PSYC388 - Module 1: Intro to biological rhythms
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Biological rhythm
a process that repeats itself regularly over time, including behaviour
Period (t)
time to complete 1 full cycle (time between ocean wave crests)
frequency
reciprocal of period; # of cycles per unit time
Hertz (Hz)
frequency unit when time is in seconds (ie. 6Hz = 6 cycles per second)
What is the range of biological rhythms? (time and species variance)
biological rhythms vary from milliseconds to years
occurring in genes, cells, organs, organisms, and populations
What are the 3 period classifications of biological rhythms?
1. Ultradian
2. Daily
3. Infradian
period less than 24 hours (2-4, 6-12)
ultradian rhythms
period about 24 h
daily rhythms
period more than 24 hours (seasonal, annual)
infradian rhythms
What do we mean when we say that biological rhythms have no strict cut off?
ultradian rhythms are usually less than 20h and infradians are more then 30h
but there is no strict cut off
What are circa rhythms?
biological rhythms with periods that approximate natural environmental cycles
what are the 4 circa rhythms?
circatidal
circadian
circalunar
circannual

what are circatidal rhythms?
12.5h rhythms that match the tides (ultradian)
what are circadian rhythms
24 h rhythms that match the solar day (daily)
what are circalunar rhythms?
29.5 day rhythm cycles that matches the lunar month (infradian)
what are circannual rhythms?
365 day rhythms that matches the solar year (infradian)
what are the 2 unique features of the 4 circa rhythms?
1. approximate to geophysical/environmental cycle periods
2. persist for many cycles even w/o environmental cues
