ENDOCRINE - Pituitary Gland, Thyroid, Adrenal Gland Disorders
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1. Hyperpituitarism (Growth Hormone Excess)
2. Hypopituitarism (Growth Hormone Deficit)
Anterior Pituitary Gland Disorders
1. Gigantism
2. Acromegaly
Clinical conditions of hyperpituitarism
Gigantism/Giantism
Occurs before the closure of the epiphysis of the long bone
Before the closure of the long bone
When does gigantism ocur
Early childhood/puberty
Onset of gigantism
Proportional
Excessive growth in giantism is ____
1 - 8 ft
2 - 300 lbs
Children can grow as tall as (1) and weigh over (2)
Giantism
Which disease in which children are usually not healthy and die at a young age?
Acromegaly
Occurs slowly at 3rd, 4th, 5th decade of life
1 - SLOWLY
2 - 3rd, 4th, 5th
Acromegaly occurs (1) at (2) decade of life
1. Enlargement of hands & feet
2. Deformity of spine & mandible
3. Coarse facial features
4. Abdominal distention
5. Diaphoresis
6. Oily skin
Physical features of acromegaly
1. Thickening of cheeks
2. Widened nose opening
3. Thickened lips
4. Absence of neck
Coarse facial features include
Hypopituitarism
Decrease in one or more of APG hormone
1 - nonspecific
2 - weakness, fatigue, HA, diminished tolerance to stress, poor resistance to infection
Symptoms of hypopituitarism are (1) and include (2)
Menstrual irregularities, diminished libido, changes in secondary characteristics (decreased breast size).
In women, hypopituitarism could manifest as
Testicular atrophy, loss of libido, impotence, decreased muscle mass
In men, hypopituitarism could manifest as
Replacement of hormones including corticosteroids, thyroid hormones, sex hormones
Management for hypopituitarism
Dwarfism
Failure to grow
1 - slow
2 - proportional
Dwarfism is (1) but (2) growth
1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Hypothyroidism
Thyroid gland disorders
Located in anterior portion of neck in front of the trachea with 2 encapsulated lateral lobes connected by a narrow isthmus; A HIGHLY VASCULARIZED ORGAN
Structure and function of thyroid gland
Thyroid
Drawing ya
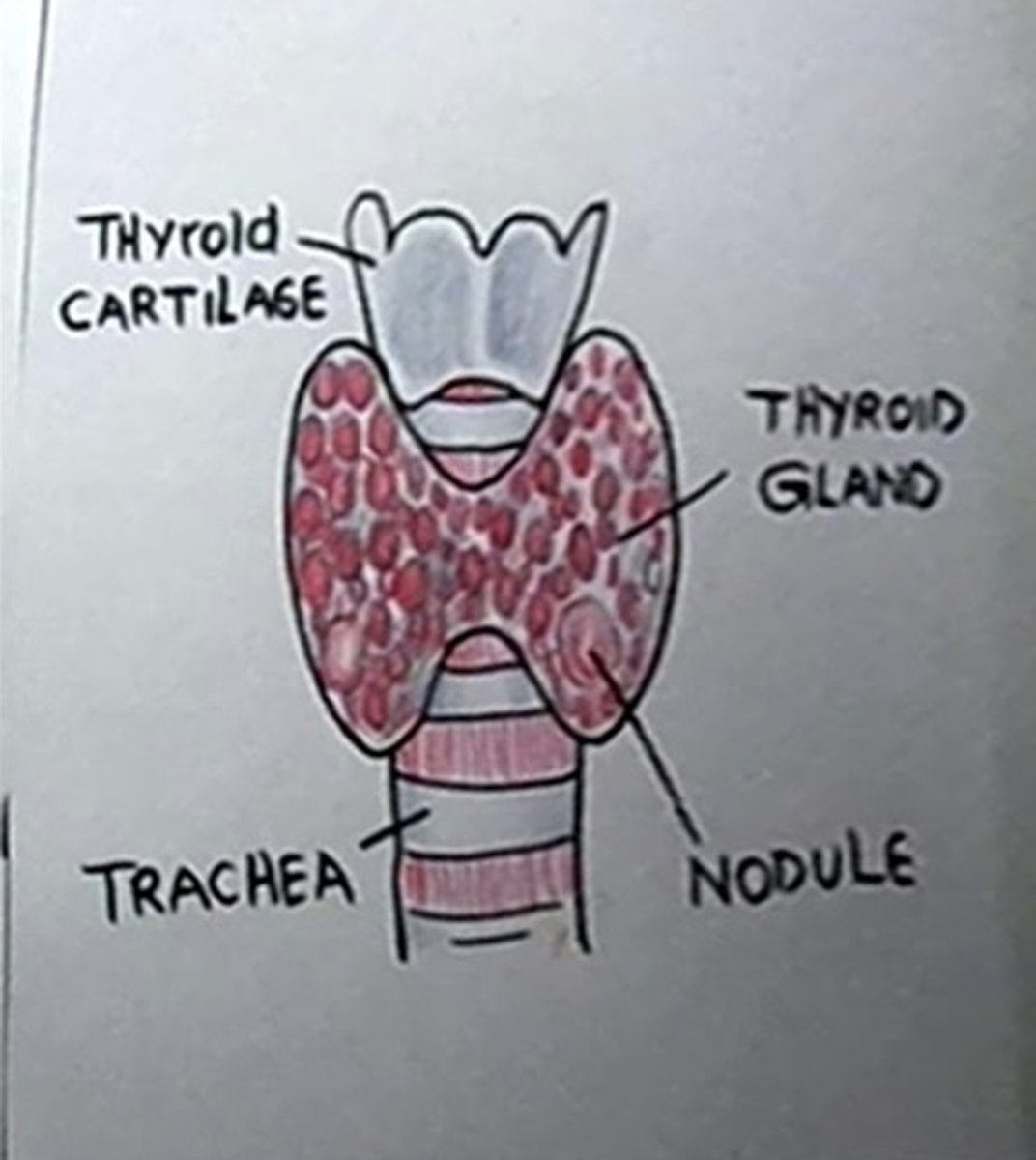
T3, T4, Thyrocalcitonin
Thyroid gland secretes
T3 (triodothyronine) and T4 (tetrathyroxine)
T3 and T4 means
1 - T4
2 - T3
(1) is the precursor of (2)
T3
The more active hormone
Iodine
Is necessary for the synthesis/production of thyroid hormones
Seashells and seaweed
Iodine rich food include
Thyroid hormones
