Hematology Instrumentation SOLO 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
coagulation
the process by which liquid blood changes into a semi-solid gel-like structure
prevents blood from escaping the vessel lumen
Fibrinolysis
the process by which enzymes in the blood stream consolidate or dissolve unnecessary clots
keeps the blood flowing in a liquid state
Thrombosis
the action of inappropriate clot formation that are no longer confined to the site of injury and may pose a risk of vessel occlusion
deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism…
Hemorrhage
the inability of the body to sufficiently form clots and plug damage to vessels which can potentially lead to severe blood loss
excessive blood loss, hemorrhagic shock…
hemostasis
the process ofclot formation that arrests blood loss from injured vessels while maintaining blood flow in a liquid state
balanced through coagulation (Pro-clot) and fibrinolysis (anti-clot)
In a normal person, hemostasis is maintained in a ….
neutral state
What can disrupt balance of hemostasis and cause a shift in either direction?
trauma, medication or other abnormal events
What are the three distinct stages of hemostasis?
vascular reaction
primary hemostasis
secondary hemostasis
Vascular reaction
Vasoconstriction
the action of the damaged blood vessel in order to reduce blood flow through the affected area
improves the platelets ability to adhere to damaged surfaces
achieved through smooth muscle, nerve damage, and damage of the endothelial cells which release endothelin
formation of platelet plug
mediated by the coorperative action of the damaged blood vessel and platelets
healthy endothelial cells promote an anti-clotting environment and are non-reactive towards platelets
damaged endothelial have exposed areas (collagen) and release compounds (tissue factor and Von Willebrand factor) that encourage platelets to adhere and activate
formation of platelet plug steps
platelet adhesion
initial contact mediated by von Willebrand factor and glycoprotein 1b
platelet activation
platelet stimulation through a variety of chemicals which can induce granule release which activated nearby platelets
platelet aggregation
platelet shape change due to activation causes cross-linking between platelets with the aid of fibrinogen mmolecules and GPIIb/IIIa
Stabilization of the platelet plug
conversion of fibrinogen into an insoluble fibrin clot
made possible by the coagulation cascade
at the same time, platelets are releasing platelet derived growth factor which promotes regeneration of the blood vessel walls
Extrinsic pathway
activated by tissue factor
factor VII
measured by PT/INR
affected by coumadin/warfarin
Intrinsic pathway
activated by negatively-charged surfaces
factors XII, XI, IX, VIII
measured by aPTT
affected by heparin
common pathway
merging point of both pathways
factors X, V, II, I
measured by both PT/INR and aPTT
Testing on the ACL TOP 750
coagulometric/turbidimetric
