Comprehensive Guide to Learning, Development, and Emotional Intelligence
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
What is classical conditioning?
A type of learning where a neutral stimulus produces a response after being paired with a stimulus that naturally produces a response.
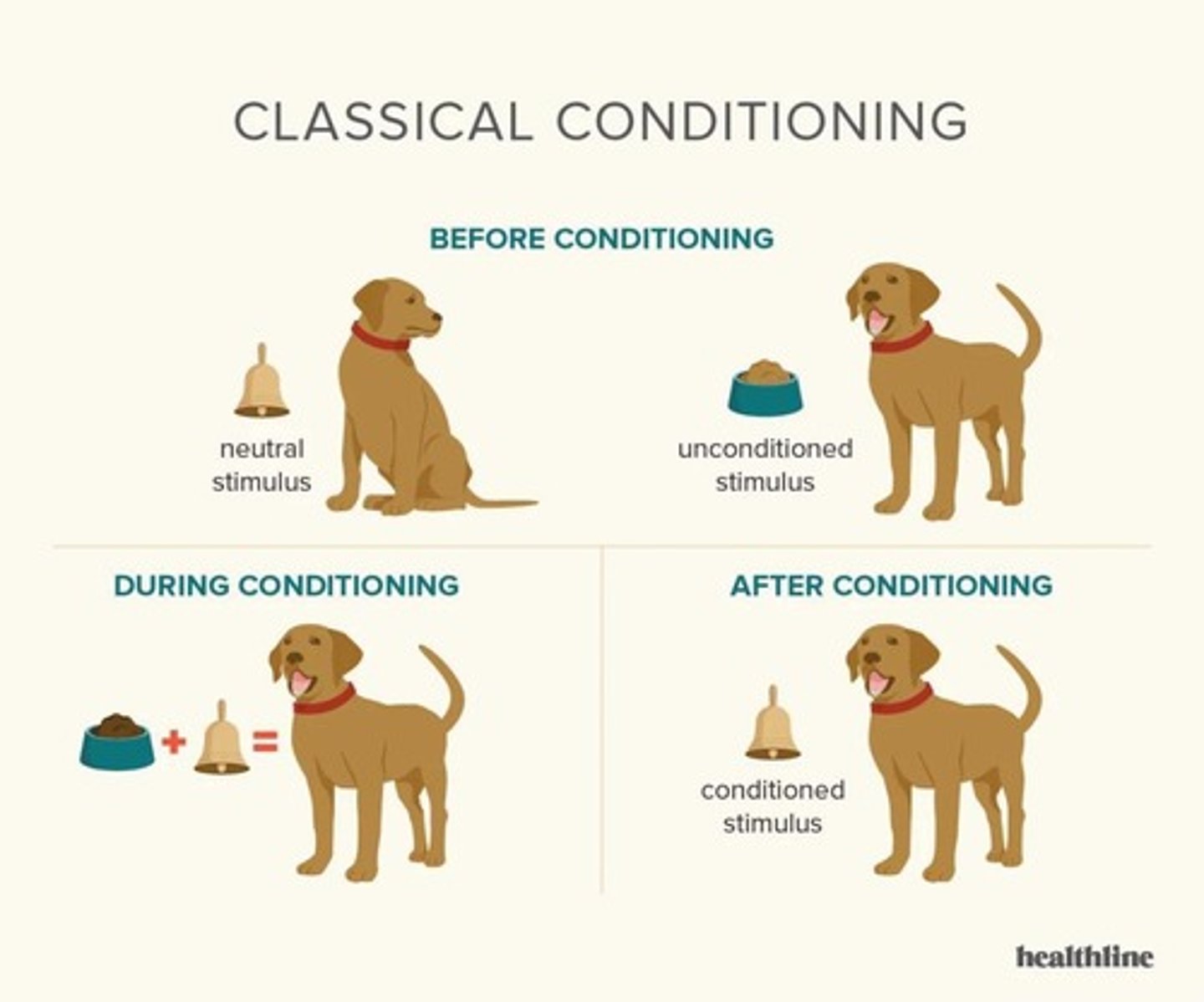
What is the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) in Pavlov's experiment?
Food, which naturally produces a response (salivation) in dogs.
What is the conditioned stimulus (CS) in Pavlov's experiment?
The bell, which becomes associated with the food and elicits salivation.
What is the difference between unconditioned and conditioned responses?
