ch14 - circadian rhythms and sleep
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
circadian
biological/metabolic patterns in humans
2 main biological rhythms
ultradian and infradian rhythms
ultradian + example
happens multiples IN one day. ex: rest/activity cycle
infradian + example
cycles longer than a day. ex: menstrual cycle
other potential bio rhythm
endogenous circannual rhythms
endogenous circannual rhythm + example
annual cycle. ex: bird migratory patterns, hibernation
all animals/life have..
endogenous circadian rhythms
endogenous circadian rhythms regulate:
eating
drinking
body temp
hormones
pee
drug sensitivity
endogenous circadian rhythms can be ____ but NOT _____ by light and dark cycles, since they’re independent.
influenced/ changed
example of end. circadian being independent:
plant leaf still goes ⬆ for one half of the day and ⬇ for the other: maintains pattern even without L/D cues
purpose of circadian rhythm (3)
body’s internal 24 hour clock
optimizes energy use
keeps internal workings
free-running rhythm
rhythm with NO stimulus (not connected to outside world)
phase shift
change in stimulus (environment) = changes in activity (ex: time zones)
zeitgeber
“time giver”: external signals (light, food, meals) that set/reset internal bio ⏰
if external cues are removed, the rhythm will become…
free-running. body adjusts
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
part of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms
location of SCN 📍
dorsal to optic chains
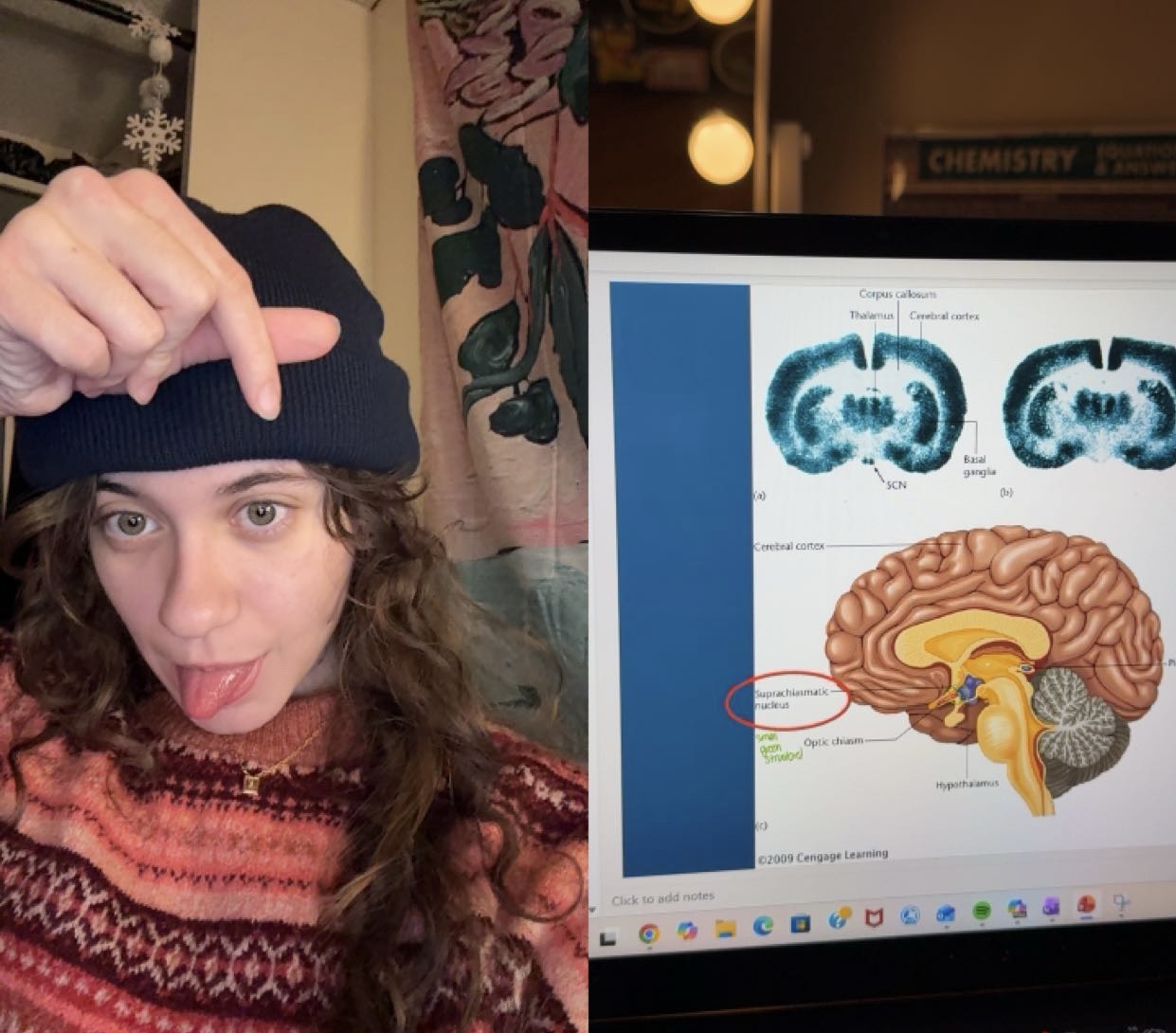
damage to SFN leads to
inconsistent rhythms; de synchronization to L/B. still work, but activity pattern is ERRATIC
SCN info flow about body temp/hormones
SCN → hypothalamic nuclei → (ind.) pineal gland
if SCN lesion rats are placed in constant darkness (no L/D), activity pattern becomes ____ _____.
