KHS 325 - TEST 2 REVIEW
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
40 multiple choice and short answer, 5 math problems, 2 bonus; 30% of test is old materal, 70% is new material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is a scalar quantity?
measure that only considers magnitude
does not consider direction
ex: distance, temperature, money

What is a vector quantity?
describes both direction and magnitude
represented by arrows
ex: displacement, force, velocity, acceleration

What is position?
the linear location of an object at interest at a given instant
unit: m (meter)
What is linear distance?
measure of length of path followed by an object from initial to final
scalar quantity
unit: m (meter)
What is linear displacement?
the straight-line distance in a specific direction from starting to ending position
displacement = final distance - initial distance
vector quanitty
unit: m (meter)
What is the Pythagorean theorum?
a2 + b2 = c2 (leg2 + leg2 = hypotenuse2)
used to calculate a missing side length in a right triangle
What are the trigonometric functions?
SOH CAH TOA
sine = opp/hyp
cosine = adj/hyp
tangent = opp/adj
used to find a missing side length or a missing angle in a right triangle
What is vector resolution/decomposition?
breaking down a vector (the hypotenuse and angle) into components (x and y side lengths)
What is vector composition?
making a vector (the hypotenuse and angle) out of components (x and y side lengths)
How do you describe the direction of a vector?
*think of it like a graph with an x-axis and y-axis!
1st direction: angle does not touch this axis
2nd direction: angle touches this axis
ex: “35 degrees East of due North” means 35 degrees to the right of the positive y-axis
it is NOT 35 degrees above the positive x-axis
What is speed?
rate of motion of an object; rate at which an object’s position is changing
scalar quantity
v = d/t (speed = distance/time)
unit: m/s (meters/second)
*NOTE: the “v” and “d” are not bolded!!!
What is linear velocity?
rate of change in linear position; rate of linear displacement; how fast an object moves in which direction
vector quantity
v = d/t (velocity = displacement/time)
unit: m/s (meters/second)
*NOTE: the “v” and “d” are bolded!!!
What is cyclical velocity?
v = cycle length * cycle frequency
ex: swimming velocity = stroke length (m/stroke) * stroke frequency
What can cause a change in acceleration?
change in magnitude of velocity
change in direction of velocity
What is scalar acceleration?
change in speed/elapsed time
positive = speeding up
negative = slowing down
unit: m/s2
What is vector acceleration?
change in velocity/elapsed time
positive = speeding up of a positive velocity or slowing down of a negative velocity
negative = slowing down of a positive velocity or speeding up of a negative velocity
unit: m/s2
How many degrees are in 1 revolution?
360 degrees
What is a radian?
angle with which the length of the arc becomes the same to the radius
1 radian = 57.30 degrees
What is angular position?
angular location at a given instant
unit: rad (radian)
directions: counterclockwise (+) and clockwise (-)
What is angular displacement?
change in angular position; net effect of angular motion
vector quantity
unit: rad (radian)
directions: counterclockwise (+) and clockwise (-)
What is angular velocity?
rate of change in angular position with angular displacement
ω = Δd/t (angular velocity = angular displacement/time)
unit: rad/s (radians/second)
What is angular acceleration?
α = Δω/t (rate of change in angular velocity over elapsed time
unit: rad/s2 (radians/second2)
ex: ceiling fan rotation acceleration
What is the relationship between linear velocity, the radius, and angular velocity in circular motion?
v = r * ω (linear velocity = radius * angular velocity)
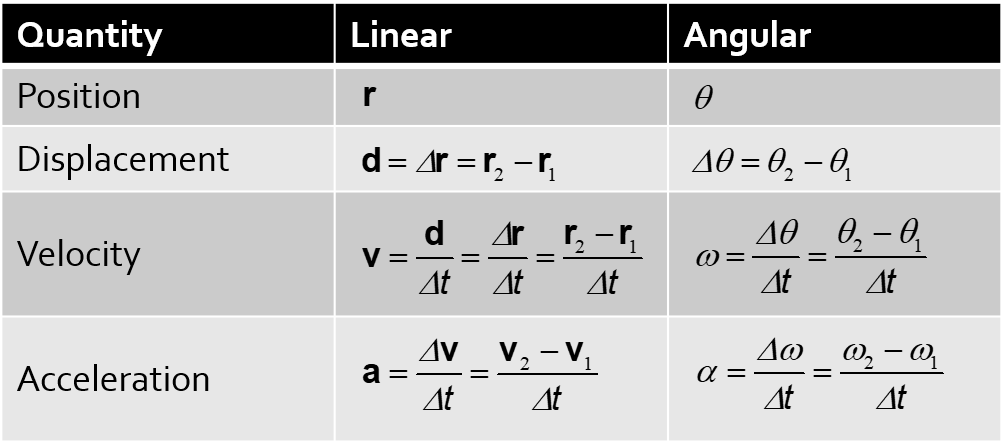
What are the differences in units and formulas between linear and angular quantities?
