⋆. 𐙚 ̊ Anatomy and Physiology Exam One(ch. 1 - 3)
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam Monday 9/8/25!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
name the anatomical postions
-transverve plane
-coronal plane
-sagittal plane
-proximal
-distal
-lateral
-middle
transverse plane
divides body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower)
coronal plane
divides body from Anterior (front) and posterior (back) of body.
sagittal plane
divides body vertical left to right
proximal
the limbs that are closest to your body
distal
the limbs located furthest away from the body (point of attachment)
lateral
toward the side
medial
toward the middle
anatomy
The study of structures of living organisms
physiology
the study of how the human body works
list the terms of movement
-adduct/abduct
-flexion/extension
-elevation/depression
-ipsilateral/contralateral
adduct
body part moves toward center of body
abduct
move body part away from the center of body
flexion
bending or folding a joint
extension
straightening the joint
elevation
upper body (shoulder shrug)
depression
lower body
Ipsilateral
same side of body
contralateral
opposite side of body
Cranial/caudal (terms of location)
toward head of your skull, towards the tail of your brain
medial/lateral (terms of location)
closer to the midline, further from the midline
superior/inferior (terms of location)
higher, lower
anterior/posterior (terms of location)
front, back
rostral/caudal (terms of location)
towards the nose, toward the tail of brian
ventral/dorsal (terms of location)
