AP Psychology Unit 2.8 Intelligence
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations

general intelligence (g)
the idea that one general factor underlies intelligence
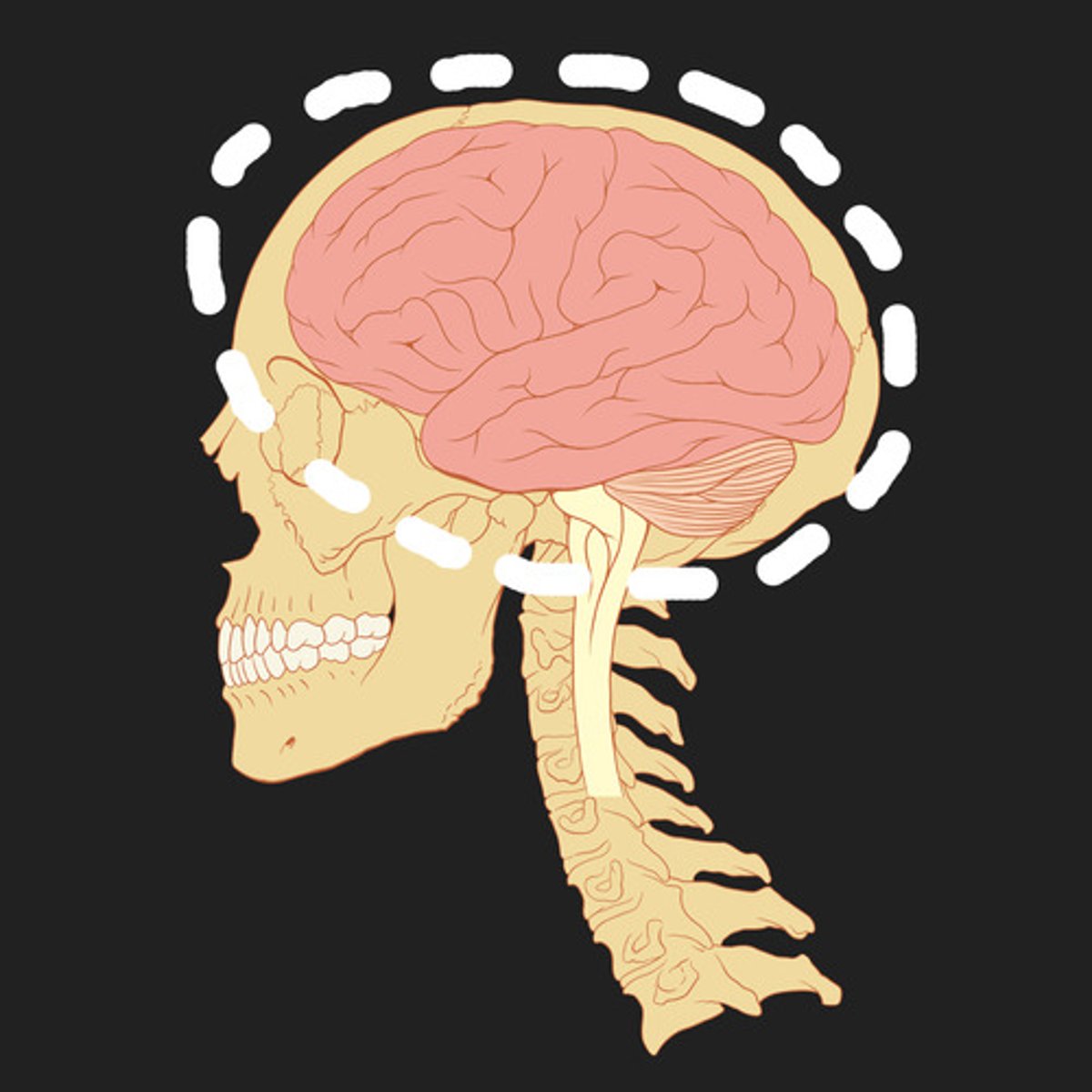
fluid intelligence (Gf)
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood

crystallized intelligence (Gc)
one's accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age

grit
passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals

intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores

achievement test
measures how much a person has learned in a given subject or area

aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance

mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance

intelligence quotient (IQ)
defined originally as the ratio of mental age to chronological age multiplied by 100

standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group

test bias
systematic differences in test scores among groups of students that arise from factors unrelated to their actual abilities.
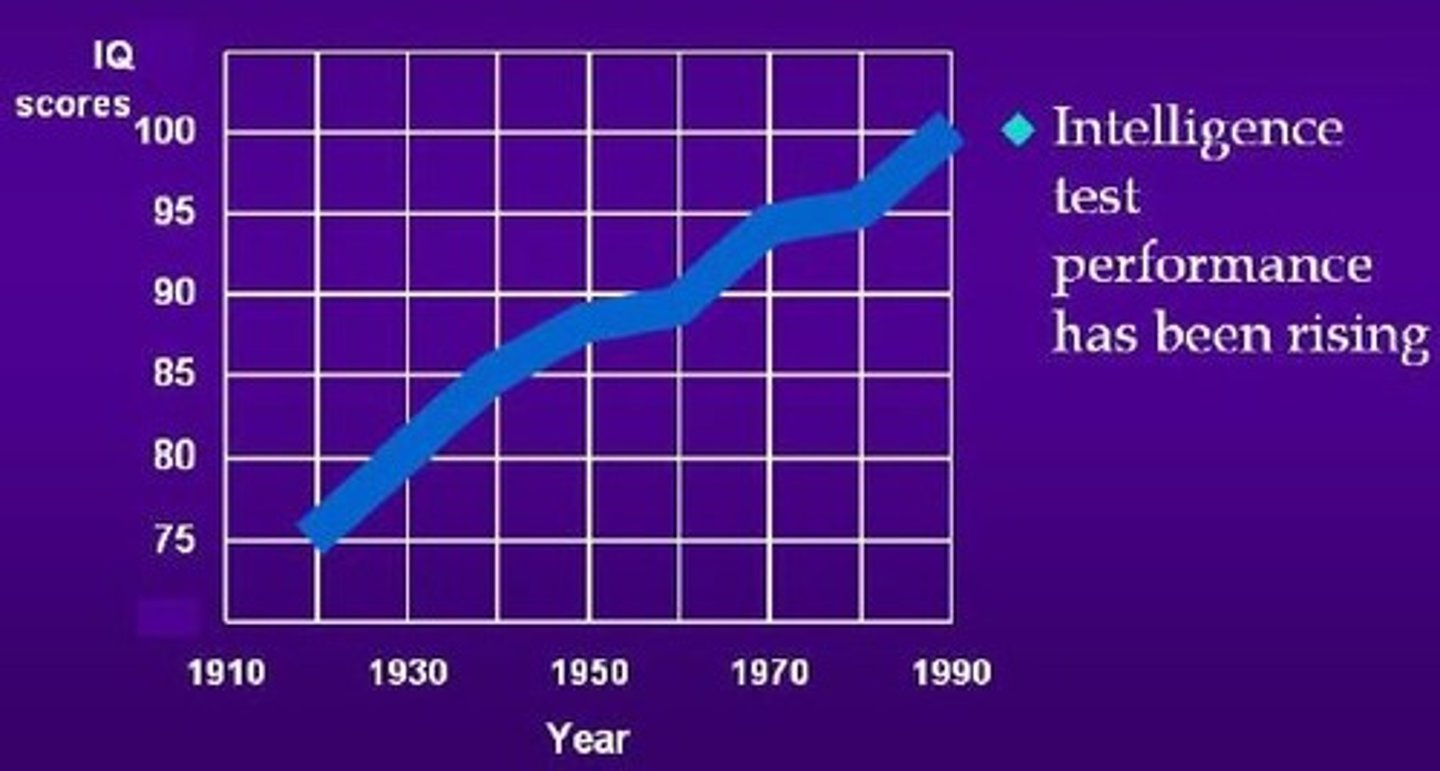
Flynn Effect
the worldwide phenomenon that shows intelligence test performance has been increasing over the years
reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, on alternate forms of the test, or on retesting

validity
The ability of a test to measure what it is intended to measure

construct validity
The extent to which there is evidence that a test measures a particular hypothetical construct.

predictive validity
the extent to which a score on a scale or test predicts scores on some criterion measure

cross-sectional study
research that compares people of different ages at the same point in time

longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
cultural test bias
partiality of a test in favor of individuals from certain backgrounds at the expense of individuals from other backgrounds.
Growth vs Fixed Mindset
Fixed mindset: intelligence is biologically set and unchanging
Growth mindset: intelligence is changeable if you learn more (better mindset for career success)