PT/INR
aPTT
Q.F.A
chromogenic assay
Anti-Xa
AT III
immunoturbidity
D-dimer
coagulometric (turbidimetric) clot detection
used to measure and record the amount of time required for a plasma specimen to clot
assesses coagulometric endpoint by measuring change in optical clot density
clot detection is based on the principle that light passing through a medium in which fibrinogen is converted to fibrin is absorbed by the fibrin strands
light transmittance through the sample continuously decreases and is measured by the photodetector
Chromogenic assay
direct chromogenic tests: the analyte of interest acts directly on a specific chromogenic substrate
indirect chromogenic tests: residual enzyme activity is measured using a specific synthetic substrate with a fixed quantity of enzyme to form inactive complexes
the reaction is measured at 405nm by continuous release of paranitroanaline from a synthetic substrate
light passes through the cuvette is read by an optical sensor
light absorbed by the solution in the cuvette
amount of light reaching the photodetector is converted to an electrical signal and proportional to the enzyme activity
Immunoturbidity assay
assess the physical concentration of the analyte by measuring change in optical density
measured the reduction of light transmittance due to agglutination of Antigen-Antibody complexes
light complexes are inversely proportional to the D-Dimer
Analyzer components ACL TOP
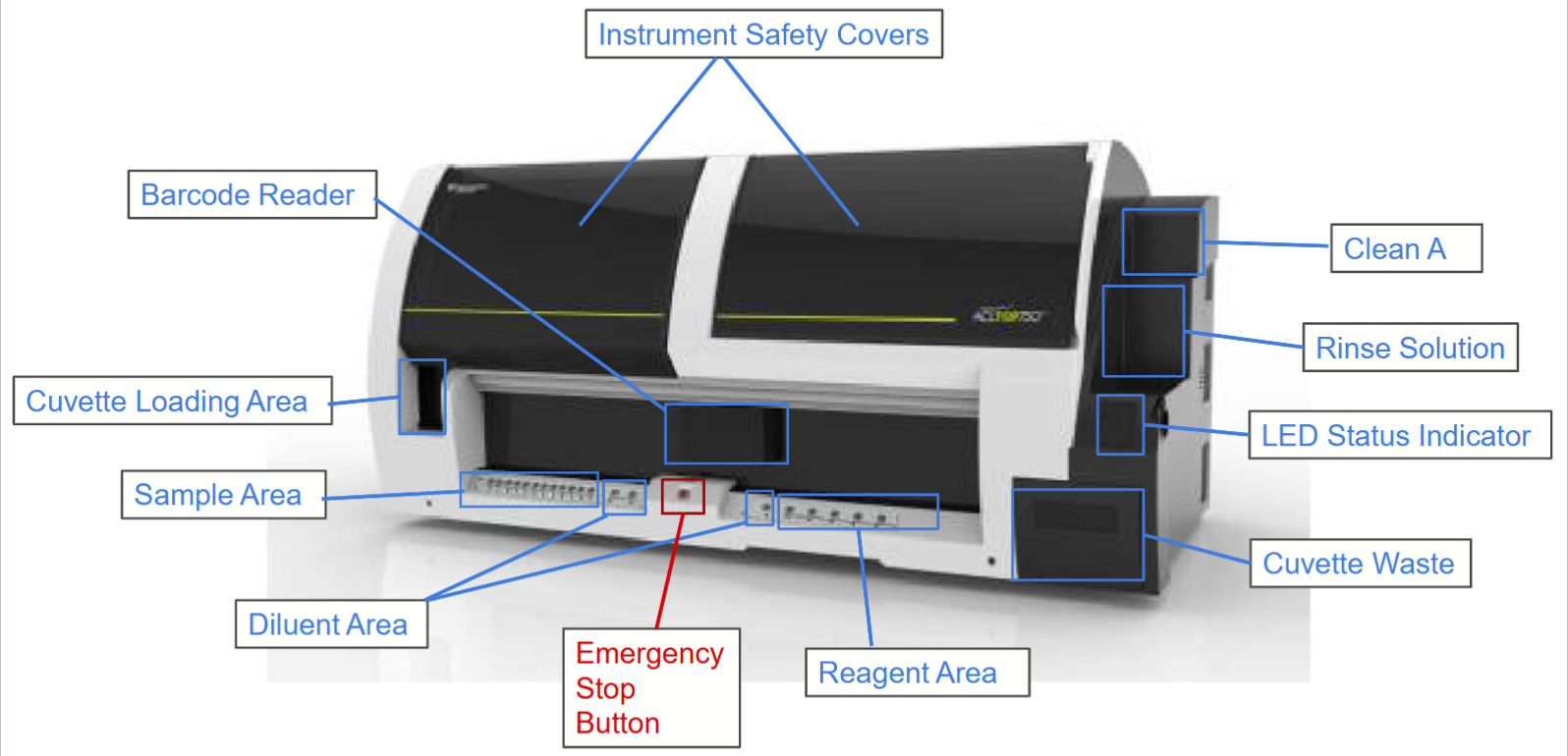
Overfilled specimens will not contain enough coagulant and will have
falsely shortened PT/aPTT
Under-filled specimens will have excess coagulant and will have
falsely prolonged PT/aPTT
ACL TOP specimen requirements
must be ran within 4 hours of collection
aliquotted specimen plasma into false bottom can be stored for 1 month at -20C and 6 months ar -70C
hemolyzed or clotted specimens must be recollected
ACL TOP Pre-analytical flags
Hemolysis, Icterus, Lipemia
tube fill height check
clog detection
PT/INR reagents
RecombiPlasTin2G
diluent
aPTT reagent
SynthASil (ss)
calcium chloride
Fibrinogen reagent
QFA thrombin (bovine)
D-Dimer HS 500 regents
latex reagent
reaction buffer
Liquid Anti-XA reagent
chromogenic substrate
FXa reagent
Special testing reagents ACL TOPS
Liquid antithrombin (AT III)
chromogenic substrate
FXa reagent
Factor Assay
factor deficient plasma
RecombiPlasTin 2G/SynthASil and CaCl2
factor diluent
PT/INR test
screens the extrinsic/common pathways
factors VII, X, V, II, I
monitors coumadin/warfarin therapy
aPTT test
screens the intrinsic/common pathways
factors XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, V, II I
monitors heparin therapy
fibrinogen test
quantitative measurement
necessary to form clots
help diagnose DIC, cardiovascular disease
D-Dimer test
measurement of fibrin split/degradation production
indicator of clot formation/breakdown
high D-dimer can indicate higher risk of DVT, PE, or DIC occurring
Anti-Xa test
