Physics HSC
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Low Earth Orbit Satellites
orbit approx 500km
1 orbit approx 90 mins
used for:
weather
military monitoring purposes
Geostationary Satellites:
orbit every 24 hours
around 35,000 km above
used for
tv broadcasts
mobile phones.
Keplar’ 1st law
The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the foci.
Keplar 2nd Law
A line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
Keplar 3rd law
The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi‐major axis of its orbit. T2 R3
Unit for magnetic flux
wb webber - Tm²
Define Emf. + measurement
Volts
electric force from converting any form of energy into electrical energy
when a conductor cuts magnetic field lines.
faradays law
induced emf is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
Lenz’s law building upon faradays
minus sign
direction of induced emf
induced current’s magnetic field opposes the original change in flux
N
number of coils increases induced emf.
Conservation of energy + lenz’s law working
because the the magnetic field opposes the motion, work needs to be done to either the coil or the magnet.
this works is being converted into electrical energy.
If conservation of energy law is broken lenz’s law?
if magnetic field doesn’t oppose motion
magnet moves and cuts flux lines, this attracts magnet and it moves faster.
as it moves faster more flux cut per second, field strength increases, magnet moves perpetually faster.
break law of conservation of energy.
4 ways transformers are inefficient
heating effect of current in coil
heating effect of induced eddy currents
flux leakage
magnetism of the iron core
How is power lost from heating of core from current in transformers + how to resolve this?
How:
As a current flows through the coil, it heats
lower is lost as heat I²R.
Fix:
thick copper wires - low resistance
use coolant to reduce the temperature of the transformer.
How is power lost from heating of core from eddy currents in transformers + how to resolve this?
How:
when the magnetic field in the iron core fluctuates, eddy currents are generated in the iron core - heating
Fix:
use a laminated iron core, where layers are insulated with enamel paint
resistance reduces prevalence of eddy currents and heating.
How is power lost from flux leakage in transformers + how fix?
How:
some of the induced magnetic flux in the primary coil is not transmitted to the secondary coil, thus emf in the secondary coil is decreased.
Fix:
secondary coil coils tightly intertwined with the primary coil, to increase flux linkage.
Iron core forms a closed loop.
How is power lost from magnetisation of iron core in transformers + how fix?
How:
the energy used to magnetise and de-magnetise the iron core each time the current changes direction is known as HYSTERESIS.
Fix:
Use a soft iron core that is more easily magnetised and de-magnetised.
DC motor parts + Roles -6
Magnets:
supply magnetic field.
Armature:
carries coils, has laminations to reduce eddy currents
Coils:
provides torque, as current in coil cuts magnetic flux
Split Ring commutator:
point of contact between rotor coils and external circut
serves to reverse direction of current flow in each half revolution, this maintains torque.
Brushes:
fixed electrical contacts between circuit and commutator
Axle:
centre of rotation for moving parts of rotor.
Operation of an AC induction Motor
as the magnetic field rotates the conductive metal rods in the rotor cut the magnetic flux, inducing an emf and current in the rotor bars
this current induces an opposite magnetic field, lenz’s law
newtons 3rd law (every action has an equal and opposite reaction), so the magnetic repulsion (force) between the induced B feild and rotating feild causes the rotor to rotate (anti-clockwise, same direction as field).
the torque causing the rotor to rotate is induced and the rotor always rotates slower than the feild.
this converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
How Magnetic Breaking Works?
Examples of Magnetic Breaking
trains
amusement Park
Energy Conservation in magnetic breaking
energy is seen to be conserved as kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy in the conductive material.
