Inorganic Chemistry Test 3
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Magnesium
High charge density: Hard acid, more covalency, can contribute to water hardness
Used to synthesize pure boron: B2O3 + 3 Mg → 2B +3MgO
Grignard reagents
MgSO4×7H2O is epsom salt
burns white hot
will take O from CO2 when burning
Mg(OH)2 suspension in water is milk of magnesia
Tooth Enamel
Hydroxyapatite, Ca5(PO4)3(OH), adding F- to water replaces the OH minus, F- is a weaker base and less likely to degrade
Calcium
cause of water hardness: ion exchange where 2Na+ replaces 1 Ca2+
NaAl(SiO3)2 is what is in water softeners
reacts with soap to form sop scum [calcium(sterate)2].
Used in slaked lime: Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Gypsum(main component of sheetrock): CaSO4 × 2H2O
CaS + H2O → CaO (Ca(OH)2) + H2S
CaO gives off bright white “lime light” when burned
Aluminum
Al4C3 is a carbide that gives methyl upon hydrolysis
Can be used to polish Ag:
3Ag2S + 2Al → 6Ag + Al2S3
excellent electrical and thermal conductor
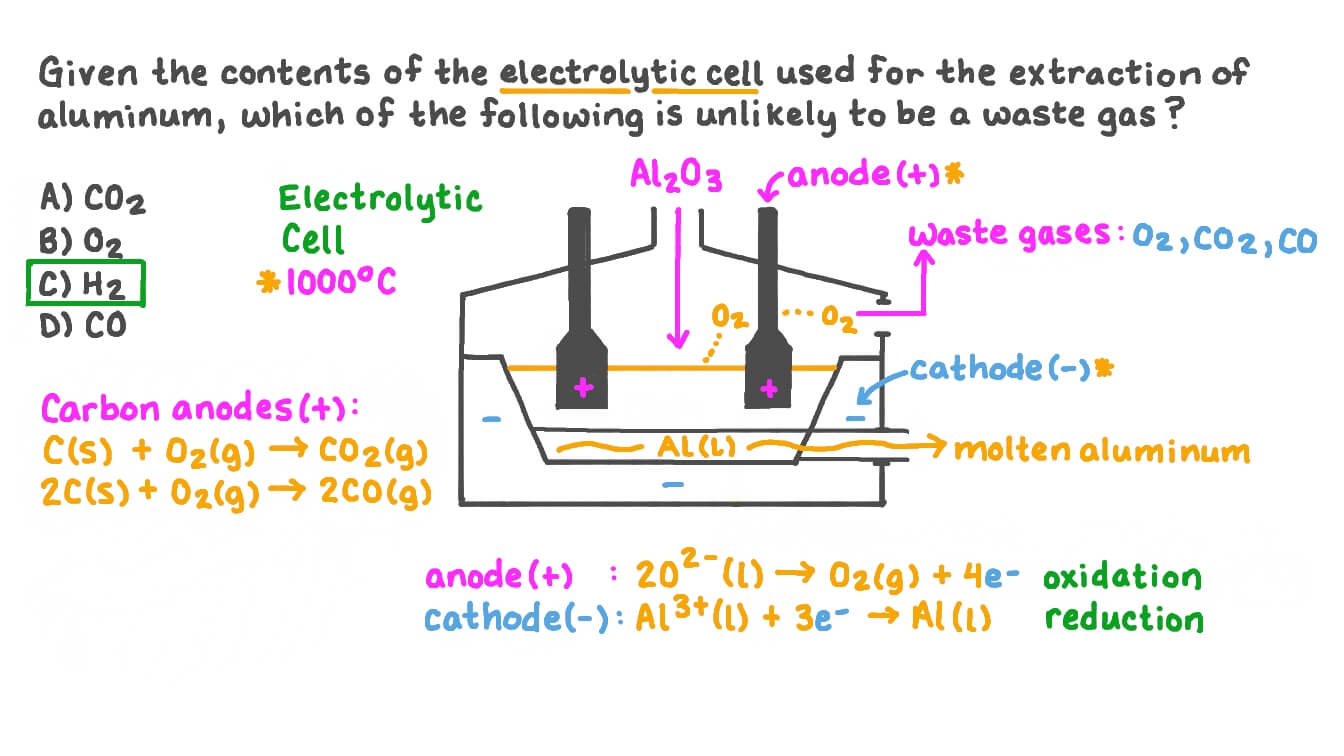
Hall Heroult Process: In picture
Al2O3 is the source of aluminum, called bauxite
AlCl3 is a lewis acid
Remember: NaAl(SiO3)2 is in water softeners for Na+ ion exchange
Strontium
Product of nuclear fallout
Substitutes for Ca(Sr2+ → Ca2+), which is why it causes cancer
Radium
Glows in the dark so it used to be used on expensive watches and plane instruments
Inert Pair Effect
Al 3+ is the only oxidation state, but as you go down the column the 1+ oxidation state becomes more and more common with Tl 1+ being its only oxidation state. Because of a tendency of the pairs electrons in the s shell to not be shared as they are more effectively bound to the nucleus in the larger molecules.