Unconditioned responses occur naturally (like salivating at food), while conditioned responses are learned (like salivating at the bell).
What is the social intuitionist model?
A theory suggesting that moral judgments are primarily driven by quick, automatic, emotional intuitions shaped by social influences.
What was the Little Albert study about?
A study demonstrating conditioned fear, where a baby learned to associate a rat with a loud sound, resulting in fear of the rat.
What is spontaneous recovery in classical conditioning?
The temporary return of an extinguished response after a pause.
What is the process of extinction in classical conditioning?
Occurs when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus, leading to a decrease in the conditioned response.
What is operant conditioning?
A learning process where behavior is modified by its consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment.
What is Thorndike's Law of Effect?
The principle that behaviors followed by satisfying outcomes are likely to be repeated, while those followed by unpleasant outcomes are less likely to be repeated.
What is the difference between unconditioned and conditioned reinforcers?
Unconditioned reinforcers meet primary biological needs, while conditioned reinforcers gain their value through association with unconditioned reinforcers.
What is chaining behavior in operant conditioning?
A process where behaviors are reinforced by opportunities to engage in the next behavior in a sequence.
What is a continuous reinforcement schedule?
A schedule that provides reinforcement every time a response occurs, leading to fast learning but quick extinction.
What is a fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule that provides reinforcement after a specific amount of time has passed, such as a paycheck every two weeks.
What is the variable-ratio schedule of reinforcement?
A schedule that provides reinforcement after a variable number of responses, leading to high persistence and resistance to extinction.
What is the overjustification effect?
The phenomenon where external rewards undermine intrinsic motivation, leading individuals to become less interested in activities they once enjoyed.
What is intrinsic motivation?
The motivation to engage in activities that are inherently rewarding, without external incentives.
What is the impact of praising intelligence on students?
Praising intelligence can lead to a fragile boost in self-esteem, causing students to avoid challenges and feel anxious.
What is the difference between performance goals and learning goals?
Performance goals focus on proving ability, often leading to anxiety, while learning goals focus on mastery and persistence.
What is systematic desensitization?
A behavioral therapy technique that gradually exposes individuals to the object of their fear to reduce anxiety.
What is contextual fear conditioning?
A process where the environment becomes part of the conditioned stimulus, influencing fear responses.
What role does the hippocampus play in fear conditioning?
The hippocampus helps learn cues related to the environment, which can influence fear responses.
What is optogenetics?
A technique that makes neurons light-sensitive, allowing researchers to control their activity using light.
What is conditioned taste aversion?
A learned aversion to a specific food after experiencing illness following its consumption, often established after a single trial.
What does the incremental view of intelligence suggest?
Performance reflects current skills, efforts, and a little luck, not intelligence and self-worth.
What is habituation in infants?
A decrease in looking time with repeated exposure to the same stimulus.
What is dishabituation?
The increase in looking time when a new stimulus is presented after habituation.
How do babies demonstrate operant conditioning?
Babies suck more when a new sound is produced to hear it again.
What do babies prefer regarding sounds?
They prefer the sound of their mother's voice and can distinguish phonemes.
What is core knowledge in infants?
The idea that specific brain systems are designed to learn about the world in domains like language, physics, math, and psychology.
How can babies segment words?
They can identify word boundaries in speech, even in an artificial language.
What does the violation of expectation paradigm test in infants?
It tests object permanence and understanding of basic physical laws.
What is infantile amnesia?
The inability to remember memories from infancy, typically before age 3-4.
How do babies show social preferences?
They look longer at stimuli with facial features and prefer attractive faces.
What is attachment in developmental psychology?
An emotional bond with a primary caregiver that influences later relationships.
What are the four attachment styles identified in infants?
Secure, ambivalent (anxious), avoidant, and disorganized.