toward the belly of structure, toward the back of structure
superficial/deep (terms of location)
toward the surface, away from surface
supine/prone (terms of location)
faced up, faced down
ligament
bone to bone
tendons
muscle to bone/cartilage
joints
moveable in some way
muscles
contract/constrict to shorten the
contract/constrict to shorten the distance between the two points
origin
less moveable joint of attachment
incertion
moves as a result of contraction
agonists
muscles that moves a structure
antagonist
muscles that oppose movement
what are the subsystems of speech?
-respiratory
-phonatory
-resonatory
-nervous
respiratory
lungs, breathing
phonation
vocal folds
articulatory
how we articulate sounds
resonatory
within the throat, mouth, and nasal passages
nervous
brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves
epithelial tissue
the most outer part of the tissue layers
connective tissue
supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues
muscles tissue
contracts to produce movement (striated, smooth, cardiac)
nerve tissue
main function is to receive, process, and transmit information throughout the body
Invertebral disc (C1 + C2)
-made of fibrocartilage
-containing a gelatinous core and a fibrous ring cushions vertebrae
-equalizes pressure
C1 aka
-atlas
C2 aka
-axis
the pectoral girdle consists of the scapula and…
-clavicle
-scapula
-sternum
-ribs
at rest, the rib cage has a______slope.
downward
Vertebrosternal ribs
true ribs
Vertebrochondral ribs
false ribs
Vertebral ribs
floating ribs
pectoral gridle acts a an…
anchor for spinal cord