Boron
Synthesized with Mg: B2O3 + 3 Mg → 2B +3MgO
Borosilicate: This creates class with a lower coefficient of thermal expansion making it stronger and less susceptible to shattering when their is a temperature change
Boranes
Carbon
Diamond structure
tetrahedral atoms
wide band gap
Black tires, britta filters to absorb impurities
carbon dating, ration of c14 to c12, c14 decreases after smt dies
CO
toxic
makes meat pink
CO2
complete combustion
carbonation in sodas
Chlorofluorocarbons: decay the ozone layer
Used to synthesize silicon & Hydrogen:
SiO2(s) + 2C(s) → Si(l) + 2CO(g)
C(s) + H2O → CO + H2
CO +H2O → CO2 + H2
Si
Comes from SiO2:
SiO2(s) +C(s) → Si(l) +CO(g)
Used in NMR in the form of TMS(Tetramethylsilane) as the “zero”
SiO2 is quartz
Silica gell chromatography for separating and purifying products
Siloxanes
used for caulk
breast implants
Used in semi conductors, can be doped with negative delocalization (n-type) or positive delocalization (p-type)
Tin
Semiconductor tin is diamond structured and stable below 13 degrees celsius
Tin cans are “tinned cans” with a tin coating to preen oxidation of the iron in the steel of the can, forms an adhesive oxide layer that won’t just chip off
SnF2
anti microbial found in tooth paste
Sn + Cu makes bronze
Degrades at low temperatures, napoleons army losing tin buttons when invading Russia in the winter
Lead
Lead acid car batteries
Pb(s) +PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
Mimics Ca2+ which is why it is toxic
Used in paint to discourage corrosion
Nitrogen
78% of the air
NH3 dissolves in water to form ammonium hydroxide, N in ammonia can act as a reducing agent
Haber Bosch Process
N2(g) +3H2(g) → 2NH3(l)
exothermic, need catalyst (nitrogenase)
Used in rocket fuel: (CH3)2NNH2
NaN3 is used in air bags for your car
Nitrogen Oxides
N2O: Laughing gas, propellent in pressurized cans (whip cream) anesthetic, nitrous in drag cars
NO: paramagnetic, vasodilator (viagra - cause blood vessels to widen or dilate), nitroglycerin (bombs)
NO2: component of smog, brown
N2O4: colorless
Catalytic converters reduce nitrogen oxides to N2 and O2
Phosphorus
Made by: Ca3(PO4)2 +10CO → 6CaO + 10 CO2 +P4
White waxy solid
Chemiluminescence: reacts with O2 to give off light
Important component in fertilizer “KPN”
Ca3(PO4)2 + H2SO4 → Ca(H2PO4)2 + CaSO4
PCl3: removes OH group from an alkyl
Phosphorous Acid is an important blood buffer
Arsenic
Originally used to cure syphillus
we know now that it is toxic
[AsO4]3- can replace (PO4)3-
Bismuth
peptobismal for indigestion, works as an antacid
Anti bacterial
Oxygen
O-O single bond is weak
liquid O2 is blue
Left side of periodic table oxides are basic, right side oxides are acidic
Mixing Bleach and Hydrogen Peroxide:
(Na+)OCl- + H2O2 → H2O + O2 + Cl-
