AP Bio-enzymes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
kinetic energy
energy of motion
potential energy
stored energy
chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
thermodynamics
the transfer of energy as it’s passed from molecule to molecule
anabolic
small molecules that combine and become large molecules
catabolic
large molecules that break down into small molecules
spontaneous reaction
releases free energy, reactants have more free energy
nonspontaneous reaction
consumes free energy, products have more free energy
catalysts
increases the rate of chemical reactions but emerges from the process unaltered
exergonic
releases free energy
endergonic
requires free energy
activation energy
input of energy needed to reach transition state
transition state
time in reactions when chem bonds in reactants are broken and new bonds in products are formed
substrate
reactant
active site
portion of enzyme made up of amino acids that binds substrate & converts to product
activators
increase activity of enzymes
inhibitors
decrease activity
irreversible inhibitor
substances that permanently inactivate an enzyme by forming a strong, often covalent bond at the active site, which blocks the substrate from binding
reversible inhibitor
temporarily binds to an enzyme via non-covalent interactions, slowing its activity without permanently altering it, and can be easily removed to restore the enzyme's normal function
competitive inhibitor
molecules that compete with a substrate for binding to an enzyme's active site
allosteric site
a site other than the active site for a noncompetitive inhibitor to bind
allosteric enzymes
regulatory enzymes that change their catalytic activity upon binding a molecule at a site other than the active site
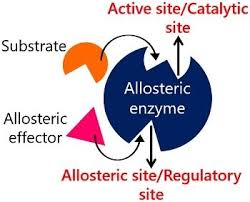
noncompetitive inhibitor
a substance that reduces an enzyme's activity by binding to a site other than the active site, altering the enzyme's shape
metabolic pathway
a series of connected chemical reactions within a cell that convert one molecule into another through a sequence of steps
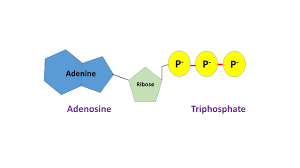
ATP
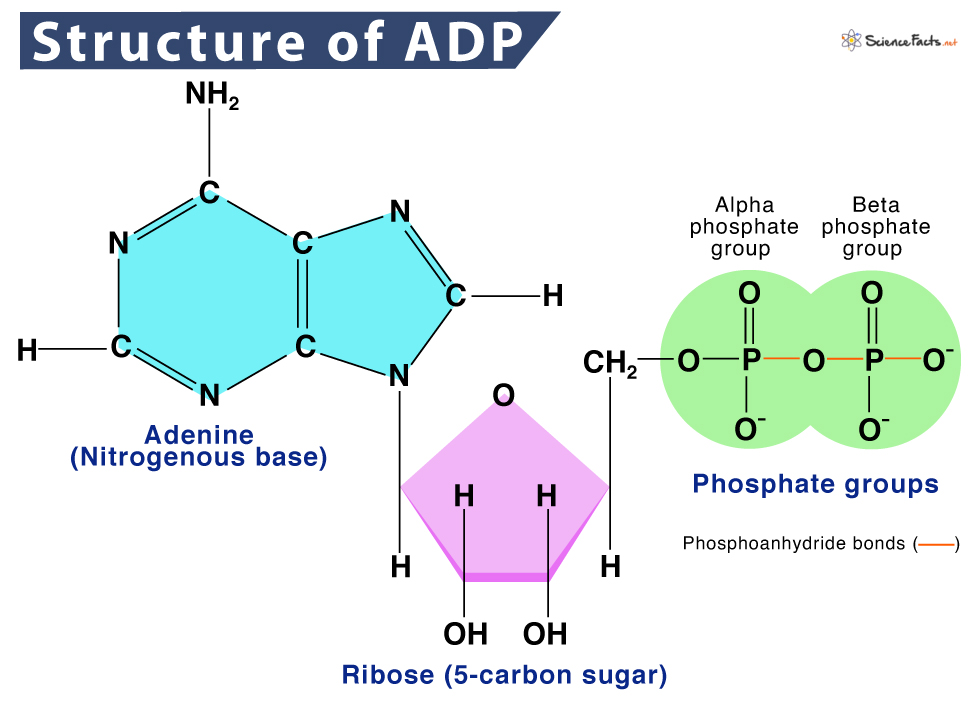
ADP
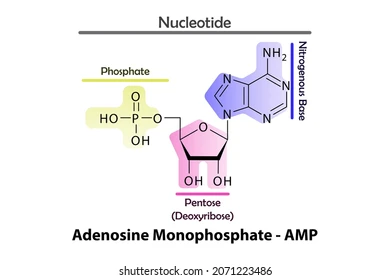
AMP
1st law of thermodyamics
law of conservation of energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another
2nd law of thermodynamics
some of the energy recycled from previous reaction is unusable/entropy
entropy
unavailability of thermal energy
forward reaction
reaction from left to right, reactants are converted into products
reverse reaction
products are converted back into reactants, right to left
Gibbs Free Energy (G)
a thermodynamic potential that measures the maximum amount of non-expansion work a system can perform at constant temperature and pressure.
Endergonic
requires input of energy, absorbs more free energy than it releases
Exergonic
releases free energy
energetic coupling
the process where energy released from one reaction (exergonic) is used to drive another reaction that requires energy (endergonic)
catabolism
the metabolic process where complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones, releasing energy to fuel the body
anabolism
the set of metabolic processes that build complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy to do so