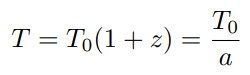Astrophysics Equations
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Newtons Law
F = ma
Pressure
ρ = M/V
Volume of a sphere
V = 4/3πr3
Magnitude when m0 is known
m = -2.5logF + m0
Magnitude (two stars)
m1 - m2 = -2.5logF1/F2
Momentum
p = mv
Angular Momentum
L = r x mv
Gravitational Force
F = -GMm/r2
Distance Modulus
m - M = -5 + 5logd (d in parsec)
Centripetal force
F = mv2/r
Photon Energy
E = hf
Photon momentum
p = E/c
Kinetic Energy
Ek = ½mv2
Wien’s Displacement law (estimating the surface temp of a star)
λmax ∝ 1/T
Potential Energy
Ep = -GMm/r OR mgh
Stefan-Boltzman law (Observational Astrophysics)
F = σT4
Escape velocity
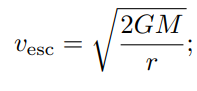
Orbital Velocity
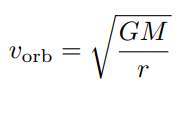
Effective Temperature
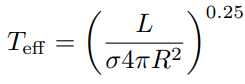
Distance and Parallax
d = 1/p (d in parsec; p in arcsec)
Lens Formula
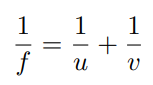
Lens Magnification
M = -v/u
telescope Magnification
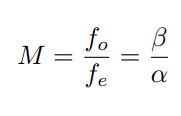
proper motion and velocity (speed of movement of a star in the sky)
v = µ x 4.74 x d (in arcseconds/year)
Flux and Luminosity relationship
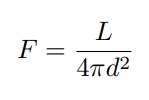
Resolution
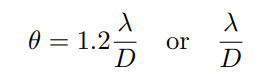
Gravitational potential energy for a star
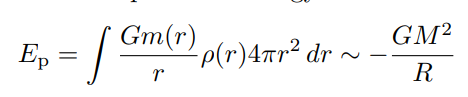
Snells law
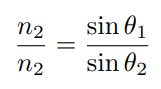
Kelvin_Helmholtz timescale (over which internal energy is radiated away in a star)
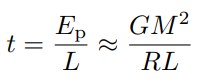
Grating
d sin θ = mλ
Schwarzschild radius
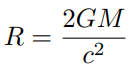
Orbital period (kepler)
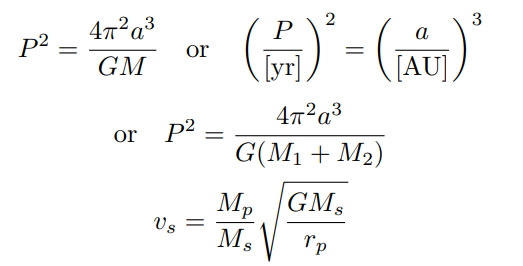
Rotation Curves (galaxies)
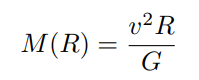
redshift
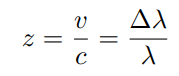
Temperature of a planet
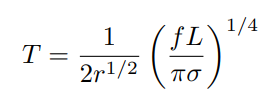
Hubble Law
v = H0r; H0 = 70 ± 5 km s-1Mpc-1
Hubble Time
t = 1/H0
Virial Theorem
Ep + 2Ek = 0 or Ep + 2Eth = 0
Critical Density
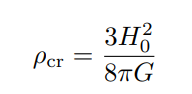
Hydrogen Line Spectrum
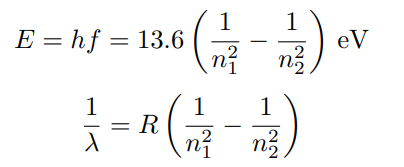
Dynamical Timescale
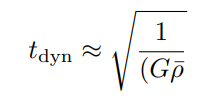
Hydrostatic equilibrium and gravity
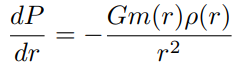
ideal gas law
P = nkT
Thermal Energy
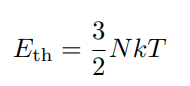
Scale factor
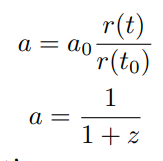
Hubble ‘constant’
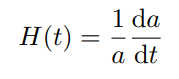
density parameter (relating to hubbles law)
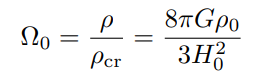
Friedmann equation
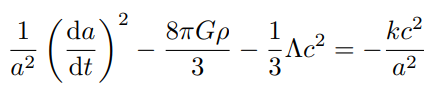
CMB Temperature