Ochem Chapter 8- alkene reactions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
H-X
HCl
HBr
HI
etc
markovnikov
carbocation rearrangement
stereospecific!
both TS are closer to the intermediate
H-X with radical RO-OR + heat
antimarkovnikov
rearrangement- radical stability
Acid Hydration
H2O + H2SO4
Markovnikov
carbocation rearrangements
1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O
2) NABH4
Oxymercuration- Demuercuration Hydration
Markovnikov
No rearrangments
Anti addition of OH+H
1) Hg(OAc)2, CH3OH
2) NABH4
Alkoxyl Mercuration
Markovnikov
No rearrangements
Anti addition of ROH
1) BH3, THF
2) H2O2, NaOH
Hydroboration Hydration
Antimarkovnikov
No rearrangements
Syn addition H+OH
X2
Inert solvent
Br2
Ch2Cl2
Anti addition of X2
X2
polar protic solvent
Cl2
H2O
Markovnikov
anti addition of H+OH (halohydrin formation)
halohydrin: has both halogen and OH
H2
Catalysts: Pd, Pt, Ni
alien spaceship
syn addition of H+H
doesn’t effect aromatic rings
CH2N2
heat
Diazomethane
syn addition of carbene
CH2I2
Zn(Cu)
Simmons Smith
syn addition of carbene
CHBr3, CHCl3
strong base
alpha elimination
syn addition
O3- RCO3H or mPBA
CH2Cl2
syn addition of epoxides
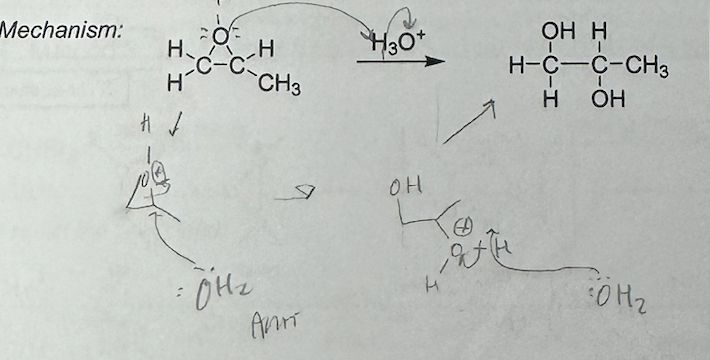
acid catalyzed opening of epoxides
markovnikov
anti addition of OH+OH
OsO4/ H2O2
KMnO4/ OH
syn addition of OH+OH
KMnO4 + H3O
KMnO4 + (warm, concerted)
Oxidative cleavage
separate two and add =O
replace the cleaved part H with OH
H3O acidic environment causes CO2 and H2O formation through keto enol
O3
(CH3)2S
Ozonolysis
Miilder; Produces Ketones and aldehydes
separate two and add =O, H doesn’t turn into OH