Practicum 1 Bios 114
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is the magnification of the oculars alone on a microscope?
10x
What is the total magnification when using the high-power objective lens?
400x
Name the item we use to clean the objective lens on the microscope:
Lens paper
Name the locomotion structure that is used by Pelomyxa (Amoeba-like organism):
Psuedopodia
Name an organism from lab that uses cilia to move:
Paramecium
What movement structure does the blood parasite Trypanosoma use?
Flagella
In a partially shaded dish, where would you expect to find the highest concentration of green protists?
a.) In the shaded/dark section
b.) In the lit section
c.) Randomly distributed
b.) In the lit seciton
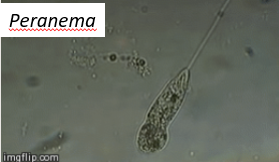
Identify the structure used to move by the organism on the screen
Flagella
If the diameter of the field of view at 4x is 4 mm, what would the diameter of the field of view at 40x?
0.4 mm
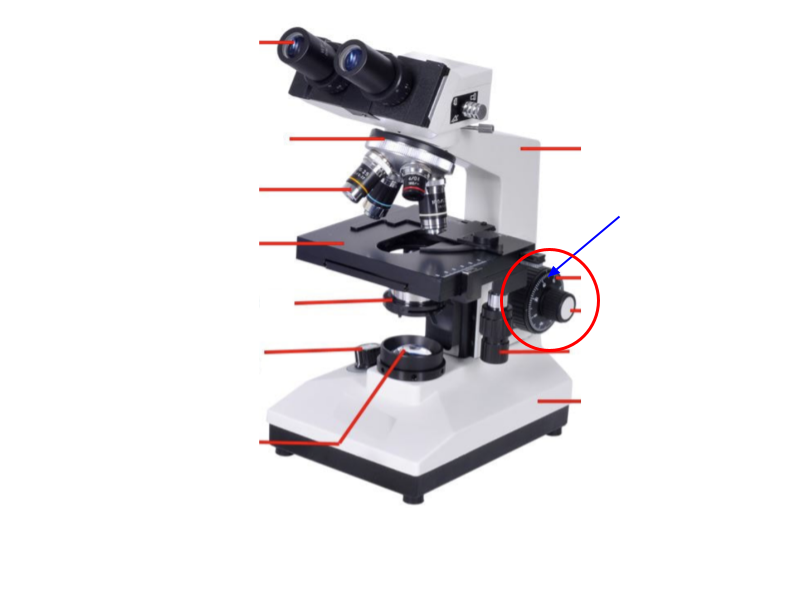

On the microscope, identify the labeled part: (blue arrow)
Coarse focus knob
The microscopes we use have three main objective lenses. What is the total magnification when using the high-power objective lens?
400x
The microscopes we use have three main objective lenses. What is the total magnification when using the scanning objective lens?
40x
List the three objective lenses in order of decreasing diameter of field of view.
Scanning objective lens, low-power objective lens, high-power objective lens
What is the only objective where you can use the coarse focus knob?
Scanning objective lens
What are the three domains in the three-domain system?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
List three types of structures used for protozoan locomotion.
Cilia, Flagella, Pseudopodia
Which domain consists of prokaryotes that often reside in extreme environments?
Archaea
What term describes organisms that produce their own organic nutrients?
Autotrophs
What is this organism?
Paramecium
What kind of locomotion does it use?
Cilia
What environment is it found in?
Fresh Water
What structure on kelp is used to lift the blades and stipe toward the water surface where more sunlight is available?
Gas bladder
Is Volvox colonial, filamentous, multicellular, or unicellular?
Colonial
What color algae is Rhodophyta?
Red
What type of microalgae have morphologically distinct gametes?
Oedeogyeum
Fungi have several structures, some of which are invisible to the naked eye. What is the term for the threadlike, filamentous projections that make up the fungus vegetative body?
