L3 Drosophila (Imported from Quizlet)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Who established drosophila as a genetic model?
Thomas Hunt Morgan
What is drosophila used for as a genetic model?
To understand the basis of hereditary and genetics
The genes residing on chromosomes are the basis of what?
Hereditary
Many genes that control development of the fly were discovered and they are very similar to genes that control the development of ...?
Vertebrates (including humans)
Evolution reuses and adapts _____ and _____ rather than inventing new ways
Genes, principles
Genetic distance is measured in a unit named after Thomas Hunt Morgan, what is the name of this unit?
The Centi Morgan
What does one centi Morgan distance mean?
That two genes that are linked on a chromosome have a 1% chance of being separated in the progeny of an animal
What did Christiane Nusslein-Volhard and Eric Weischaus realise?
That drosophila genetics could be applied to find genes controlling development
What is meant by forward genetics?
If they are mutated they should lead to developmental defects that illustrate their function
A mutation in a gene required for head development should lead to what?
Headless embryos
Forward genetics starts with a _______, what is known and what must be determined?
Mutant, function known, gene sequence needs to be determined
What is forward genetics used for?
Positional identification/cloning
Reverse genetics starts with a _______, what is known and what must be determined?
Gene, gene sequence known, gene function needs to be determined
What is reverse genetics used for?
Gene knockout
Forward genetics is a technique that does what?
Identifies gene function first, once you have identified an interesting gene function the responsible gene sequence needs to be identified
Researcher often work backwards, if you have an interesting looking gene and want to know the function this is often done using what technologies?
Gene knockout
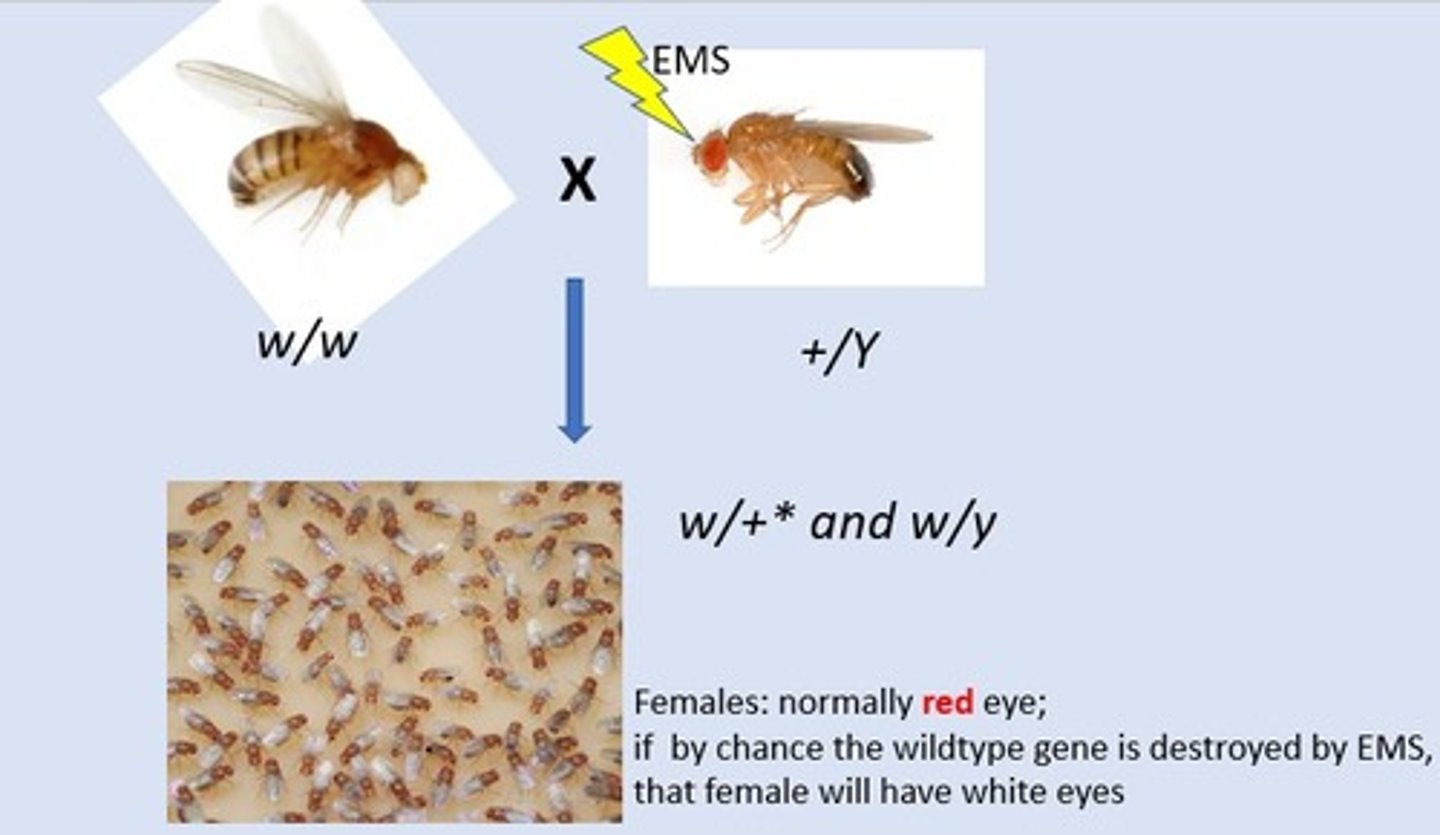
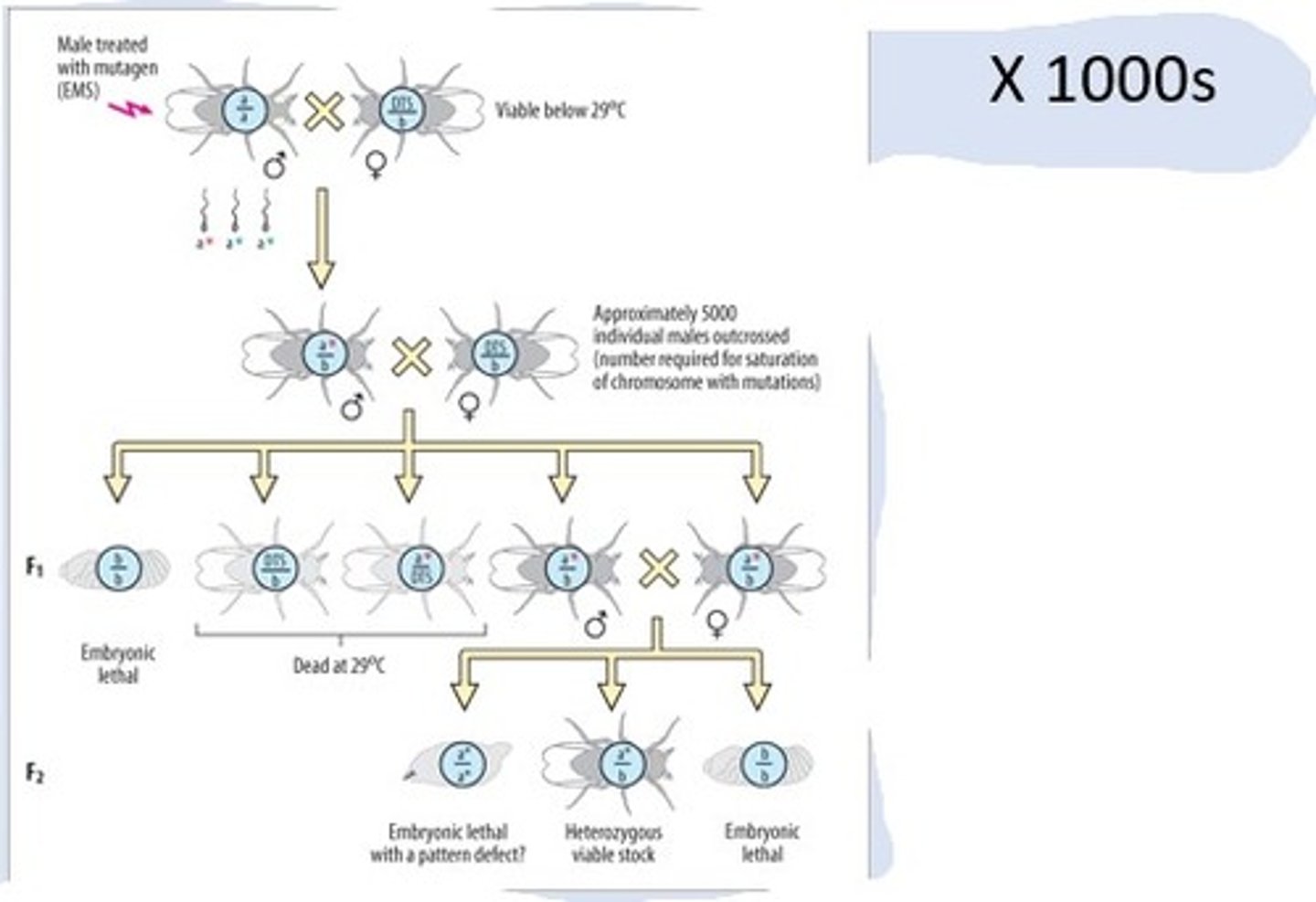
What does saturate screening rely on?
