Bio Exam #1
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:53 AM on 1/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Eukaryote
\- has a nucleus
\- animals, plants, fungi
\- animals, plants, fungi
2
New cards
Prokaryote
\- no nucleus
\-
\-
3
New cards
3 domains of life
archaea, bacteria, eukarya
4
New cards
metabolism
chemical process that by which cells convert energy from one form to another, and build and break down molecules
5
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy of motion
6
New cards
potential energy
stored energy that is released by a change in an object’s structure or position
7
New cards
catabolism
the set of chemical reactions that break down molecules and produce ATP to meet the energy needs of the cell
8
New cards
anabolism
the set of chemical reactions that build molecules utilizing an input of energy (ATP)
9
New cards
hydrolysis
a chemical reaction of the interaction of chemicals with water, leading to the decomposition of both the substance and water
10
New cards
phototrophs
energy from sunlight
11
New cards
chemotrophs
energy from chemical compounds
12
New cards
chemoheterotrophs
energy and carbon from organic molecules
\- animals, bacteria etc
\- animals, bacteria etc
13
New cards
gibbs free energy (change in G)
\- amount of energy free to do work
\- overall energy released during reaction
\- overall energy released during reaction
14
New cards
spontaneous reaction
exergonic reaction: more free energy on the reactant side, so energy is released and available to do work
\- neg gibbs free energy
\- neg gibbs free energy
15
New cards
non-spontaneous reaction
endergonic reaction: more energy on the product side, so energy is required to drive the reaction
\- pos gibbs free energy
\- pos gibbs free energy
16
New cards
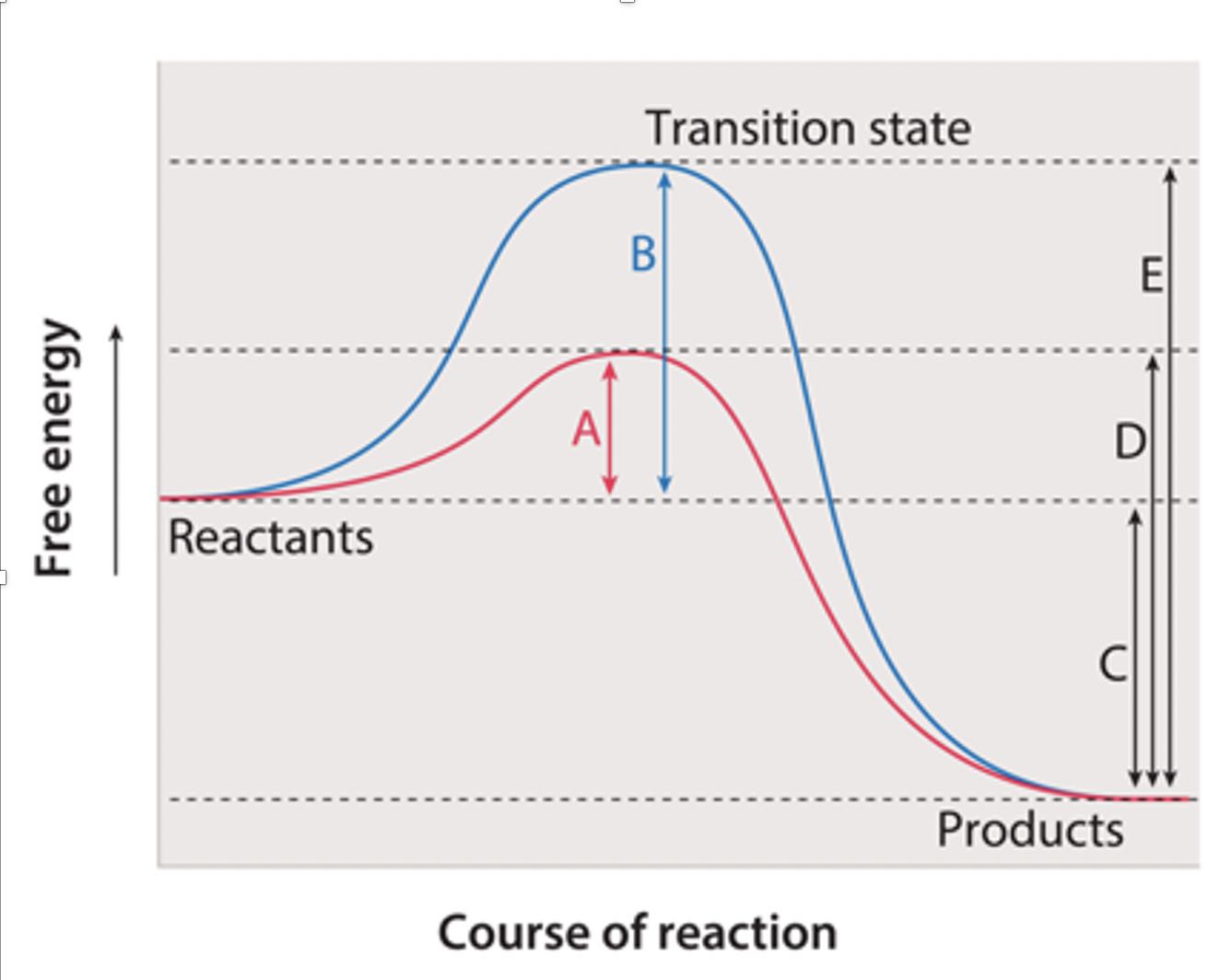
identify each aspect
A: activation energy for catalyzed reaction
B: activation energy for uncatalyzed reaction
C: gibbs free energy
D:
E:
B: activation energy for uncatalyzed reaction
C: gibbs free energy
D:
E:
17
New cards
transition state
a brief period where old bonds are being broken and new ones are being formed
\- very unstable
\- lots of free energy
\- very unstable
\- lots of free energy
18
New cards
activation energy (EA)
the energy input needed to reach the transition state
19
New cards
reaction coupling
an energetically favorable reaction (like ATP hydrolysis) is directly linked with an energetically unfavorable (endergonic) reaction to help drive the endergonic reaction
20
New cards
enzyme
a protein that functions as a catalyst to accelerate the rate of chemical reactions
\- stabilizes the transition state
\- less gibbs free energy
\- stabilizes the transition state
\- less gibbs free energy
21
New cards
inhibitors
decreases the activity of enzymes by binding to the active site (competes with the enzyme), or by binding to another part of the enzyme to which changes its shape
22
New cards
activators
increase the activity of enzymes
23
New cards
allosteric site
a site that allows molecules to either activate or inhibit (or turn off) enzyme activity
different than the active site on an enzyme, where substrates bind.
different than the active site on an enzyme, where substrates bind.
24
New cards
carbon
\- can form 4 bonds due to 4 valence electrons
\- oriented at the center, so it can freely rotate
\- oriented at the center, so it can freely rotate
25
New cards
heterotrophs
carbon from organic compounds
26
New cards
autotrophs
carbon from inorganic compounds
27
New cards
cellular respiration
in: glucose and oxygen react to create ATP
out: carbon and H2O released
out: carbon and H2O released
28
New cards
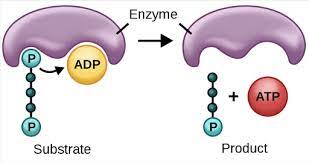
substrate-level phosphorylation
a way of generating ATP in which a phosphate group is transferred to ADP from an organic molecule, which acts as a phosphate donor or substrate.
