gene regulation, cell specialization > cell differentiation, mutations
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
promoter region
a base sequence that signals the start site for gene transcription; this is where RNA polymerase binds to begins the process
operator
a short sequence near the promoter that assists in transcription by interacting with regulatory proteins (transcription factors)
operon
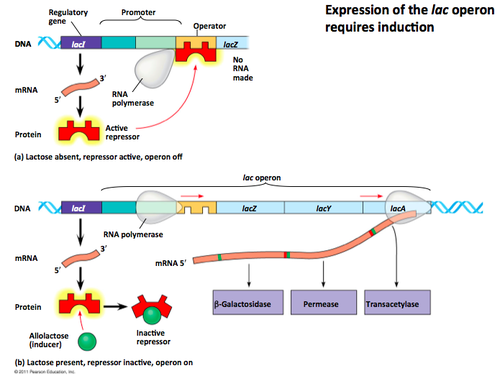
a promoter/operator pair that services multiple genes; the lac operon is a well-known example → helps bacteria digest lactose
repressor
protein that prevents the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter site
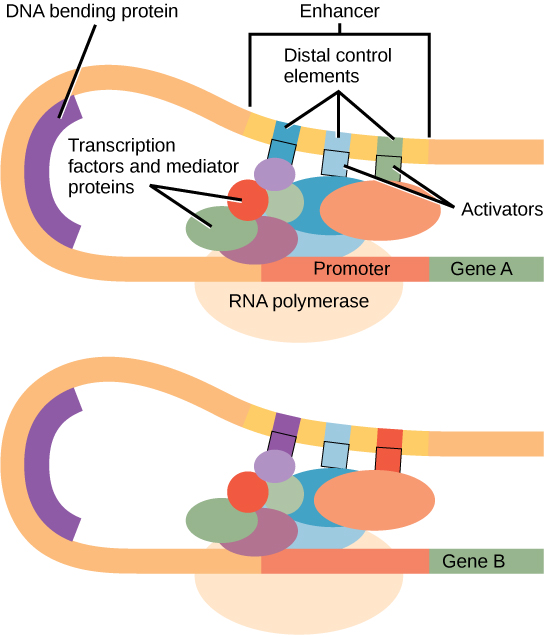
enhancer
DNA region, aka “regulator”, that’s located thousands bases away from the promotor; it influences transcription by interacting with specific transcription factors
inducer
molecule that binds to and inactivates a repressor (eg. lactose for the lac operon)