Stereotype Threat
the apprehension experienced by members of a group that their behavior might confirm a cultural stereotype

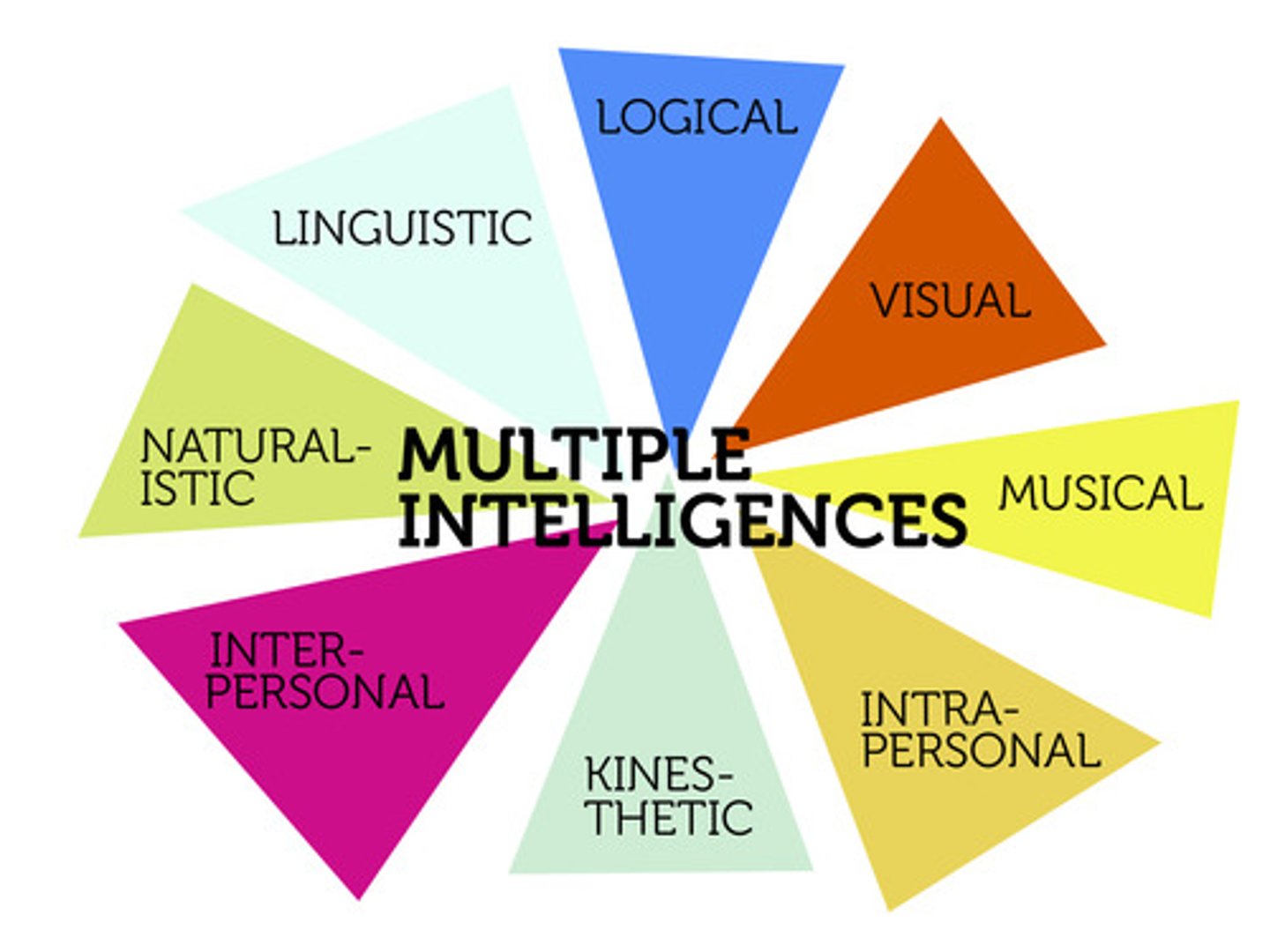
Multiple Intelligence
individuals possess different types of intelligence beyond traditional measures, such as linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic intelligences.
test-retest reliability
assesses consistency by administering the same test to the same group twice. It measures how stable scores are over time

split-half reliability
divides a test into two halves and compares scores between them. It measures internal consistency by checking if both halves yield similar results.