Hyphae
When two different mating types of Rhizopus stolonifer make contact, they produce specialized hyphae that grow toward each other, producing gametes which them fuse. Which structure results from the fusion of these gametes?
Zygote
The final step in the fusion of two eukaryotic cells is the fusion of the two nuclei. What is this process called?
Karyogamy
What is this type of general fungal structure?
Sporangium
From the screen, what is this structure (it denotes sexual reproduction)?
Zygote
Name the type of lichen you see on the screen.
Foliose
Which algae phylum is very delicate and found in deep ocean ecosystems? What “color” is it?
Rhodophyta; Red
Which algae phylum is tough and found close to the ocean surface? What “color” is it?
Phaeophyta; Brown
Algae is found within which kingdom?
Protista
Is Spirogyra colonial, filamentous, or unicellular?
Filamentous
Organisms derive their nutrients in different ways. What do we call organisms that derive their energy from consuming dead or decaying material?
Saphotrophs
What is the scientific name for the mushroom fruiting body?
Basidiocarp
Lichens consist of which two types of organisms existing in a symbiotic relationship?
Fungi and Algae
Lichens consist of a symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit. If one organism were to benefit at the expense of the other organism, what would their relationship be called?
Parasitic
What is the name for the structure in which fungal spores are produced?
Sporangium
In fungi of the phylum Ascomycota, spores develop in groups of eight inside which structures?
Asci
What characteristics are used to assign fungi to their taxonomic groups?
Reproductive structures
What is this organism?
Volvox
Many plants alternate generations. What is the dominant generation in mosses?
Haploid gametophyte
Conifers have two types of cones. Which type is very small with thin scales, and is often called the “pollen” cone?
Staminate
Ferns have an underground stem that is anchored by the roots. What is the underground stem called?
Rhizome
Seed plants are divided into two major categories according to whether or not their seeds are exposed. Name the group which has seeds enclosed in a fruit.
Angiosperm
What are the modified leaves that form an outer whorl around the petals?
Sepal
In the flower, which structure is responsible for producing pollen?
Anther
The seed-protecting seet of a plant develops from which anatomical part?
Ovary
What type of venation does this leaf show?
Net venation
What structure in plants move nutrients such as sugars?
Phloem
Name the terrestrial plant and the structure shown.
Moss; antheridia
In which structures do ferns house their spore-containing sporangium, and where are these structures located?
Sori; leaves
What generation of ferns is formed when the spores germinates?
Gametophyte
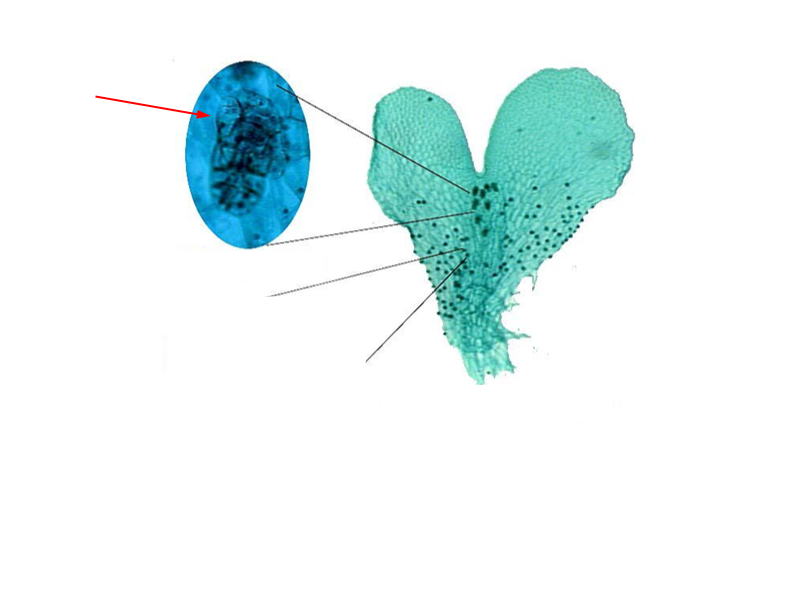
What is this structure, and what is it from?
