Polymers, Structures and Types
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
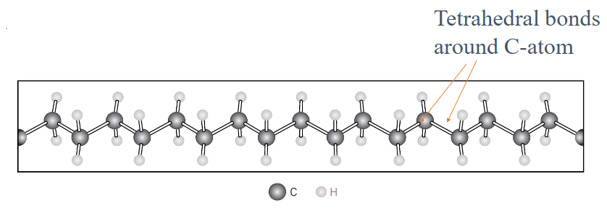
What is the basic backbone structure of most polymers?
A carbon–carbon (C–C) covalently bonded backbone, with tetrahedral bonding around each carbon atom
What defines a linear polymer molecule?
Very long chains built from repeating monomer units
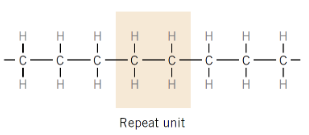
What type of bonding exists within polymer chains?
Strong covalent bonds
What holds polymer chains together?
Van der Waals forces between chains
What is the C–C bond angle in polymer chains?
Approximately 109°, defining a possible cone in 3D
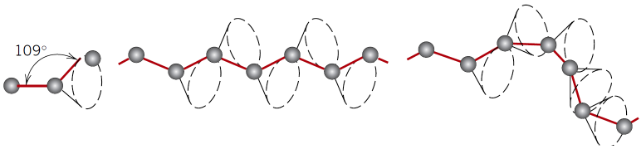
Why don’t polymers form simple crystal structures?
Chains are very long, tangled, and exist in 3D space

What is polymer crystallinity?
Regular packing of polymer chains despite the lack of a simple crystal lattice
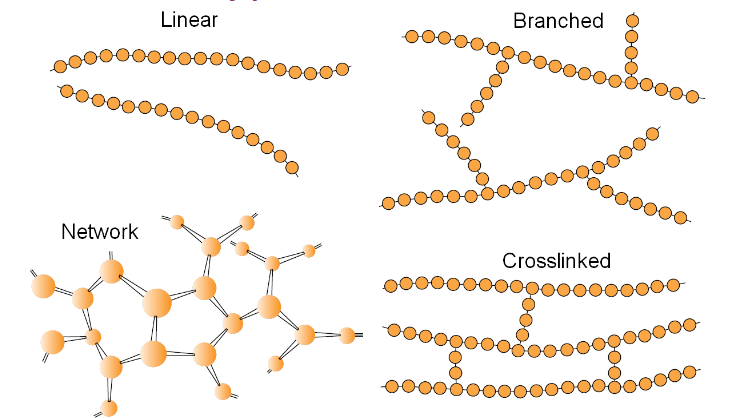
What are the 3 main polymer chain structures?
• Linear
• Branched
• Cross-linked (or network)
Do polymers have uniform chain lengths?
No, they have a distribution of chain lengths after polymerisation
What are linear polymers also called?
Thermoplastics
Why does tensile strength increase with molecular weight?
Longer chains are more entangled and better anchored
Why do polymers flow and deform more at high temperatures?
Van der Waals forces weaken, allowing chains to slide
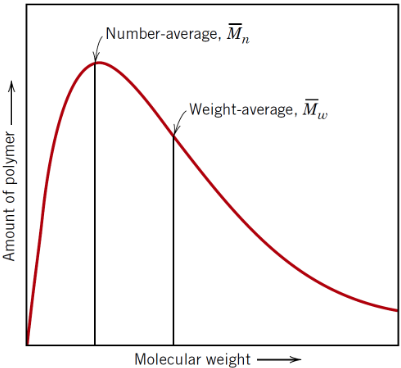
What is number-average molecular weight (Mn)?
Average molecular weight per molecule in a polymer sample, counting all molecules equally

Formula for number-average molecular weight (Mn)
• Mi = Mean molecular weight of size range i
• xi = Fraction of the total number of chains within the size
range
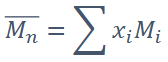
What is weight-average molecular weight (Mw)?
Average molecular weight of a polymer sample, weighted toward heavier chains (making it especially useful for predicting material properties)
Formula for weight-average molecular weight (Mw)
• Mi = Mean molecular weight of size range i
• wi = Weight fraction of the total number of chains within the
size range
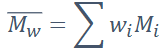
What happens when polymers cool from the liquid state?
They may become amorphous or crystalline at the melting temperature (Tm)
How does crystallinity affect specific volume?
It reduces specific volume due to increased order
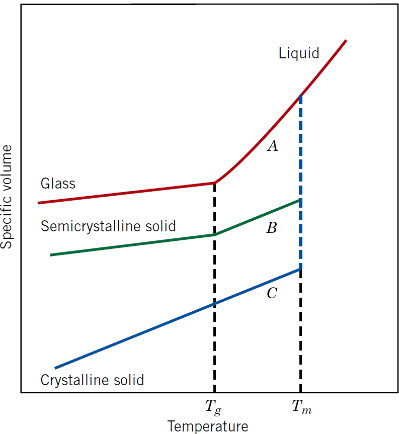
Why is crystallisation easier in smaller, regular chains?
They pack more efficiently
How does molecular structure affect movement in crystalline polymers?
Molecular movement is difficult because the chains are tightly packed
What is Tg?
Glass Transition Temperature, below which polymer chain movement is restricted
What happens below Tg for amorphous and semicrystalline polymers?
Molecular movement (chain sliding) is prevented
Why is polymer crystallisation usually partial?
Chains have different lengths and cannot pack perfectly

How does crystallinity affect mechanical properties?
Increases stiffness and strength due to closer chain packing
What is a spherulite?
A 3D crystalline structure made of lamellar chain-folded crystallites, it is the most common crystalline structure in polymers
What separates lamellae in a spherulite?
Amorphous polymer regions

What optical feature do spherulites show under crossed polarised light?
A Maltese cross pattern

What is the structure of elastomers?
Lightly cross-linked polymer chains, such that chain sliding (i.e.
deformation) is still possible
Why do elastomers return to their original shape?
Chains are lightly pinned and so return to their original shape when stress is removed
Why do polymer chains want to coil?
Chains prefer a coiled, high-entropy state (i.e. rubbers are effectively entropy springs)
How do elastomers differ from thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics (thermosets)?
They are lightly cross-linked and behave as entropy-driven elastic materials
What defines thermosets?
A 3D covalently bonded network structure
Why can’t thermosets be remelted?
The covalent network is destroyed at high temperatures
Describe the mechanical properties of thermosets
• Higher stiffness and strength than thermoplastics, but brittle with poor impact properties (i.e. chains can’t slide)
• Good dimensional stability (i.e. no creep as chains can’t slide)