Choices under uncertainty
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finance chap1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
risk vs uncertainty
risky situations have a probability attached to it which can be estimated, uncertainty cannot be
Expected value
average amount one would expect to earn from repeatedly playing the game
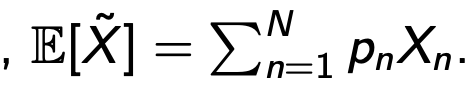
St Petersburg Paradox
challenges the idea that people make decisions based only on expected values because E[X] = infinity here
Law of Diminishing Utility
marginal benefit consuming diminishes with each additional unit
How much should you pay to play a classic coin flip game according to expected value
5 (think through the methodology)
Expected Utility
weighs outcomes by their utility than ,monetary values
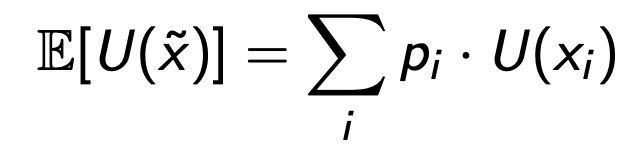
fair lottery
where expected value of the outcome is zero, ie price of the game is equal to the expected value
Risk aversion
Additional utility from each extra dollar diminishes across time- concave utility function
Certainty equivalent
it is the level of wealth which gives a person the same utility as the expected utility of the lottery
Risk premium (pi)
the amount you are willing to give up to avoid the lottery; pi= expected value of lottery - certainty equivalent
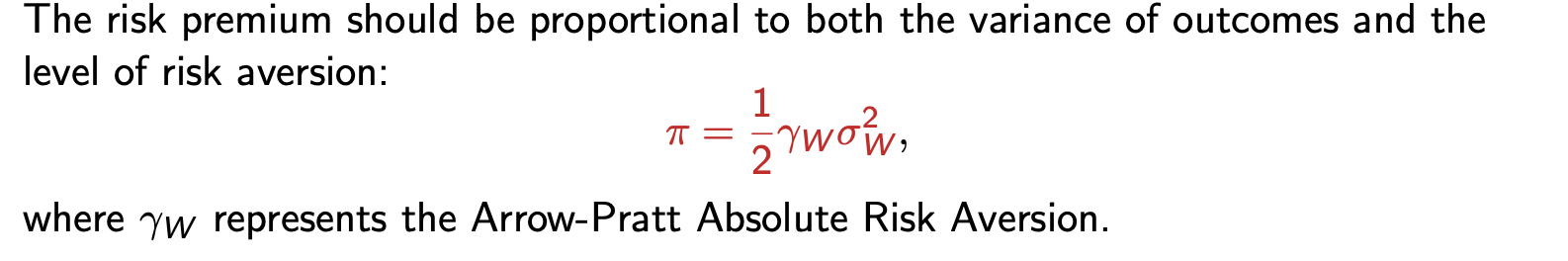
what does the arrow Pratt absolute risk aversion measure
allows systematic determination of compensation for risk aversion
how would risk neutral preferences look
U(W)= W, constant marginal utility over wealth so a linear function
what does a risk neutral person choose
they would choose whatever offers the highest expected value,
how would risk loving preferences look
convex function so arrow pratt would change accordingly
CARA utility function
1-e-cW/ c where c is the arrow Pratt absolute risk aversion