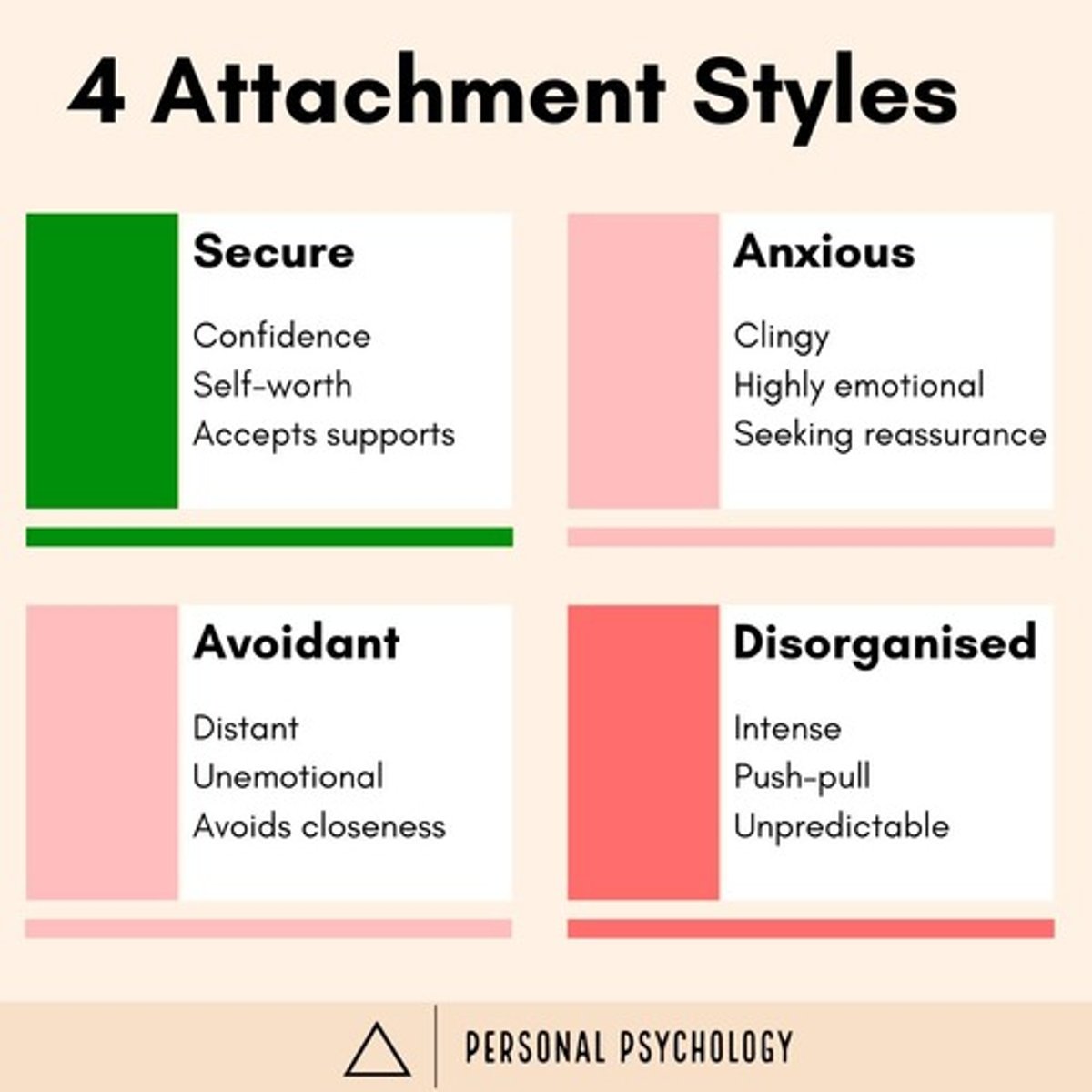
What is the role of temperament in attachment?
Temperament is a biologically based pattern of attentional and emotional reactivity that influences attachment.
What are the stages of Piaget's cognitive development?
Sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operations, and formal operations.