location: cytoplasm and in the mitochondria
in: ADP
out: ATP, phosphate group
location: cytoplasm and in the mitochondria
in: ADP
out: ATP, phosphate group
29
New cards
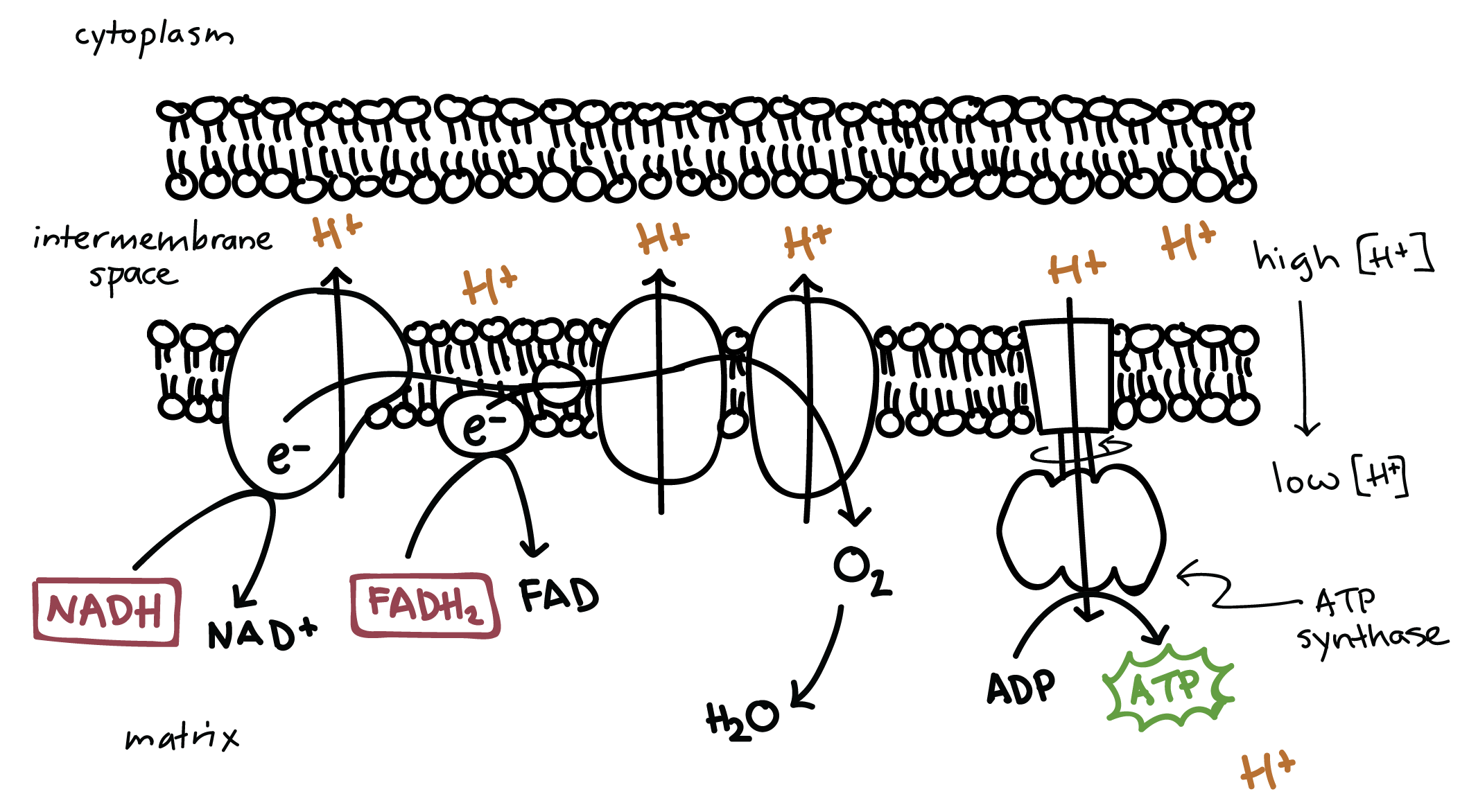
oxidative phosphorylation
a set of metabolic reactions that occurs by passing electrons along an electron transport chain to the final electron acceptor, oxygen, pumping protons across a membrane, and using the proton electrochemical gradient to drive synthesis of ATP
location: inner membrane of the mitochondria
in: FADH2, NADH, ADP
products: ATP, NAD+, FAD, and H2O
location: inner membrane of the mitochondria
in: FADH2, NADH, ADP
products: ATP, NAD+, FAD, and H2O
30
New cards
chemical reaction of cellular respiration
oxidized: glucose molecules
reduced: oxygen to generate water molecules
reduced: oxygen to generate water molecules
31
New cards
stage 1 of cellular respiration
glycolysis
location: cytoplasm
in: 6-carbon molecules
out: 2 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate
location: cytoplasm
in: 6-carbon molecules
out: 2 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate
32
New cards
stage 2 of cellular respiration
pyruvate oxidation
location: cytoplasm to mitochondrial matrix
in: pyruvate
out: 2acetyl-CoA, NADH, CO2
\
NAD+ oxidizes the pyruvate which releases CO2
CoA attaches to the oxidized pyruvate to create acetyl-CoA
\- the CoA allows the molecule to pass through the membrane.
location: cytoplasm to mitochondrial matrix
in: pyruvate
out: 2acetyl-CoA, NADH, CO2
\
NAD+ oxidizes the pyruvate which releases CO2
CoA attaches to the oxidized pyruvate to create acetyl-CoA
\- the CoA allows the molecule to pass through the membrane.
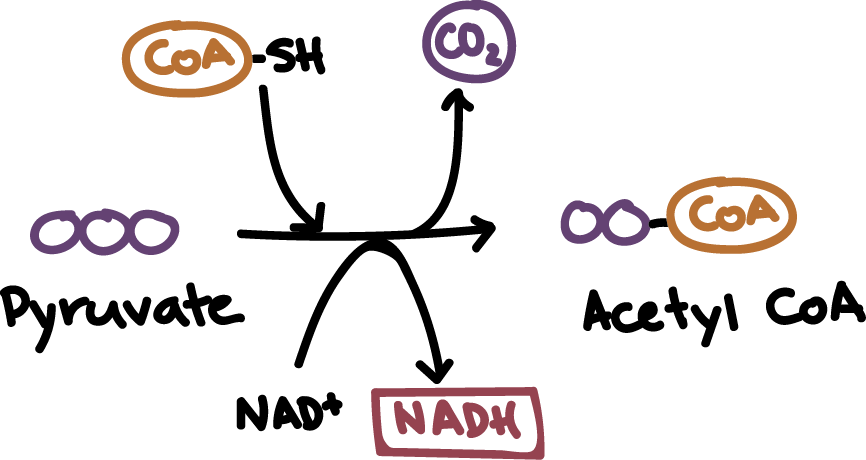
33
New cards
state 3 of cellular respiration
citric acid cycle