what is entrainment?
the mechanism where internal biological clock is adjusted to align with external environmental cycles
not the same as synchrony, but a way to achieve it
1. studied daily rhythms in physiology & behaviour of mice and humans
2. coined "circadian"
3. used math curve fitting (cosine) to analyze rhythmic data
Franz Halberg (1950s-60s)
circadian means...
about a day (24 hours)
When it comes to data visualization of circadian rhythms, time of day is plotted
a) vertically
b) horizontally
b) horizontally
When it comes to data visualization of circadian rhythms, what goes along each row?
a different physiological variable (running, activity, etc.)
when it comes to data visualization of circadian rhythms and graph representations, the horizontal bars with dots show what?
peak time (acrophase) of each rhythm
when it comes to data visualization of circadian rhythms and graph representations, error bars indicate...
indicate variability in acrophase (peak) timing (with 95% confidence interval)
t or f: difference in timing of rhythms is constant within and between species
false
t or f: not a lot of physiological and biochemical processes in mice and humans both follow 24 hour cycles because they're different species
false
around _____% or more of gene transcription in some tissues also varies by time of day
a) 10%
b) 20%
c) 30%
b) 20%
gene __________________ regulation is one mechanism underlying biochemical rhythms
transcription
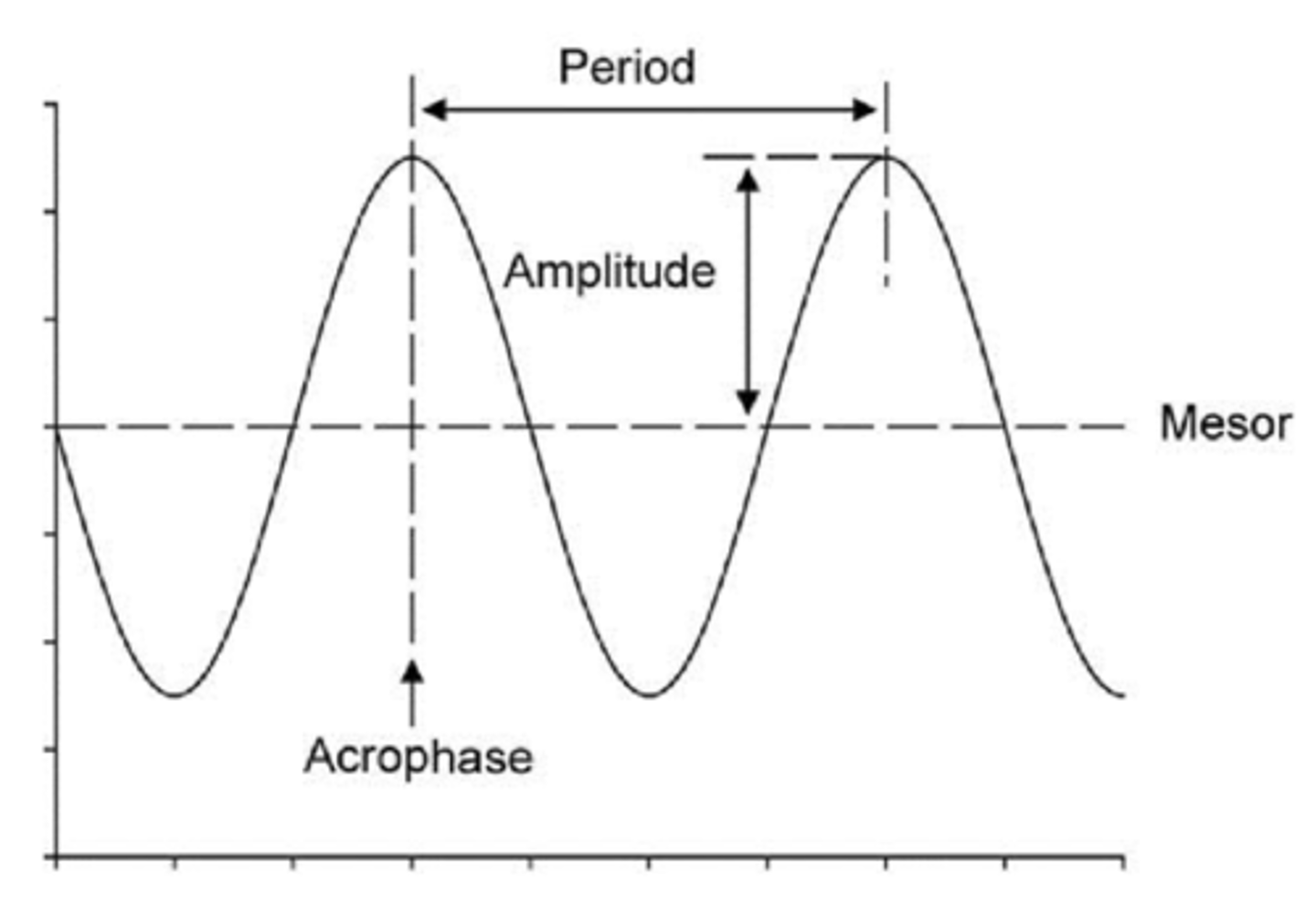
acrophase:
peak time of a rhythmic cycle identified by curve fitting
time series:
sequence of data points collected over time
What were the contributions of Jean Jacques d'ortus de Mairen (1729)?