in bacteria, operons are a major method of …
in bacteria, operons are a major method of gene expression control
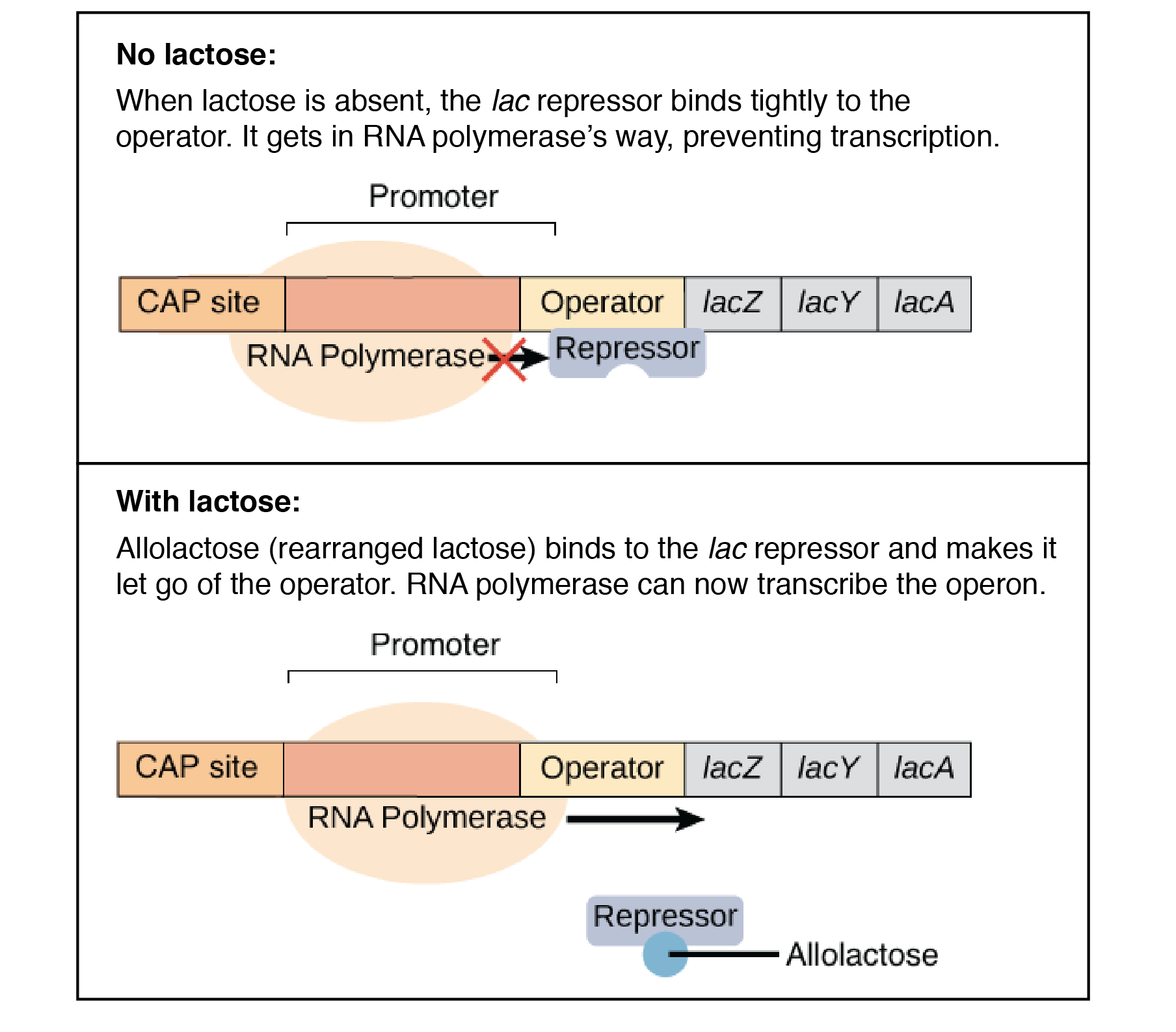
what happens when there is no more lactose in bacteria? (Lac operon)
repressor binds to the promoter region and prevents transcription from occurring
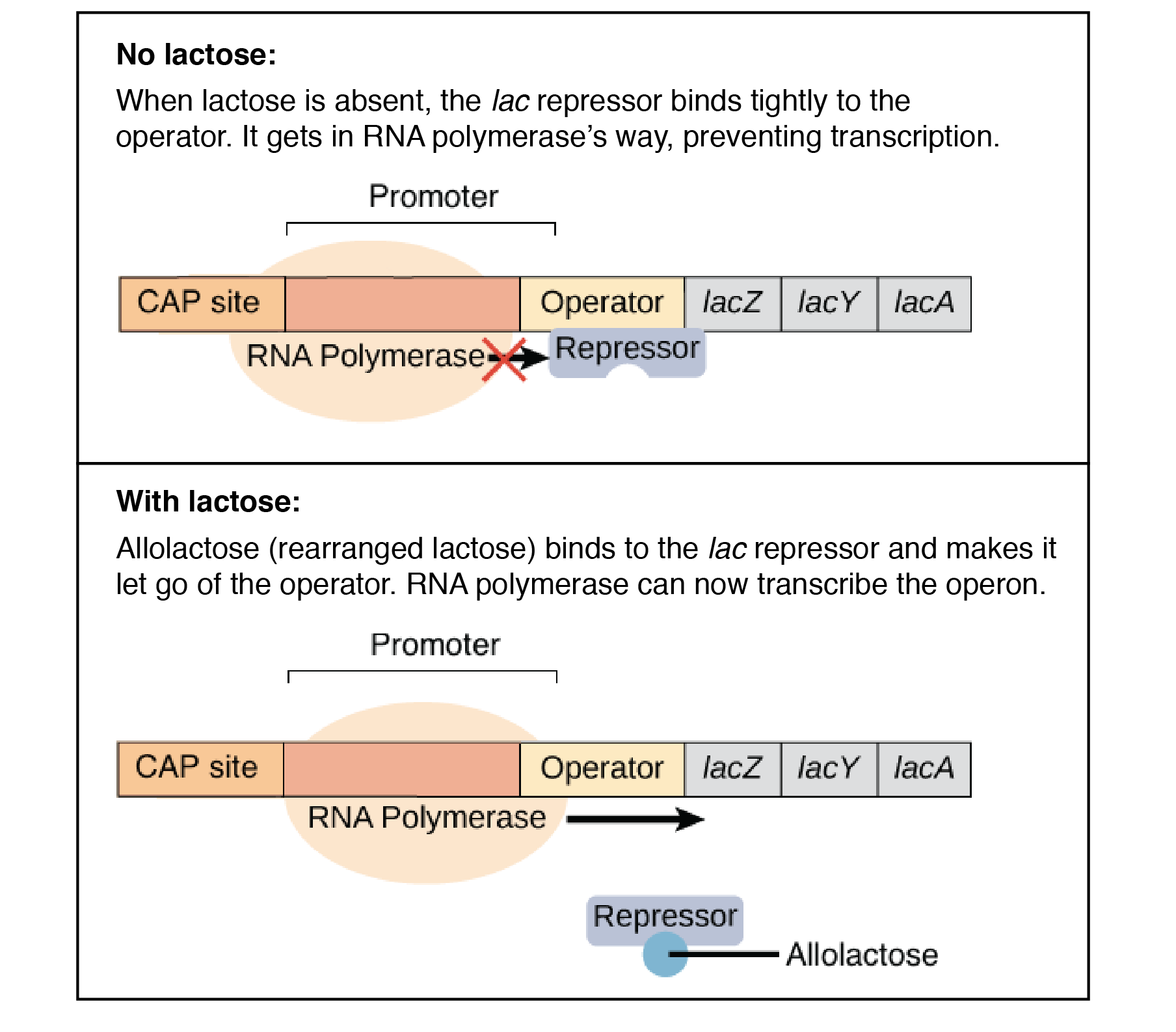
what happens when there is lactose present in bacteria? (lac operon)
binding site on the repressor where lactose attaches, causing repressor to let go of the promoter region → RNA polymerase can bind to that site & start transcription until lactose is gone
activators
regulatory proteins that bind to DNA at enhancers. When DNA folds so that the enhancer is brought into proximity with the initiation complex, the activator proteins interact with the complex to increase the rate of transcription
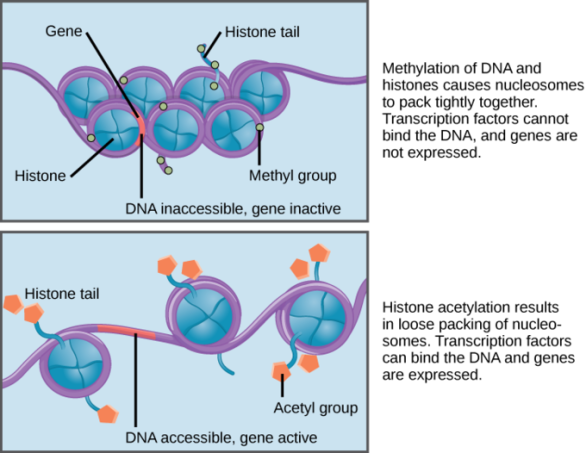
methylation of DNA bases in chromatin
