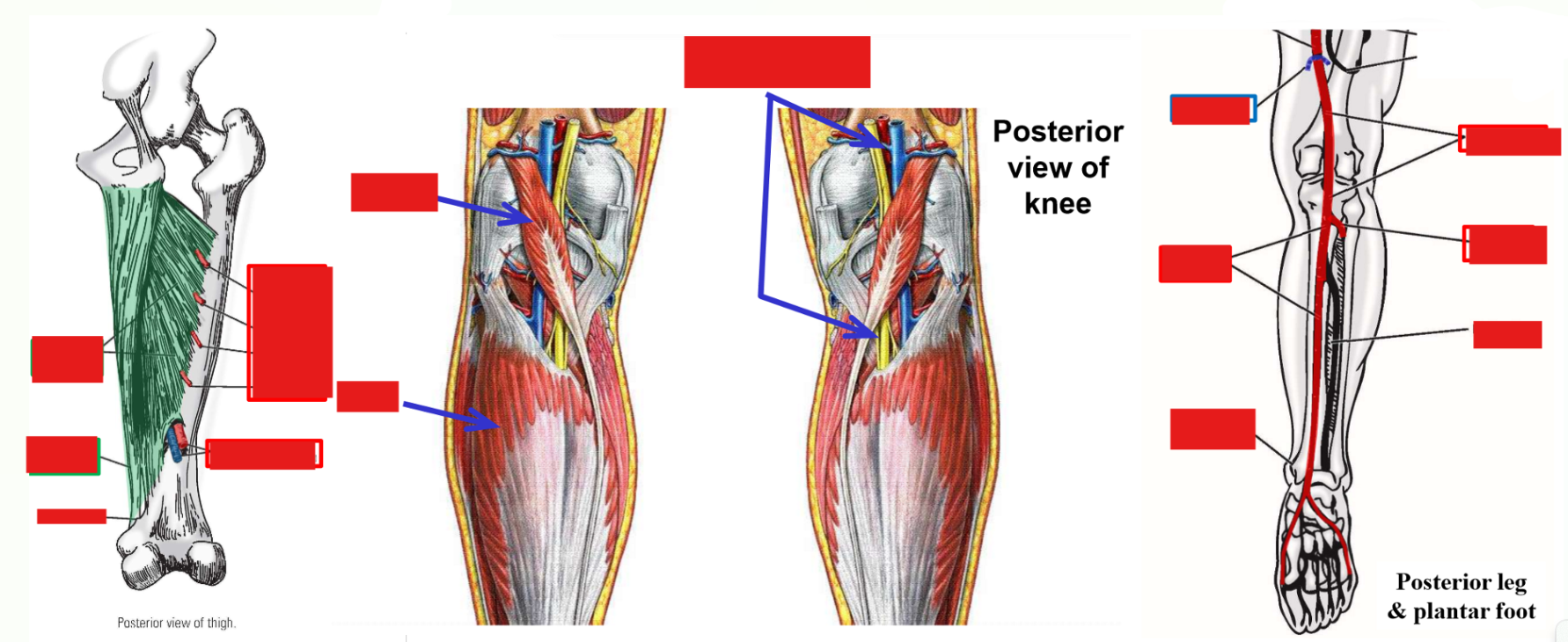
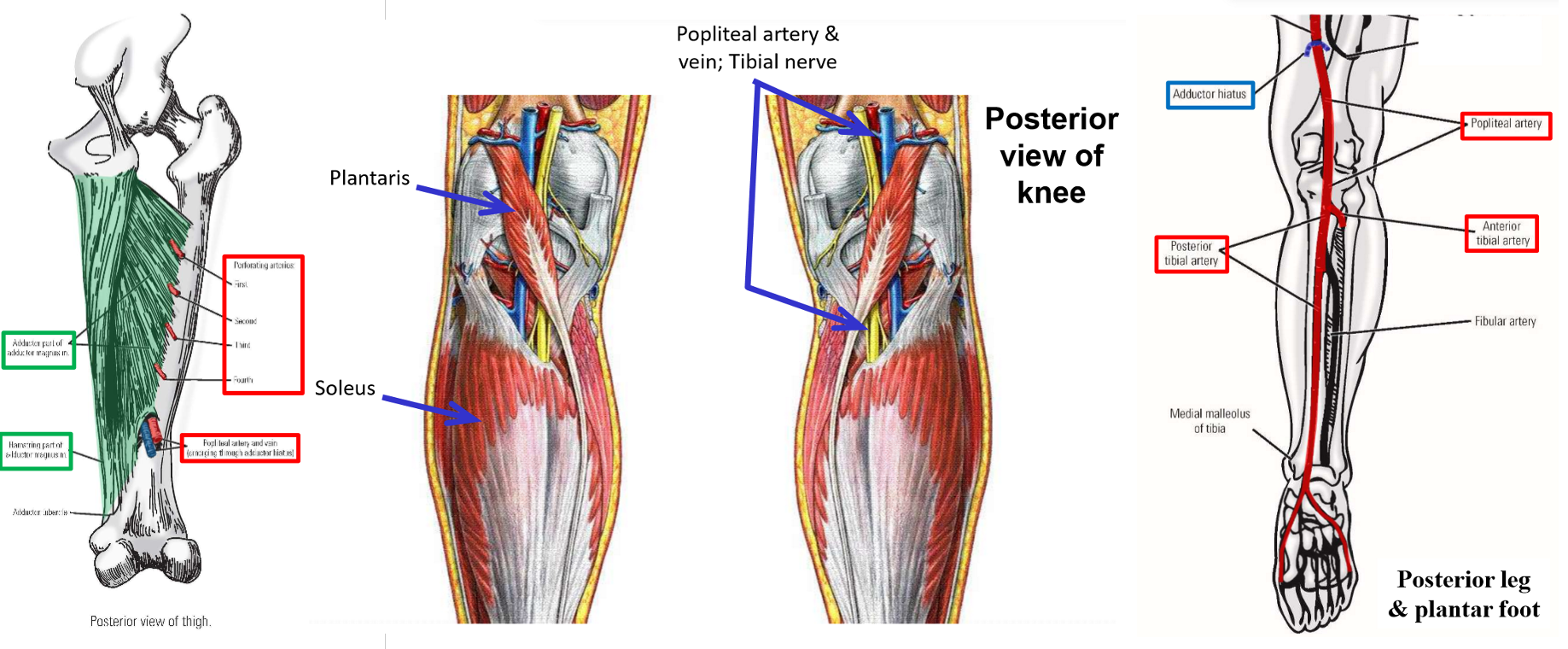
Anterior Tibial Artery
Anterior tibial artery - arises in posterior leg as terminal branch of popliteal artery
–Passes through interosseous membrane to enter anterior compartment of the leg
Runs inferiorly - supplies all muscles of anterior leg compartment