1. noticed plants open & close leaves daily
2. tested mimosa pudica plants in continuous darkness, leaves still moved rhythmically
3. did not fully rule out unknown env. cues
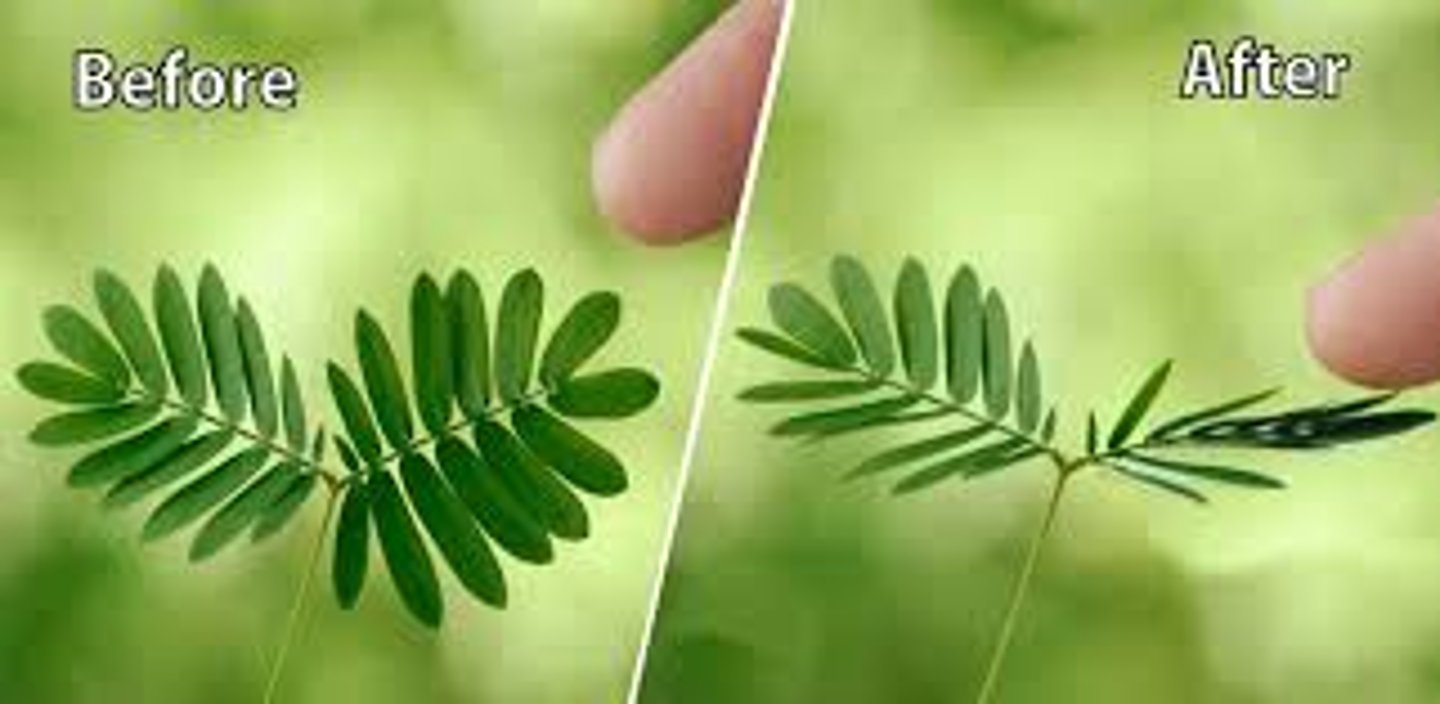

what were the contribution of Robert C. Bolles?
1. encouraged asking ridiculous questions (ie. challenging untested assumptions)
2. sparked interest in further pursuing the mimosa plant rhythms
What were the contributions of Duhamel du Monceau
1. replicated de Mairen's findings
2. showed rhythm persists even under constant temp conditions
what were the contributions of Augustin de Candolle (1800s)?
1. used a cave to shielf plants from all sunlight and remove env conditions
2. found leaf movement rhythm continued with a periiod of 23.8h
3. demonstrated the rhythm continued is intrinsic and not by env cues
4. first clear demonstration of a circadian rhythm
What was the significance of the 23.8h period of the mimosa pudica?
proves that rhythm is generated internally, not by unseen env cues
What were the contributions of August Forel (1910)?
1. observed honey bees visiting breakfast site daily @ the same time
2. called this "zeitgedächthis" ("time-memory")
zeitgedächthis
time-memory
what were the contributions of Inge Beling? (1920s)
1. confirmed bees learn & remember feeding times using an internal 24 h clock
2. experiments done deep in salt mines
3. Bees cant learn feeding intervals that differ from 24h (19h)
4. demonstrated an endogenous circadian clock in beed
what were the contributions of Renner (1950s)
1. trained bees to feed baily at noon in NY
2. After bring flown across 3 time zones to California, beees arrived 3 hrs early (NY time > Cali time)
3. Demonstrated jet lag in bees, confirming internal clock use
Why do bees need such a precise clock?