(1) directly related to intellectual functioning
Hyperthyroidism
Excessive circulating levels of T3, T4, or both
T3 & T4.
Hormones related to hyperthyroidism
ADULT onset, 30-40 years old
Onset of hyperthyroidism and their age
1. Graves Disease
2. Multinodular goiter
3. Exophthalmus/Exophthalmus
Clinical conditions associated with hyperthyroidism
Small, discrete, autonomously functioning nodules that is secreting thyroid hormones
Explain multinodular goiter
Benign or malignant
Nodules may be
Multisystem, autoimmune syndrome marked by increased thyroid hormone
Explain graves' disease
Insufficient iodine supply
Precipitating factors of graves' disease
Excessive iodine supply
Precipitating factors of multinodular goiter
Eyeballs protrude from the orbit
Explain how exophthalmus works
Upper lids are retracted
Eyeballs are forced outward
Sclera is visible - characteristic stare and protrusion
Signs and symptoms of exophthalmus
Hypofunction of the thyroid gland, lower thyroid secretion, slowing of metabolic process
Explain hypothyroidism
1. Cretinism (children)
2. Myxedema (adults)
Clinical conditions of hypothyroidism
Slow mental and intellectual functioning
Explain cretinism
Thickening of face muscle (moon face)
Eyeballs are thickened
Cheek are thickened
Nose is widened
Lips is thickened
Characteristics of myxedema
Hyper - irritability, agitation, hyperactive movements, tremors, heavy sweating, insomnia
Hypo - fatigue, lethargy, slow clumsy movements
HYPERTHYROIDISM VS HYPOTHYROIDISM ASSESMENT
1. MS
Hyper - increased appetite and peristaltic activity, hyperactive bowel sounds, loose bowel movements BUT noted weight loss
Hypo - decreased appetite and peristaltic activity, hypoactive bowel sounds, dry, hard stools BUT noted weight gain
HYPERTHYROIDISM VS HYPOTHYROIDISM ASSESMENT
1. GIT
Hyper - palpitations, intolerance to heat, tachycardia, increased BP, CARDIAC ARREST
Hypo - slow thready pulse, intolerance to cold, bradycardia, decreased BP, CARDIAC ARREST
HYPERTHYROIDISM VS HYPOTHYROIDISM ASSESMENT
1. CVS
Hyperthyroid crisis (Thyroid Storm/Thyrotoxicosis)
Hyperthyroidism could lead to
Myxedema coma
Hypothyroidism could lead to
1. Serum TSH (T3,T4,) aka Thyroid Panel
2. Radioactive iodine uptake (RAI)
3. Thyroid scan/Thyroid scintigraphy
Diagnostic assessments
1. Anti-thyroid drugs
2. Radioactive I-131 therapy
3. Thyroidectomy
Management of Hyperthyroidism (DRUGS)
Propylthiouracil (PTU)
Methimazole (Tapazole).