–Continues across anterior ankle to dorsum of foot
Supplies intrinsic muscles of dorsal foot (m. extensor hallucis brevis and m. extensor digitorum brevis)
Posterior Tibial Artery
Posterior tibial artery - arises in posterior leg as terminal branch of popliteal artery
–Posterior tibial artery runs inferiorly within deep posterior leg compartment
Runs with tibial nerve
Supplies all muscles of deep posterior leg compartment
–Gives off fibular artery - to muscles of lateral leg
–Crosses ankle by passing posterior to medial malleolus of tibia and enters plantar foot
Supplies all intrinsic muscles of plantar foot
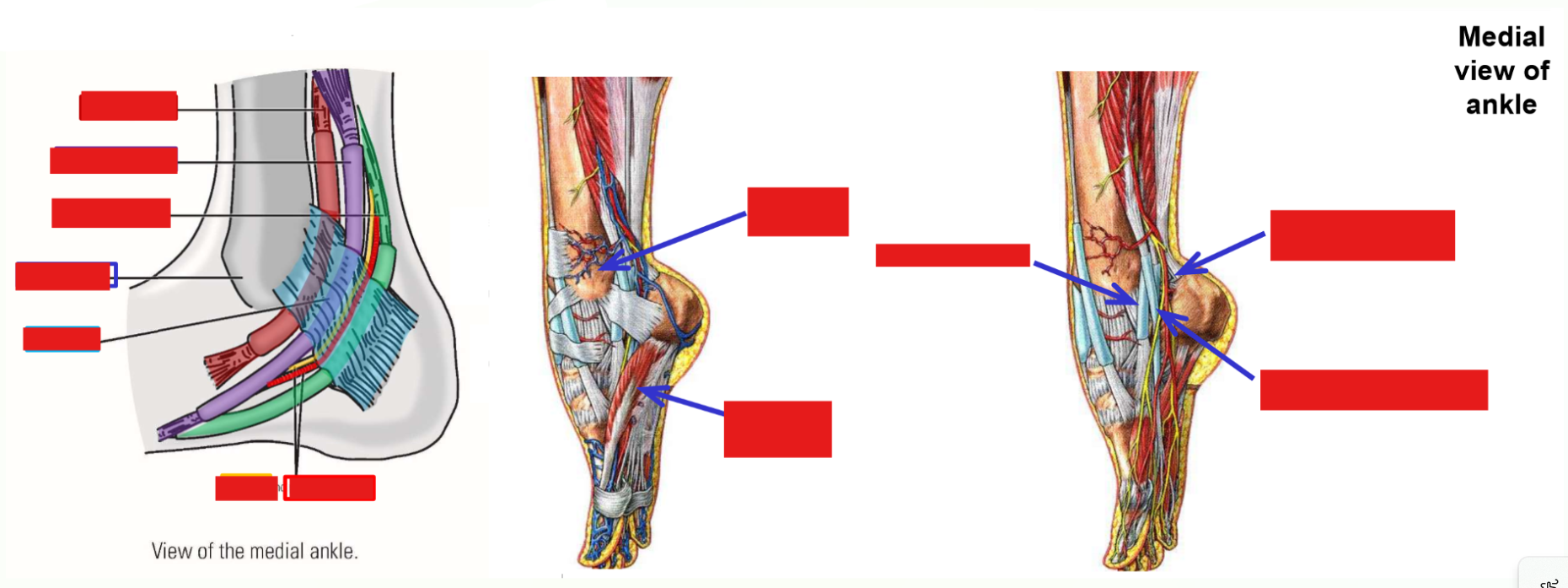
