BIOL 111 powerpoint 11
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This one is a bit harder - maybe
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
▪ Exchange of gases
▪ Regulation of pH
▪ Sense of smell
▪ Air filtration
▪ Sound production
▪ Exhalation of heat and water
what are the functions of the respiratory system?
upper
is the upper or lower respiratory system conducting
lower
is the upper or lower respiratory system for gas exhange
conducting zone
what zone conducts air to lungs
respiratory
what zone the the main site of gas exchange
conducting zone
what zone includes these areas?
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi,
bronchioles and terminal bronchioles
respiratory zone
what zone includes these areas?
Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar
sacs, and alveoli
filter/warm/moisten air
detect olfactory stimuli (smell)
modify speech vibrations
what are the three functions of the nose
mucus lymph tissue
(for me) what is MALT?
passageway for air and food
resonating chamber (sounds)
houses tonsils
what are the functions of pharynx?
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
what are the three anatomical regions of the pharynx?
nasopharynx
what is the top yellow box called?
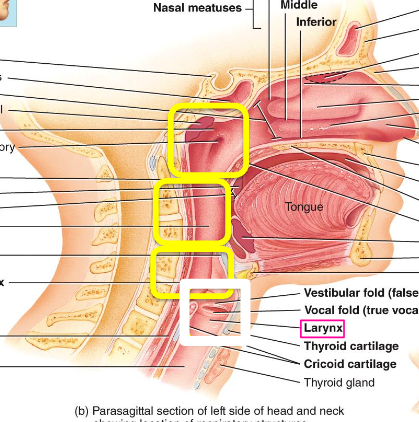
oropharynx
what is the middle yellow box called
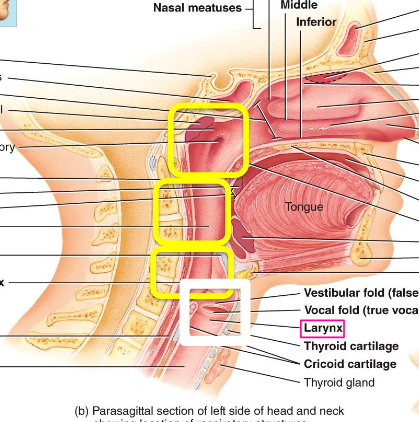
laryngopharynx
what is the bottom yellow box
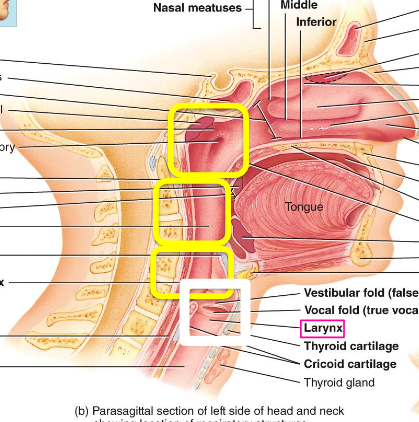
larynx
where are vocal folds that produce sound when the vibrate located?
cartilage
thyroid
cricoid
arytenoid
what is the larynx composed of?
epiglottis
what closes off glottis during swallowing
to hold breath against pressure in thoracic cacity
what is the function of ventricular folds
muscles are attached to hard cartilages of the larynx and vocal folds
folds can move apart or together, elongate or shorten, tighten or loose
vibrate and produce sound with air
what are the functions of vocal folds
ventricular fold - superior vocal folds - inferior
which is superior and which is inferior: ventricular folds, vocal folds
trachea
where does the respiratory system divide to left and right pulmonary bronchi
carina
what in the bronchi triggers a cough reflex
Right and left main bronchi divide → lobar bronchi → segmental bronchi → Larger bronchioles → smaller bronchioles → terminal bronchiole
list order bronchi divides
respiratory bronchioles
alveolar ducts
alveoli
list the order bronchi divides after reaching the lungs
lobar bronchus
what supplies each lobe in the lungs?
segmental bronchi
what supplies each bronchopulmonary segment in the lungs?
Terminal bronchioles → respiratory
bronchioles → alveolar ducts → alveoli
what is the order of branches in the lungs?
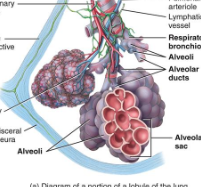
2 or more alveoli sharing a common opening
what is an alveolar sac?
form continuous lining, more numerous than type II, main site of gas exchange
describe type I alveolar cells
free surfaces contain microvilli, secrete alveolar fluid with surfactant
Describe type II alveolar cells
it would collapse in on itself
What would happen if there was too much surface tension within the alveolus
respiration
what is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells called
ventilation
external respiration (pulmonary)
internal respiration (tissue)
what 3 process are required for respiration to occur
by transporting gas
How does the cardiovascular system assist the respiratory system
inhalation and exhalation
exchange of air between atmosphere and alveoli
What does pulmonary ventilation include
exchange of gasses between alveoli and blood
What does external (pulmonary) respiration include
exchange of gasses between systemic capillaries and tissue cells
supplies cellular respiration (makes ATP)
What does internal (tissue) respiration include
pressure differences
alveolar surface tension
compliance of the lungs
airway resistance
what factors effect pulmonary ventilation
thyroid
The largest cartilage, the _____cartilage, is seen anteriorly and has a prominence called the Adam’s apple
glottis
The ____ is the opening that allows air into the larynx.
epiglottis
the oval-shaped ______ is attached to the internal surface of the thyroid gland. It is composed of elastic cartilage and closes over the glottis during swallowing.
ventricular
the superior folds are the ______ , or false vocal cords
vocal
the ______ folds or true vocal cords are inferior and medial.
arytenoid
The vocal folds attach via small muscles to the _____ cartilage.