r —> θ
d —> ∆θ
v —> ω
a —> α
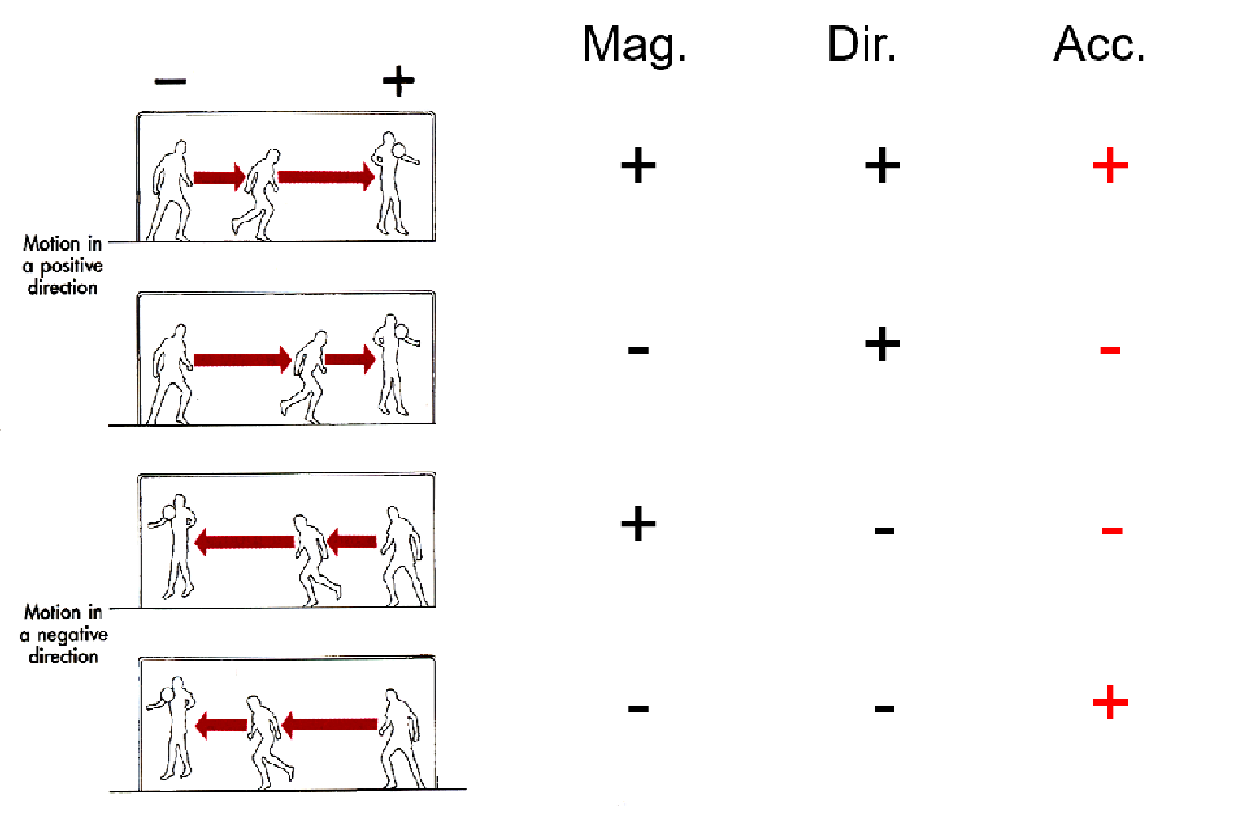
How do you determine if a vector acceleration is positive or negative?
double positive or double negative = positive acceleration
one positive and one negative = negative acceleration
What is linear motion?
all points on body show same trajectory; orientation of object does not change
rectlinear — straight path (ice skating)
curvilinear — curved path (skiing down hill)
What is angular motion?
rotation about an axis of rotation; orientation changes constantly
axis of rotation can be within body (lifting legs while lying down) or outside (trapeeze)
What is force?
push or pull acting on a body that causes motion
symbol: F
standard unit: N
What are 3 important properties of force?
direction
magnitude
point of application
What is pressure?
amount of force acting over a unit area
P = force / contact area
standard unit: Pa (aka N/m²)
What is torque?
rotary force that produces angular motion
T = F * moment arm
standard unit: Nm
vector quantity (uses - and +)
What is mechanical advantage?
gain of the system = output / input
What are the types of bones?
short bones
long bones
flat bones
irregular bones
How are joints classified?
either by function or structure
synarthroses — fibrous joints; immovable
skull sutures, mid-radioulnar, midtibiofibular
amphiarthroses — cartilaginous joints; slightly moveable
1st sternocostal, epiphyseal plate, vertebrae, pubic symphysis
diarthroses — synovial joints; freely moveable
major joints of body
What is joint stability?
ability to resist dislocation
prevents injuries to surrounding ligaments, muscles, and tendons
high stability desired —> increase via strength
What is joint flexibility?