Maxwell’s 4 equations?
any electric charge produces an electric field. (gauss’s law)
magnetic monopoles can never be found in nature (gauss’s law in magnetism)
a changing magnetic field induces an electric field (faraday’s law of induction)
a changing electric field induces a magnetic field. (ampere-maxwell law)
Maxwell’s contributions
showed that light was an electromagnetic wave
he theorised that electromagnetic waves:
can propagate through empty space
propagate through space at the speed of light
generated by oscillating electric charges.
carry energy and momentum
cover many frequencies
Hertz validating maxwell’s predictions?
used an induction coil with a high voltage source, connected to a transmitter
transmitter has two spherical electrodes
a spark was seen to jump between the electrodes - energy transferred at the speed of light
this showed the em spectrum exists by detecting em waves (radio waves).
original bar used to measure a meter
platinum iridium bar
what is black body radiation and what is a black body.
radiation emitted from a heated object
a black body is a cavity in a material which only emits thermal radiation, incoming radiation is absorbed in this cavity
Application of black body radiation
cooler objects:
emit less radiation
appear reddish
hotter objects:
emit more radiation
appear yellowish
As a black body heats up, increases in intensity, wavelength for max intensity reduce
Examples of a black body
lava
sun and other stars
heated metal
What unit is weins displacement law in and conversion
in kelvin - to convert degrees to kelvin + 273
when is diffraction optimised?
when the size of the gap is equal to the wavelength of the incident wave.
Newton’s theory of light - what is it?
Theory:
waves are particles - called corpuscles
corpuscles travel in straight lines in all directions at high speed
when corpuscles enter the eye = sensation of vision.
different sized corpuscles = different colours
repelled by reflective surfaces, attracted by transparent surfaces.
Newtons theory of light positives + negatives
Positives:
explains rectilinear propagation
explains refection + refraction separately.
Negatives:
cannot explain simultaneous reflection + refraction.
cannot explain diffraction
though velocity of light was faster in a denser medium.
if particle emitted from source, mass should reduce.
Huygen’s theory of light - what is it?
because light travelling in particles would collide - proposed light as a longitudinal wave.
Wavelets:
light spreads out evenly in all directions
all wavefronts could be a source of spherical wavelets - with same velocity, frequency and phase.
when wavelets are in phase they combine to create a new wavefront.
waves propagate due to the superposition of wavelets.
Huygen’s theory positives + negatives
Positives:
explains diffraction
explains partial reflection + refraction
light moves slower in a denser medium.
Negatives:
assumed the existence of an ether
cannot explain rectilinear propagation.
cannot explain light bending.
thought waves were longitudinal
Classic model vs quantum model
Classic:
frequency - affects colour
Intensity - amplitude
Quantum:
frequency - energy
intensity - number of photons
Photoelectric effect process + Results
light shone onto a metal plate
if light has enough energy it should knock photoelectrons off.
in an electric field to attract disturbed photoelectrons, and in a vacuum.
Results:
below a threshold frequency, increasing intensity did not produce photoelectrons.
above threshold frequency Increasing intensity produced more photoelectrons
increasing frequency of incident light, made escaping photoelectrons move faster.
KE of emitted photons was dependant on frequency.
What is planks constant
rate at which Kmax of escaping photoelectrons is changing with respect to frequency (gradient of work function graph).
What is a work function
minimum ammount of energy required for a photoelectron to escape
What is an inertial frame of reference?
a frame with no net external forces acting upon it
no acceleration
where newtons 1st law will be obeyed
What are Einstiens postulates?
all inertial frames of reference are equivalent.
the speed of light in a vacuum is an absolute constant.
what does Einstiens 1st postulate mean?
there is no absolute frame of reference
no experiment can be performed entirely within and intertial frame to determine whether it is resting or stationary.
Einstein’s thought experiment 1
superman flying at the speed of light can or cannot see his reflection.
yes - light would have to exceed c
no - he must know he is travelling at c
Einstein’s thought experiment 2
light bulb in the centre of a carriage with doors at either end with light sensors.
person inside see at same time
person outside see rear door open first.
What is a muon?
Subatomic particles created by interactions between cosmic rays and gas molecules in the upper atmosphere.
travel towards earth at speeds close to c.
have an average lifespan of 2.2 microseconds
How are Muons evidence for special relativity?
live only 2.2μs
newtonian physics predicts in this time they could only travel 660m but they are created multiple kilometres above earths surface, should shouldn’t ever reach the surface.
