5.2.1 - Photosynthesis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
a) What is the interrelationship between respiration and photosynthesis?
Products of photosynthesis and is the raw materials for respiration
Important for the cycle of CO2 and O2
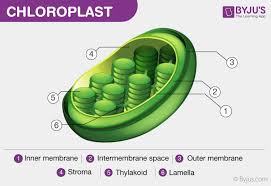
b) Label the diagram of chloroplasts?
What are the two main sites in the chloroplasts used for photosynthesis?
Thylakoids
Stacks of thylakoids = grana
Grana this is were LDR occurs due to large SA increases light absorptions
Contains its own DNA to create proteins to hold photosynthetic pigments in place / photosystems
Stroma:
Surrounds thylakoids so products from LDR can be used in LIDR
ci) What is the importance of photosynthetic pigments ad examples?
They absorb light at different wave lengths
Trap light energy
Example:
PS1 = 700nm
PS2 = 680nm
cii) How can you separate photosynthetic pigments and how do you work out Rf value?
Thin Layer Chromatography
Distance of spot/ Distance of solvent
d) What is the non- cyclic Light Dependent Stage of Photosynthesis?
Light hits PS2 - causing electrons to get excited
This causes them to pass across ETC with electron carriers and forms ATP
Electrons in PS1 is then lost due to the light striking
H+ ions from photolysis of water passes with electron which then binds to NADP to form reduced NADP = NADPH
Electrons oxidised from PS2 replaces electrons lost from PS1
Protons take part in chemosis and forms ATP then the NADP is in the stroma for LIDR
What is the cyclic process for Light Dependent Stage of Photosynthesis?
Only occurs in PS1 of 700nm
Light hits PS1 - causes electron to get excited and gain energy
They leave chloroplasts to go to the ETC
Through the ETC it doesn’t go through photolysis which means doesn’t produce reduced NADP/ O2/ H2 is formed but forms small amount of ATP
Goes back to the PS1
Why does chloroplasts only have PS1?
Only form ATP
Allows K ions to enter cell to lower water potential
Allows guard cells to cell and stoma to open
e) What happens in Light Independent Stage of Photosynthesis?
Calvin Cycle
Uses products from LDR which lead from the stroma
CO2 used for carbon fixation
Explain the Calvin Cycle?
Carbon dioxide combines with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a reaction catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO
Forming an unstable six-carbon compound which splits into two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP).
GP is then reduced to triose phosphate (TP) using ATP and reduced NADP from the light-dependent stage.
Some TP is used to produce glucose and other organic molecules.
Most TP is used to regenerate RuBP, which requires ATP.
Regeneration of RuBP allows the Calvin cycle to continue.