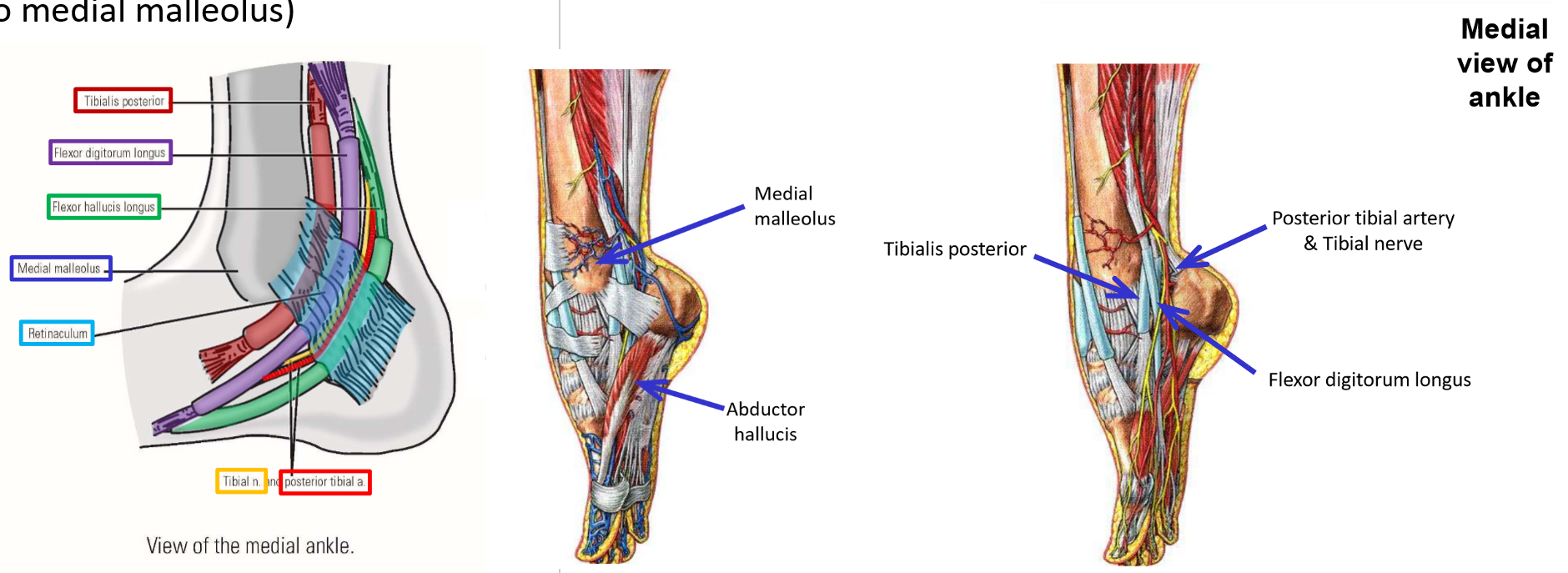
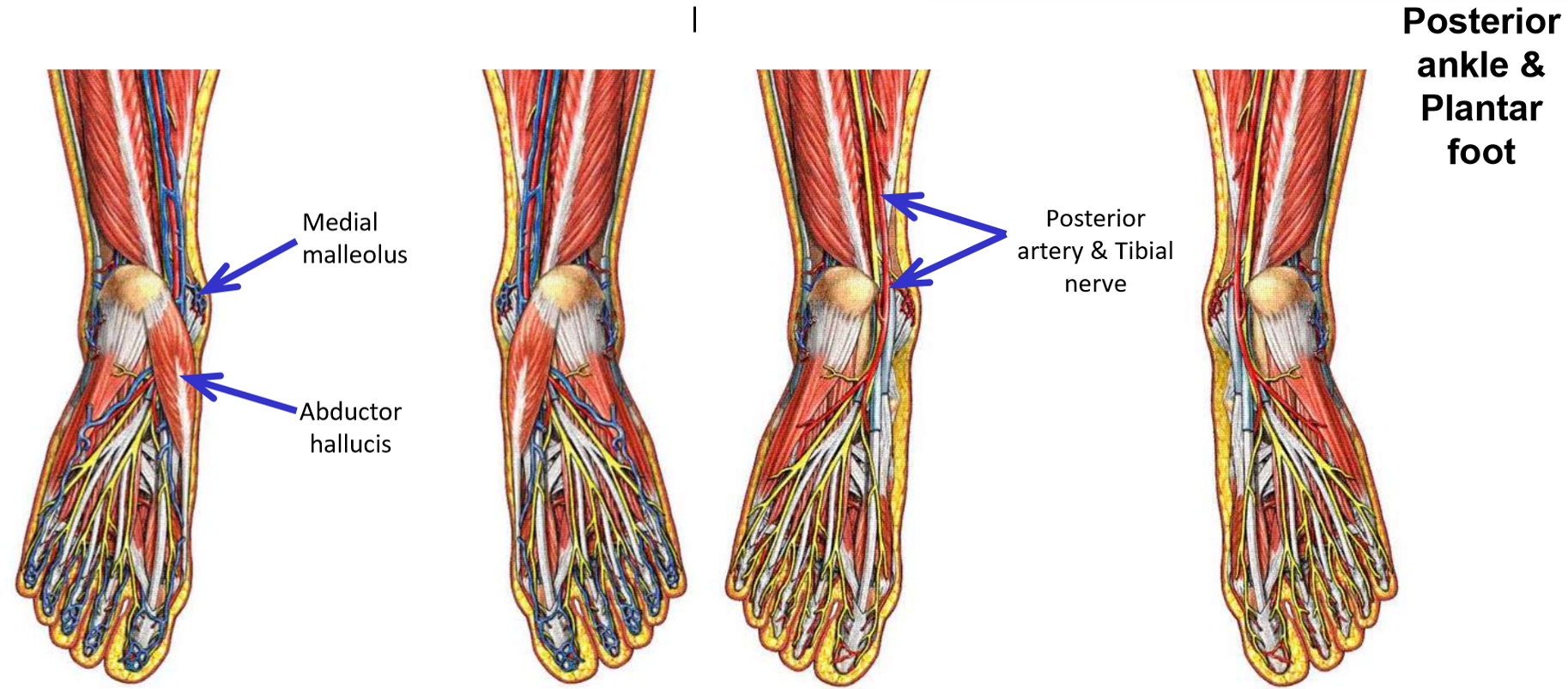
Structures at Medial Malleolus
Three muscles, an artery, and a nerve all pass posterior to medial malleolus of the tibia to enter the plantar foot
Use pneumonic “Tom, Dick, and Harry”
T: tibialis posterior (1st muscle tendon; located immediately posterior to medial