measures the concentration of heparin in patient’s sytem
more accurate than aPTT for monitoring heparin
ATIII test
measures patient’s own amount of anti-thrombin and therefore their ability to neutralize thrombin
Factor assays
quantitative determination of factor concentration
determine if patient has factor deficiency or inhibitor
QC performed during each shift on ACL TOP
normal 1
abnormal 3
fibrinogen
UFH
LMWH
D-dimer HS 500
Daily maintenace for ACL TOP
enhanced clean for all probes
replace factor diluent
replace diluted clean B
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
the rate at which RBCs sediment in an hour, measured in mm/hr
a non-specific measurment of the amount of inflammation
Inflammation affect on ESR
acute phase reactants are realsed into the blood stream and disrupt normal negative charge
fibrinogen, CRP, C3/C4, haptoglobin
gives the RBCs the ability to stack and cause them to settle faster due to increased weight (rouleaux)
conditions that increase the ESR
inflammation
preganancy
anemia
autoimmune disorders
infections/sepsis
some cancers
conditions that decrease the ESR
polycythemia
sickle cell anemia
leukemia
liver disease
congestive heart failure
inappropriate specimen (clotted/bubbles)
Traditional method ESR
Westergren method
involved filling long narrow tubes with citrated blood and waiting 1 hour to read level of RBCs compared to palsma
iSED principle
utilizes quantimetric photometry to capture the moment of initial RBC rouleaux formation and calculate intensity of RBC aggregation
small sample is injected into a microcell and then is monitored for aggregation using changes in light transmittance
iSED specimen requirements
collected in EDTA tubes
minimum testing volume is 100 uL
must perform within 4 hours of collection
clotted specimens not acceptable
Platelet Function Analyzer principles
performs a qualitative test on patient’s blood sample (platelets)
screens for patient’s ability to perform primary hemostasis (Plt plug formation)
specially designed cartridges are used in conjunction with the PFA to create an in vitro model of a damaged blood vessel
PFA abnormal results can be caused by…
acquired conditions
uremia
alcohol abuse
inherited dysfunctions
von Willebrand disease
Bernard-Soulier
Glanzmann Thrombasthenia
induced deficiency
aspirin
plavix
PFA cartridges
consists of a collagen-coated membrane infused with a platelet agonist that initiates platelet aggregation and activation
collagen epinephrine ran initially
collagen ADP ran is COL/EPI gives abnormal result (>179 s), which rules out the possibility of ASA-containing drugs
PFA specimen requirements
whole blood specimens insodium citrate tubes (NOT spun down)
must be ran within 4 hours of collection, but at least 10 minutes after collection
must be hand delivered to the lab
minimum volume: 800 uL
maximum volume: 900uL
PFA abnormal result
>179 sec
What need to be obtained if you must run a COL/ADP cartridge on the PFA?