spinous process corpus (C3)
majority of the (vertabre) bone
why are our ribs sloped downward?
to help us breathe
manubrium sterni
clavicle at first rib
second rib at juncture
corpus sterni
-ribs #3-7
-ribs # 8-10
ensiform/xiphiod process
brestbone (lower section of sterum)
what is the point of bifurcation of the treachea
the carnia
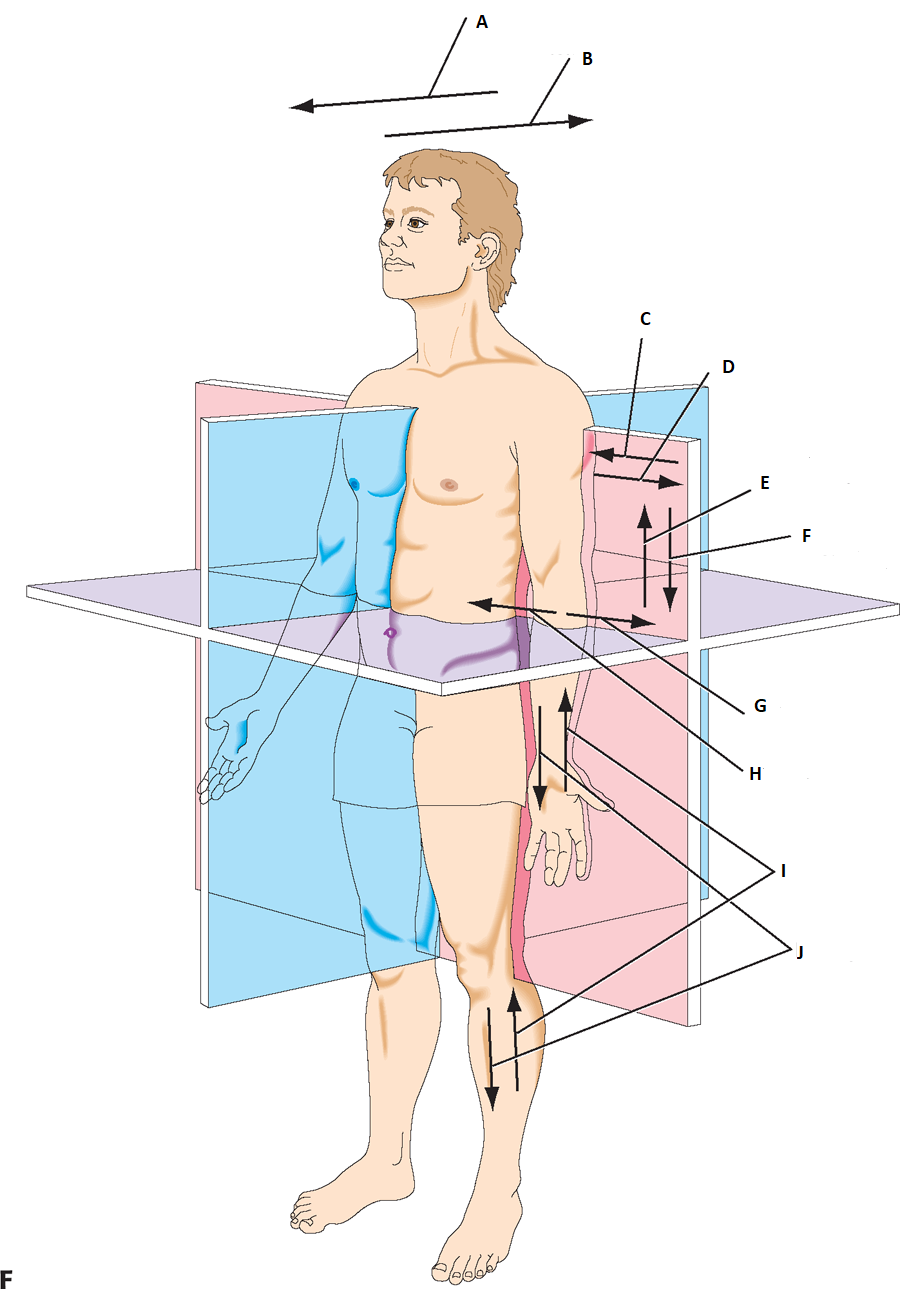
can you label a & b
anterior, postier
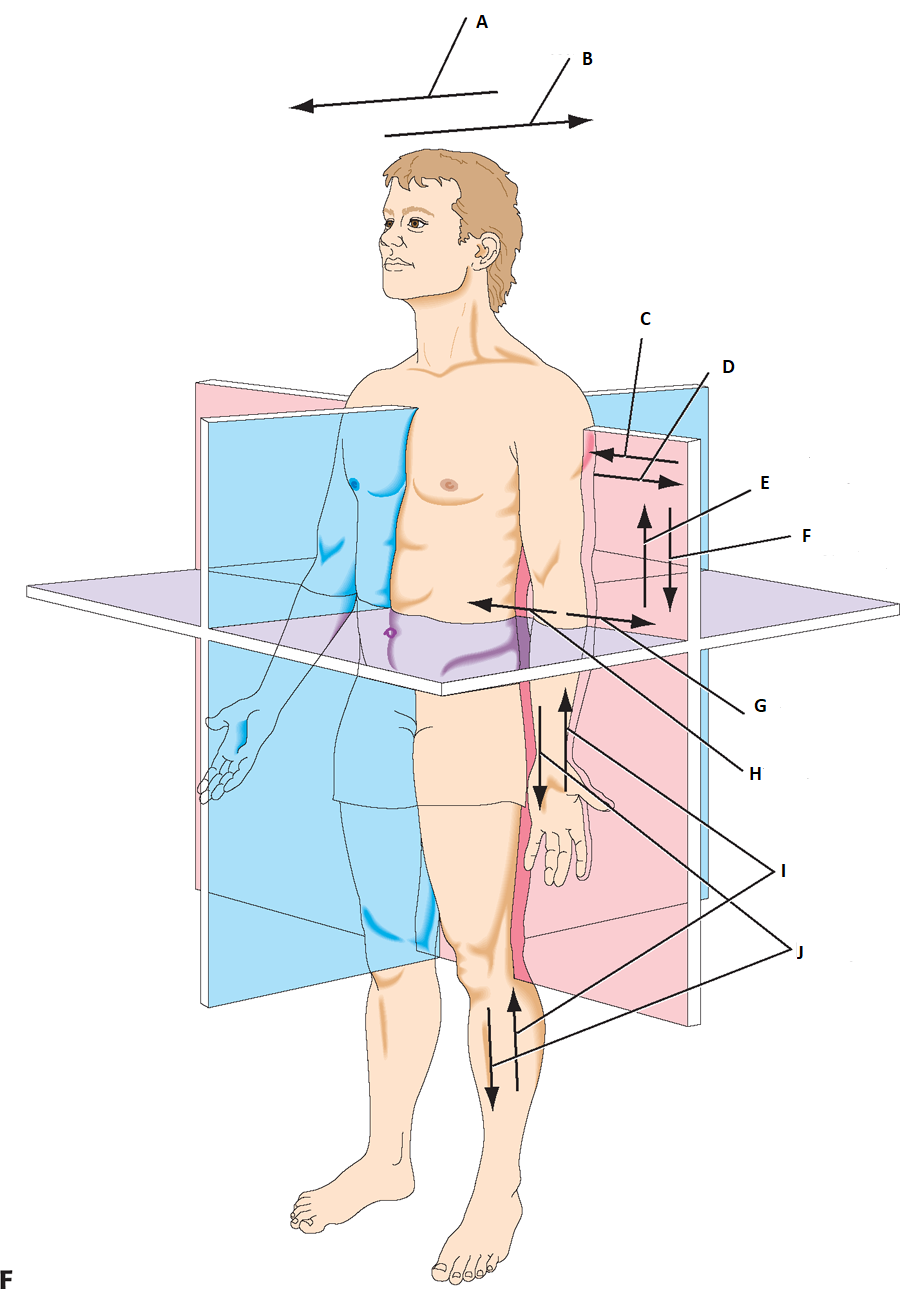
label c & d
medial, lateral
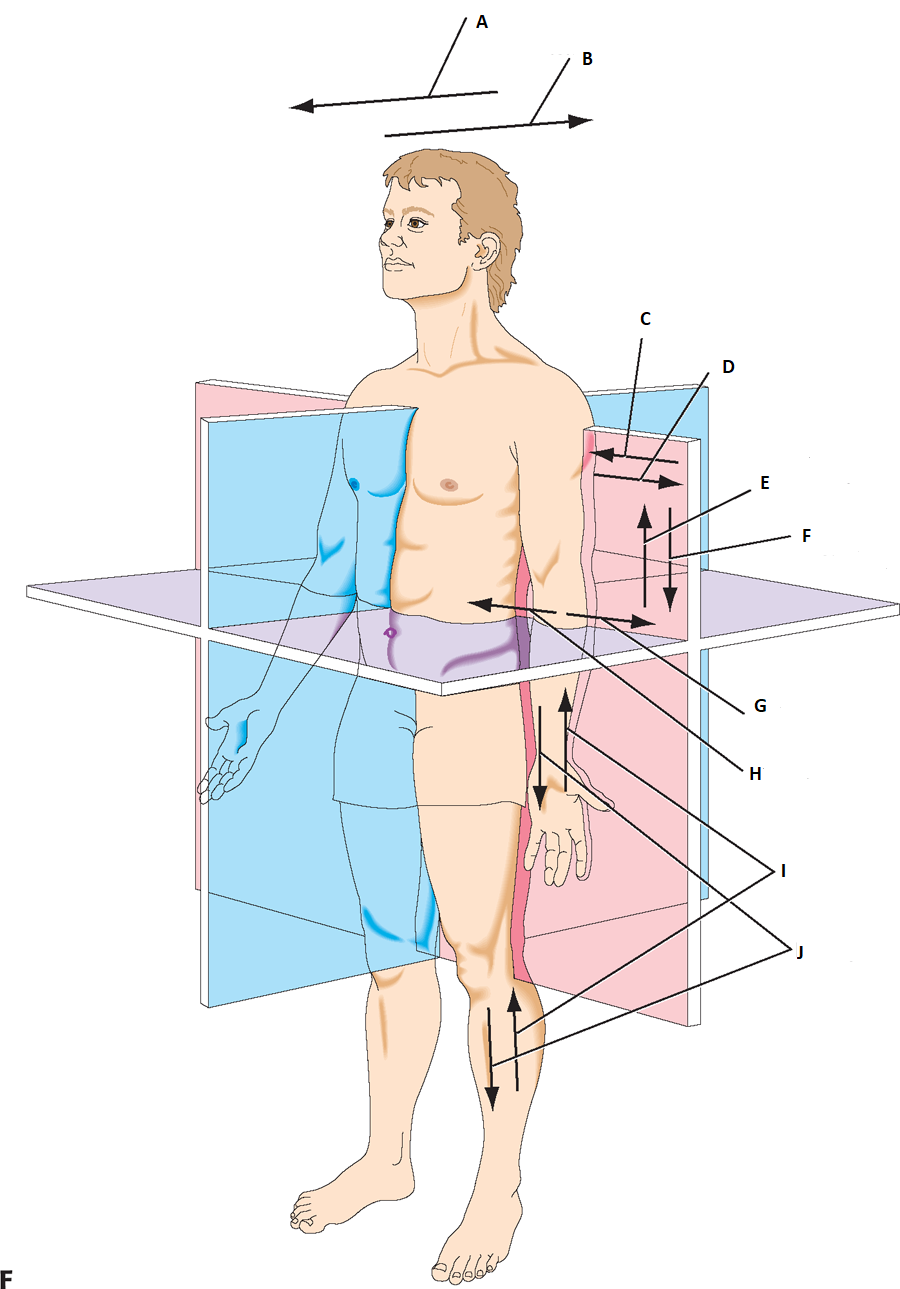
label e & f
superior(cranial), Inferior(caudal)
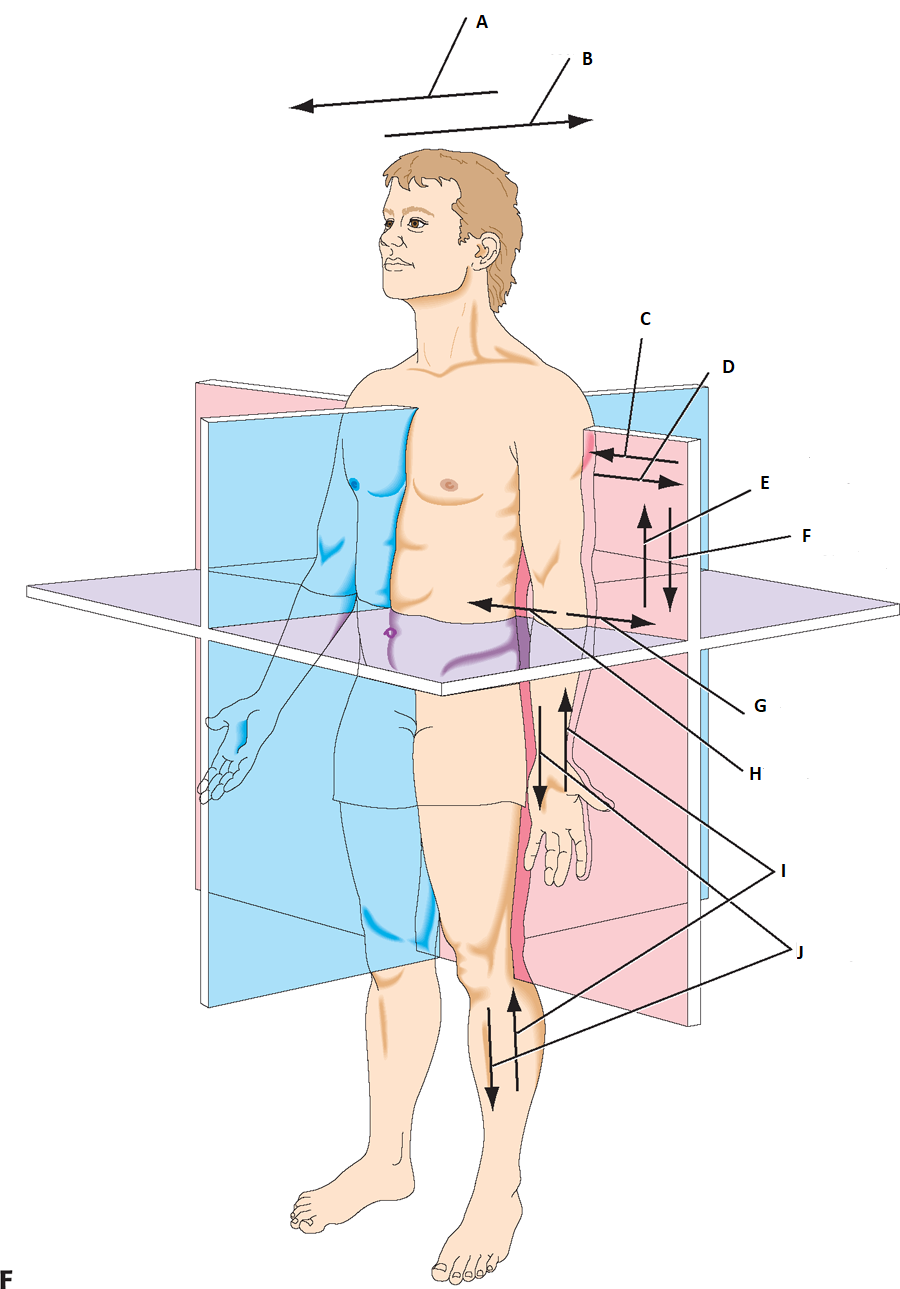
label g & h
abduct, adduct
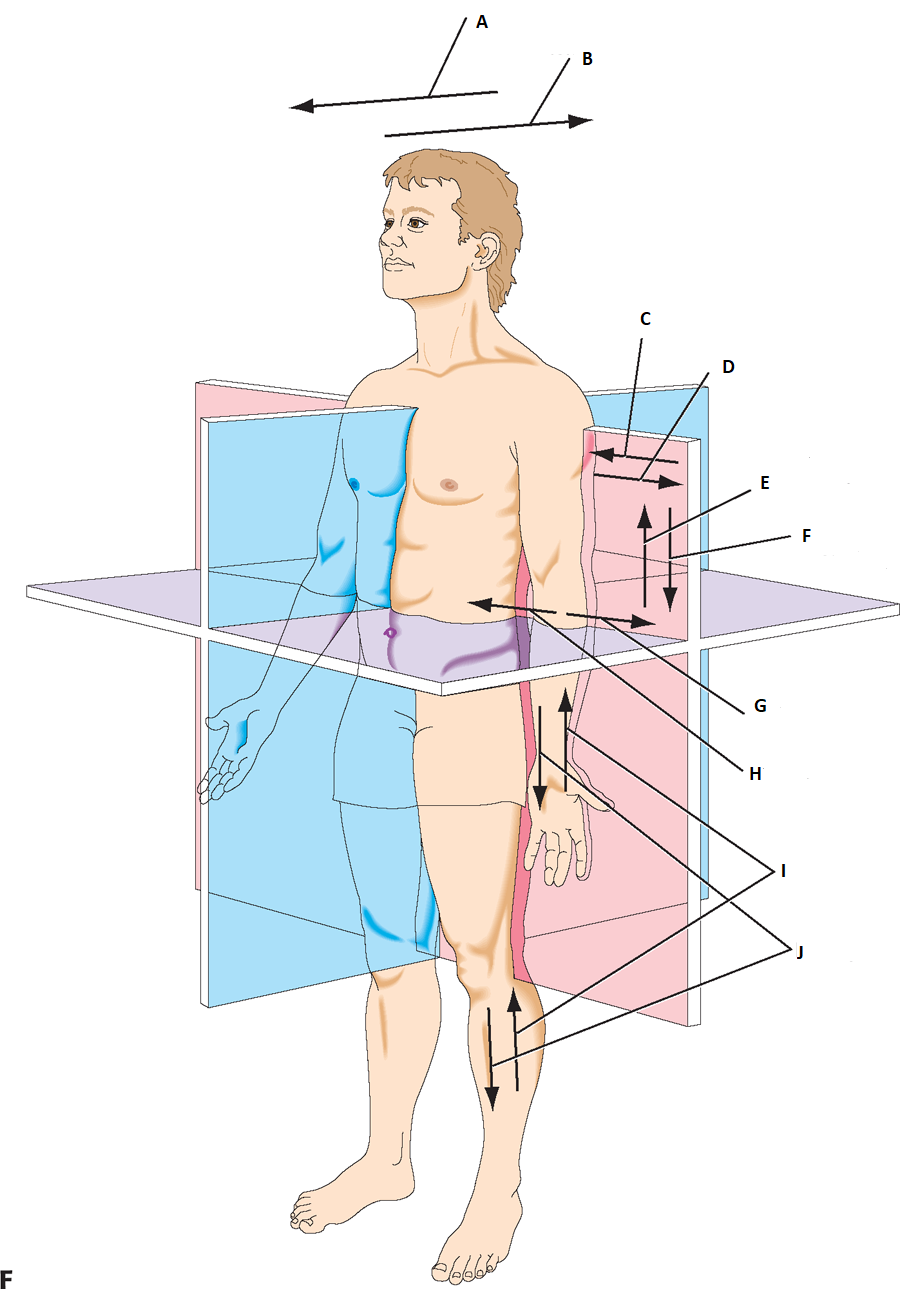
label I & J
proximally, distally
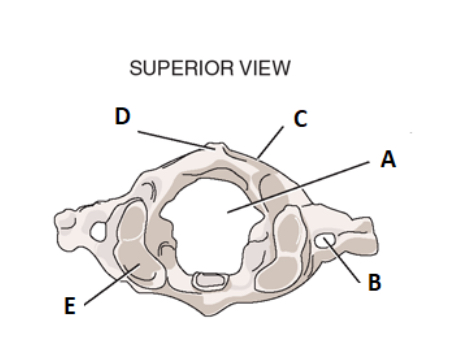
take a look at the surpior view for c1. label a