Statistics
What was known about saturation screening?
That treatment with DNA damaging chemicals could destroy an "average" gene with a decent frequency, for example 1 in 500
These frequencies in saturation screening can be estimated by using genes that influence what?
Eye colour
In order to make a mutation a chemical (____) was used which acts at ______, this treatment was adjusting such that an average gene would be destroyed with a chance of 1 in 500
EMS, random
So if there is one gene that is specifically required to form a head and you search 1 line = ___% of finding it, 10 lines = ____%, 100 lines = ___%, 500 lines = ____%, 1000 lines = ____%, 2000 lines = _____%
If there are 5 genes required for making a head you will find them all
0.2, 2, 19, 64, 87.5, 98
An important part of the innovation was developing methods for ______ and ______ eggs from 1000s of lines very efficiently
Keeping, screening
Flies are ____ploid
Di
What did mutant screens lead to?
Basic understanding of how genes are controlling the elaboration of a body plan
Molecular identification of many new genes and biological signalling pathways
Confirmed "genetics" as an extremely powerful way to dissect biological processes
These genes are not just important during development but often remain important throughout life during _____, ______, ______ and ______
Homeostasis, cancer, regeneration, ageing
Principles and genes identified and also the methods employed drove a lot of progress in the understanding of ...?
Human disease
The screen led to a basic understanding of the logic of how genes do what?
Pattern the developing embryo, a complex hierarchy of signalling molecules
The fly has a conveniently short life cycle of about __ days, to go from a _________ ___ of a zygote to a ________ mature adult
9, fertilised egg, sexually
Dependent on ________, flies have a maximal lifespan of around ____ days at ____
Temperature, 140, 18°C
The fly embryo develops into a larvae that hatches around ____hpf then the hatched larvae starts feeding and grows, it needs to malt __ times in order to grow because of what?
24, 2, its cuticle is rigid
The stages of a fly's life cycle are called ____, _____ and _____ instar larva, it then _____ and undergoes _______ before hatching out of the pupa as an adult fly
1st, 2nd, 3rd, pupates, metamorphosis
What is a micropyle?
A small hole in the insect egg for sperm entry
Drosophila embryos initially develop as a ______ this is very important later when what is set up?
Syncytium, A/P axis
3 hours post fertilisation the embryos consists of a single layer of cells enclosing the yolk (containing a few nuclei) at the posterior of the embryo, what is separated off and what do they form?
Pole cells are separated off which will form the germ line
The egg is fertilised through the ______, which consists of two flaps (dorsal appendages)
Micropyle
The sperm and egg nucleus fuse and then the zygotic nucleus undergoes very rapid ______, no membrane is _______ between the nuclei so the embryo is a _______
Division, formed, syncytium
After 90 minutes most of the nuclei migrate to the ______, a few cells at the end of the embryo are _______, what are these called?
Periphery, segregated, pole cells
What do pole cells do?
Form the germ line which will make the next generation
What will the membrane of the syncytial blastoderm do?
Invaginate and become enclose peripheral nuclei, thereby creating a cellular blastoderm
Once a cell has been specified to one of these fates (______, ______, _____) all dependents will ________ that fate
Mesoderm, endoderm, ectoderm, adopt
What is meant by anterior?
Head
What is meant by posterior?
Tail
What is meant by dorsal?
Back
What is meant by ventral?
Belly
What is the endoderm?
Gut
What is the mesoderm?
Muscle
What is the ectoderm?
Epidermis and nervous system
At the ______ _____ several regions can be identified
Cellular blastoderm
What is the axis nomenclature?