patient’s current hematocrit and platelet count
Normal patient PFA results
COL/EPI- normal
COL/ADP- normal
Patient on aspirin PFA results
COL/EPI- abnormal
COL/ADP- normal
What disease states can result in an abnormal COL/EPI and COL/ADP
von Willebrand disease
Glanzmann thrombasthenia
PFA pre-analytical errors
microthrombi/mini clots (abnormally high results/flow obstruction_
hemolysis and lipemia (false increase)
PFA error messages
maximum test time exceeded
possible vacuum leak
abnormal patient
test terminated due to air leak
no sample added to cartridge
air bubbles
test terminated due to flow obstruction
microthrombi
test terminated due to insufficient sample
low hematocrit
low platelet count
test terminated due to maximum syringe travel
possible vacuum leak
low hematocrit
Thromboelastograph Principles
allows us to monitor the kinetic changes of patient homeostasis as their sample clots, retracts and/or lyses
end results help determine patient’s potential to perform hemostasis
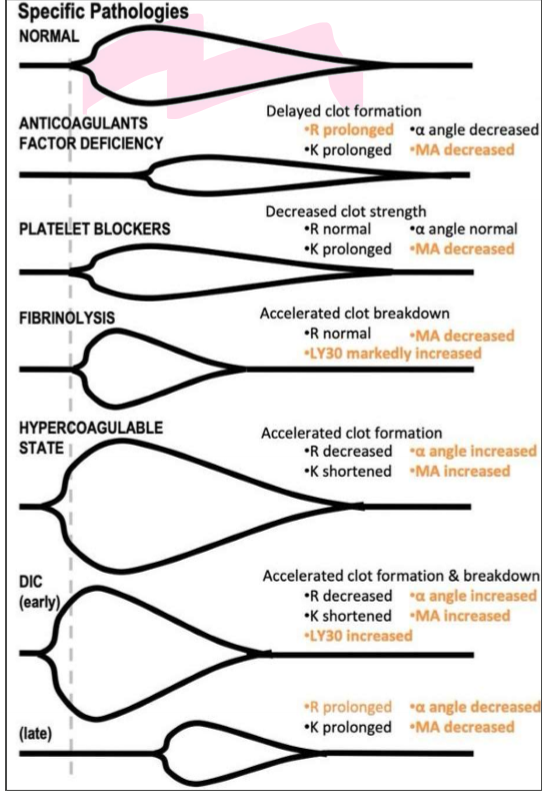
clot’s rate, strength and stability determine if the patient ha hypo-, hyper-, or normal coagulation processes
In what two ways is the TEG analyzer used?
thromboelastograph
surgical/trauma patients to determine current homeostatic ability and what products to transfuse
platelet mapping
non-surgical patients that have received platelet inhibiting drugs and need their platelet function assessed
TEG specific principle
monitors the harmonic motion of a pendant drop of blood inresponse to external vibration
modulus of elasticity and resonant frequency increase during clotting
analyzer measures variations in resonant frequency during clotting and lysis
TEG testing requirements
testing must be started within 2 hours of blood collection for TEG Global hemostasis with lysis and platelet mapping
Testing must be started within 4 hours for TEG global hemostasis
citrated whole blood for TEG
Heparinized whole blood for platelet mapping
TEG clot parameters
R- reaction time, amount of time between teh start of the test and the beginning of coagulation
Angle- the speed of clot strengthening due to the rapidity of fibrin build-up and cross-linking
K- speed of formation of the clot from R time to a specific clot strength
MA- maximum amplitude, the ultimate strength of the clot
LY30- percent lysis 30 minutes after MA is finalized, based on the reduction of the tracing area that occurs between the time that MA is measured until 30 minutes after MA is finalized