location: mitochondrial matrix
in: 2acetyl-CoA, 6NAD+, 2FAD, 2ADP, H2O
out: 2ATP, 2CoA, 6NADH, 2FADH2, GTP, 4CO2
location: mitochondrial matrix
in: 2acetyl-CoA, 6NAD+, 2FAD, 2ADP, H2O
out: 2ATP, 2CoA, 6NADH, 2FADH2, GTP, 4CO2
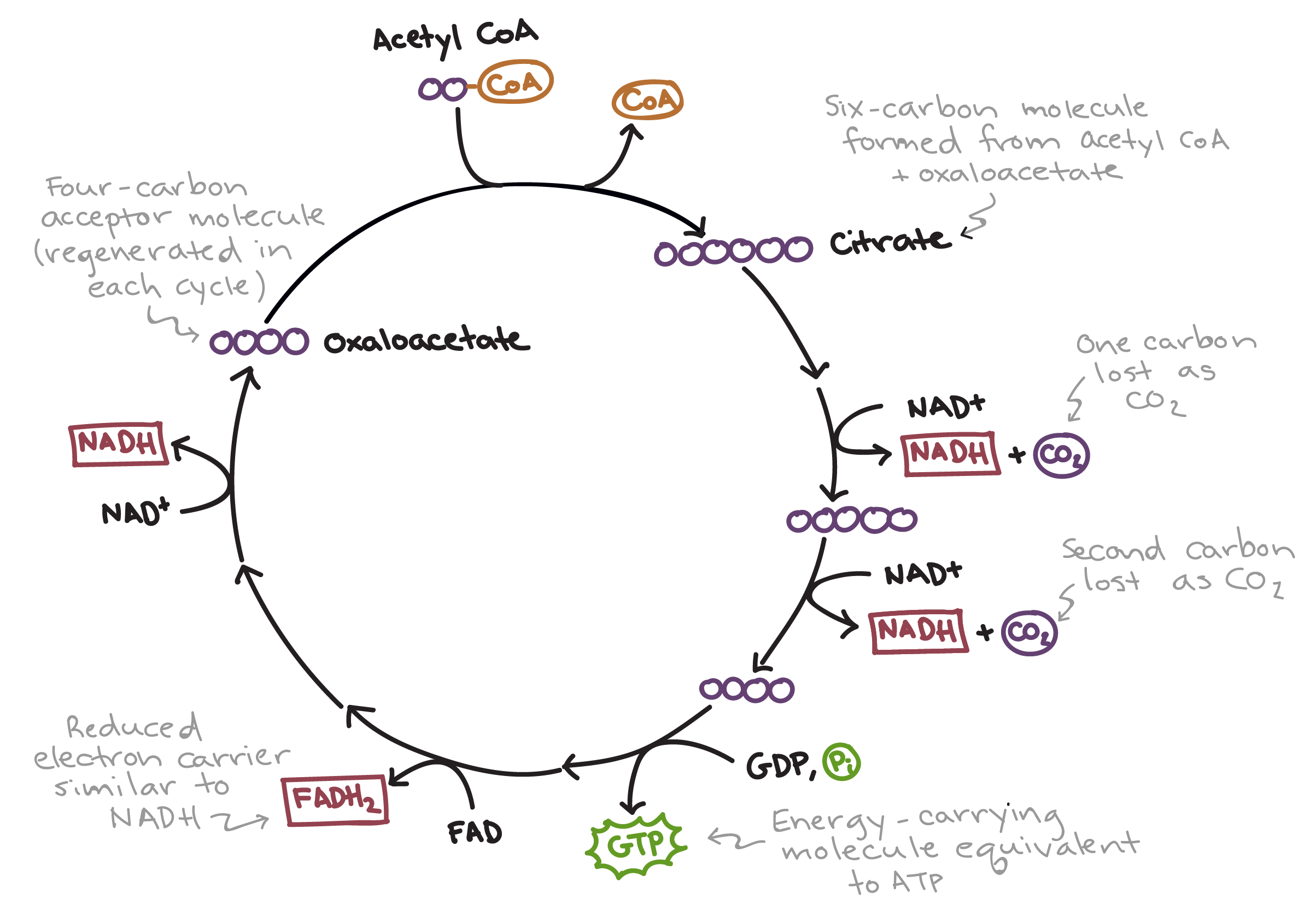
34
New cards
stage 4 of cellular respiration
oxidative phosphorylation
location: inner membrane space
in: ADP, NADH, FADH2 and O2
out: ATP, NAD+, FAD+ and H2O
\
a cellular process that harnesses the reduction of oxygen to generate high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of ATP
location: inner membrane space
in: ADP, NADH, FADH2 and O2
out: ATP, NAD+, FAD+ and H2O
\
a cellular process that harnesses the reduction of oxygen to generate high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of ATP
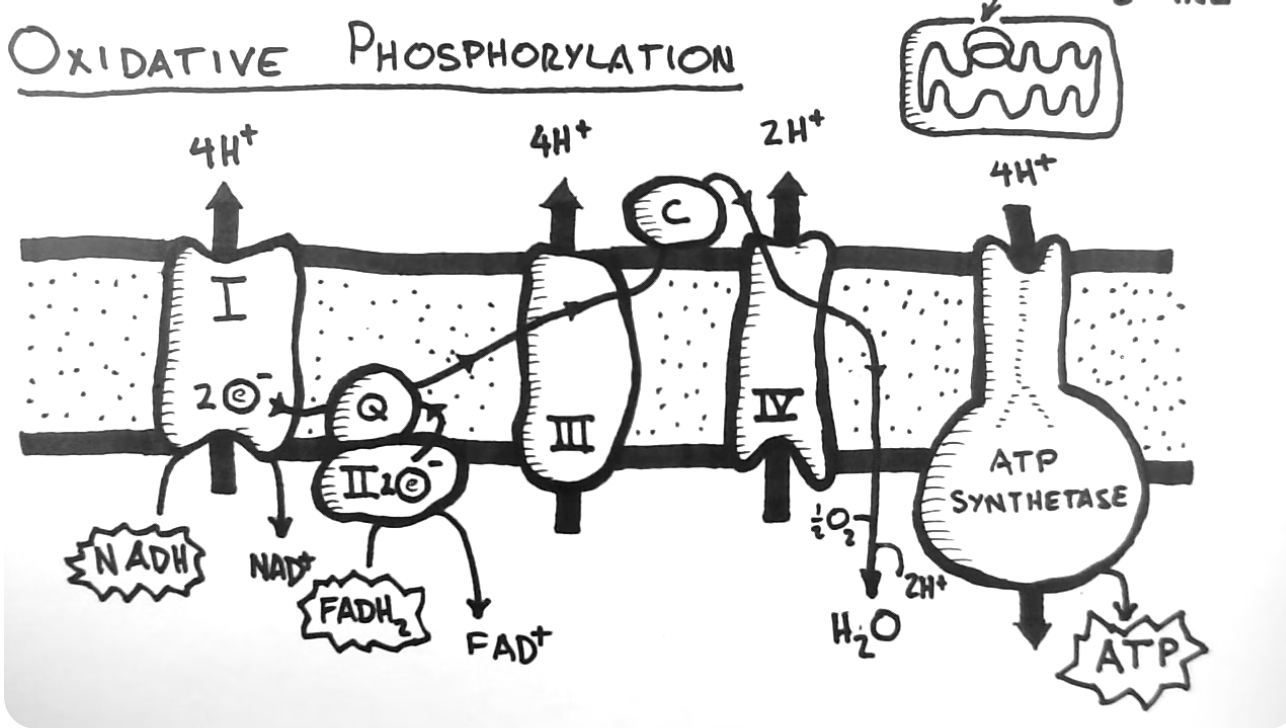
35
New cards
mitochandria
inner membrane space, matrix, membrane, inner membrane
36
New cards
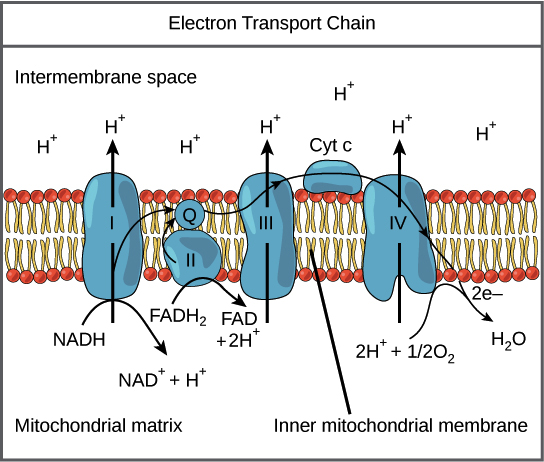
electron transport chain
The electrons flow through the electron transport chain, causing protons to be pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space. Eventually, the electrons are passed to oxygen, which combines with protons to form water.
37
New cards
proton gradient
The proton gradient has two components: a chemical gradient that results from the difference in concentration and an electrical gradient that results from the difference in charge between the two sides of the membrane
\
intermembrane space - protons
matrix - negatively charged
\
intermembrane space - protons
matrix - negatively charged
38
New cards
fermentation
A variety of metabolic pathways that produce ATP from the partial oxidation of organic molecules without oxidative phosphorylation or an electron acceptor, such as oxygen.