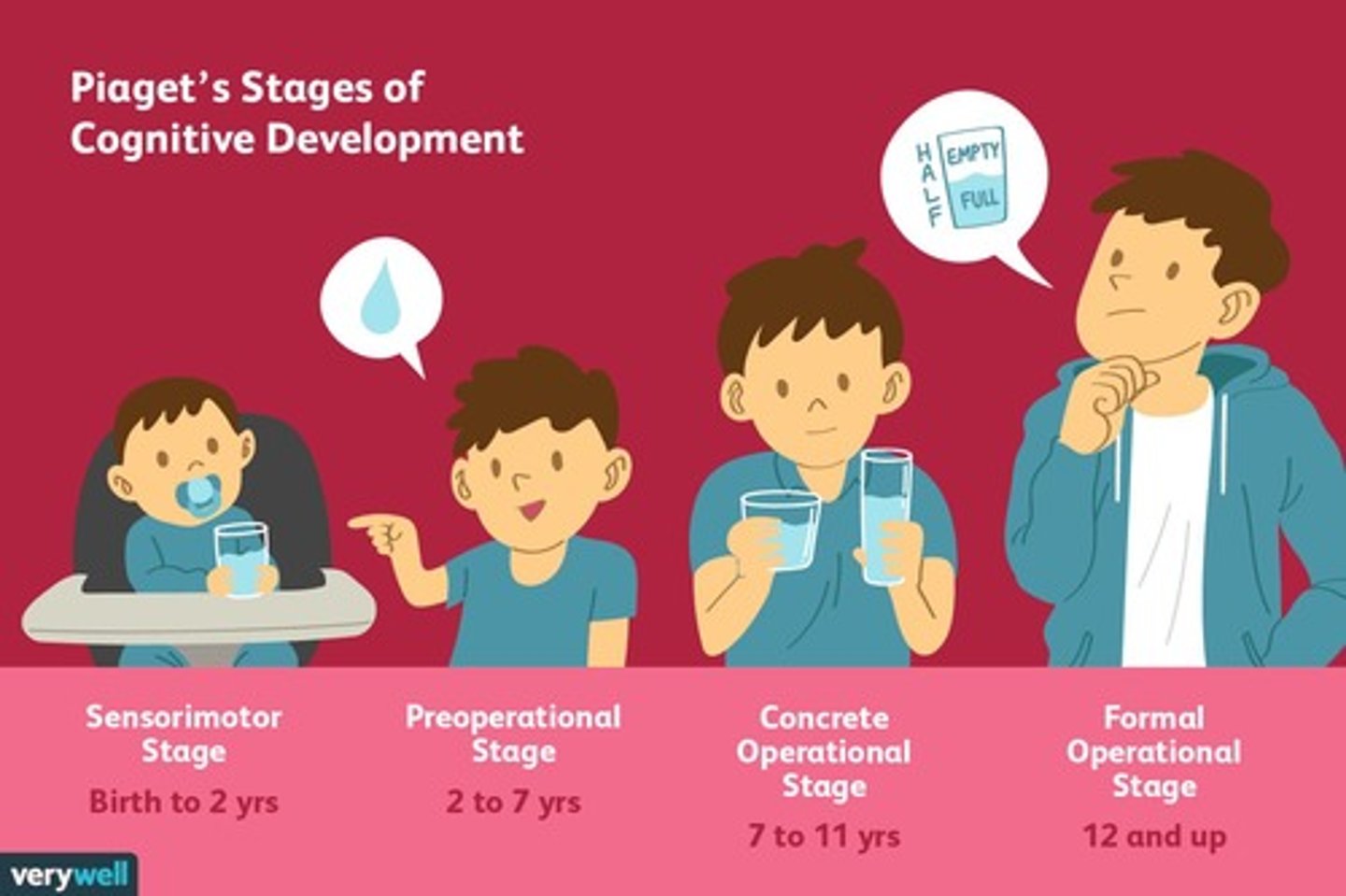
What characterizes the sensorimotor stage?
Infants use sensory and motor capabilities to explore and understand the world.
What is egocentrism in the preoperational stage?
The inability to see things from perspectives other than one's own.
What is theory of mind?
The ability to understand that others have their own mental states, different from one's own.
How does autism affect theory of mind?
Individuals with autism may struggle to understand the mental states of others.
What is the concrete operations stage?
Children can perform mental operations on concrete objects but struggle with abstract concepts.
What is the formal operations stage?
Adolescents can think abstractly and engage in logical reasoning.
What are some critiques of Piaget's theory?
Stages are not distinct, transitions are gradual, and social environment is underestimated.
What is the impact of social comparison on students?
Higher GPA can correlate with lower overall well-being and no correlation with future salary.
What are some tips for flourishing in life?
Focus on commitments that bring enjoyment, prioritize quality over quantity, and maintain good sleep and exercise habits.
What is the role of self-compassion in motivation?
Practicing kindness to oneself can enhance motivation and improve interactions with others.
What did Harlow's monkey experiments demonstrate?
Monkeys preferred contact comfort from a cloth mother over the wire mother providing food.
What benefits does skin-to-skin contact provide for newborns?
Regulates heart rate, breathing, body temperature, improves sleep, weight gain, and bonding.
How do grades in high school compare to college in terms of importance?
Grades matter less in college than in high school.