Time dialation:
from earths perspective, the time of the muon dilates, so earth see’s them make it to the surface.
Length Contraction:
from the muon’s perspective, the distance to the earth is shorter, length contraction, so they see themselves making it.
What is an atomic clock
very precise clocks
use the frequency of radiation emitted during electron transitions within atoms to measure time.
this allows them to measure very small time differences.
Hafele keating + atomic clocks evidence for special relativity.
three atomic clocks were used, one on earth, one on a plane travelling west, and one on a plane travelling east.
earth rotates to the east, so relative to earth, the west travelling plane moved faster.
the time relative to earth on west travelling plane dilated more than the eastward plane.
Big bang before -2
hot point of energy called a singularity
high radiation and heat
Within the first second of the big bang - 5
cosmic inflation
4 fundamental forces separate (strong, weak, electromagnetic, gravitational)
fundamental particles called quarks are created from energy - ‘quark soup’
quarks, leptons and neutrinos make up most of the universe’s matter
as the universe expands, it cools, quarks collide, this forms hadrons (protons + neutrons).
3 mins after the big bang to 380,000 years after -4
leptons and anti leptons annihilate each other leaving a surplus of matter particles, (electrons).
primordial nucleosynthesis - temperature drops and nuclei form through nuclear fission (hydrogen, helium, lithium)
electrons and nuclei are unattached
universe is opaque
380,000 years after the big bang and onwards - 5
temperature drops below 3000K, electrons start to orbit nuclei, forming the first atoms.
universe is transparent.
lots of photons released from recombination, cosmic background radiation.
temperature low + gravity = first galaxies.
heat from gravitational compression - thermonuclear reactions = first stars formed.
evidence for the big bang
Cosmic background radiation
radio waves
longer wavelength than visible light
suggests universe expanding, and has expanded from a singularity - big bang.
Hubble’s constant
the further a galaxy away, the more redshifted em radiation is.
suggests galaxies are moving away and the universe is expanding.
how to determine the temperature of a star
wiens law.
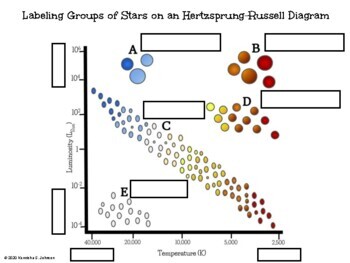
hertzsprung russell diagram
plots luminosity (or magnitude) against surface temperature.
A - blue giants
B - supergiants
C - main sequence stars
D - red giants
E - white drawfs
apparent magnitude vs absolute magnitude
apparent magnitude - how bright the star appears from earth
Absolute magnitude - how much light is actually given off.
Main sequence stars
90% of stars
younger only fuse hydrogen - pp chain
older main sequence fuse hydrogen but use PP chain and CNO cycle.
Red Giants + Red super giants
Fused most of their hydrogen
now fuse helium, becomes carbon - tripple alpha process.
White drawfs
no more nuclear fusion
energy from residual heat.
Life cycle of stars - small stars
nebula
protostar
main sequence star
red giant
planetary nebula
white dwarf
Life cycle of stars - large stars
nebula
protostar
main sequence star
red super giant
super nova
neutron star - or - black hole.
Proton-Proton chain summary
fuses hydrogen into helium in two nuclear fusion reactions
converts 4 hydrogen nuclei into a helium nucleus.
this process is called nucleosynthesis
as the mass of the individual hydrogen molecules is greater than the two combined - some mass must be converted into energy
e=mc²
energy is released in the form of gamma ray photons
Proton-Proton chain process
A hydrogen nucleus = a proton
2 1hydrogen nuclei combine to form a 2hydrogen (deuterium) - positron and neutrino produced
a 1hydrogen collides with a deuterium to form helium (tritium) - gamma radiation released.
two 3helium collide, to form 4helium - two 1hydrogen released.
CNO Cycle
a series of nuclear fusion reactions which occur in main sequence stars - like our sun
involves carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen
a He-4 nucleus is normed fro every one cno cycle.
gamma radiation is produced.