39
New cards
fermentation
\- can break down pyruvate in the absence of oxygen
\- extracts energy from fuel molecules without the electron transport chain
\- uses an organic electron acceptor
\- for anaerobic organisms, or when oxygen isn’t delivered fast enough
location: cytoplasm
\- extracts energy from fuel molecules without the electron transport chain
\- uses an organic electron acceptor
\- for anaerobic organisms, or when oxygen isn’t delivered fast enough
location: cytoplasm
40
New cards
fermentation pathways
\- ethanol
\- lactic acid
\- lactic acid
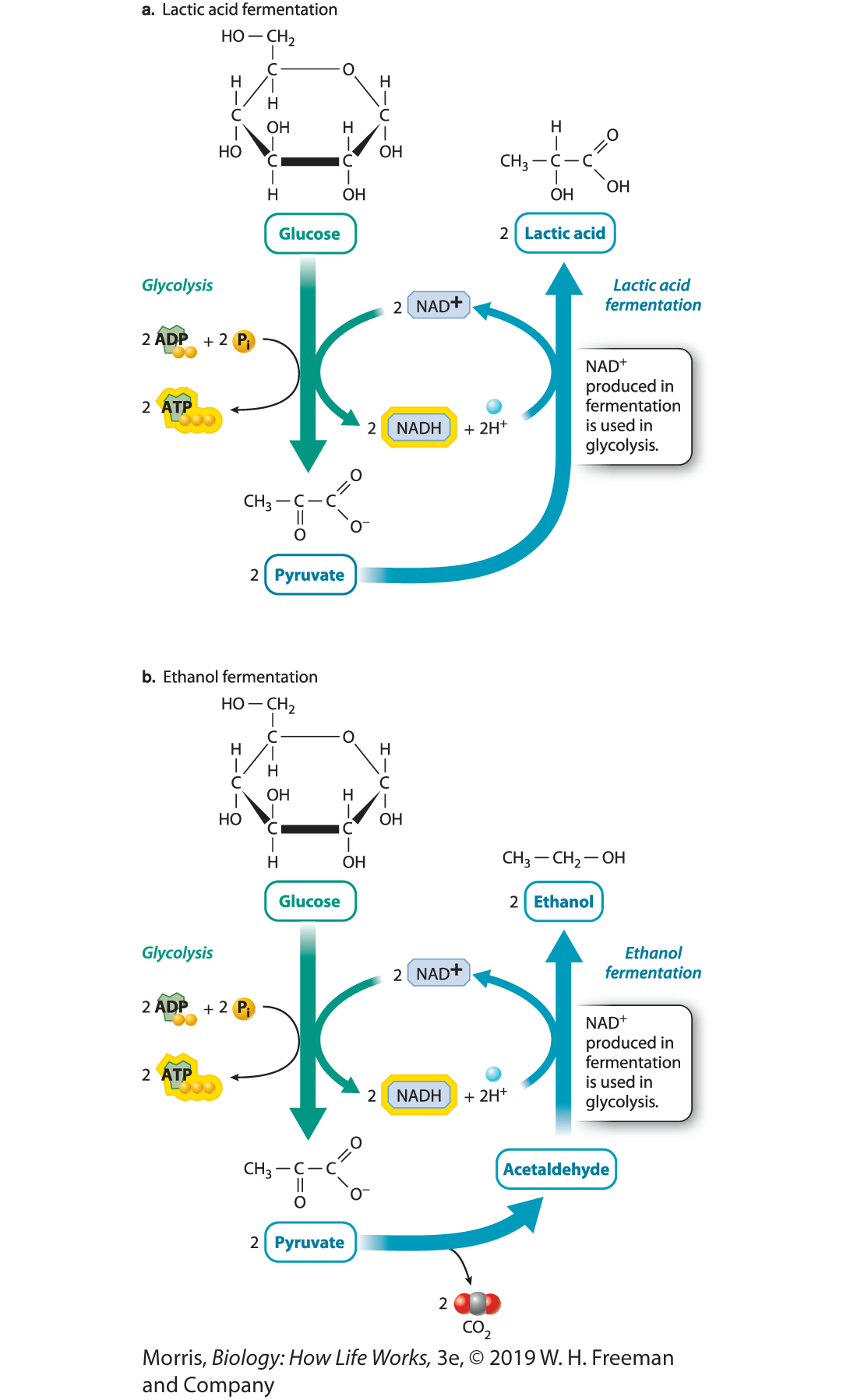
41
New cards
glycogen
the stored form of glucose that's made up of many connected glucose molecules
42
New cards
photosynthesis
energy from sunlight is used to synthesize carbohydrates from CO2
43
New cards
redox in photosynthesis
oxidation: H2O (electron donor) is oxidized and O2 is released
reduction: CO2 is reduced to form carbohydrates
reduction: CO2 is reduced to form carbohydrates
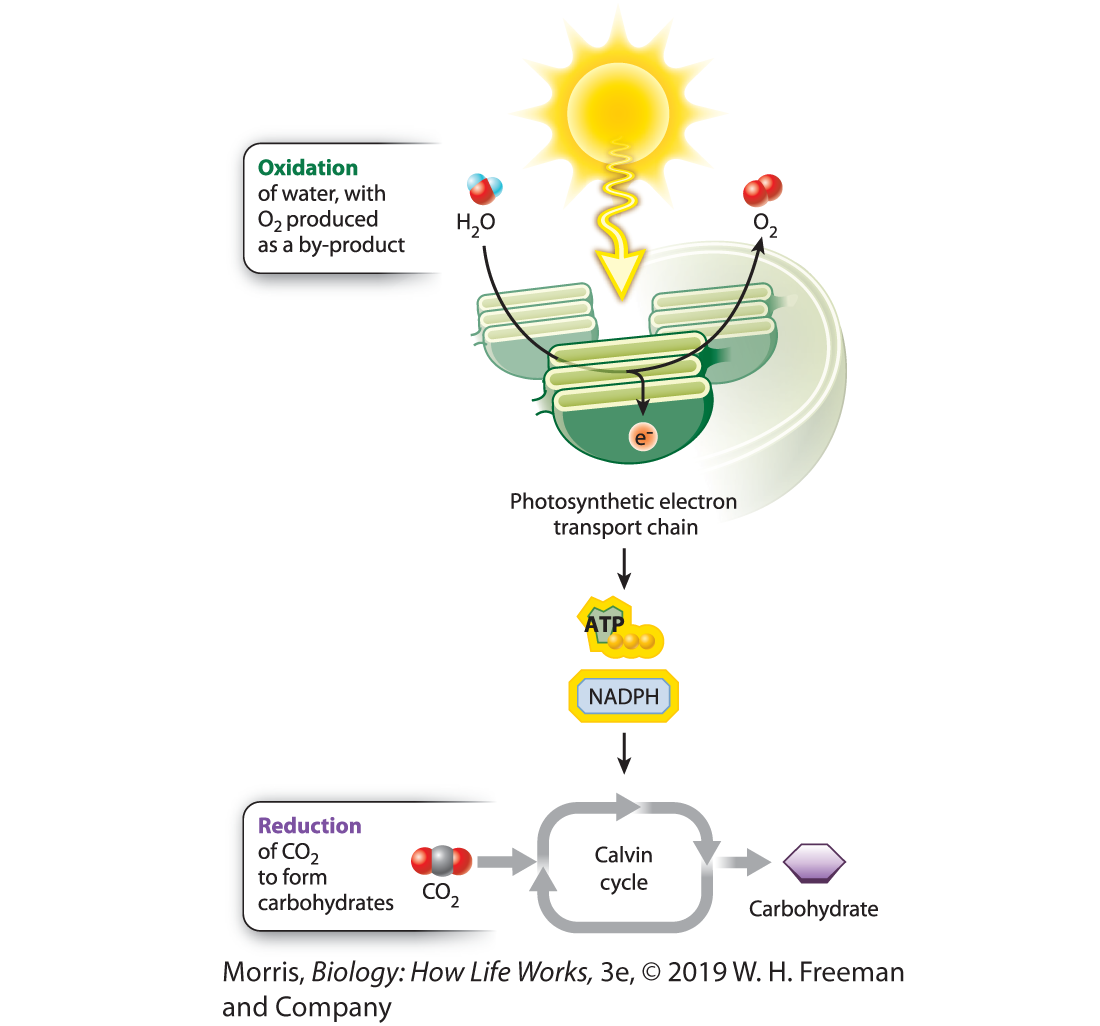
44
New cards
chloroplast
where photosynthesis takes place
thylakoid: disk
grana: stack of thylakoid
storma: surrounding liquid
lumen: inside of the thylakoid
thylakoid: disk
grana: stack of thylakoid
storma: surrounding liquid
lumen: inside of the thylakoid
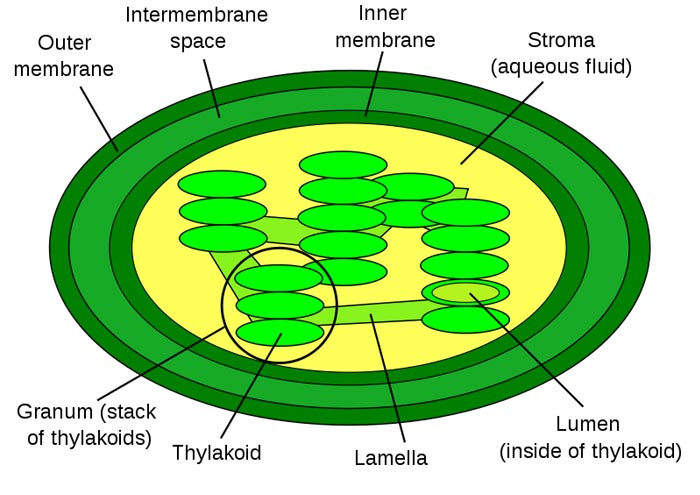
45
New cards
calvin cycle
synthesis of __carbohydrates__ from CO2
1. carboxylation: CO2 is added to a 5-carbon molecule
2. reduction: energy and electrons are added to the compound
3. regeneration: 5-carbon molecule recreated to keep the cycle moving
1. carboxylation: CO2 is added to a 5-carbon molecule
2. reduction: energy and electrons are added to the compound