genes being “turned off”
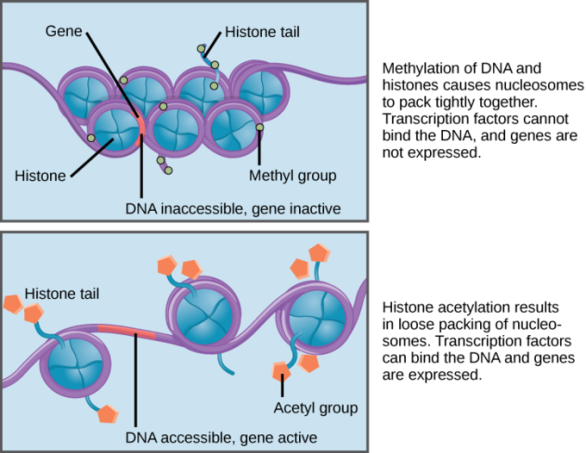
acetylation of DNA bases in chromatin
genes being “turned on”
cytoplasmic distribution
asymmetry contribute to differentiation → different areas have different amounts of cytoplasm, thus different organelles & cytoplasmic structures
cytoplasm contains organelles & stuff
asymmetry sets the stage for differentiation & perform distinct functions
eg. a cell with more mitochondria may become specialized for energy production
induction
influence of 1 group of cells on the development of another through physical contact/chemical signaling
Hans Spemann experiments
notochord induces cells of the dorsal ectoderm to develop into the neural plate
cells from the notochord of an embryo are transplanted to a different place near the ectoderm
neural plate will develop in the new location
cells from the notochord region act as “project directors” telling the ectoderm where to produce the neural tube and CNS
