GU 6, 14, 22 Pharm - Estrogen and Progesterone, Pregnancy and Lactation, Urology
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NOTE: I haven't yet added the gender affirming hormone therapy, as we will be learning more specific information on this from Dr. Cozens
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
In the follicular phase, the ovary produces _______, and in the luteal phase, it mainly produces _______ and _________.
follicular - estrogens
luteal - estrogens and progesterone
What are some contraindications to using estrogen? (note: these are the same contraindications to combination OC which includes estrogen)
Hx of DVT or PE, stroke, MI
current pregnancy
vaginal bleeding without cause (this could be endometrial hyperplasia)
Hx of liver disease (estrogen is metabolized in the liver; a major substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2. someone with a Hx of liver disease may not process the exogenous estrogen as well and will be at a higher risk for the AEs of estrogen (clotting, stroke, endometrial hyperplasia, etc.)
What route of administration for estrogen will have less AEs - oral or transdermal
transdermal has less AEs
Transdermal - patches, gel, spray, emulsion
Total dose required is reduced
Less Nausea and vomiting
Less fluctuation in blood levels
Lower risk of clotting
The following drugs are examples of what class of medication? What are they often used to treat?
Which of these drugs can increase risk of endometrial cancer?
Tamoxifen, Toremifine, Raloxifine, Bazedoxifene
SERMs
selective estrogen receptor modulators
- breast cancer drugs
Tamoxifen and Toremifine can increase risk for endometrial cancer
Why isn’t progestin indicated as a part of hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women who have undergone a hysterectomy?
Progestin is present only to counterbalance effects of estrogen; in women without a uterus, we aren’t concerned about endometrial hyperplasia (which can occur due to unopposed estrogen)
Use of depot progestin should be limited to < ___ years, because of the adverse effects of… __________
< 2 years
reduces bone mineral density and causes irreversible bone loss
How do Leuprolide and Nafareline work in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia?
These are GnRH agonists that lead to an initial surge of GnRH, then cause a negative feedback loop, leading to very low levels of LH, FSH, estrogen, and progesterone.
This make the body think that menopause has occurred, leading to shrinking endometrial tissue
What sort of AEs are you concerned about with GnRH agonists (Leuprolide and Nafareline)?
How should therapy be limited?
menopause like ssx: hot flashes, vaginal dryness, headaches, bone loss
manage vasomotor ssx with B6 and Vit E supplements
Limit therapy to no more than 6 months (test bone density)
How can hot flashes be relieved (esp with GnRH therapy)?
vit B6, Vit E supplements
A patient on warfarin and insulin begins taking oral contraceptives. What will the effect on these drugs be, if any?
OC s will reduce the effects of warfarin and insulin

True or False - Oral contraceptives can increase the effect of the following drugs: tricyclic antidepressants, Diazepam (Valium), and Theophylline (a bronchodilator)
True

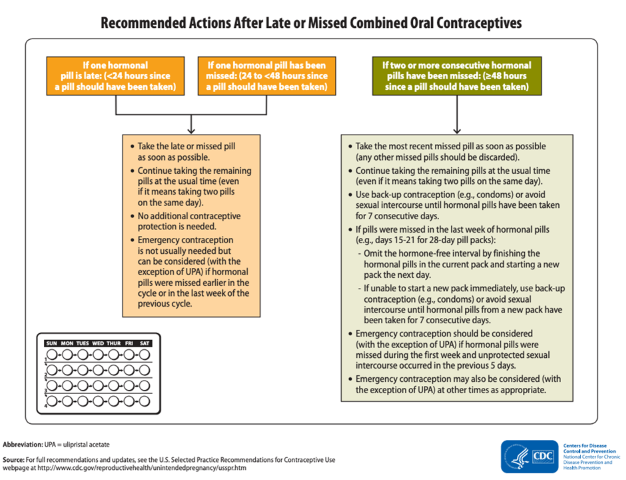
Your patient calls the clinic because they forgot to take their COC yesterday (they usually take it at 8 am, and it’s now 10 am the following day. They already took today’s pill.) What should you advise them to do?
Is any additional contraceptive protection needed?
take late or missed pill ASAP and continue taking remaining pills at usual time, even if it means taking two pills on the same day.
no additional contraceptive protection is needed
Someone missed two days of their COCs.
How many missed pills should they take (ASAP), and what back up contraception should be used?
take most recent missed pill and discard other missed pills, and continue taking remaining pills at the usual time. Back up contraception for 7 days.
see image for more nuance
Your patient is starting the mini-pill. They start taking the pill 5 days after the start of their period. When are they protected from pregnancy? What if they start the pill after 5 days?
immediately, since it’s only been 5 days since the first day of their menses.
After 5 days, they need to use condoms or spermicide as back up for the first two days