1. flowers open and close at specific times to regulate nectar availability
2. Linnaeus/ flower clock concept (1751) categorizes flowers by opening behaviour
3. bees must visit flowers soon after opening to get nectar (early bee advantage)
4. This endogenous niche favours bees with accurate time-memory - linked to 24hr internal clock
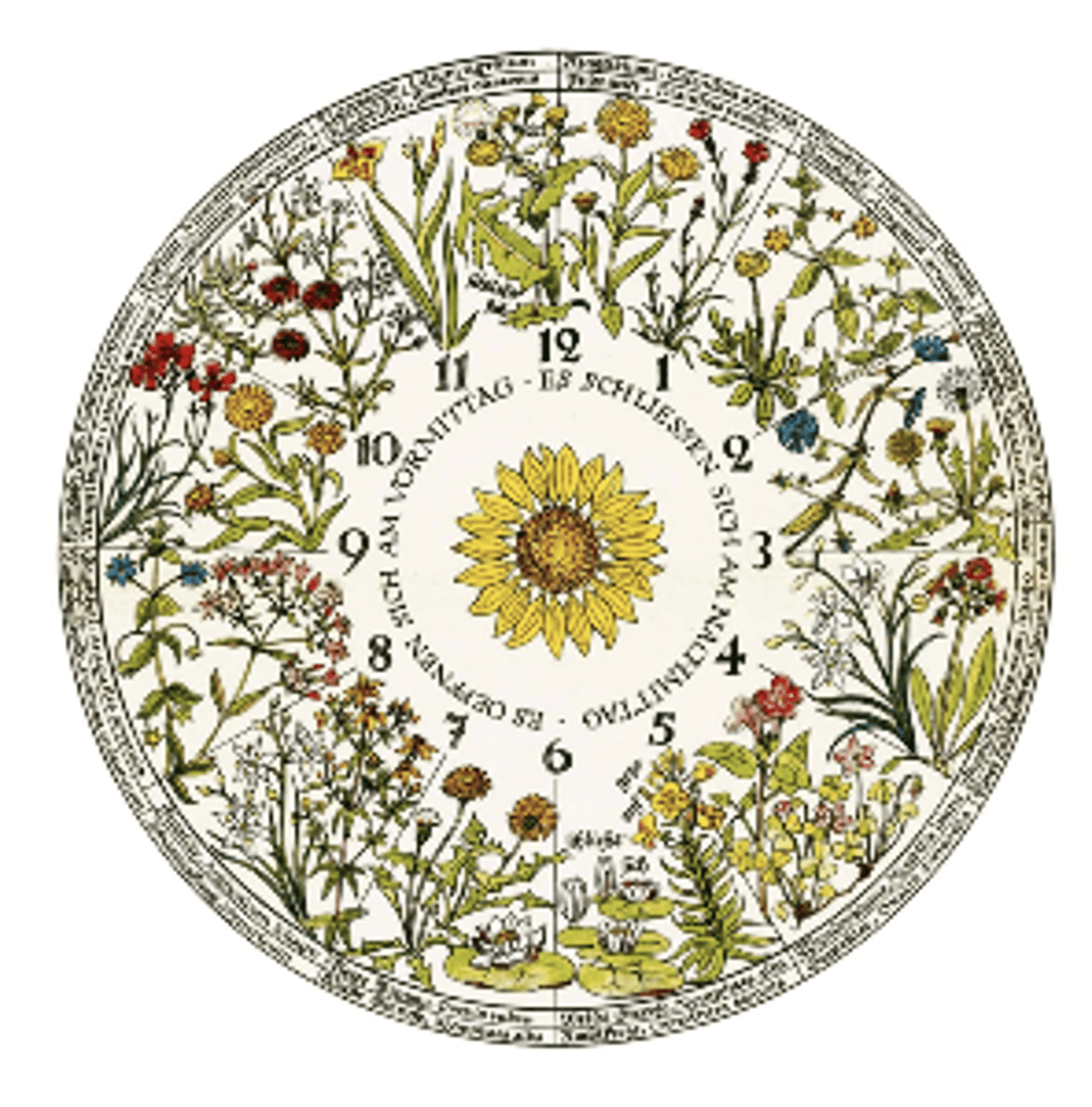

Linnaeus/ flower clock concept (1751) categorizes flowers by opening behaviour
what were the categories?