Archegonium; fern
What structure is formed by the anther and filament?
Stamen
What is the tissue made of columnar cells called?
Palisade mesophyll
Guard cells are lip-like cells that are found on the underside of the leaf. What is the opening called that forms when the guard cells open up?
Stomata
In the woody dicot, an additional annual ring of vascular tissue forms with each growth season. Which is darker, summer wood or spring wood?
Summer wood
Vascular plants have two types of vascular tissue. Which tissue carries water?
Xylem
What anatomical term describes the longest arms of a squid?
Tentacles
Platyhelminthes have a body plan without an internal cavity in addition to the gut. They are known as which of the following: Acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, or coelomate?
Acoelomate
What structure in tapeworms contains hooks or suckers and is used to attach the worm to the intestinal wall?
Scolex
Jellyfish commonly have life cycles consisting of two separate stages. Which stage involves a tubular body attached to a substrate?
Polyp
Nematodes have what kind of symmetry?
Bilateral
What is the epidermis of the roundworm called?
Cuticle
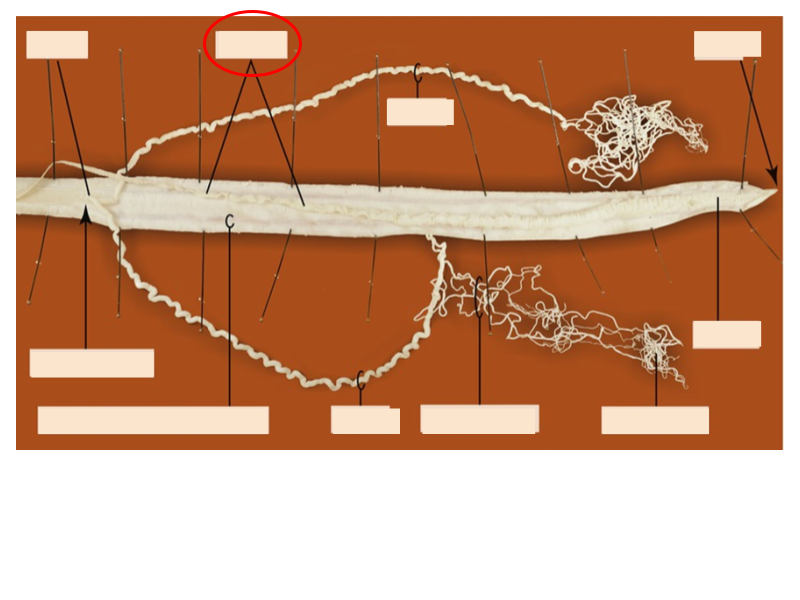

What structure is this?
Intestine
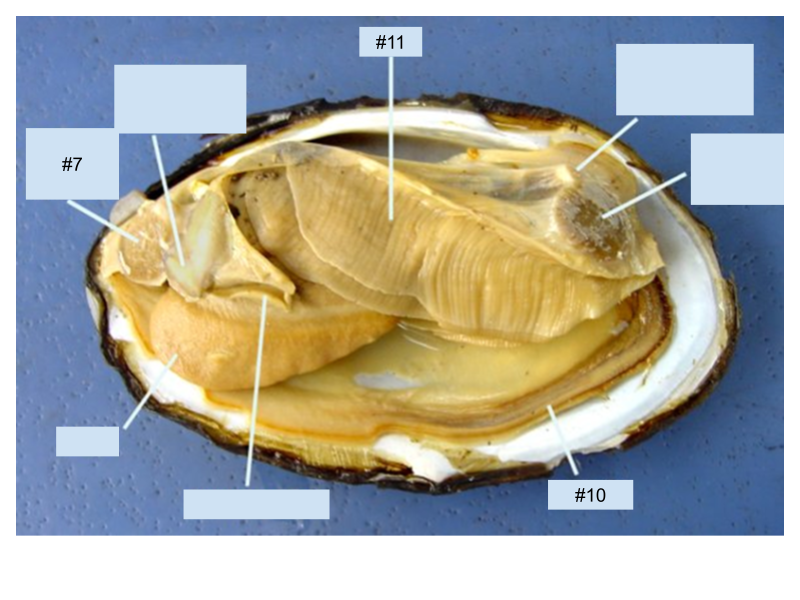
What structure in the clam is labeled #11?