ROMs allowed at joint; joint specific
increase via stretching
What is a motor unit?
single motor neuron + skeletal muscle fibers innervated
functional unit of muscle
all muscle fibers in one unit are the same fiber type
What is the size principle?
determines sequence of recruitment of motor units
smallest recruited first
SO —> FOB —> FG
fatigued —> recruit new motor units
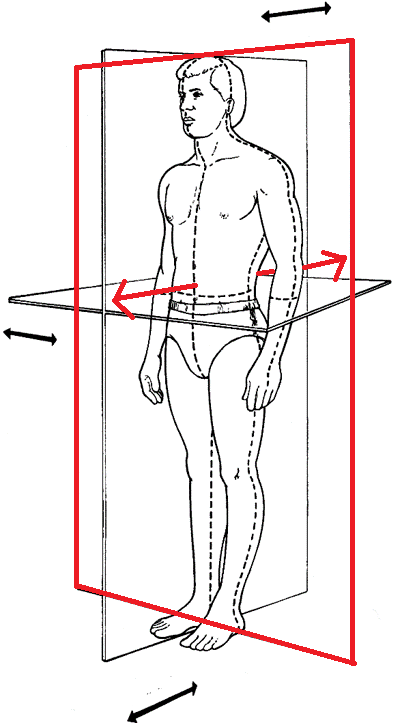
What plane and axis is this?
frontal/coronal plane
antero-posterior axis (AP axis)
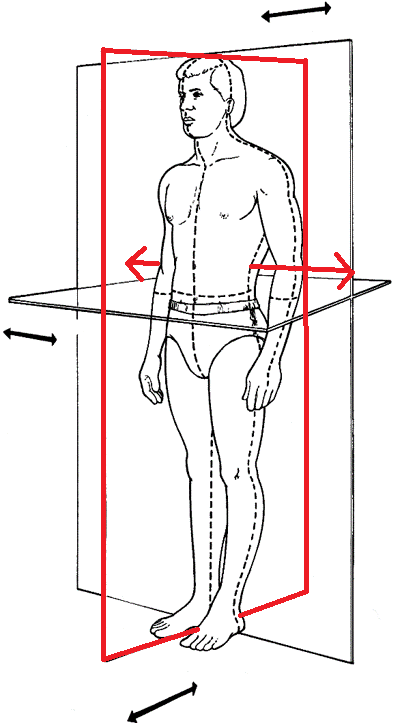
What plane and axis is this?
sagittal plane
medio-lateral axis (ML axis)
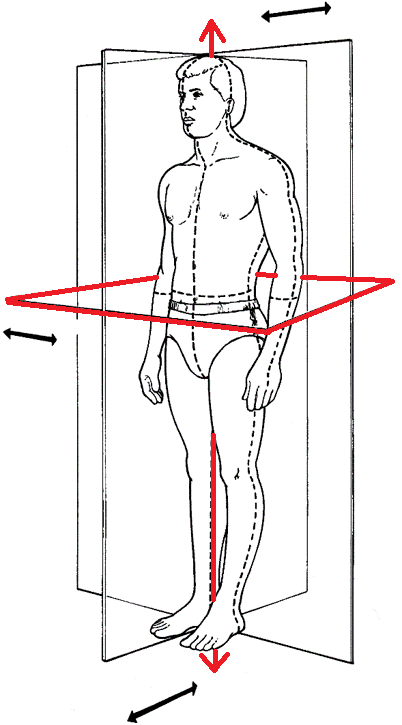
What plane and axis is this?
transverse plane
longitudinal axis (L axis)
What are the types of synovial joints?
gliding/plane
ex: intermetatasral, intercarpal, intertarsal, facet joints (vertebrae)
hinge
ex: humeroulnar (elbow)
pivot
ex: proximal and distal radioulnar joint, atlanto-axial joint
condyloid
ex: radiocarpal joint
saddle
ex: carpometacarpal of thumb
ball-and-socket
ex: acetabulofemoral joint, glenohumoral joint
What are types of muscle fibers?
SO
slow-twitch oxidative
type I
high endurance, low max tension
FOG
fast-twitch oxidative glycolytic
type IIa
lower endurance, larger max tension
FG
fast-twitch glycolytic
type IIb
lowest endurance, largest max tension
What is the difference between kinematics and kinetics?
kinematics — study of description of motion; focuses on the effects
kinetics — study of action of forces/explanation of motion; focuses on the cause of motion
summary: description vs explanation
What are the main themes of biomechanics?
safety
effectiveness
efficiency