malleolus)These structures are held in place by a retinaculum and have specific positions at the medial malleolus
D: flexor digitorum longus (2nd muscle tendon)
an: posterior tibial artery and tibial nerve
H: flexor hallucis longus (3rd muscle tendon; located the most posteriorly from medial malleolus)
Superficial Veins of Lower Limb
Superficial veins run within the superficial fascia (superficial to deep investing fascia)
Unaccompanied by arteries
Connected to (can drain to) deep veins of the limb
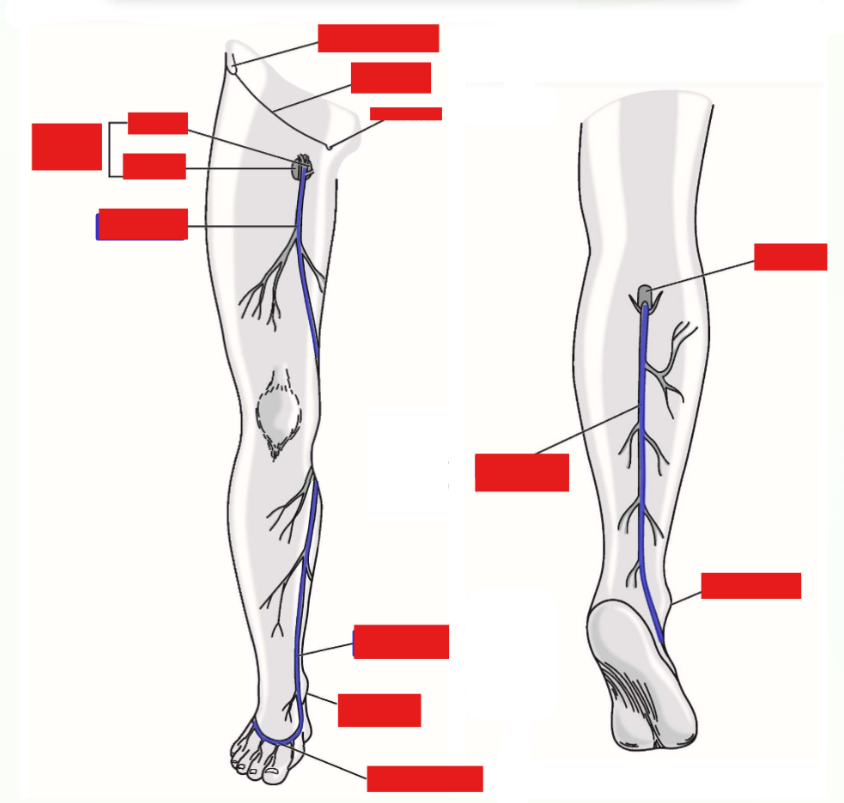
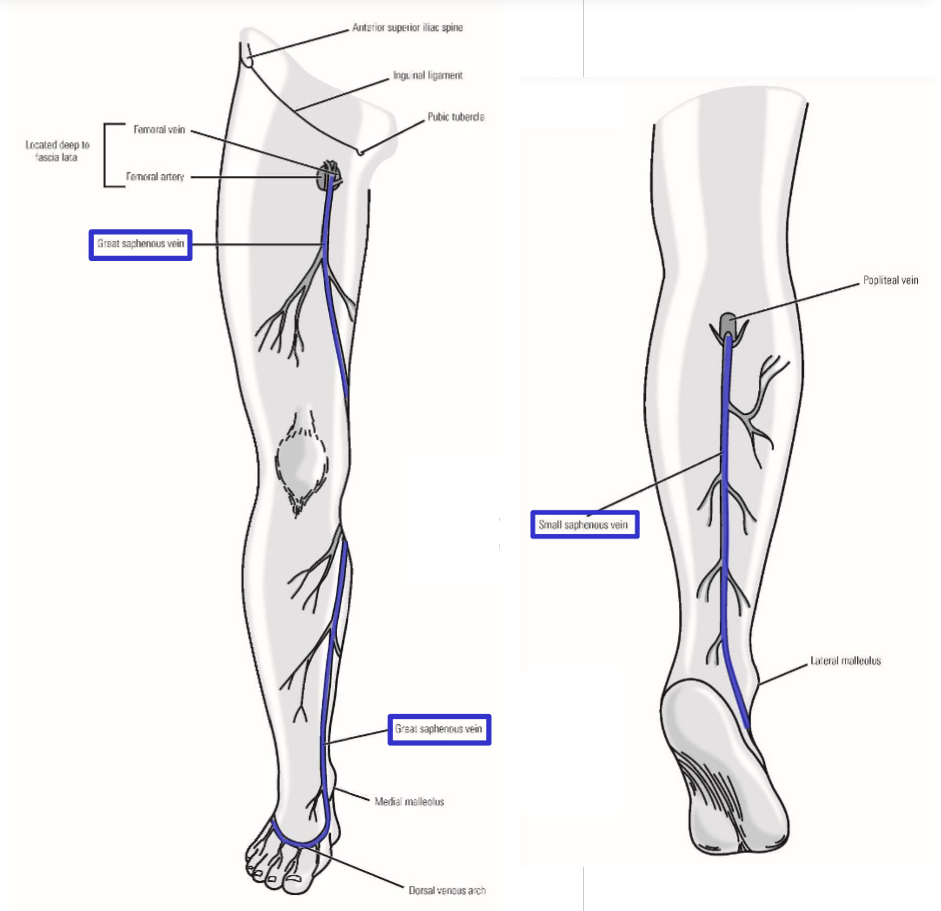
Dorsal venous arch
Formed by veins on dorsal side of foot - receive drainage from toes and foot