Gills
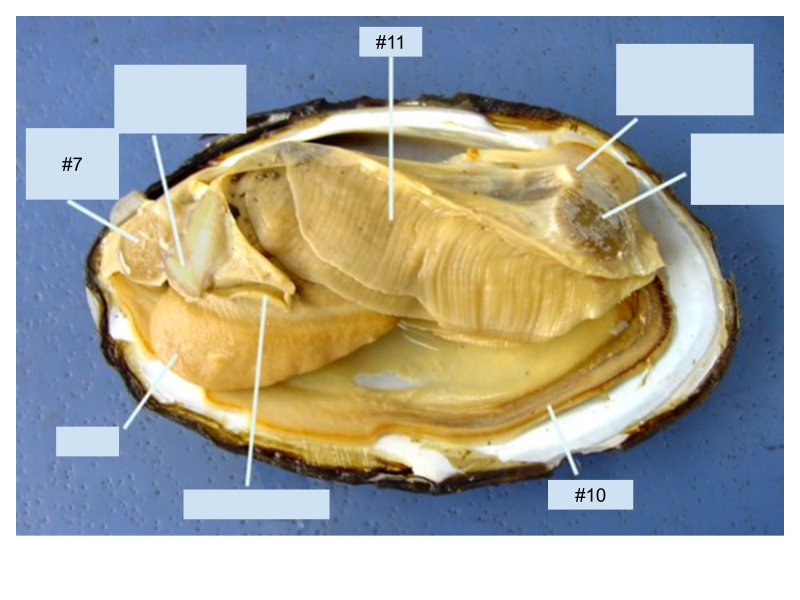
What structure in the clam is labeled #7?
Anterior adductor muscle
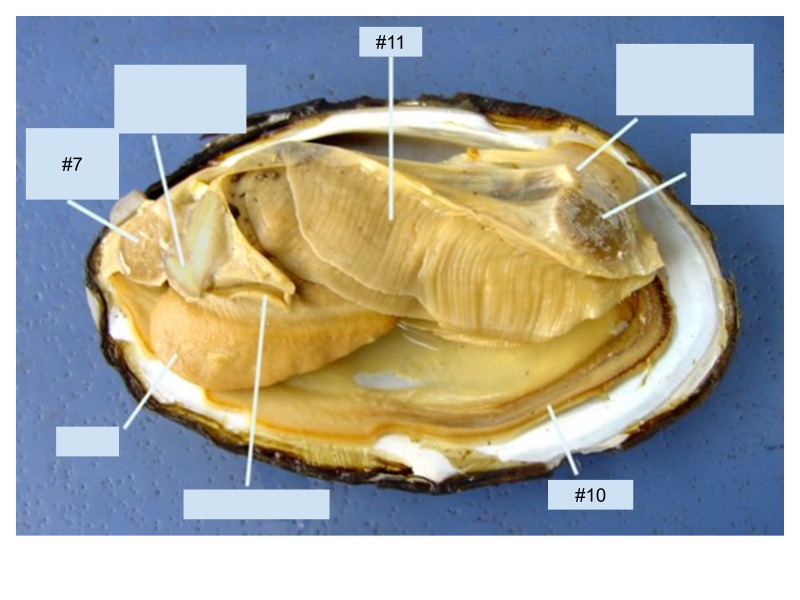
What is the function of the structure in the clam is labeled with the #10?