1. meteorici - open/close with weather changes
2. tropici - follows daylight hrs
3. aequinoctales - open/close at certain hrs daily
What was the contribution of Andrew Marvell?
wrote a poem in 1678 called "The Garden"
hints at the dance of floral timing and bee activity
described how bees compute their time as well as us
What was included in the hypothesis that there is an unknown environmental cue (factor x) living in space?
electromagnetic field variations
the ________ hr rhythm in cave plants (de Candolle) argues strongly against 24h environmental factors causing rhythms
23.8h
Some doubted biological clocks exist, so to satisfy skeptics, what happened?
experiments needed to be done off the planet for no earth based env cues
What was the space shuttle Columbia experiment all about?
-organism
-method
organism: neurospora crassa (filamentous bread mold)
method: mold placed in "race tubes" with food, grows linearly procuding spores rhythmically
each batch of spores appears apprx. every 24 hrs (10cm spacing)
tubes kept in constant darkness during week-long space flight
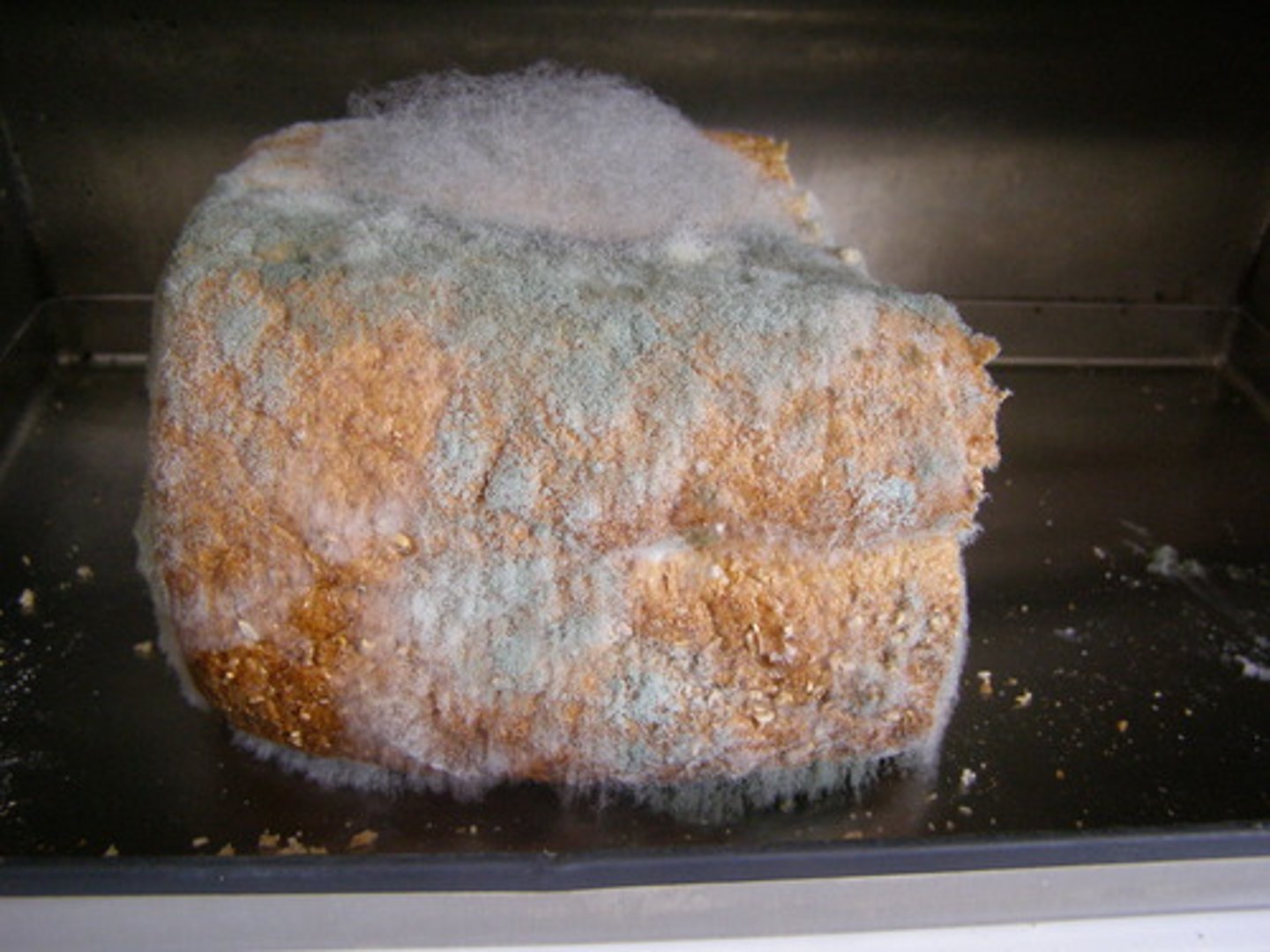

what were the results of the space shuttle columbia experiment?