What is the predictive value of college GPA on salary five years later?
College GPA is not predictive of salary five years later.
What are some critiques of Piaget's theory of development?
Stages are not distinct, transitions are gradual, underestimated abilities, and ignored the role of social environment.
What are the benefits of play in child development?
Play aids in skill development and learning about rules and roles.
What is joint attention and its significance?
Joint attention involves focusing on what another person is focused on, which is important for language learning.
What is the concept of imitation in child learning?
Children mimic what they see adults do, even unimportant actions.
What is social referencing in children?
Children look to another person's reactions to guide their own behavior.
How does praise affect children's learning?
Praise the process encourages persistence and effort in children.
What is the impact of adult intervention on children's persistence?
Children are less likely to persist in tasks when adults repeatedly solve challenges for them.
What is the value of persistence in child development?
Persistence is crucial for overcoming academic and interpersonal challenges.
What effect does witnessing effort have on children's behavior?
Children who see adults exert effort are more likely to try harder on novel tasks.
What are the characteristics of helicopter parenting?
Helicopter parenting can lead to lack of independence, low confidence, struggles with failure, anxiety, and depression.
What defines authoritarian parenting?
Authoritarian parenting attempts to control behavior according to absolute standards and lacks warmth.
What are the consequences of authoritarian parenting?
Associated with externalizing behavioral problems like aggression and defiance.
What is permissive parenting?
Permissive parenting is nonpunitive and avoids external control, leading to similar behavioral problems.
What is authoritative parenting and its benefits?
Authoritative parenting is rational and empathetic, associated with high school performance and social skills.
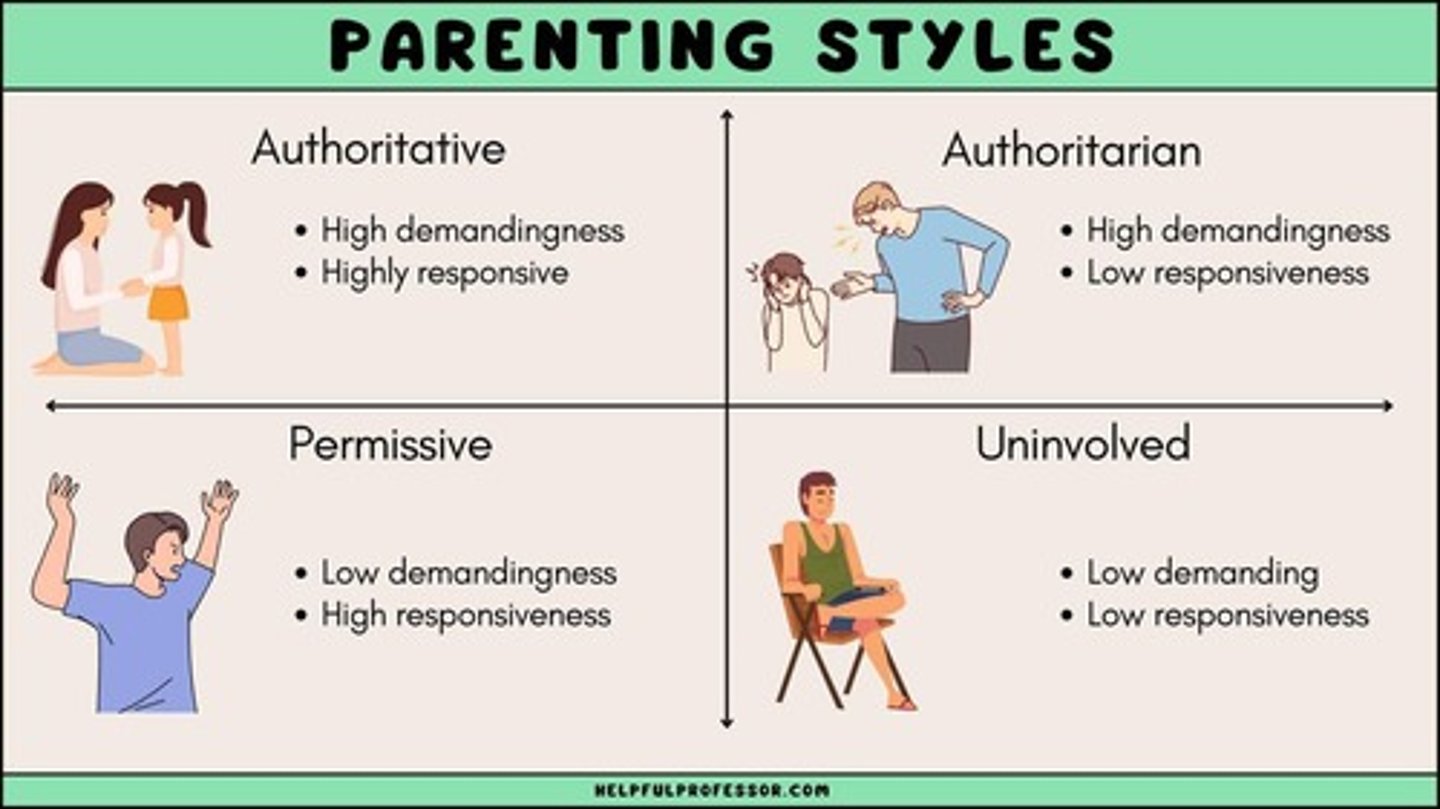
What parenting style is considered the best?