Anti-thyroid drugs include
Blocks synthesis of thyroid hormones
MOA of anti-thyroid drugs
1. Thyroid hormones
Management of hypothyroidism
1. LevothyroXINE (Synthyroid) - T4
2. Thyroglobulin (Proloid)
3. Dessicated thyroid (cytomel)
Thyroid hormones for drug therapy are
Newborn screening
Done to newborns to diagnose hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is the most commonly diagnosed
Why must newborn screening be done to newborns in relation to the thyroid
Thyroidectomy
Removal of the thyroid glands
1. Complete/Total thyroidectomy
2. Partial/left-right lobe thyroidectomy
Kinds of thyroidectomy
1. Complete cardiac status review
2. Give anti thyroid meds 5-7 days prior to surgery
3. Administer with iodine prep
PRE OP FOR THYROIDECTOMY
EKG, cardiac isoenzymes, 24 hr. Holter monitoring
Cardiac status review includes
Because these patients are at risk for a cardiac arrest
Why do a cardiac status review?
5-7 days
Anti-thyroid meds must be given how many days PTO?
Lugolis solution - 15 cc PO BID x 3 days
What iodine prep is given to pre-op thyroidectomy + dosage
Reduce the size of the thyroid and vascularity (to prevent hemorrhage)
Why give lugolis solution?
1. Check dressing behind the neck
2. Observe for respiratory distress
3. Observe signs of tetany
4. Absence of thyroid storm
5. Relieve the discomfort of sore throat
6. Check for voice-laryngeal nerve damage
POST OP FOR THYROIDECTOMY (very important, comes out in boards)
Patient is supine, tendency is discharges will seep to the back
Why check dressing behind the neck?
1. WHITE piece of cloth @ head of the bed
To prep at bedside for dressing
Could be s/o trauma, edema, hemorrhage
Why observe for respiratory distress?
O2 set up, suction machine, tracheostomy set
Prepare @ bedside for respiratory distress
Attach to ventilator
What to do after putting a tracheostomy?
Spasms, tremors, seizures
Signs of tetany include
Calcium gluconate in tubex (IVTT) in case of emergency
Prepare @ bedside for tetany
Increase temp, pr, bp
Thyroid storm is positive when pt exhibit s
Anti HPN meds
DOC: calciblock (calcibloc) 10 mg SL start
Cooling blanket
Prep @ bedside for thyroid storm
Encourage oral fluids
Cool mist humidifier
Prep at bedside for sore throat
Report to surgeon
Bedside care when you notice voice-laryngeal nerve damage
Enlargement of the thyroid gland not caused by inflammation or neoplasm
Explain simple goiter
Endemic
Type of simple goiter caused by nutritional iodine deficiency
Sporadic
Type of simple goiter caused by ingestion of large amounts of goitrogenic foods
Cabbage, soybeans, peanuts, peaches, peas, strawberries, spinach, radish
Kinds of goitrogenic foods
Sporadic - large intake of seafood and seaweed
What kind of goiter would people living in coastal areas get and why?
Endemic — less intake of seafood and seaweed
What kind of goiter would people living in mountain areas get and why?
Inflammatory process in the thyroid where thyroid tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue
Explain thyroiditis
Hard upon palpation
If thyroid tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, what do you see upon assessment?
autoimmune disease
Thyroiditis is a kind of?
Stress
Thyroiditis as an AID is aggravated by?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Another name for thyroiditis
Located in the upper pole of each kidney
Location of the adrenal glands
90%
How many percent of the gland is the cortex?
50+ hormones
Adrenal glands secrete about how many hormones?
Glucocorticoids (GCC)
Mineralocorticoids (MCC)
Sex hormones
Some hormones secreted by the adrenal glands include
1. Cushing Syndrome
Adrenal gland disorders
Spectrum of clinical abnormalities caused by excess of GCC
Explain cushing syndrome
Excess of GCC
2 - CORTICOSTEROIDS
Cushing syndrome is caused by (1) particularly by (2)
Women
Cushing syndrome/excess use of corticosteroids is more common in
Iatrogenic
Result of a medical treatment (DT prolonged use of steroids)
Cortisone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone, prednisone, betamethasone
Corticosteroid treatment common preparations (DRUGS)
Oral/tablet
Solution/liquid
Eyedrop
Injectables
Cream, lotion, ointment
Inhalation
Corticosteroid treatment common preparations
Anti inflammatory agents
- inflammation, allergic, immunoreactive, edematous, skin problems, malignancies, degenerative, chronic conditions
Therapeutic effects/ INDICATIONS of corticosteroid treatment