3. regeneration: 5-carbon molecule recreated to keep the cycle moving
46
New cards
rubisco
enzyme that catalyzes the incorporation of CO2 to the 5-carbon molecule
47
New cards
chlorophyll
\- in the photosynthetic membrane system
\- key role in the cell’s ability to capture energy from the sunlight
\- key role in the cell’s ability to capture energy from the sunlight
48
New cards
photosystem
a protein pigment complex that absorbs light energy to drive redox reactions and thereby sets the photosynthetic electron transport chain in motion
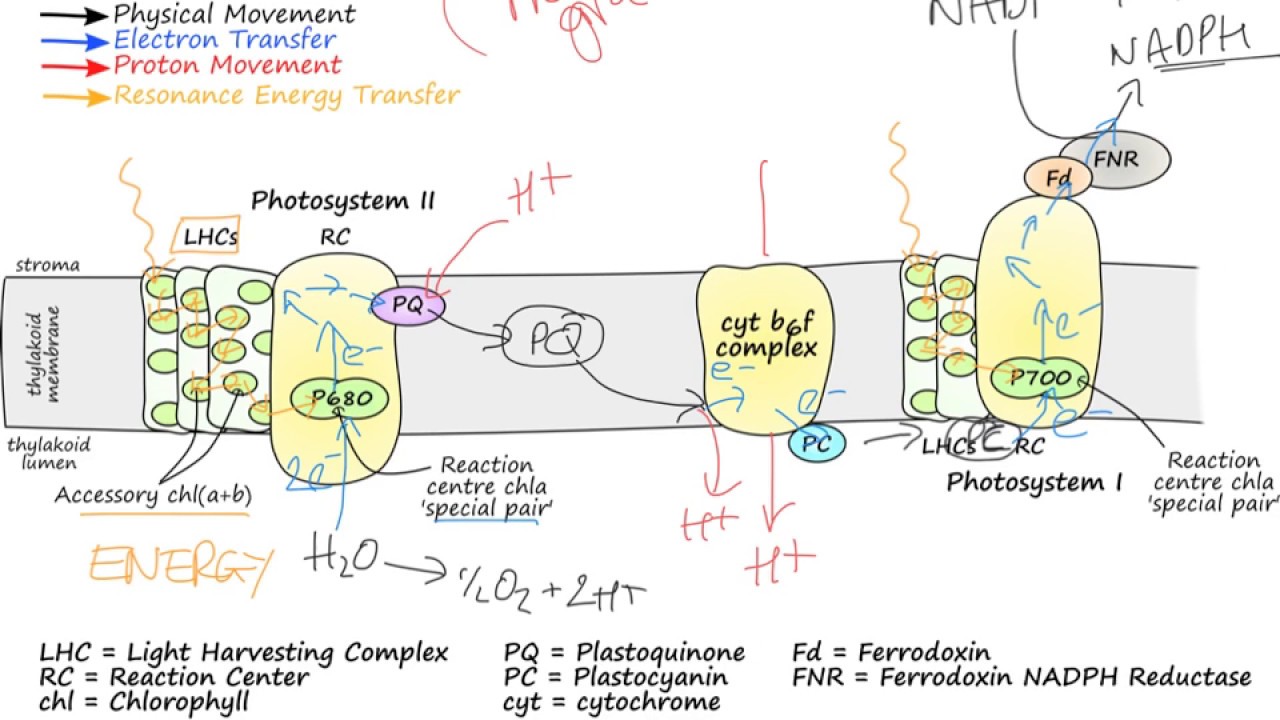
49
New cards
accessory pigment
another light-absorbing pigment in the photosynthetic membrane
50
New cards
antenna chlorophyll
energy is transferred between chlorophyll molecules until it is transferred to a specifically configured pair of chlorophyll molecules known as the reaction center
51
New cards
reaction center
specifically configured chlorophyll molecules where light energy is converted
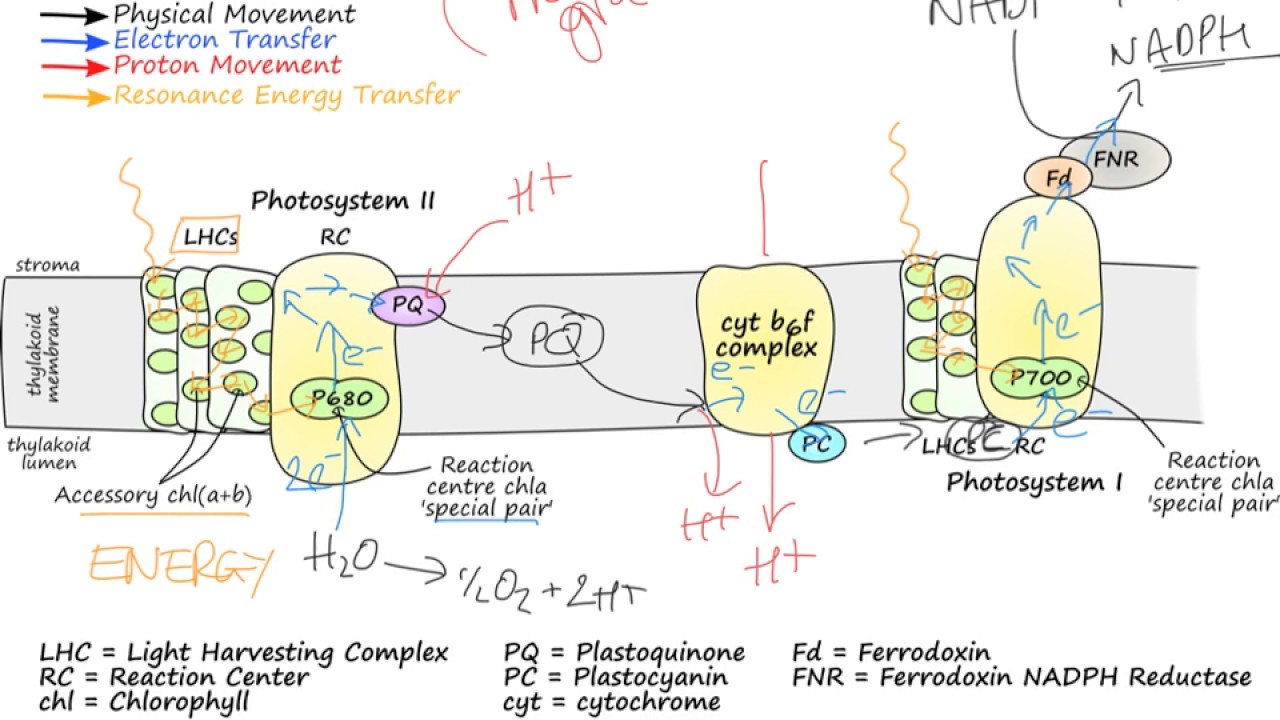
52
New cards
photosystem II
oxidation of water
\- H2O donates an electron
\- releases O2
\- H2O donates an electron
\- releases O2
53
New cards
photosystem I
reduction of NADP+
\- photosystem gives an electron to NADP+ to form NADPH
\- photosystem gives an electron to NADP+ to form NADPH
54
New cards
proton pump
lumen: high proton concentration
stroma: low proton concentration
atp synthase pumps the protons
stroma: low proton concentration
atp synthase pumps the protons
55
New cards
why are two photosystems needed
it takes a lot of energy to break water apart, so they electron transport chain needs an extra surge of energy to keep the chain moving.