O3 is ozone and it absorbs ultraviolet light
Sulfur
yellow, powery/crystalline solid
S-S bond is relatively strong
Made through the Frasch Process
pumped out of the ground by pumping air and water into the ground
Sulfur is added to rubber to make tires harder
H2S is rotten eggs
SO3 is bad, can turn into H2SO3
SO2 helps preserve wine, antimicrobial agent
Fluorine
H bonding
CaF2 + H2SO4 → 2HF + CaSO4
HF + NaOH → NaF + H2O
Degrades glass b/c F is a harder base than O and silicon is a hard acid
Chlorine
2 NaCl → 2Na + Cl2
HCl: NON-oxidizing strong acid
HNO3 & HClO4 are oxidizing acids
Bleach
Cl- + O3 → ClO- +O2
Ammonium Perchlorate is rocket fuel
Iodine
Used to purify water on the space station b/c it is a solid (as opposed to Cl which is a gas)
I- is needed for thyroid function
Helium
finite
refrigerant in NMR
comes from alpha decay: radioactive decay that yields and alpha particle (helium) and the daughter nucleus
[Pt(NH3)4]Cl2
tetraammineplatinum (II) chloride
CO (name of its group when part of a ligand?)
Carbonyl
NH3 (name of its group when attached to a ligand?)
ammine
OH2 (when on a ligand?)
aqua-
Prefix for multiple ethylenediamines
bis, tris, tetrakis; two, three, four, respectively
K2[NiCl4]
potassium tetrachloridenickelate (II)
[CoCl(OH2)5](NO3)2
pentaaquachlorocobalt (III) nitrate
[CoCl2(en)2]ClO4
dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt (III) perchlorate
Ni(CO)4
Tetracarbonylnickel (0)
Diammineoxalatocopper (II)
Cu(NH3)2(ox)
Hexaaminechromium (II) tetrachlorocuprate (II)
[Cr(NH3)6][CuCl4]
Potassium hexocyanomanganate (II)
K4[Mn(CN)6]
hexaaguavanadium (III) Nitrate
[V(OH2)6](NO3)3
(NH4)2[CoCl2]
diammoniumdichlorocobalate (II)
(not sure why the cobalt is 2+ which would cancel out the chloride’s negative but then somehow the compound is neutral even thought NH4 is +1 but thats what he wrote down)
[CrCl2(OH2)4]Cl
tetraaguadichlorochromate (III) chloride
[Fe(ox)3]3-
tri(oxalato)ferrate (III)
tetrahydroxozincate
[Zn(OH)4]2-
tetraaminedichloroplatinum (IV) hexachloroplatinate (IV)
[PtCl2(NH3)4][PtCl6]
Ga, In, Tl
Gallium is used in LED’s
GaAs can emit in IR
GaP emits green light (n-type doping)
GaN emits blue light
Indium is part of indium tin oxide which is a transparent electrode
Thallium used to be a rat poison
Baking Power: What and How?
Formula for baking powered is NaHCO3
Reacts with acid to produce CO2 which causes things to rise
Chromate (think the ion)
(CrO4)2- can replace (SO4)2- which makes it toxic
Fertilizers (what main elements? Molecular formulas?)
KPN/KNP etc.
Potassium: KNO3
Nitrogen: NH4NO3
Phosphate: Ca(H2PO4)2
Precious Gems
Diamonds are carbon
Sapphire’s and Ruby’s are Al2O3
Colors in fireworks
K+ is purple, Li+ is red, Sr2+ is red, Ba2+ is green
How is Hydrogen Formed
C+H2O → H2 + CO
CO + H2O → CO2 + H2