completely random
SCN lesions will damage
the endogenous rhythm
SCN is activated
by light
how does the SCN lock onto externals like L/D cycle?
mammals: retinal ganglion cell that conveys info to SCN
invertebrates: photoreceptors outside eye (pineal gland)
resetting SCN happens with the small branch of optic nerve called
retinohypothalamic tract! (retina→ SCN)
retinohypothalamic has a photopigment called ___, meaning they don’t need rods or cones.
melanopsin
how do cells in SCN know how to maintain circadian rhythm?
let’s find out👀
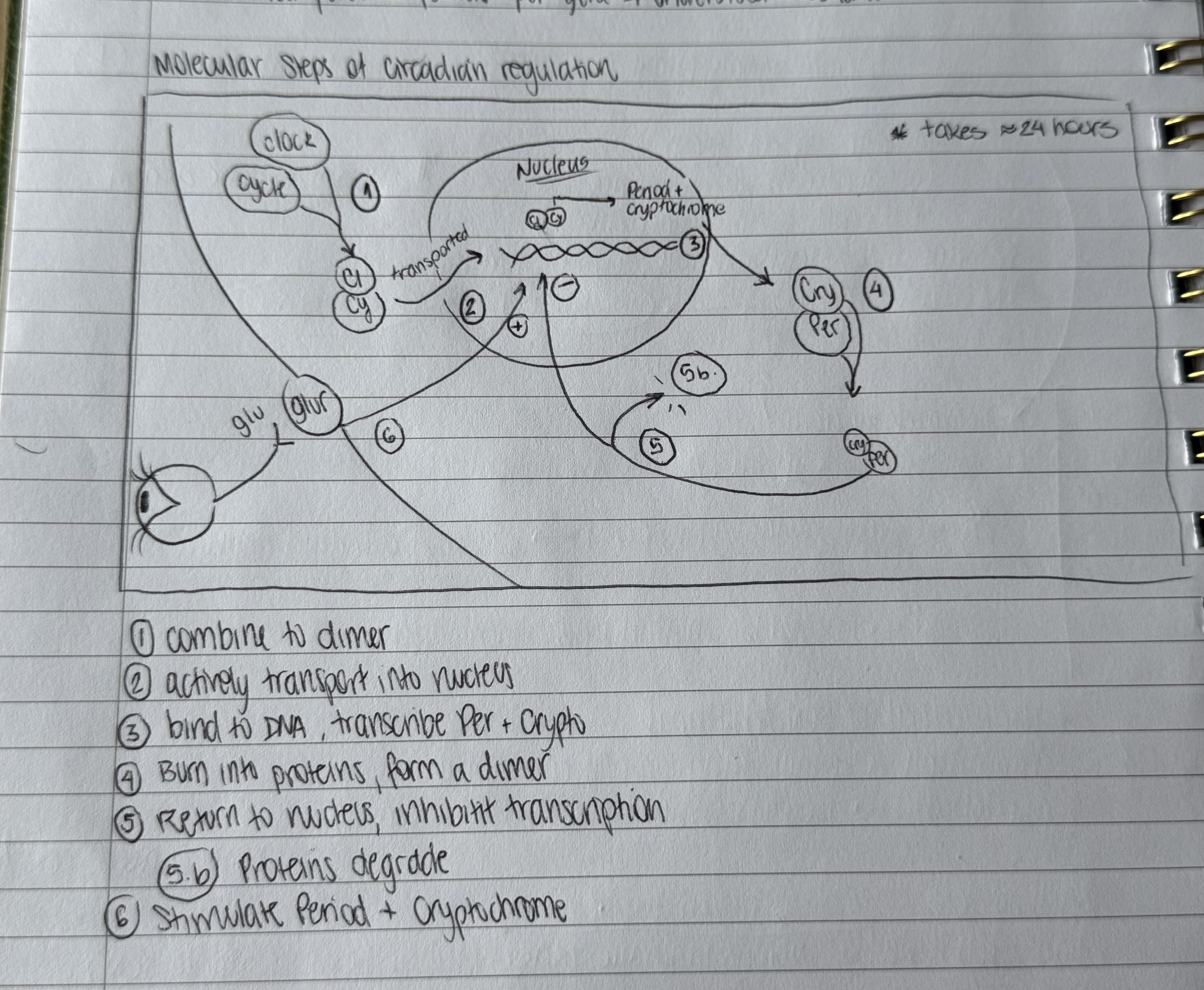
steps for circadian cell regulation (5):
combine to dimer
transport into nucleus
bind to DNA, transcribe per + cry genes
burn into proteins, form a dimer
either return to nucleus to inhibit transcription or break down
glutamate stimulates period + cryptochrome genes
tap to reveal steps of circadian regulation diagram!
your body’s preference for sleep/wake times may differ from other depending on (2):
alleles for genes in SCN
change with age
pineal gland is an ____ gland controlled by the ___.
endocrine/ SCN
pineal gland secretes ____.
melatonin😴
jet lag
disruption of rhythms due to time zones
jet lag is characterized by
sleepiness during day, awakeness during night
travelling WEST ___ our rhythms, while traveling EAST ____ them.
delays/ advances
jet lag remedies
none that were scientifically proven