Mantle secretes the shell
What type of body symmetry do Cnidarians have?
Radial
What flagellated cells function to move water into the spongocoel?
Choanocytes (collar cells)
Which structures are used by free-living flatworms to detect light?
Eyespots
While you are working in the hospital emergency department, a patient arrives complaining of abdominal discomfort and appearing jaundiced (has yellow-tinted skin). After running a series of tests, you determine that these symptoms are being caused by a parasitic flatworm within the patient’s liver. What type of flatworm is known to occupy this organ?
Liver fluke
Tapeworms are classified under which phylum?
Platyhelminthes
What is the feeding structure of mollusks?
Radula
What structure do mollusks use to burrow themselves?
Ventral muscular foot (foot)
Squids obtain oxygen by bringing water into the mantle cavity and over the gills, after which the water can be forcefully ejected out of the organism. Which structure is used to draw up water into the cavity and subsequently force it outward–often as a means of locomotion?
Siphon
Free-living flatworms feed using a structure that is extendable. What is this structure called?
Pharynx
Clams, which are enclosed by two halves or “valves”, use strong muscles to close these two valves together. What are these muscles called?
Adductor muscles
Annelida have what type of circulatory system?
Closed circulatory
What structure in an earthworm is located just posterior to the esophagus and stores food before the food is mechanically disgusted?
Crop
Segmented worms are composed of repeated segments which, aside from internal organs, share the same arrangement of blood vessels, muscles, and excretory ducts. What are these repeating units called?
Somites
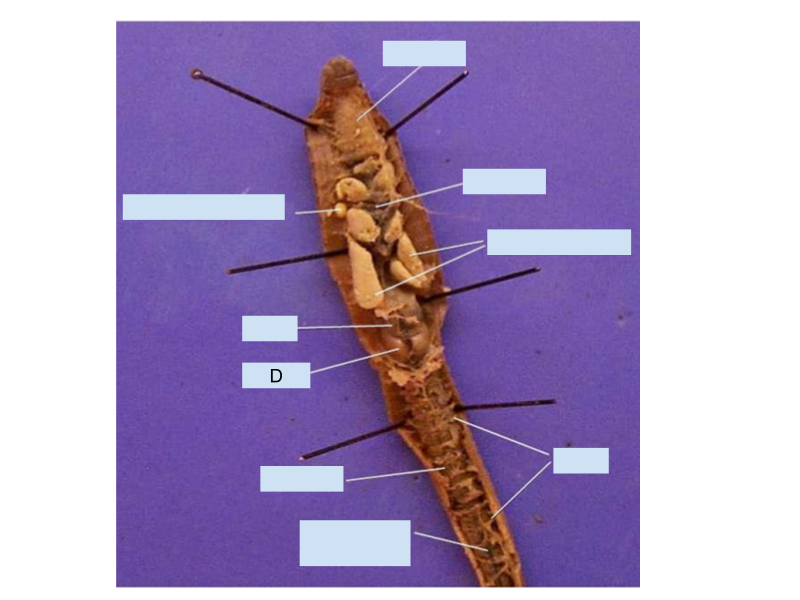
What does the structured labeled letter “D” in the earthworm store?
Gizzard
Crayfish have five pairs of walking legs. The most anteriorly-located pair look like claws and are used for grasping and defense. What is this pair of specialized legs called?
Chelipeds
In the Crayfish, which structure is responsible for removing metabolic waste from the blood?
Green glands
What is the term for the tine openings in the exoskeleton of grasshoppers that allow air to enter into the tracheal system?