Gives rise to great saphenous vein (from medial side of dorsal arch) and small saphenous vein (from lateral side of dorsal arch)
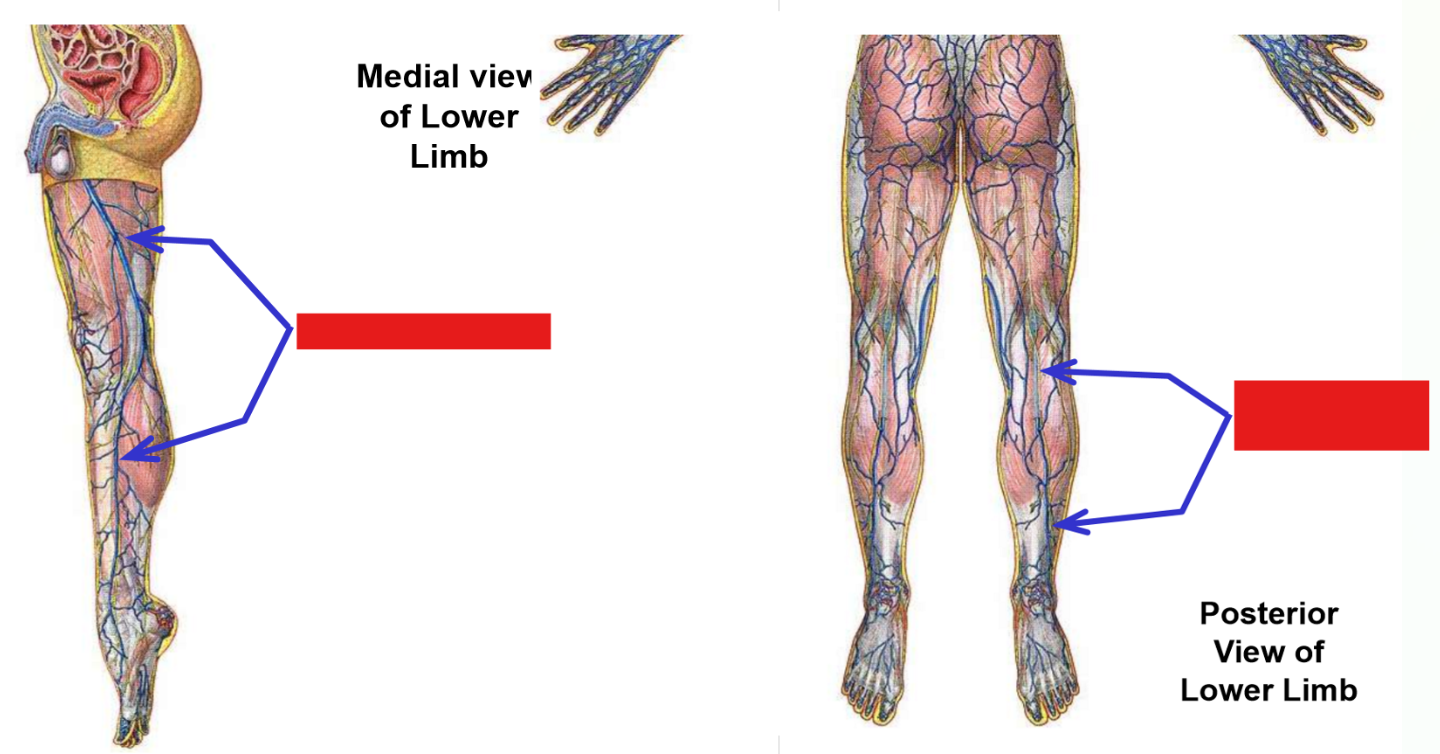
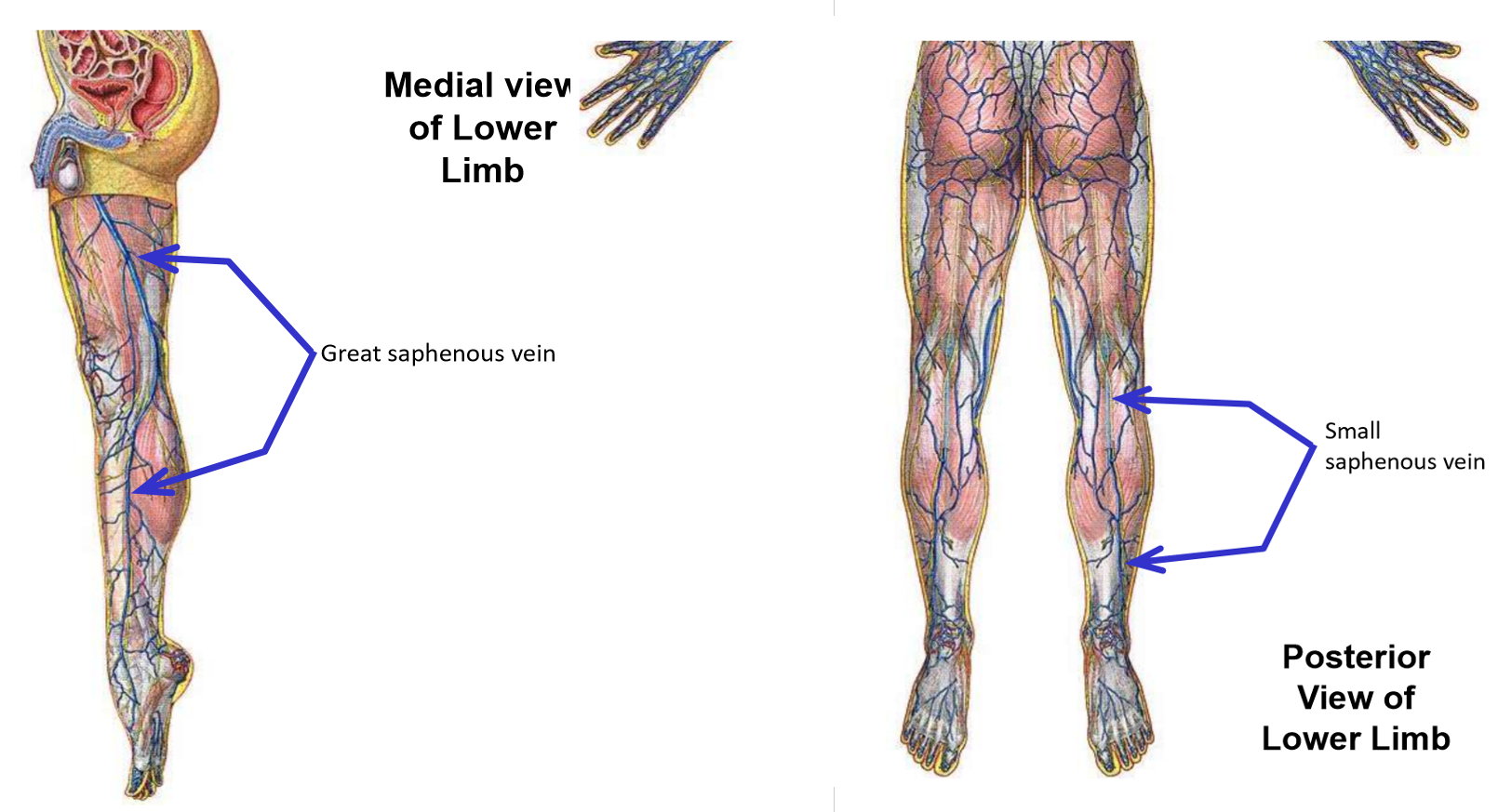
Great saphenous vein. Where does it drain into?
Begins on medial side of dorsal foot
Runs up medial side of leg and thigh
—» Passes posterior to medial knee
In proximal thigh (just inferior to inguinal ligament), vein dives deep (penetrates through fascia lata) and drains into femoral vein
Small saphenous vein
Begins on lateral side of dorsal foot
Runs up posterior leg
Posterior to knee, dives through popliteal fascia to drain into popliteal vein