vertebral foramen
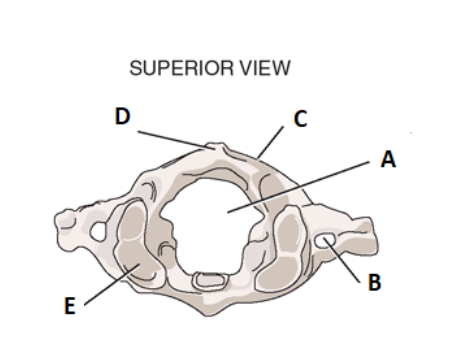
label b
transverse forman
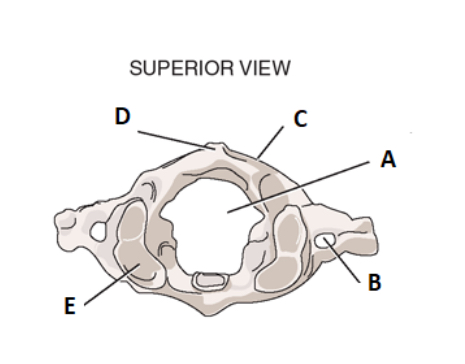
label c
posterior arch
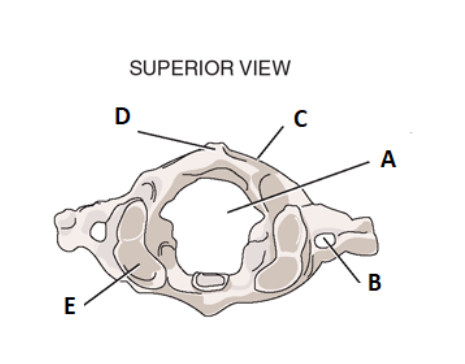
label d
posterior tubercle
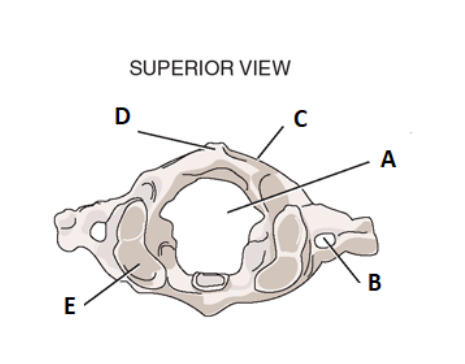
label e
facet for occiput
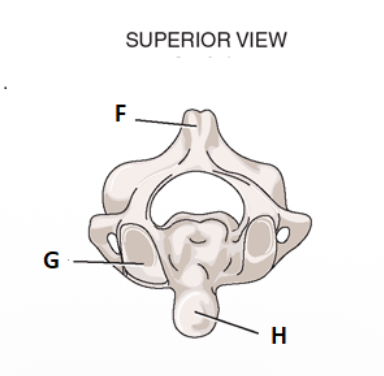
take look at the superior view for C2. label f.
spinous process
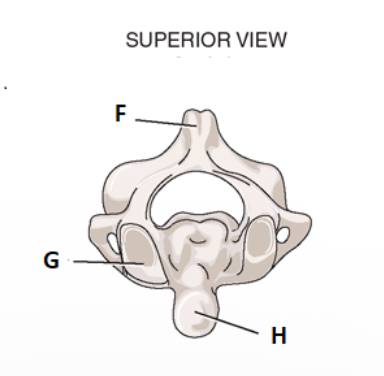
label g
facet for atlas
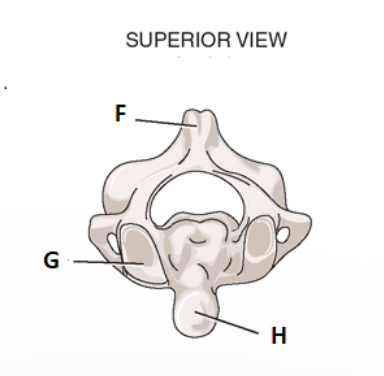
label h
odontoid process
transevrse foramen
vertebral artery and vein (only in cervical vertebrae)
intervertebral foramen
the hole that’s formed when two vertebral foramen come together
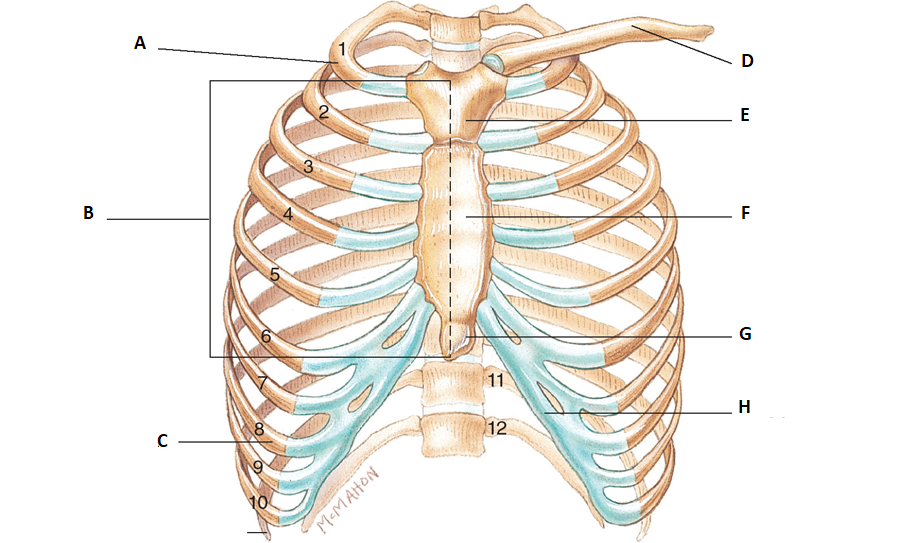
This is the Pectoral Girdle. what are a, b and c pointing to?