56
New cards
ATP synthase
ADP + phosphate group = ATP
powered by the proton gradient
powered by the proton gradient
57
New cards
photorespiration
A process in which rubisco acts as an oxygenase, resulting in release of carbon dioxide and a net loss of energy.
58
New cards
phospholipid
structure: hydrophilic head, and hydrophobic tails
59
New cards
amphipathic
a molecule that has both a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region
60
New cards
phospholipid bilayer
structure formed in aqueous solutions
creates a membrane
hydrophilic head on outside
hydrophobic tails on inside
creates a membrane
hydrophilic head on outside
hydrophobic tails on inside
61
New cards
micelle
structure formed with one tail rather than 2
62
New cards
saturated fatty acid tail
straight tail
no double bonds, so they are tightly packed which limits lipid mobility
no double bonds, so they are tightly packed which limits lipid mobility
63
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid tail
kinks in tail
double bonds which is the reasoning for the kinks in the tail
this enhances lipid mobility
double bonds which is the reasoning for the kinks in the tail
this enhances lipid mobility
64
New cards
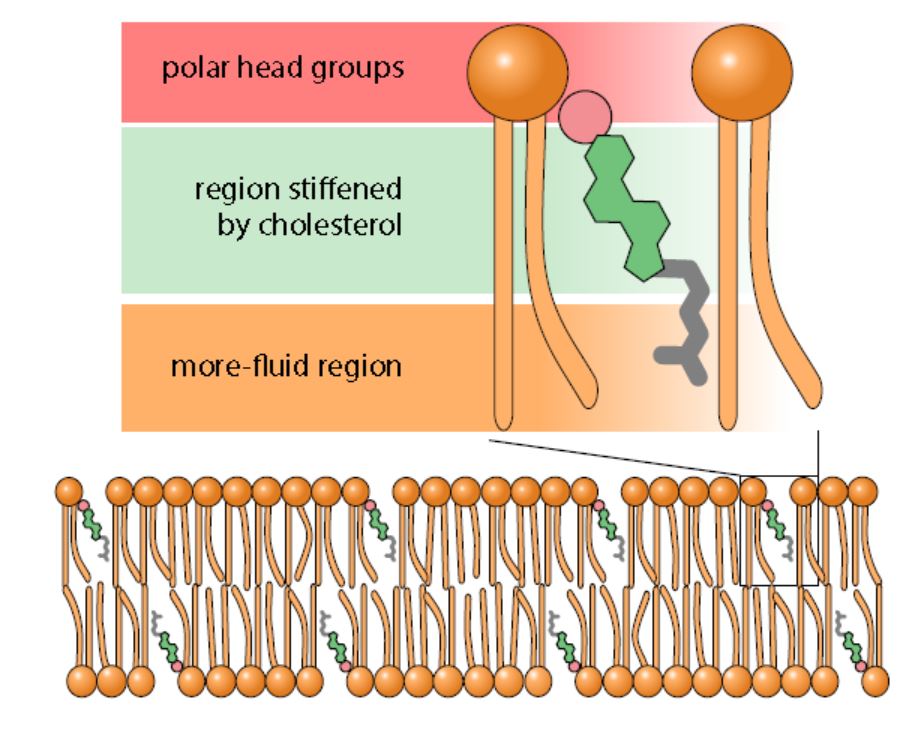
cholesterol
hydrophilic head, hydrophobic body & tail
attaches
helps the phospholipid bilayer maintain its fluidity in different environments
attaches
helps the phospholipid bilayer maintain its fluidity in different environments
65
New cards
why do lipids not “flip-flop”?
It is energetically unfavorable for the hydrophilic heads to pass through the hydrophobic regions
66
New cards
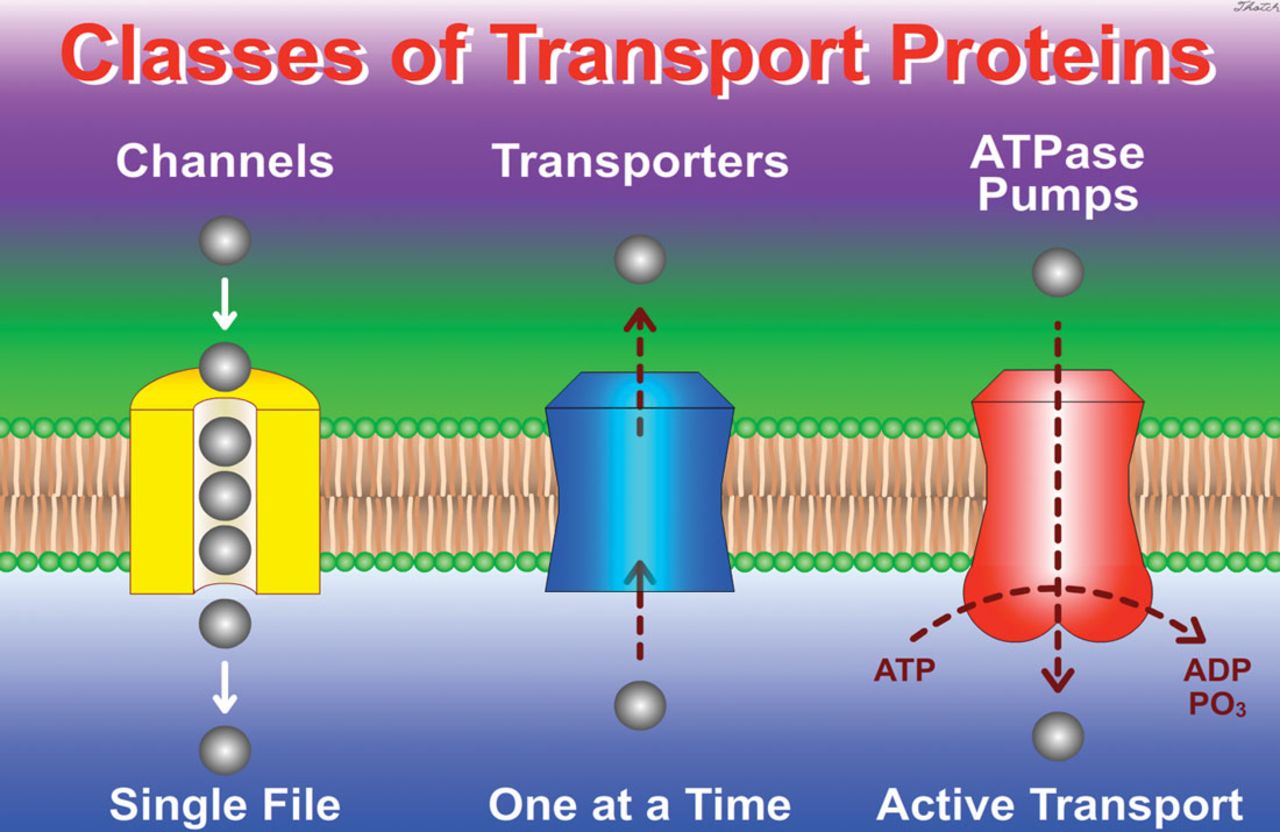
transporter proteins
membrane proteins that move ions or other molecules across the membrane
67
New cards
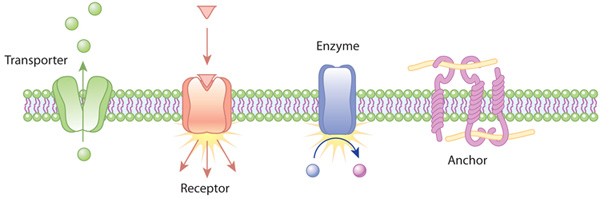
anchor proteins
attaches to other proteins and helps maintain cell structure and growth
68
New cards
receptor proteins
a molecule on cell membranes that detects signals outside of the cell
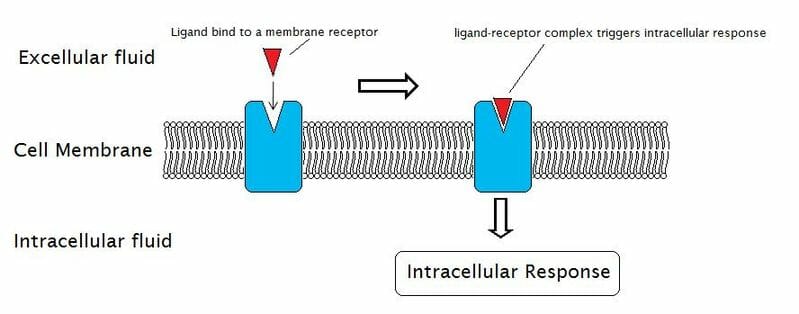
69
New cards
enzymes
catalyze chemical reactions
critical in determining which reactions take place in a cell
critical in determining which reactions take place in a cell
70
New cards
integral membrane proteins
permanently attached to the cell membrane, cannot be removed without destroying the bilayer
