2.2.3 carbohydrates
1/40
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is an isomer?
where a molecule has two different forms- same chemical formula but different structures (glucose)
What is an OH group known as?
hydroxyl group
What are the two isomers of glucose?
(Alpha)α-glucose and (Beta)β-glucose
Whats the difference between α-glucose and β-glucose?
In α-glucose the OH group at carbon 1 points below the ring whereas in β-glucose, the OH group points above the ring
Whats the structure of glucose?
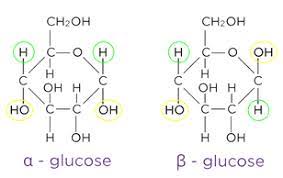
What are examples of carbohydrates?
sugar and starch
Whats the formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
What are the only elements carbohydrates contain?
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What are monosaccharides with 6 carbon atoms called? Whats an example?
hexose monosaccharides - glucose
Whats a monosaccharides?
singles sugar molecules
What are exampes of monosaccharides?
fructose, galactose and glucose
What does a molecule being hydrophillic mean?
they dissolve in water
Whats the solubility of glucose like? Why is it useful?
Its structure makes it very soluble because its the main energy source in animals and plants so needs to be easily transported
What are monosaccharides with 5 carbon atoms called? Whats an example?
pentose monosaccharides - ribose
Whats the stucture of ribose?
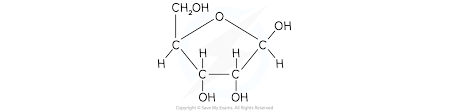
What happens when a disaccharide is formed?
two monosaccharides are joined together by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction - during synthesis a hydrogen atom on one monosaccharide bonds to a hydroxyl group on the other, releasing a water molecule
what happens when disaccharides are broken down?
the reverse of the synthesis reaction is through a hydrolysis reaction- a water molecule reacts with the glycosidic bond, breaking it apart
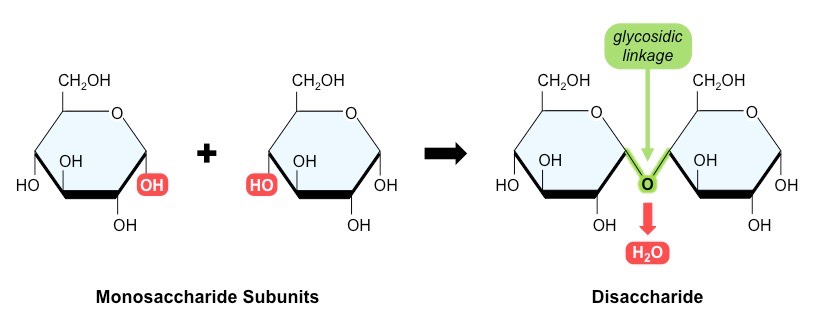
what happens when two a-glucose molecules form a disaccharide?
they are joined together by a glycosidic bond to form maltose
when is the disaccharide sucrose formed?
when a-glucose and fructose join together
when is the disaccharide lactose formed?
when galactose and either a/b glucose join together
when does a polysaccharide form?
when more than two monosaccharides join together
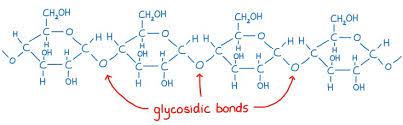
what happens when many a-glucose join to form a polysaccharide?
they are joined together by glycosidic bonds to form amylose
what are 3 examples of polysaccharides?
starch, glycogen and cellulose
What is the main energy storage material in plants?
starch
How do glucose and starch link within plants?
plant cells get energy from glucose and plants then store excess glucose as starch for when they need more(starch gets broken down into glucose again)
Why is starch good for storage?
its insoluble in water =doesnt cause water to enter cells by osmosis which would make them swell
glucose is soluble so gets stored as starch
what polysaccharides is starch a mixture of? What are they formed from?
amylose and amylopectin - formed from alpha glucose
Whats the structure of amylose like?
long UNbranched chain of a-glucose linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
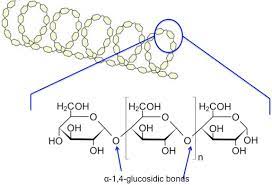
Why is the structure of amylose good for storage?
the angles of the glycosidic bonds = coiled structure almost cylinder like = makes it compact= good for storage as can fit more in to a small space
Whats the structure of amylopectin like?
long branched chain of a-glucose linked by 1,4 and 1,6(branches) glycosidic bonds
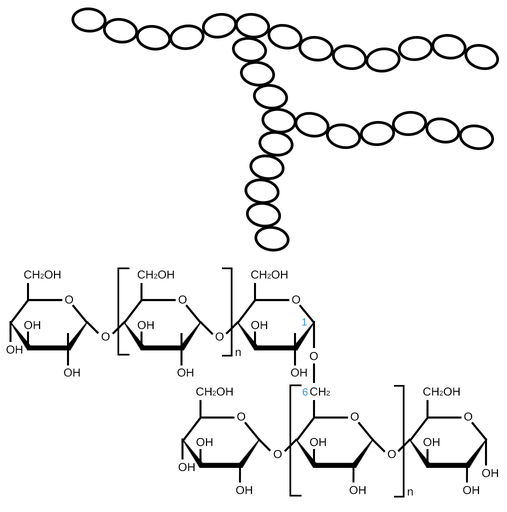
Why is the structure of amylopectin good for releasing glucose quickly?
side branches = allow enzymes to break down the glycosidic bonds easily = glucose released quickly
How do you test for starch?
iodine solution= turns from orange/brown to blue/black
What is the main energy(glucose) storage material in animals?
glycogen
What is the structure of glycogen like?
highly branched chain of alpha glucose units linked by 1,4 and 1,6 (branches) glycosidic bonds
How is glycogen good for storage?
loads of branches=stored glucose can be released quickly as glycosidic bonds can be broken easier
very compact molecule= more can fit in to a small place easier
Why is glycogen more branched than starch?
animals are more metabolically active than plants so they need more glucose readily for glycolysis
What is the major component for cell walls in plants?
cellulose
Whats the structure of cellulose like?
long straight UNbranched chains of beta glucose linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
How are cellulose chains linked together?
via hydrogen bonds
What do many cellulose chains linked together create?
microfibrils (strong fibres)
What is the function of microfibrils(strong fibres) in cellulose?
means cellulose provides strong structural support for cells (eg plant cell walls)