a. True ribs (1-7)
b. Sterum
c. Fasle ribs (8-10)
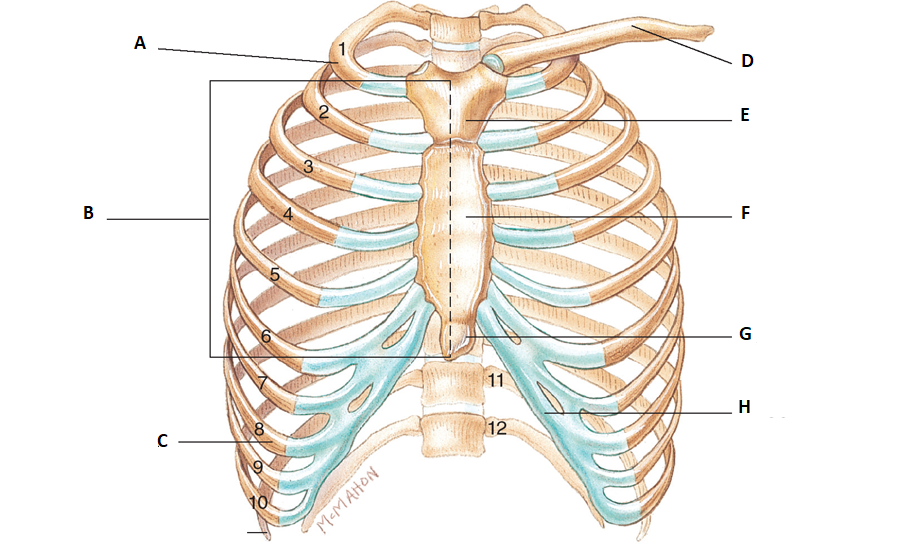
what numbers are floating ribs?
11 & 12
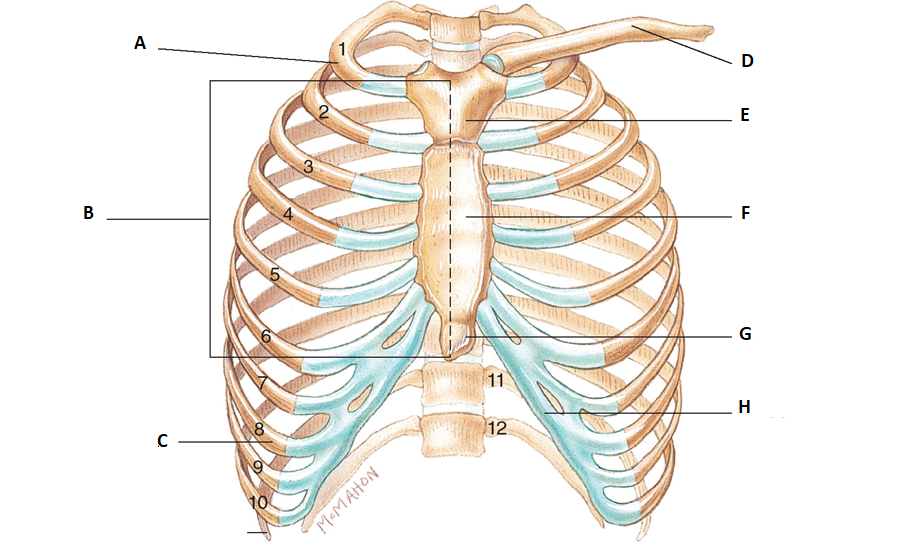
label d, e, f, g, & h
d. clavicle
e. manubrium
f. body
g. xiphoid process
h. costal cartilage
Where is the sternum with respect to the vertebral column?
the vertebral column runs along the posterior(back), the sternum is positioned along the anterior(front) chest wall.
Where is the visceral pleural layer with respect to the parietal pleural layer?