1. the 24h rhythm of spore production persisted in outer space
2. no earth-based env cues could have influenced it
3. zero-gravity caused some asymmetry in spore distribution but didn't disrupt rhythm
4. settled the long debate of internal vs. external control of biological rhythms
t or f: true circadian rhythms persist without time cues
true
What did Simpson & Galbraith discover in 1906?
body temp rhythms in macques monkeys persisted in constant light and dark
what technological progress was done to enable better studies?
1. kymograph adopted for rat locomotion (Stewart, 1898)
2. Running wheels & motorized chart recorders (Richter, 1920s)
3. Transition to computerized analysis in 1980s
What was the importance of Colin Stewart, 1898
kymograph adopted for rat locomotion
-placed rats inside rotating drum linked to kymograph
-automated recording of voluntary running
what was the importance of Richter in the 1920s?
Running wheels & motorized chart recorders
What are actograms?
visual representations of activity over days, showing rhythms and free running patterns
t or f: circadian rhythms are endogenous and persist only in sighted animals
false: also work in blind animals
in what ways do behavioural rhythms differ by species and behaviour type?
1. rats and hamsters show clear nocturnal activity rhythms
2. eating & drinking rhythms may be weaker/diff from locomotor activity
Explain the invention of the kymograph
1. invented by Carl Ludwig in 1840s
2. originally for BP
3. adapted by Colin Stewart in 1898 to record rat locomotion
What were the further refinements of the kymograph after:
1. invented by Carl Ludwig in 1840s
2. originally for BP
3. adapted by Colin Stewart in 1898 to record rat locomotion
James Slonaker (1908) allowed long term recordings of activity levels but didn't docus on daily rhythms or light conditions
What were Carl Richter's studies in the 1920s?
1. used kymographs connected to cages to measure spontaneous rat behaviours in barren environment
2. the behaviours shown rhythmicity over hrs and days without external cues
Explain the evolution of old equipment to running wheels and motorized chart recorders
1. Richter replaced kymographs with slow moving chart recorders triggered by wheel rotations
2. produced ink every 24 hr periods
3. multiple days of data were pasted tgt into actograms to visualize activity rhythms
Describe the importance of the digital revolution in the 1980s
1. personal computers replaced manual graphing
2. enabled statistical analysis of circadian parameters
What were 4 key findings on mammalian circadian rhythms?
1. Rats are mainly nocturnal, and blind rats also have persistent activity rhythms but drift with free running rhythms
2. Different behaviours show varying rhythm precision & amplitude
3. Syrian hamsters show strong nocturnal wheel running but weaker daily rhythms in food intake, which occur around the clock due to food hoarding behaviour
4. beyond wheel running, other devices help study circadian rhythms
______________________ is often the most clear indicator of circadian rhythms
wheel running
Actogram formation is widely used in showing:
rest-activity cycles
Early data collection methods lacked what?
numerical values, limiting analysis
Early data collection methods lacked numerical values, limiting analysis
Modern methods of data collection include:
microswitches to count wheel rotations, producing numerical time-series data
Data was stored in spreadsheets for daily rhythm collection. What are the characteristics of these spreadsheets
1. rows = days (24 hrs each)
2. columns = unique hours (time bins)
3. Read like a book
Graphical representations of time sheets are good for visualization because of these features:
1. shaded cells resemble actograms
2. colour coded heat maps represent activity intensity
3. bar graphs can stimulate actogram detail
What is bi-variate plotting?