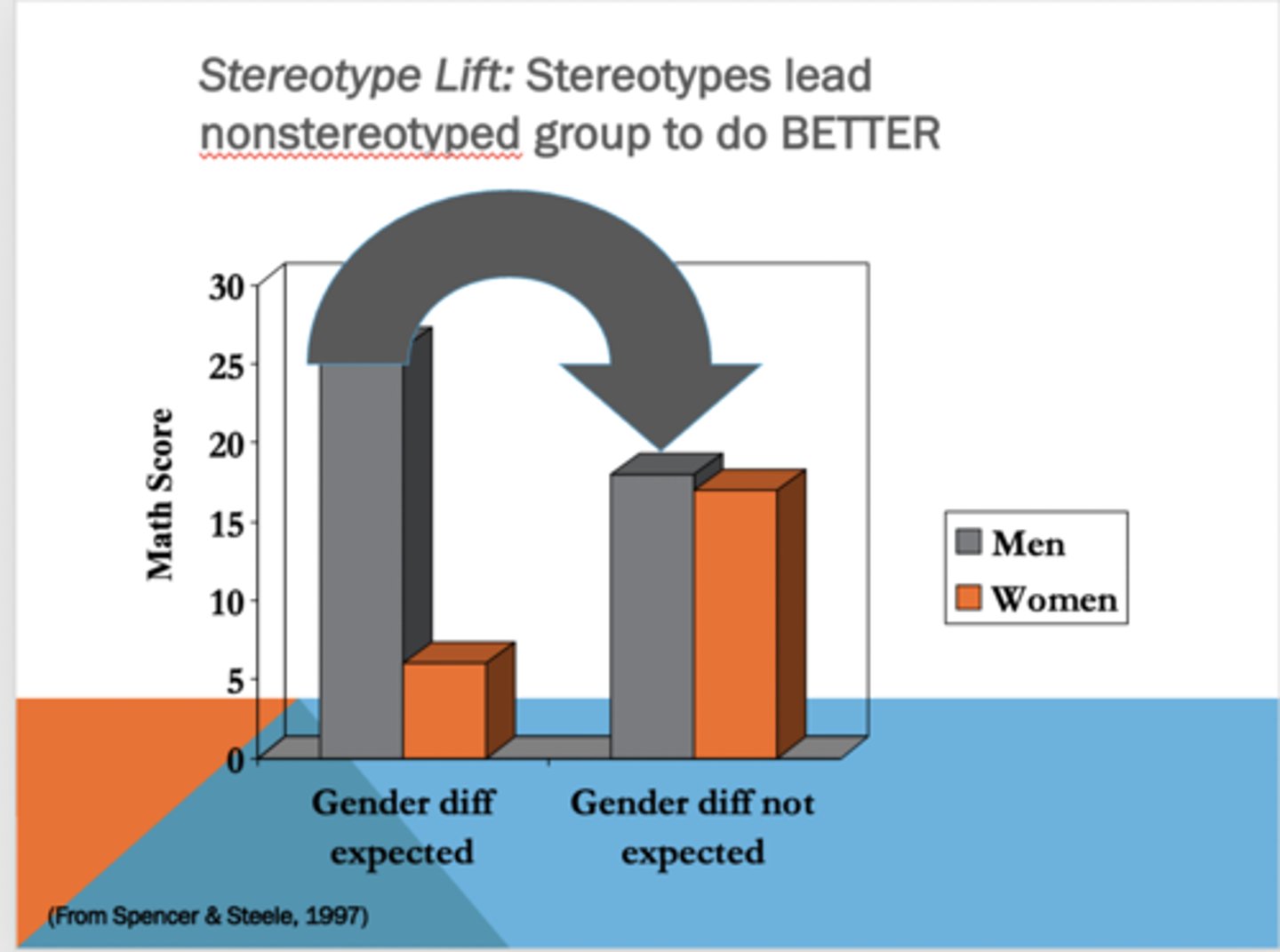
Stereotype Lift
occurs when individuals from stereotypically advantaged groups perform better on tests due to the positive expectations associated with their group
Chronological Age
actual age
self-fulfilling prophecy
an expectation that causes you to act in ways that make that expectation come true.