FLEV- calculates the value for the functional fibrinogen level from the MA parameter for Functional Fibrinogen tests
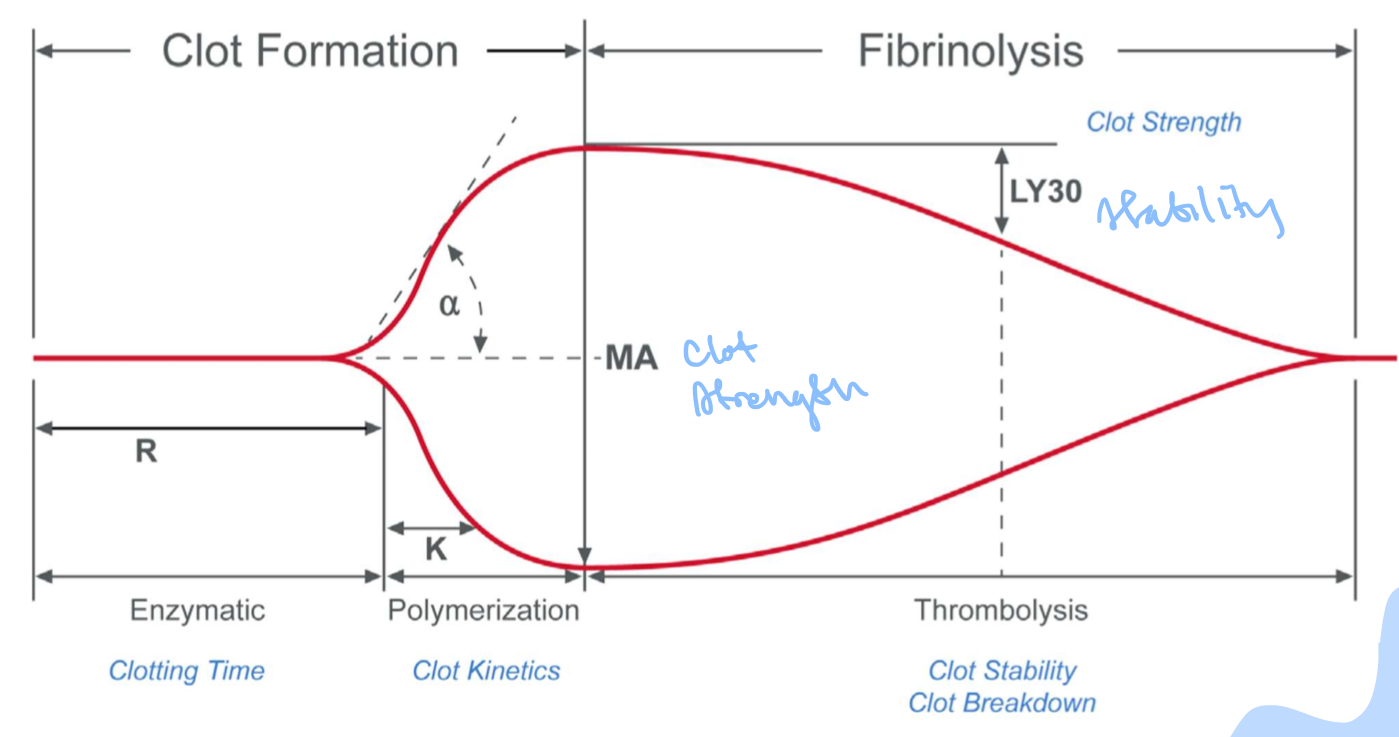
R is affected by …..
coagulation factor availability
prolonged may be resolved by FFP infusion
Angle, K, CFF-MA, and FLEV are affected by…
fibrinogen levels
small angle/prolonged K resolved by cryo infusion
MA is affected by….
platelet count
narrow resolved by platelet infusion
LY30 is affected by…
t-PA
high may be resolved by anti-fibrinolytic (TXA) infusion
Clot parameters curves
VerifyNow principle
anti-platelt therapy works to inhibit platelet activation and reduce the chance of any inappropriate clot formation
able to analyze whole blood and determine the ability of the drug to inhibit platelet activity
uses fibrinogen-coated beads in order to quantitate the patient’s therapeutic rnage
result is calculated base on the amount of light transmitted
platelets will be encouraged to adhere to the beads and aggregate with nearby platelets (higher transmittance)
patients that are on plavix will have inhibited that will be discouraged from forming aggregates with the beads (lower transmittance)
TXA2 receptor
signals the platelet to produce TXA2 from thr Arachidonic Acid via the COX-1 enzyme
TXA2 is a platelet activator and a vasoconstrictor
inhibited by aspirin
P2Y12 receptor
releases ADP stored in platelet granules
ADP is a platelet activator
inhibited by plavix (clopidogrel)
GPIIb/IIIa receptor
involved with platelet aggregation with the help of fibrinogen
inhibited by integrilin
Verify now Specimen requirements
requires a special partial-fill sodium citrate tube
tubes have white inner cap
Verify now reagents
PRU Test device which is an all-in-one test cartridge
Free response Q (describe PFA)
The platelet function analyzer performs a qualitative test on a patient’s blood sample, specifically the platelets. It screens for the ability to perform primary hemostasis/platelet plug formation. Specially designed cartridges are used in conjunction with the PFA to create an in vitro model of a damaged blood vessel. Abnormal results can be caused by acquired conditions, inherited dysfunctions, or induced deficiency from drugs. It uses cartridges consisting of a collagen coated membrane infused with a platelet agonist that initiates platelet aggregation and activation. A COL/EPI cartridge is ran initially and if it comes back abnorml/>179s, then a COL/ADP cartridge is run. A trigger solution is also used as a wetting agent that rehydrates the membrane for testing. It requires whole blood from a sodium citrate tube.