homeotic genes
regulatory genes that determine how segments of an organism will develop
mutation
heritable change in the genes of an organism → can either cause changes to phenotype or silent
frameshift mutation
deletion/addition of DNA nucleotides that doesn’t add/remove a multiple of 3 nucleotides (cuz dna is read in triplets aka codons)
produces non-functional protein unless happens late in protein production
eg. original DNA: THE FAT CAT ATE HER HAT [remove F] → THE ATC ATA THE ERH AT
![<ul><li><p>deletion/addition of DNA nucleotides that doesn’t add/remove a multiple of 3 nucleotides (cuz dna is read in triplets aka codons)</p></li><li><p>produces non-functional protein <strong>unless</strong> happens late in protein production</p></li><li><p>eg. original DNA: THE FAT CAT ATE HER HAT [remove F] → THE ATC ATA THE ERH AT</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/95f733ba-f8bc-4520-86dc-b7b168c23141.png)
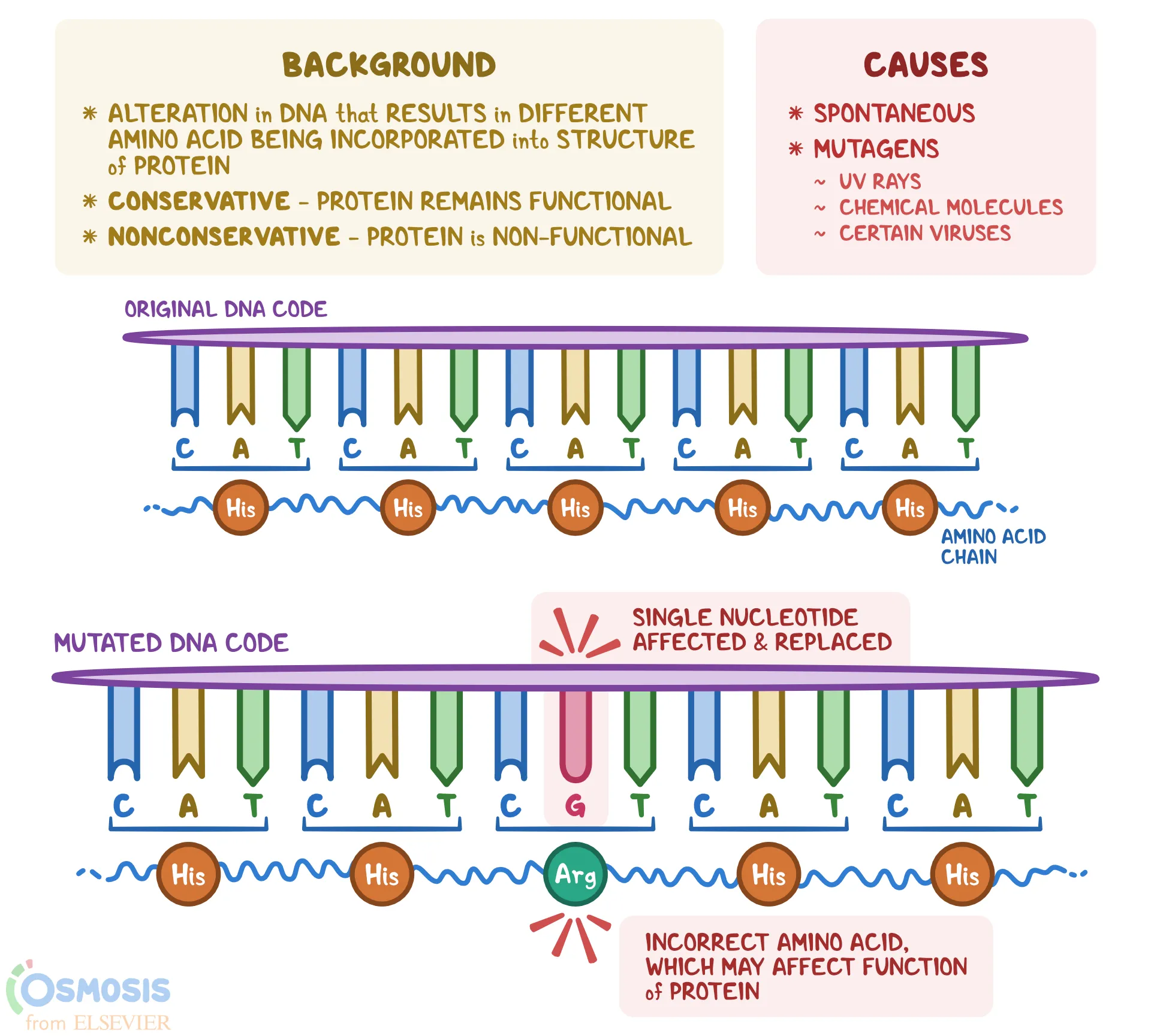
missense mutation
substitution of wrong nucleotides into DNA sequence. Leads to addition of amino acids to growing protein chain during translation, but sometimes the amino acids are not correct. → causes either big problems like sickle cell anemia or is silent
affects one amino acid since its substitution
nonsense mutation
substitution of wrong nucleotides into the DNA sequence → converts a codon that normally codes for an amino acid into a stop codon
stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA
leads to nonfunctional protein (causes the ribosome to halt translation before the full protein is synthesized, resulting in a truncated protein)

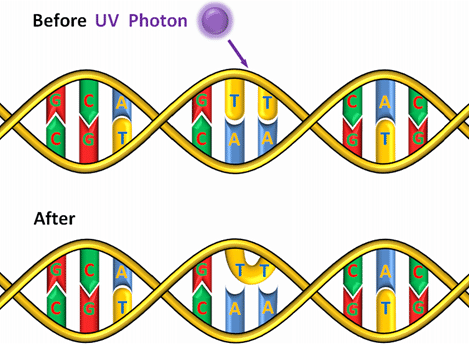
thymine dimers
result of too much exposure to UV light. Thymine nucleotides located adjacent to each other on DNA strand bind together → helps cause further mutations, can negatively affect replication of DNA