1. shows activity magnitude (y) by time (x)
2. continuous wave form; activity per day
3. average wave form/profile: mean across days with variability (SD)
Explain why time bin sizes matter
1. Larger bins (60 mins) = simpler but lose detail
2. Smaller bins (1 min) = detailed but short activity bouts and pauses
what is the most common research time bin size?
5-10 mins
What 3 things can actograms reveal?
1. nocturnal behaviour
2. persistence of rhythm in constant darkness
3. free running circadian rhythm slightly less than 24h
What are free running rhythms?
rhythms that drift L or R in constant conditions depending on period length
What are double plotted actograms?
1. show 48 hours per line (2 days)
2. each day appears 2x (L and R halves)
3. improves visualization of rhythm drift over time
Period (t) definition
length of one complete cycle
free-running
rhythm continues without external time cues
entrained
rhythm synchronized to an external cue
zeitgeber
environmental cue that entrains rhythms
phase
position/state within the cycle
can refer to a range of active/rest phase
acrophase
peak time of a fitted cosine function
alpha (a)
duration of daily active phase
Rho (p)
duration of daily rest phase
subjective day/night
perceived day/night during free running conditions
amplitude
height diff between peak and trough (or mean) of the rhythm
phase difference (psi)
time diff between 2 phases
zeitgeber time
time based on external cues (typically 24h LD cycle)
photoperiod
duration of daily light period
scotoperiod
duration of daily dark period
in curve fitting and rhythm analysis, what are the 3 curve fitting estimates from data?
1. period
2. amplitude
3. phase (acrophase)
biological rhythms often deviate from sine waves, showing square-wave components due to ____________________
masking (direct light/dark effects on behaviours)
biological rhythms often deviate from sine waves, showing square-wave components due to masking
what does this lead to?
acrophase may not align with the actual peak of raw data
What was Nathaniel Kleitman's cave study all about?
1. attempted to live on a 28 hour day
2. actual sleep-wake cycle was 25h
3. study was done to test if we can abandon the 24h day
4. data not published in actogram form, but likely resembled sleep-wake actograms
What are temporal isolation studies?
1. subjects live w/o knowledge of clock time or external cues
2. sleep wake times drift later by 2h per day (tau = 26.1h)
3. average tau for most people is closer to 25h in these conditions
compared to temporal isolation studies, more accurate circadian period estimates came from where?
1. constant routine protocol and forced desynchrony protocol
2. these yielded periods closer to 24.3h for sighted people and 24.6 hrs for blind
t or f: circadian period can be modified by experience
true
Why did we switch from temporal isolation studies to constant routine protocol?
bc temporal studies are laborious & expensive
what are 5 features of the constant routine method?
1. ppl remain awake in bed slightly tilted for 1-2 days
2. env is constant dim light
3. small meals given regularly
4. no sleeping/getting up
5. physiological measures collected frequently (temp, urine)
What were the 3 types of circadian rhythms identified via constant routine protocol?
1. sleep dependent rhythms
2. sleep independent rhythms
3. mixed rhythms
what are sleep dependent rhythms?
natural patterns tied to when you sleep and wake up.
Not directly controlled by circadian clock, but depend on sleep
ex. growth hormone rises at night but is suppressed by sleep deprivation
what are sleep independent rhythms?
processes that follow a regular pattern regardless of whether you're asleep or awake.
directly influenced by circadian clock, not just sleep
most reliable marker of circadian timing
ex. melatonin happens at night regardless of sleep deprivation
what are mixed rhythms?
rhythms jointly influenced by circadian clock and sleep-wake cycle
ex. body temp persists during sleep dep but reduced amplitude
ex. body temp fluctuates with day/night