Tripple alpha process
fuses helium to produce helium and carbon.
Cathode v anode
cathode: negative electron emitting electrode
anode: positive electron absorbing electrode
what is a cathode ray
Cathode rays were produced in partially evacuated discharged tubes called Crookes tubes
a cathode ray tube consists of two electrodes connected to a high potential difference. (cathode + anodes
energy given to cathode to emit cathode ray - eg: heating - thermionic emission
ray - streams of electrodes (scientists originally didn’t know electrons existed).
Thomson Charge to Mass ratio experiment
developed charge to mass ratio
found that the cathode ray was deflected in both E and B feilds.
found when F(E) was equal and opposite to F(B) and cathode ray was undeflected.
found electron was 1800x less than hydrogen
Atoms were made of smaller particles
Plum pudding model
Thomson deriving charge to mass ratio
B field:
FB = FC
qvb = mv2/r
q/m = v/Br
E field:
FE = qe
FE = FB
qE = qvb
v = E/B
Equate:
q/m = E/B2r
Milikans Model
Purpose: to find the charge of an electron
Process:
fine oil sprayed - falls due to gravity
x rays negatively ionise the droplets (gain electrons)
E field is applied - FE on droplets
FE is adjusted to be equal and opposite to to gravity - droplets are suspended
velocity found using kinematics
FE = mg
charge on droplets is always a multiple of -1.602×10-19
Chadwick’s experiment
discovered the neutron
How:
bombarded beryllium with alpha particles
emitted a stream of radiation
very penetrating - didn’t get reflected
the stream hit paraffin and carbonised it
the rays did not move an electroscope so was not gamma as originally thought.
using kinematics chadwick found velocity of protons
using momentum conservation and proton velocity - chadwick determined the mass of a neutron.
Paraffin has a large number of hydrogen atoms containing single protons. When the unknown radiation hit these protons, they were ejected from the paraffin.
History of the atom -6
Democritus:
solid indestructible, no electrons or hadrons
Daltons atomic theory:
tiny particles - not subdivided, created or destroyed
JJ Thomson:
discovered the electron, negatively charged so must have positive charges to counteract this - plum pudding model.
Ernest Rutherford:
gold foil, alpha particles, some defelcted/bounced/passed through - discovered the nucleus:
small
large mass
positively charged
Bohr Model:
planetary model
electrons travel in definate orbits around the nucleus
closer orbits, more stable
electrons moving between orbits - emits spectra.
Quantum mechanic model/ Schrodinger’s atom model
based on theory of wave mechanics
atom mostly empty space
two regions:
nucleus - protons+neutrons
electron cloud - where likely to find an electron
Limitations of Rutherford
an electron orbiting a nucleus should be accelerated towards the nucleus
this should cause the electron to continuously emit radiation and loose energy.
thus the electron would slow, not be able to resits the nucleus’s attraction and spiral inwards.
does not explain the arrangement of electrons in the atom.
Bohr’s postulates -4?
electrons can orbit the nucleus in metastable orbits without radiating energy or falling towards the nucleus despite having an opposite charge.
when an electron moves to a lower orbit it emits em radiation E=hf
if an electron moves to a higher orbit it must gain energy e=hf
angular momentum is a multiple of mvr=nh/2(pi)
Bohr Limitations -4
could not explain spectra Relative Intensity.
Could not explain spectral Hyperfine structure
only account for Hydrogen emission spectrum (one electron in valance shell)
cannot explain the ‘Zeeman’ splitting of spectral lines in a B field.
Balmer series
emission lines in visible light range (hydrogen) - drops to n=2
De Broglie idea
Proposed that moving matter can exhibit wave properties
postulated that electrons orbit the nucleus as standing waves.