The implant lasts for up to ______ years
5 years (see chart)
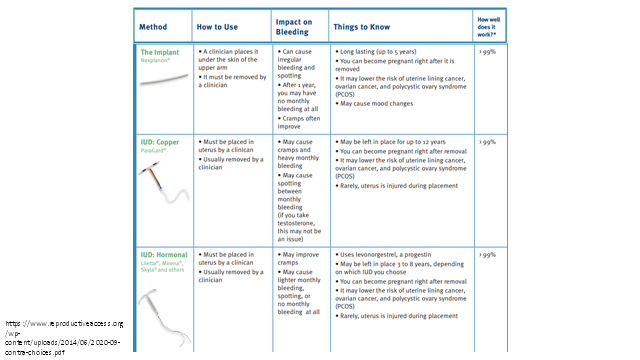
copper IUD (paragard) may be left in place for up to _____ years
12 years
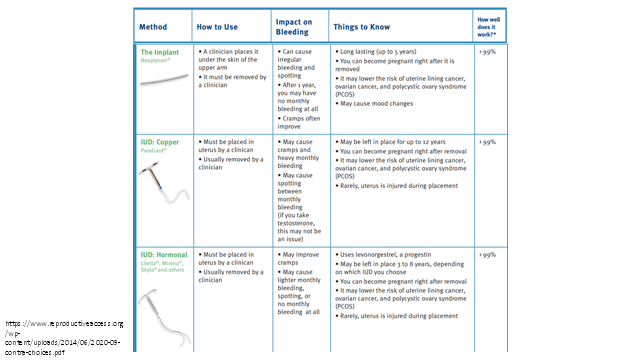
How often may the side effects of Depo-Provera last?
may last up to 6 months after stopping the shots
The copper IUD may be used for emergency contraception if used within ___ days of unprotected intercourse
5 days
Ullipristal (Ella) is an emergency contraceptive that may be used up to __ days after unprotected intercourse.
5 days
True or False - You can get Ulipristal (Ella) OTC without an Rx.
False - Rx needed (as of 3/15/2025)

How do progesterone agonists/analogs (such as emergency contraceptives, Ulipristal or Levonorgestrel) delay or inhibit ovulation?
Progesterone works via a negative feedback loop to prevent the LH surge, which leads to ovulation (see chart)
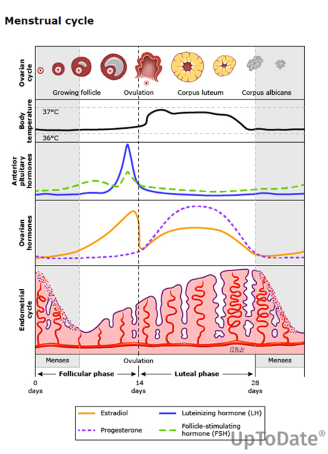
What are the upper weight efficacies for Levonorgestrel and Ulipristal? What is the risk of pregnancy for each option when BMI is > 30?
What about a patient whose BMI is 25-25.9?
Levonorgestrel - 70 kg (154 lb) if BMI >30, risk 3x higher; (risk is 1.5x higher if BMI 25-25.9)
Ulipristal - 85 kg (187 lb) if BMI > 30, risk 2x higher
A side effect of oral emergency contraceptives can include nausea and vomiting. If someone vomits after taking the medicine, when should you advise them to repeat dosing?
Ella - if vomiting occurs within 3 hours
Plan B - if someone vomits within 2 hours
True or False - Combining COCs with Plan B can lead to decreased efficacy of the emergency contraceptive.
True
(this is known as the Yuzpe regimen, which is not commonly used anymore)
Can Mifepristone be used as emergency contraceptive?
yes; it’s a synthetic steroids that acts as a progesterone antagonist/partial agonist; it blocks the LH surge and blocks or delays ovulation.
(While the increase in progesterone is often subtle, it is thought to be a physiological trigger for the LH surge, and a rise in progesterone can be a good indicator that ovulation is imminent.)
It can prevent pregnancy or cause abortion, depending on when it’s taken.
Mifepristone binds to progesterone receptors without activating them, preventing progesterone from stabilizing the endometrium.
What type of drugs will cross more easily through the placenta to the developing fetus (highly ionized or lipid soluble)?
lipid soluble
True or False - Amiodarone and Atenolol are safe for use in lactation.
false

