AP Economics UNIT 5: FACTOR MARKETS
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Physical Capital
Consists of manufactured productive resources such as equipment, buildings, tools and machines
FOUR MAIN CATEGORIES
LABOR
LAND
CAPITAL
ENTRERPRENEURSHIP
Human Capital
improvement in labor created by education and knowledge embodied in the workforce
Derived Demand
The demand of a factor it results or is derived from the output being produced
Factor Distribution of Income
Division of total income among land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship
WHERE IS IT GOING?
changes depending on the economy
E.G. industrial revolution increased portion put into factories, decreased portion put into farmers
Employment compensation
return on human capital/experience
E.G high payment/salary for doctors
Marginal Productivity
The amount of product gained with the next worker
Why does Marginal Product go down?
Law of diminishing returns
IT IS ALSO KNOWN AS Marginal Product of Labor
DOWNWARD SLOPING
In factor markets, firms buy ______ and households sell _______
inputs, inputs
Marginal Revenue Product of Labor
ALSO KNOWN AS MRP
the additional revenue generated by employing one more unit of that factor
FORMULA: MP/MPL * P
Firms continue to hire more workers until the ———- equals the —————-
MRPL/MRP, wage rate
Shifts of the Factor Demand Curve
THREE CAUSES
Changes in price of goods (P increases, MPR increases)
Changes in supply of other factors
Changes in technology
Rental Rate
the cost, explicit/implicit, of using a unit of that assets for a given period of time → mostly applies to land and capital
Equilibrium Marginal Revenue Product
The additional revenue generated by the last unit of that factor employed in the factor market as a whole
**Look at it the same as price, all inputs are paid the equilibrium marginal revenue in that market
Economic Rent
payment to a factor of production in excess of the minimum payment necessary to employ that factor
Increasing Q of productive land, High costs, finite determines inelasticity
What is this even saying?
Marginal Productivity Theory
Every factor of production is paid the equilibrium marginal revenue product
E.G. wage rate earned by chefs = MRP (of the last pastry chef)
Time Allocation
how many hours to spend on different activities
Leisure
free time of the 24 hours/everything that time available for purposes is NOT other than earning money to buy goods/work
Substitution Effect
At a higher wage, work becomes more valuable than leisure, so workers work more
Income Effect
at a higher wage, leisure is more affordable, so workers work less
hours dependent on wage
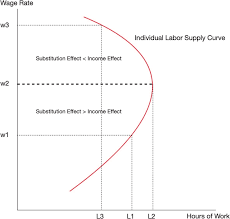
Individual Labor Supply Curve
→ demonstrates how Q of labor supplied by an individual depends on that individual’s wage rate
Top half: Income
Bottom half: Substitution
Shifts of Labor Supply Curve
4 CHANGES
Changes in preferences/social norms E.G. women in workforce
Changes in population E.G. population growth
Changes in opportunities E.G. opportunities of women in STEM
Changes in wealth E.G wealth increasing, working less
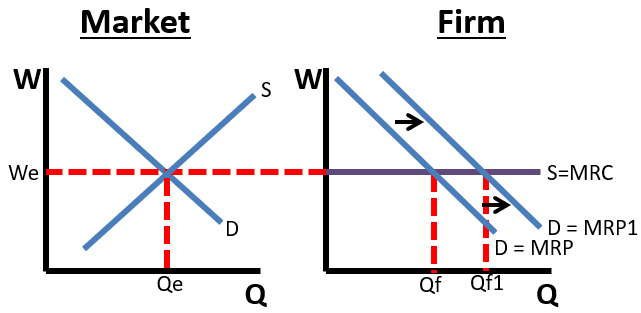
Perfect Competition
paid more + higher more workers
MANY SMALL FIRMS
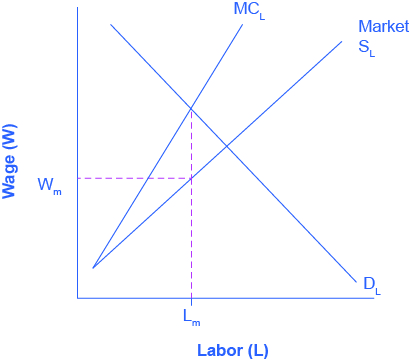
Imperfect Competition
hire fewer workers + pay less
RUN BY A MONOPSONIST
Marginal Factor Costs
The additional costs of employing the next unit of a factor of a product
Monopsonist
A single buyer of a factor/ all workers work for one person→ have to pay all workers fair + increas pay of preexisting workers
MFC
change in total labor costs per each hired worker
For Imperfect Competition + Perfect competition
Firms should hire until MRP = MFC
To get perfect competition off of a imperfect competition graph, wait until…
S=D
Firm’s profit from MRP graph
output price - (marginal factor cost * workers) OR total wage paid to workers
How to determine if perfect competition or imperfect competition
MFC constant → perfect
MFC changing → imperfect
You hire for MPR = WAGE RATE until the number is
hit, NOT AFTER
Rental rate is difference between
two demand curves
THE WHOLE CHUNK IS PROFIT THAT GOES TO THE PERSON RENTING IT OUT
increased productivity
MORE WORKERS HIRED, MORE PROFIT + PRODUCT BROUGHT IN
Wage isnt constant in imperfect competition
to balance keeping wages low and attract workers in to create a single hiring agent