Spiracles
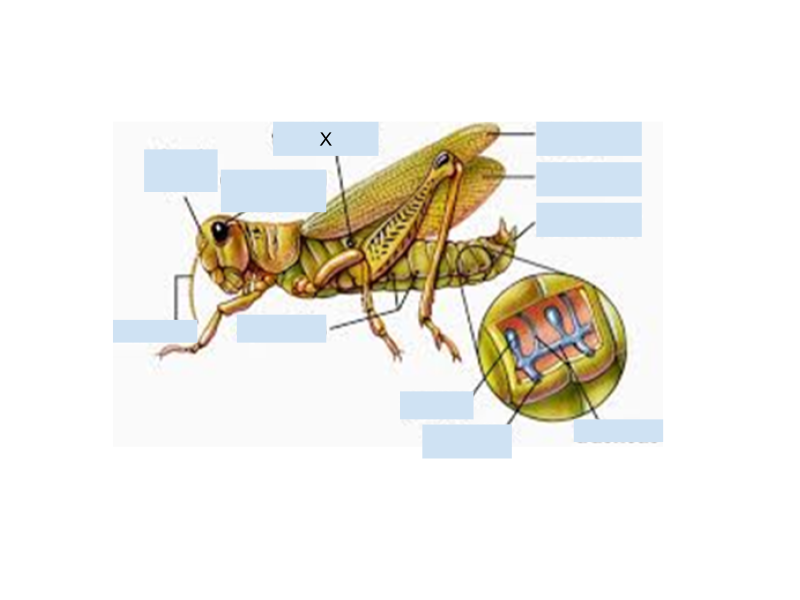
The grasshopper sense sound using which specialized structure labeled “X”
Tympanic membrane
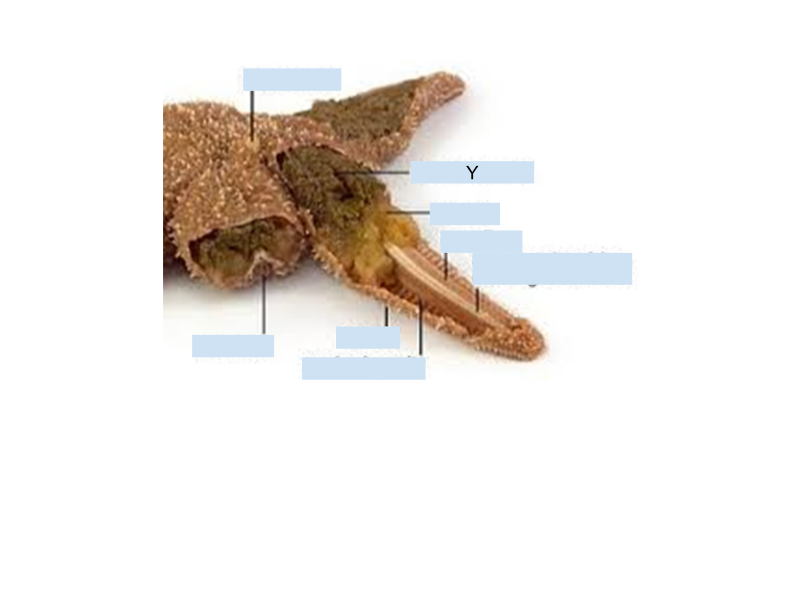
What is the name of the structure labeled “Y” on the sea stars?
Madreportie
In echinoderms, the tube feet are “powered” by a specialized hydraulics system that is specific to these animals. What is that system called?
Water vascular system
Arthropods have a tough, rigid exoskeleton composed of what substance?
Chitin
How would you distinguish male and female grasshoppers?
Ovipositor in females
What type of symmetry do echinoderms have?
Radial
In sea stars, what is the purpose of the madreporite?
Filters sea water, and is the entrance to the water vascular system
Which class of vertebrates has wings, feathers, epidermal scales, claws, and an endoskeleton?
Aves
Which class of vertebrates has a bony endoskeleton with rib cage, well-developed lungs, epidermal scales, claws, paired limbs in most, leathery-shelled eggs, and three-chambered heart?
Reptilia