if someone takes a drug which crosses into breast milk, when should they take the medicine, and how long should they wait until the next feeding?
take 30-60 min after nursing, and wait 3-4 hours before the next feeding
What is the highest risk time for teratogenic effects from drug exposure?
A) 0–2 weeks
B) 3–6 weeks
C) 6–10 weeks
D) Second and third trimesters
at 6-10 weeks gestation (this is when organogenesis occurs)
What system has replaced the "FDA Teratogenic Risk Categories” for drug pregnancy risks?
Risk summary, clinical considerations, and data must be available for drugs approved after June 29, 2001
What are testosterone esters?
Testosterone esters are simply testosterone molecules attached to fatty acids, making them last longer in the body. They help control how fast the testosterone is released into the bloodstream.
What are some AEs of testosterone when given to someone prior to their epiphyseal closure?
decreasing adult height due to premature epiphyseal closure
hepatoxicity
increased LDL and decreased HDL (lipid profiles)
promotes prostate cancer
edema - retention of salt and water
misuse potential (schedule III drug)
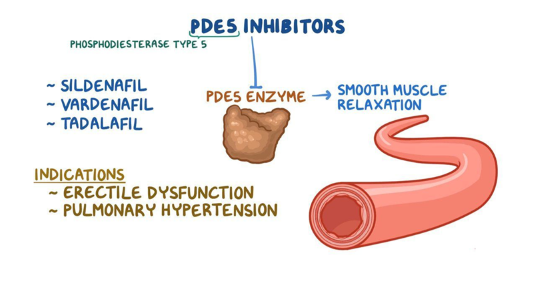
How do these drugs work: slidenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil
these are PDE5 inhibitors that lead to smooth muscle relaxation and increased blood flow; helps to maintain erections in context of sexual stimulation
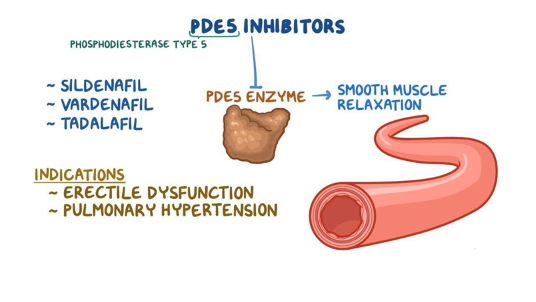
True or False - PDE5 inhibitors (such as Slidenafil) are approved for both Erectile Dysfunction AND Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
True
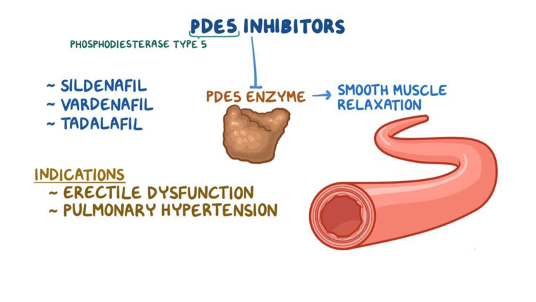
Which PDE 5 inhibitor is indicated for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia?
Tadalafil
Which of the following are common and rare side effects associated with PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil)?
A) Hypotension, Priapism, and Sudden Hearing Loss (rarely)
B) Tachycardia, Nausea, and Dizziness
C) Headache, Insomnia, and Fatigue
D) Hyperkalemia, Weight Gain, and Arrhythmias (rarely)
A) Hypotension, Priapism, and Sudden Hearing Loss (rarely)
True or False - PDE5 inhibitors are absolutely contraindicated in those taking nitrates
true
Name a second line med for Erectile Dysfunction
Alprostadil
mimics the effects of the naturally occurring prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), a vasodilator (a substance that widens blood vessels).
intracavernosal injection or transurethral suppository therapy (pellet inserted into urethra)

5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors and Alpha-1 Blockers are both indicated for the treatment of…
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Give two examples of 5-ARIs.
What is their MOA?
How long do they take to work?
Finasteride, Dutasteride
MOA - Blocks conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (active androgen in prostate)
- This is for very large prostate and/or mechanical obstruction
Shrinkage occurs slowly… 6-12 months
Give two examples of alpha-1 blockers. What is their MOA? What is their effect on levels of PSA?
Tamsulosin and Solodosin
MOA - alpha blockers selective to alpha-1 in prostate; help to relax smooth muscle in bladder neck, leading to rapid ssx improvement
no effect on PSA levels
What is an AE of tamsulosin?
abnormal ejaculation (it’s also relaxing muscles that control ejaculation, so patients can get some retrograde ejaculation)
How do antimuscarinics treat bladder dysfunction?
they block acetylcholine muscarinic receptors on the bladder, thereby decreasing contractions.
relax spasms
Which of the following medications are considered first-line for treating bladder dysfunction, such as overactive bladder or urge incontinence?
A) Oxybutynin, Solifenacin, Tolterodine
B) Tamsulosin, Finasteride, Dutasteride
C) Mirabegron, Fesoterodine, Trospium
D) Ibuprofen, Diphenhydramine, Loratadine
A) Oxybutynin, Solifenacin, Tolterodine
Oxybutynin, Solifenacin, and Tolterodine are antimuscarinics, which are first-line medications for treating overactive bladder and urge incontinence.
Tamsulosin, Finasteride, and Dutasteride are primarily used for BPH.
Mirabegron is a beta-3 adrenergic agonist and a second-line treatment for overactive bladder. However, Propranolol and Metoprolol are beta-blockers used for cardiovascular issues, not bladder dysfunction.
Ibuprofen, Diphenhydramine, and Loratadine are unrelated to bladder dysfunction treatment.
What class are the following drugs?
Darifenacin, Tolterodine, and Trospium
Antimuscarinics
Which antimuscarinic used in bladder dysfunction can be given via oral route, transdermal, or catheter?
A) Oxybutynin
B) Tolterodine
C) Solifenacin
D) Fesoterodine
A) Oxybutynin (Ditropan)
What class of med is Mirabegron (Myrbetriq)? What is it indicated for?
Beta-R Agonist that relaxes detrusor muscle in bladder, effective at treating overactive bladder