section inside of the membrane hydrophobic
section outside of the membrane hydrophilic
\
section inside of the membrane hydrophobic
section outside of the membrane hydrophilic
\
71
New cards
peripheral membrane proteins
temporarily associated with the membrane or integral membrane proteins through weak non fcovalent bonds
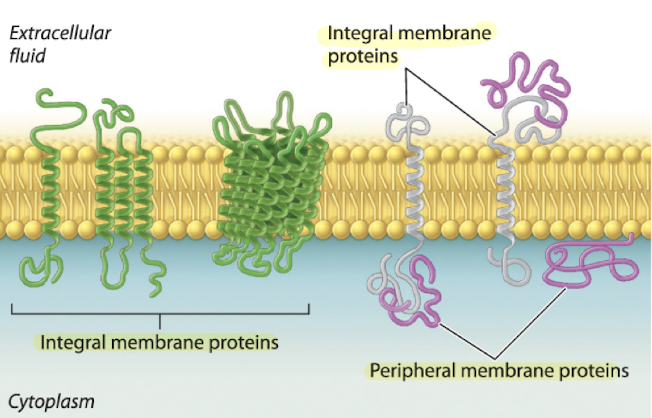
72
New cards
transmembrane proteins
these are all integral membrane proteins
span across the whole membrane
span across the whole membrane
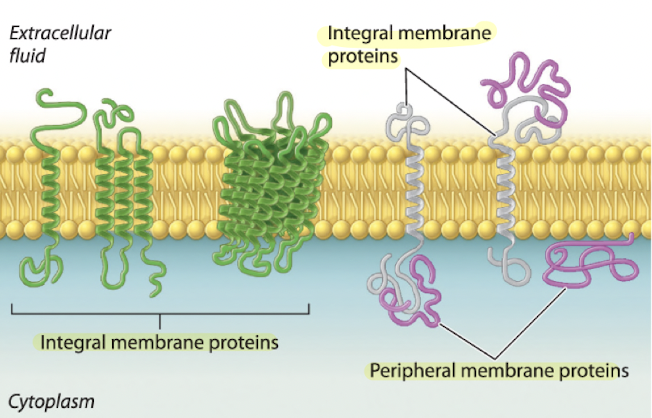
73
New cards
fluid mosaic model
proposes that the lipid bilayer is a fluid structure that allows molecules to move laterally within the membrane and is mosaic two types of molecules (proteins and lipids)
74
New cards
homeostasis
the tendency toward a relatively stable __equilibrium__ between __interdependent__ elements, especially as maintained by physiological processes.
75
New cards
selectively permeable
the phospholipid bilayer is selective about what can pass through
permeable:
gases (O2, CO2 etc..)
non polar molecules
small uncharged polar molecules (H2O)
impermeable:
ions
sugars
charged molecules
protein
permeable:
gases (O2, CO2 etc..)
non polar molecules
small uncharged polar molecules (H2O)
impermeable:
ions
sugars
charged molecules
protein
76
New cards
diffusion
the movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration (energetically favorable)
77
New cards
facilitated diffusion
diffusion through a transmembrane protein into the cell, or out of the cell
78
New cards
simple diffusion
passing directly through the membrane without assistance
79
New cards
active transport
the movement of substances against a concentration gradient requiring an input of energy
80
New cards
primary active transport
uses ATP directly to drive the movement
by a pump
by a pump
81
New cards
secondary active transport
uses the energy of a chemical gradient to drive the movement
will move with the molecule using active transport into the desired location
will move with the molecule using active transport into the desired location
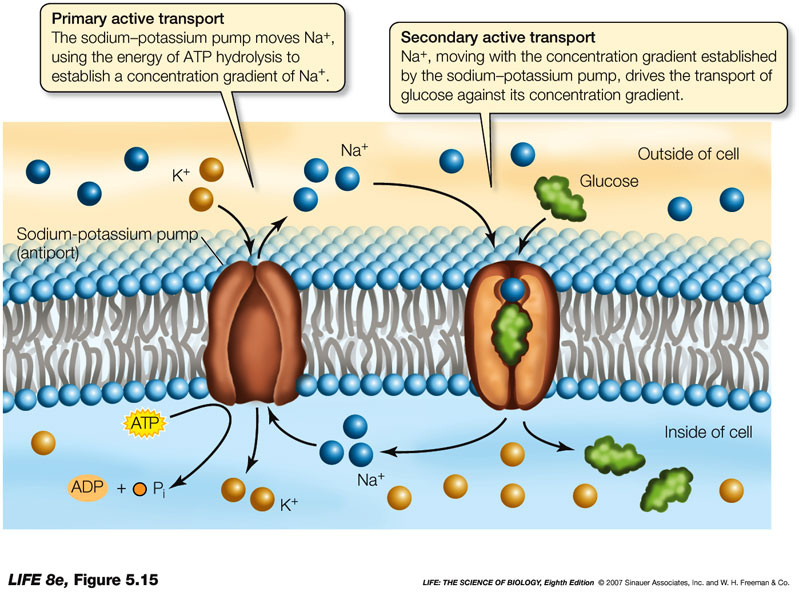
82
New cards
two domains of prokaryotic life
bacteria and archaea
83
New cards
plasmid
in bacteria, a circular molecule of DNA carrying a small number of genes.
