hematopoiesis (hematology exam 2 topic)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells
stem cells
undifferentiated cells that differentiate into specific types of cells (RBC, WBC, etc)
can stem cells renew themselves?
yes, stem cells renew themselves
compartments of hematopoiesis
1. stem cells
2. progenitor cells
3. precursors of specific cell lines
where are stem cells located
stem cells are located in the bone marrow
where are progenitor cells located
progenitor cells are located in the bone marrow
where are precursors of specific cell lines located
precursors are located in the bone marrow and in the blood
which of the three compartments of hematopoiesis are identifiable?
only precursors are morphologically identifiable
types of stem cells
1. uncommitted stem cells
2. hematopoietic stem cells
hematopoietic stem cells
-precursor for RBC, WBC, and platelets
-capable of self-renewal and pluripotency
-morphologically unidentifiable
progenitor cell compartment
-committed to one specific cell line
-form morphologically recognizable cells
-known as CFC or CFU- form colonies of cells in culture (in vitro)
-morphologically unidentifiable
erythropoiesis
formation of red blood cells
origin and development of erythropoiesis
bone marrow
progenitor cells of erythropoiesis
BFU-E and CFU-E
precursor cells of erythropoiesis
-normoblasts (nucleated red cells)
-produced in response to erythropoietin
erythropoietin (EPO)
stimulates the production of red blood cells
identifying stages of erythrocyte maturation
1. cell size and shape:
- immature cells are large and become smaller as they mature
2. cytoplasm staining reaction
- immature NRBC have lots of RNA so they stain intensely blue
3. nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio
- immature NRBC have a big nucleus at first and then it decreases with maturation (and eventually expelled)
4. nuclear staining reaction
-early stages=reddish-purple and as it condenses it becomes dark purple, almost black
5. nuclear chromatin pattern
-early stages it is evenly distributed and you can see nucleoli
normoblastic maturation sequence
1. pronormoblast
2. basophilic normoblast
3. polychromatic normoblast
4. orthochromatic normoblast
distribution of erythroblasts
-quantitative distribution of NRBC in the bone marrow
-distribution of NRBC in the blood
-if any NRBC is seen in differentiation count, they are counted separately
megaloblastic maturation
-type of dyserythropoiesis (production of abnormal erythroid cells)
etiology of megaloblastic maturation
-associated with vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency
ineffective erythropoiesis
many cells die and undergo phagocytosis in the BM
progenitor cell for megakaryocytes and platelets
CFU-MK
megakaryocytes and platelets
-thrombopoietin regulates production
-progenitors develop through endomitosis
maturation sequence for megakaryocytes and platelets
1) megakaryoblast
2) promegakaryocyte
3)megakaryocyte
4) platelets
neutrophils
-progenitor cell = CFU-GM (shared with monocytes)
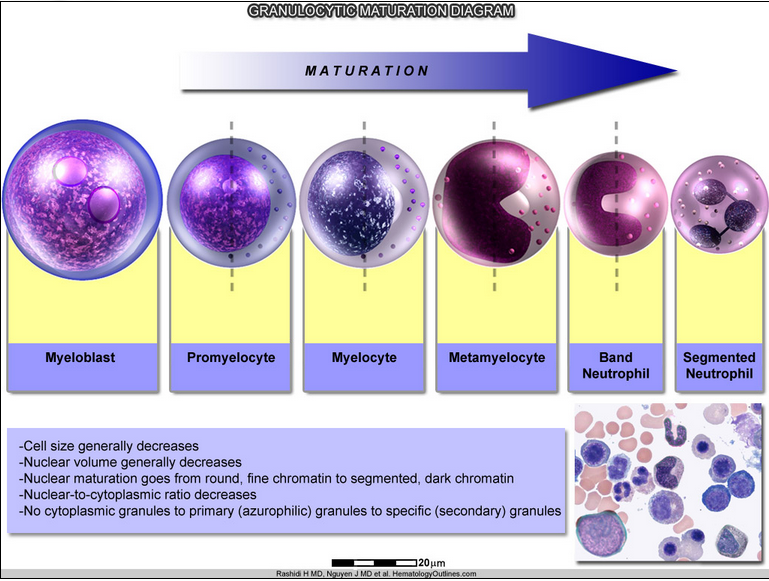
neutrophil maturation sequence
1. myeloblast
2. promyelocyte
3. myelocyte
4. metamyelocyte
5. band
6. segmented
(purple=BM, Black=blood)
neutrophilia
-increased
>7.2×10^9/L
neutropenia
-decreased
<2.0×10^9/L
neutrophils are…
bacterial related
neutrophil function
-phagocytosis and destruction of foreign bodies
-chemotaxis= brings neutrophils to site
-opsonization=neutrophil receptors recognize opsonization that potentiate phagocytosis
-degranulation=release the content of granules in other to kill pathogens
morphologic alteration in neutrophils
activated by invading organisms (“reactive changes”)
dohle's bodies
-blue/purple inclusions in cytoplasm
-remnants of ER or ribosomes
-not normal
-not specific
Eosinophil progenitor
- CFU-Eo
origin and development of eosinophils
bone marrow
maturation sequence of eosinophils
1) myeloblast
2) promyelocyte
3) eosinophilic myelocyte
4) eosinophilic metamyelocyte
5) eosinophilic band
6) eosinophil
eosinophil are…..
parasite related
function of eosinophils
-response to foreign pathogens (parasites)
-capable of phagocytosis
origin and development of basophils
Bone marrow
basophils are…..
allergy related
basophil progenitor
CFU-Baso
functions of basophils
-response to foreign proteins
-release of histamine and other mediators
monocyte and macrophage progenitor cells
-CFU-GM (shared with neutrophils)
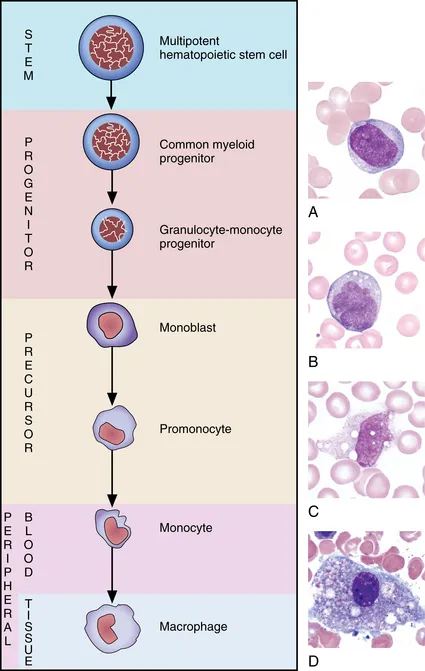
maturation sequence for monocyte and macrophage
1. myeloblast/monoblast
2. promonocyte
3. monocyte
4. macrophage
(purple=BM, black=blood, Blue= tissue)
monocytes and macrophages are…..
immune related
origin and development of monocytes and macrophages
bone marrow
function of monocyte/macrophage
-phagocytosis
-participation in immunologic reactions
origin and development of lymphocytes
-initially developed in central (primary) lymphoid organs and then further developed in peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissue.
B-cells= bone marrow
T-Cells= thymus
lymphocytes are…..
viral related
two major populations of lymphocytes
CD4+ (T helpers) and CD8+ (T cytotoxic)
T-cell functions
responsible for cellular immunity
B-cell functions
responsible for humoral immunity
function of lymphocytes
-plasma cells secrete antibodies
-response results in distinctive changes- reactive lymphocytes are formed.
all cellular components are derived from…?
haematopoietic stem cells