Authoritative parenting is considered the best method.
Are children inherently prosocial?
The note raises the question of whether kids are prosocial.
At what age do children generally start to prefer fair resource allocations?
Around age 7-8.
What is strategic prosociality in children?
Children are more generous when others are aware of their actions.
What is negative reciprocity?
A response where if one child has something taken away, they will take away something from another child in return.
What is positive reciprocity?
A behavior where if one child gives something to another, they expect to receive something in return.
How does adolescence differ from adulthood in terms of role assumption?
Adolescents experience earlier biological maturity but delayed social and economic independence.
Which brain area is known to take the longest to develop?
The prefrontal cortex.
What cognitive skill peaks and then starts to decline around age 60?
Working memory.
What is the marshmallow task used to measure?
Delayed gratification and cognitive control.
How does socioeconomic status affect neurocognitive abilities?
Lack of cognitive stimulation growing up can lead to broad negative impacts on abilities.
What factors are most important for effective teaching?
Enthusiasm, positive relationships with children, high motivation, and commitment.
What traditional view exists about emotions in relation to cognition?
Emotions are seen as chaotic and detrimental to rational thought.
How does the emotional intelligence view differ regarding emotions?
Emotions are seen as adaptive, functional, and essential for organizing cognitive activities.
What are the six qualities of effective presidential job performance?
Public communicator, organizational capacity, political skills, cognitive style, vision, and emotional intelligence.
What is the MSCEIT?
Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test, which measures emotional intelligence.
What does the universality hypothesis suggest about emotions?
There are universal emotions and facial expressions, though cultural influences may affect their interpretation.
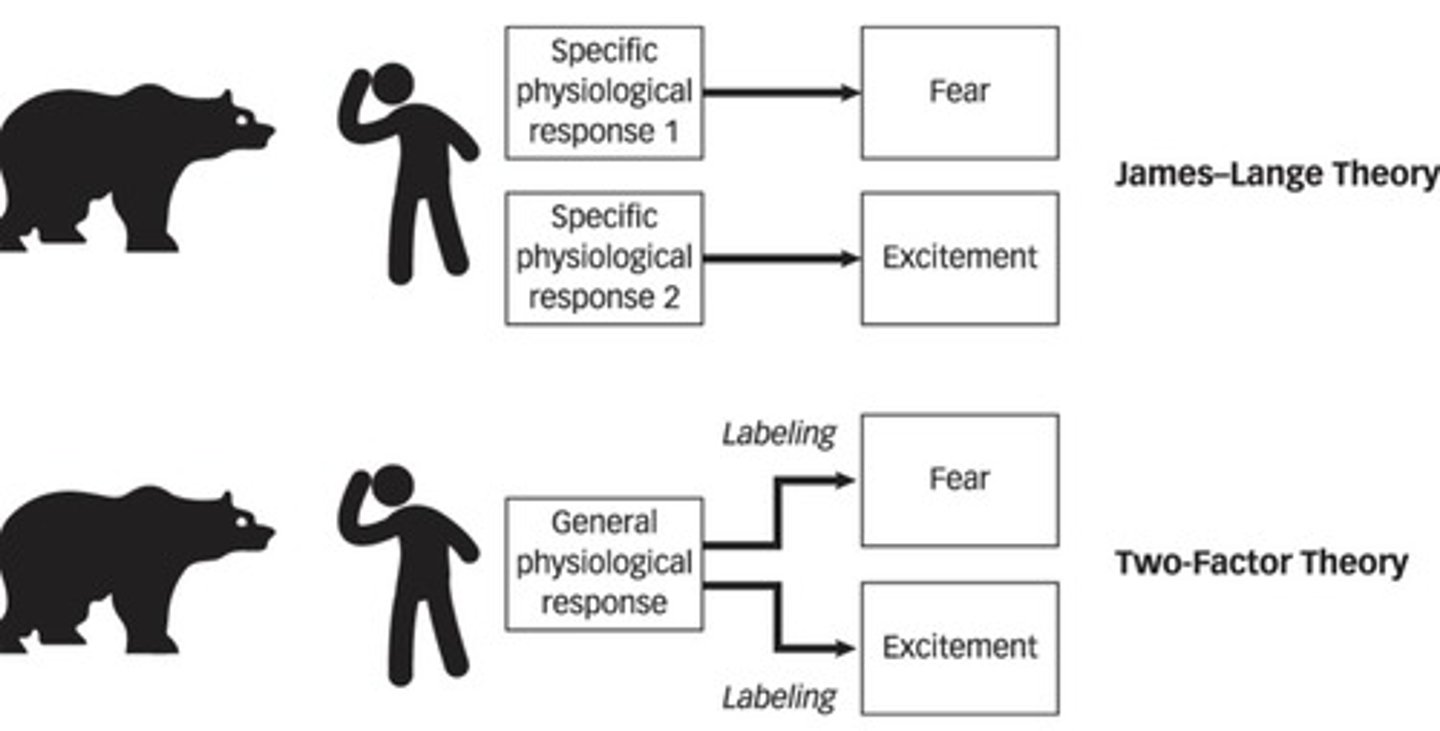
What is the James-Lange theory of emotion?
The theory that the body reacts to a situation first, then we experience the emotion.
What does the two-factor theory of emotion propose?
Different stimuli can produce the same bodily response, but emotions vary based on interpretation.
What is a common misconception about people's ability to detect lies?
People are often unaware of their poor lie detection skills.
Can expressions cause emotions?
Yes, expressions can influence emotional responses.
What is the significance of the amygdala in emotional responses?
The amygdala responds to fearful stimuli and processes fear before the cortex.
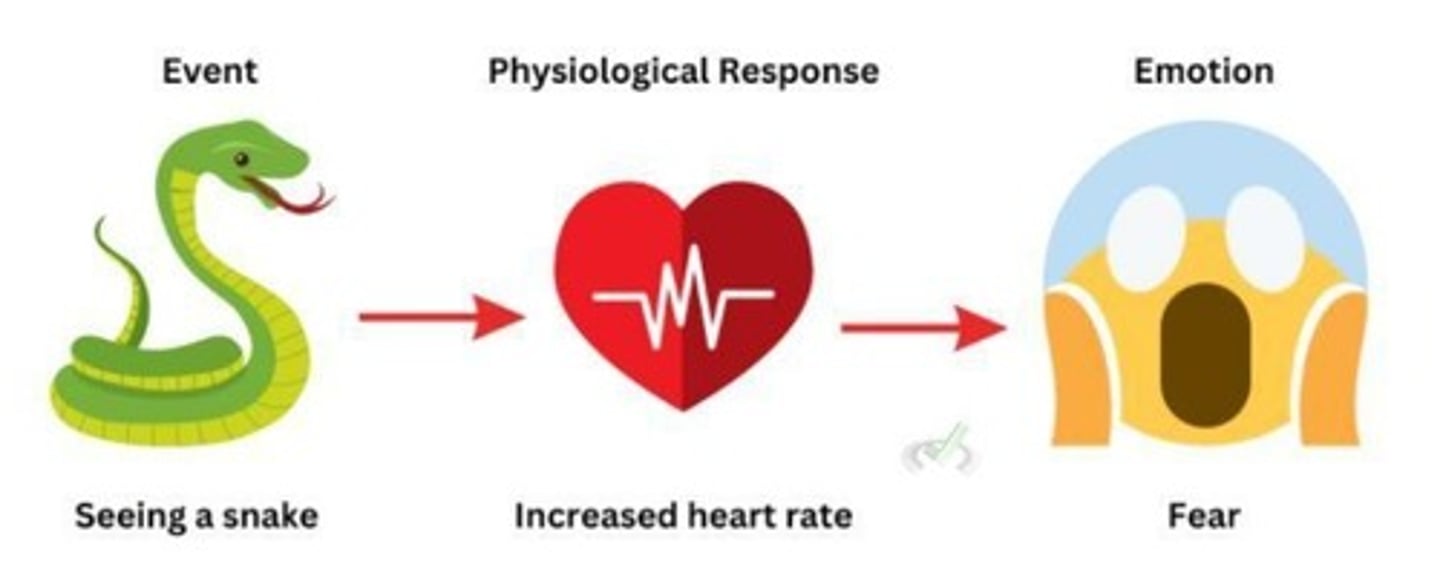
What is the role of appraisal in emotional intelligence?