A/P axis, antero/posterior axis
What does the ventral region contain?
Mesoderm
What does the anterior and posterior regions contain?
Endoderm
What is the aminoserosa?
Extra embryonic tissue and will not really contribute to structures in the embryo
The embryo undergoes a complex set of cell/tissue movements, what do these movements act to do?
Bring the mesoderm and endoderm on the inside of the animal
Where does gastrulation start?
On the ventral side
Gastrulation starts with the formation of a _____ where ______ cells invaginate moving _____
Furrow, mesodermal, internally
At almost the same time as gastrulation, at the ____ and _____ end, the ______ invaginate thus the embryo is transformed from a simple single cell sheet enclosing the yolk to a ______ _____-______ structure
Anterior, posterior, endoderm, complex multi-layered
During gastrulation the ventral part of the embryo _____ pushing aside the ______, this is called ___ _____ ______, later it will _____ again and enclose the ________
Extends, aminoserosa, germ band extension, retract, aminoserosa
What becomes obvious during germ band extension?
Segmentation of the embryo
At 24h the larvae hatches and is ready to do what?
Start feeding
The correct or abnormal patterning of the embryo can be scored precisely by making ____ ____
Cuticle preps
After hatching, the larvae start _____ but as they have a ______ cuticle they need to ____ in order to ____
Feeding, rigid, malt, grow
The larval stages are named 1 instar after ______, 2nd and 3rd instar after ____ ______ _____
Hatching, each consecutive malt
At one point the 3rd instar larva forms ...?
A pupa
During pupation the larvae will do what?
Strongly change their appearance and metamorphose into the adult fly
What causes these strong changes in appearance during pupation?
Groups of cells that are set aside during early development
Where can these groups of cells that are set aside be found, what are they called?
In feeding larvae, these groups of cells are called imaginal disc and each disc will form a particular part of the fly
Which disc is most important to us and why?
The wing disc because is is often used as a very convenient tool in genetic and molecular studies to understand functions of particular cell-to-cell signalling pathways and pattering processes
Where are sperm cells formed?
In males
What do sperm cells contain and what do they do?
Germline stem cells at their tips that divide and generate progenitor cell which will divide further and over time differentiate into mature sperm
The females have ...?
Ovaries
What do ovaries consist of?
A collection of ovarioles, these overrules similarly have a gremlin stem cell located at the tip of each overiole
The gremlin stem cells are descendants of what?
Pole cells that were set aside early during development
Each end of the larva has unique structures, each segment has a characteristic pattern of ______
Denticles
Denticles have a particular ______, this allows ______ of ________ polarity in each segment
Orientation, recognition, anteroposterior
What is the screening stage?
Where embryos are analysed for patterning defects
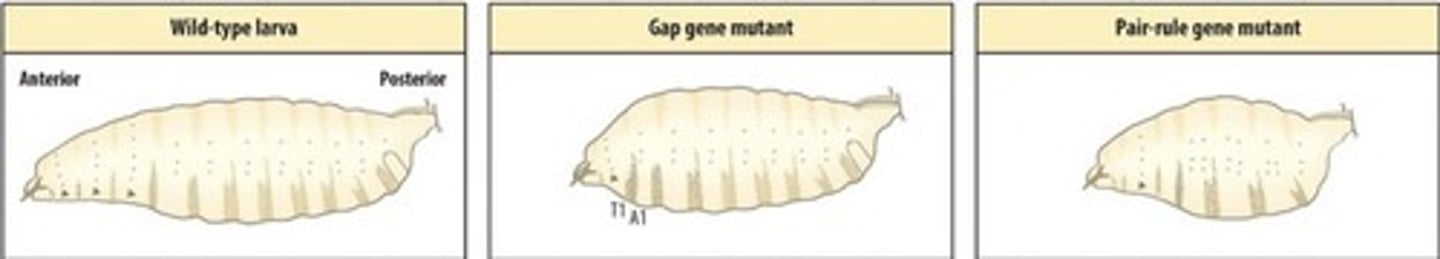
What does this image show?
2 examples of mutant phenotypes that were found
The first is a gap gene mutant here 2 segments are missing and thoracic segment T1 is fused directly to abdominal segment 1 (A1) thus the gene mutated is required for forming segments T2 and T3
In the second mutation every other segment is missing thus this gene is required for formation of alternating segments