84
New cards
peptidoglycan
a complex polymer of sugars and amino acids making up the bacteria cell wall
85
New cards
horizontal gene transfer
the transfer of genetic material between organisms that aren’t parent and offspring
86
New cards
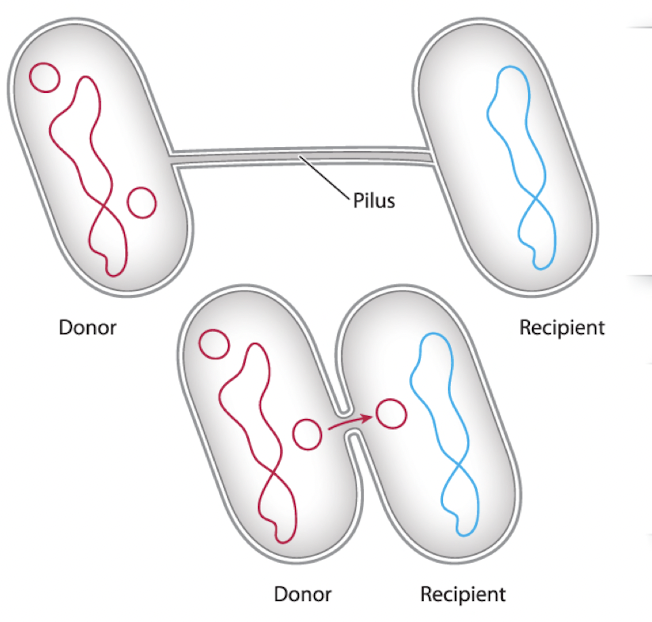
conjugation
cells connect through a pilus, DNA passes through a small opening formed between the cells
87
New cards
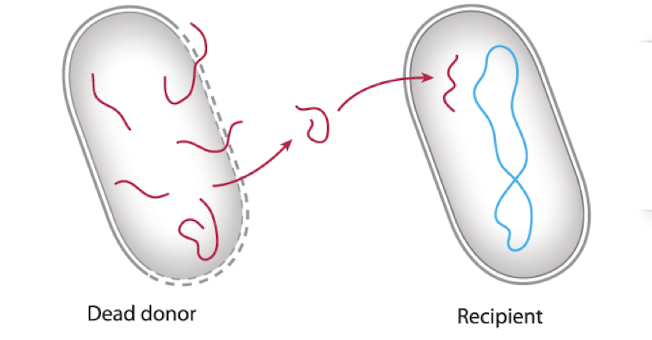
transformation
DNA released into the environment by dead cells is picked up by a recipient cell
88
New cards
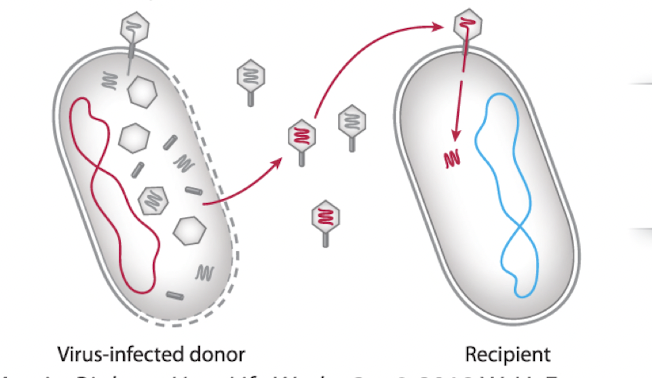
transduction
transferred through a virus
89
New cards
key ideas
1) eukaryotic cells have nuclei and membrane-bound organelles, whereas bacteria and archaea don’t
(2) eukaryotic cells have linear chromosomes, whereas bacterial and archaeal DNA is circular
(3) eukaryotes and prokaryotes have ribosomes of different sizes
(4) membrane lipids, RNA polymerase, \n and ribosomes in Archaea are more like those in eukaryotes than those in bacteria
(5) methanogenesis occurs only in Archaea
(6) nitrogen fixation and chemoautotrophy are found only in prokaryotes
(7) Both Archaea and Eukaryotes have histone proteins.
(2) eukaryotic cells have linear chromosomes, whereas bacterial and archaeal DNA is circular
(3) eukaryotes and prokaryotes have ribosomes of different sizes
(4) membrane lipids, RNA polymerase, \n and ribosomes in Archaea are more like those in eukaryotes than those in bacteria
(5) methanogenesis occurs only in Archaea
(6) nitrogen fixation and chemoautotrophy are found only in prokaryotes
(7) Both Archaea and Eukaryotes have histone proteins.
90
New cards
carbon cycle
Decomposing prokaryotes break down dead organic matter and release carbon dioxide through cellular respiration
91
New cards
aerobic respiration vs anaerobic respiration (process in which carbohydrates are broken down to create energy)
aerobic takes place in the presence of oxygen
anaerobic takes place in the absence of oxygen
anaerobic takes place in the absence of oxygen
92
New cards
respiration vs fermentation (produce energy for the cells to use)
respiration: complete oxidation of glucose into CO2 and H2O
fermentation: partial oxidation of glucose
fermentation: partial oxidation of glucose
93
New cards
sulfur & nitrogen cycles
sulfur and nitrogen cycles on Earth \n depend on some of the prokaryote-only anaerobic metabolic pathways
94
New cards
nitrogen fixation
N2 → NH3
95
New cards
nitrification
NH3 (oxidized) → NO2- → NO3
96
New cards
denitrification
NO3 reduction → N2 (released into the environment)
97
New cards
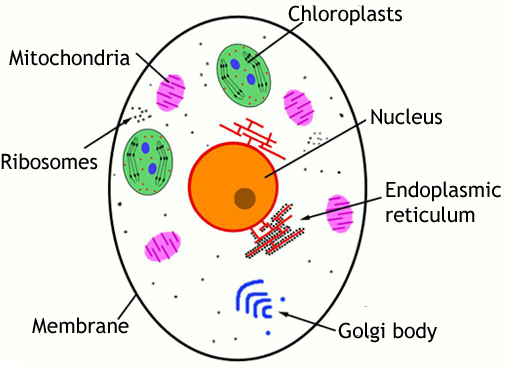
eukaryotic cell
98
New cards
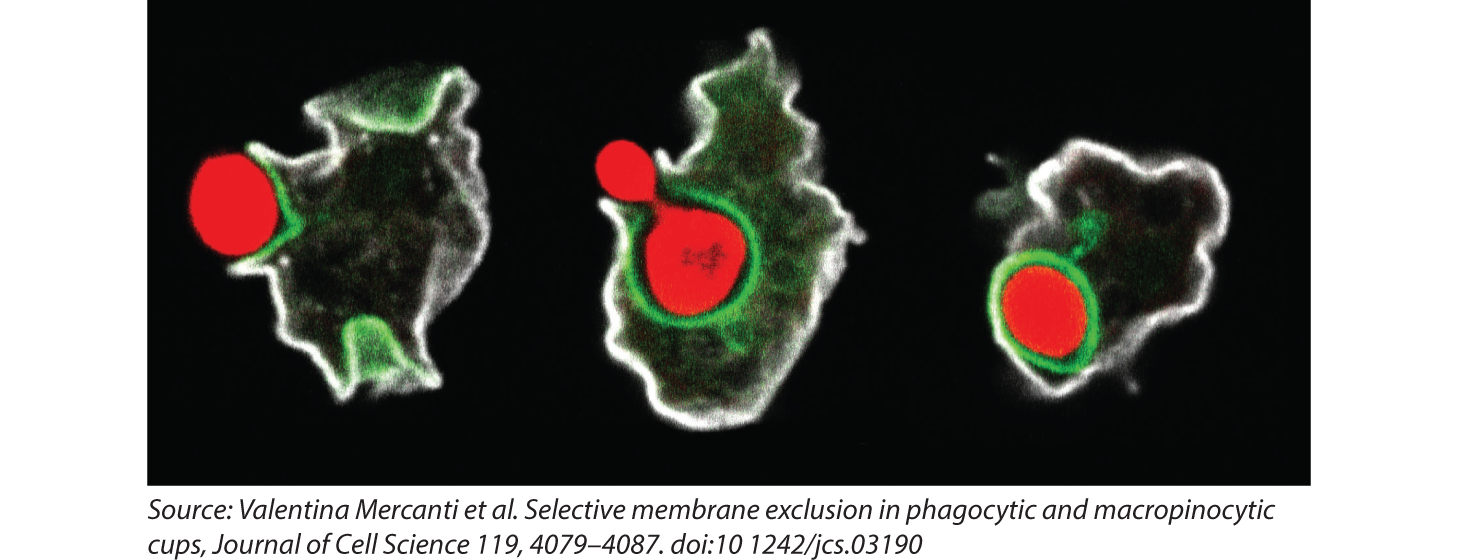
phagocytosis
eukaryotic cells surround food particles and package them in vesicles that bud off from the cell membrane
99
New cards
endocytosis
the cytoskeleton and membrane system also enable eukaryotic cells to engulf molecules or particles, including other cells, in a process called endocytosis
100
New cards
diploid
describes a cell with two complete sets of chromosomes.