When electrons behave as standing waves they no longer emit radiation - provided an explanation for bohr’s 1st postulate.
so electrons should be able to be diffracted and have interference patterns
Davisson + Gremmer experiement + de broglie confirmed
fired electrons at a nickle target.
the slits between the nickle atoms acted as a diffraction grating to diffract electrons
the image of the metals crystal lattice was then able to be obtained obtained
as the electrons were diffracted - the exhibited a wave nature - this supported De Broglie’s theory
Transmutation Def
changing one element into another by radioactive decay, nuclear bombardment, or similar processes.
alpha, beta or gamma decay.
isotopes?
same atomic number different mass number - same number of protons, different number of neutrons.
Radioactivity
spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus
to be radioactive must absorb radioactive elements
Types of radioactive emission
Alpha:
Particle type:
helium nucleus
Penetrating ability
low
ionising ability
high
Beta:
particle type:
electron
penetrating ability
medium
Ionising ability;
medium
Gamma radiation:
Particle type:
gamma ray photon
Penetrating ability:
high
Ionising ability
low
Alpha decay
helium nuclei emitted
AZX → (A - 4)(Z - 2)Y + 42He
Beta Decay minus
when a neutron changes into a proton, which causes an electron and antineutrino to be released.
AZX → A(Z + 1)Y + 0-1 e + V(anti)
Beta Decay plus
proton changes to a neutron, and a positron and a neutrino are released
AZX → A(Z - 1)Y + 0+1 e + V
Gamma Decay
when a gamma ray photon is emitted, and the nuclear energy level decreases.
typically occurs alongside other decay types
AZX → AZ Y + 00γ
Half Life summary info
nuclei decaying is randomly occurring, and it cannot be predicted when a nuclei will decay.
through examining large number of nuclei, the probability that a nuclei will decay in a given time period can be determined.
half life = time for half the nuclei to decay.
(decay curve will never reach zero).
short v long half life
short = more radioactive isotope.
long = less radioactive isotope.
Fission Def?
a large nucleus is bombarded by a neutron, and it splits into 2 smaller nuclei and neutrons.
products of fission have a smaller mass so energy produced - E=mc2
Fission Process?
neutron collides with a nucleus (typically uranium-235)
nucleus captures the neutron, which causes instability in the nucleus (uranium-236 is very unstable).
the nucleus splits into two fission fragments and releases neutrons
Uncontrolled fission reactions
a chain reaction when the fission of a nucleus produces neutrons which bombard another nucleus - chain reaction - multiple fissions
Real life fission examples
Controlled:
nuclear power - uranium-235
Uncontrolled:
Nuclear Bombs
Little boy - hiroshima
Fat man - nagasaki
Controlled fission reactions - power plant components to control
Fuel rods:
contain nuclear fuel (uranium 235),
surrounded by a moderator (eg: water) which controls the number of neutrons released.
slower release of neutrons - less nuclear reactions per second.
Control Rods:
control the rate of fission by moving in and out (absorb neutrons). (eg boron)
in = rate decreases
out rate increases
all in = stops
How nuclear power plants produce energy?
energy released heats up the reactor
water surrounding the reactor is heated, boiled to produce steam
steam drives the turbine which turns a generator - producing electricity.
Nuclear Fusion?
two nuclei with low mass numbers to produce a single nucleus with higher mass numbers.
Fusion Process
2 nuclei collide
energy (em radiation) is released + typically a nucleon also.
Binding energy
the energy binding nucleons together (per nucleon)
measure of nuclear stability - high binding energy = more stable atom.
Binding energy Fe56
most stable element - more protons = more likely to undergo fission - less protons = more likely to undergo fusion.
threshold
a reaction occurs when the products are more stable than the reactants.
Standard model what in
fundamental forces
strong
boson = gluon
em
boson = photon
weak
boson = w + z particle
gravitational
boson = graviton
Quarks:
up
down
strange
charm
bottom
top
Hadrons:
Baryons
protons + neutrons
Meysons
pions
Leptons
electron + muon
The Fundamental Forces:
EM force:
binds charges particles atoms + nucleus
infinite range
boson = photon
EM force:
binds charges particles atoms + nucleus
infinite range
boson = photon
Weak Nuclear force:
binds interacts with nuclear particles
limited range
boson = w and z particle
Gravitational Force:
draws masses together