Appraisal involves evaluations and interpretations of emotion-relevant aspects of stimuli.
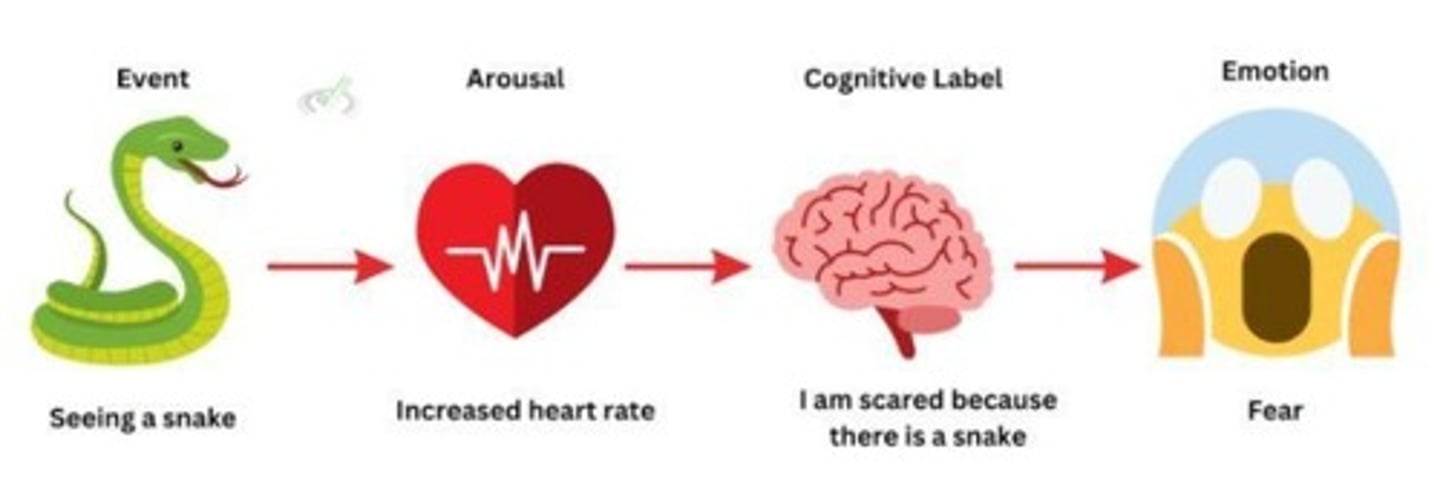
What are action tendencies in the context of emotions?
Readiness to engage in specific behaviors related to emotions.
What is a power pose thought to do?
Make you feel more confident and assertive, but it doesn't work.
What are emotion regulation strategies?
Strategies people use to influence their own emotional experience.
Which emotion regulation strategy is the most effective?
Reappraisal, which involves changing one's emotional experience by altering thoughts about the emotion-eliciting stimulus.
What effect does positive reappraisal have on brain activity?
It reduces negative affect, increases activation of prefrontal regions, and decreases activation of the amygdala.
What is psychopathy?
A personality pathology characterized by charm and engagement but also by evil actions.
At what age do signs of psychopathy typically start to appear?
As early as age 3.
What are some interpersonal traits of psychopaths?
Difficulty establishing genuine relationships, manipulative behavior, and superficial charm.
What are affective traits of psychopaths?
Minimal emotional experiences, lack of empathy, and absence of regret or remorse.
What impulsive traits are associated with psychopathy?
Poor behavioral controls, irresponsibility, and acting without thinking.
What antisocial traits do psychopaths exhibit?
Criminal versatility and early behavior problems, including antisocial behaviors seen as early as age 6.