the visceral layer lies deep to the parietal pleural layer
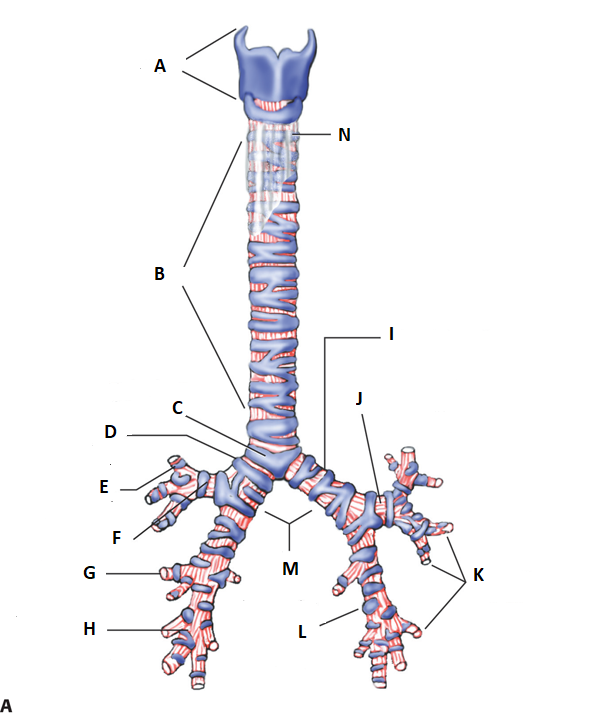
This is the trachea. label a, b, c, & d
a. Larynx
b. trachea
c. carnia treaschea
d. right main bronchus
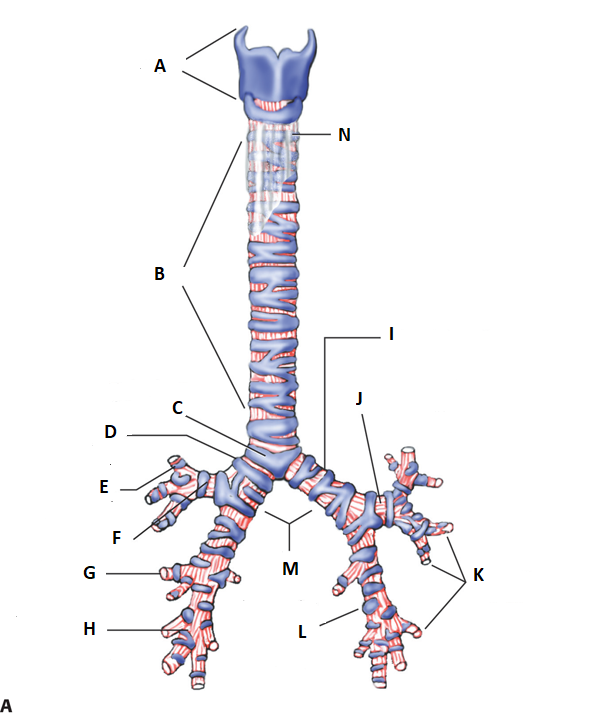
label e, f, g, & h
e. right tertiary bronchus
f. right superior lobar bronchus
g. right tertiary bronchus (again)
h. right inferior lobar bronchus
what are alveoli?
where gas exchange occurs for breathing.
how many capillaries per alveolus?
2000
what are the side of the lungs and what do they do.
-right(3), left(2)
- Respiratory passageway, warms and humidifies air
what happens in your lungs if they get too cold?
(less humid air makes tissues more susceptible to) damage and infection
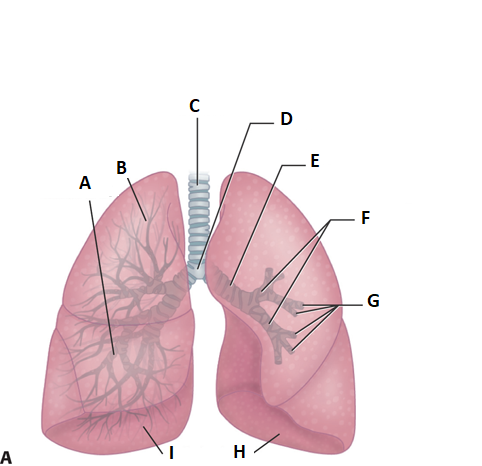
these are the lungs. label a.
middle lobe
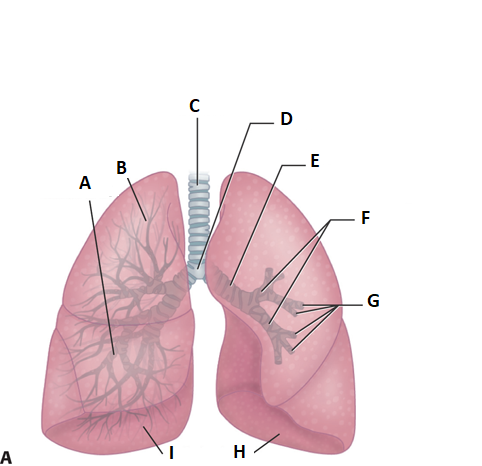
label b
superior lobe
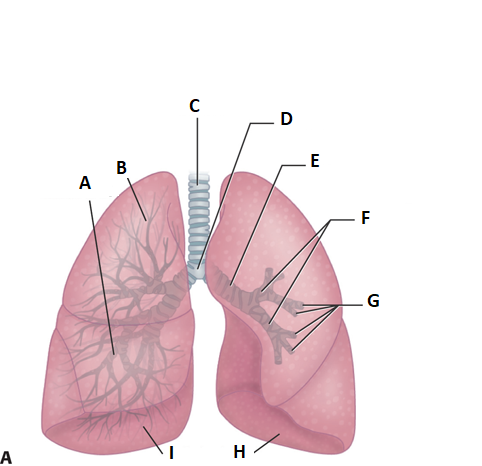
label c
treachea
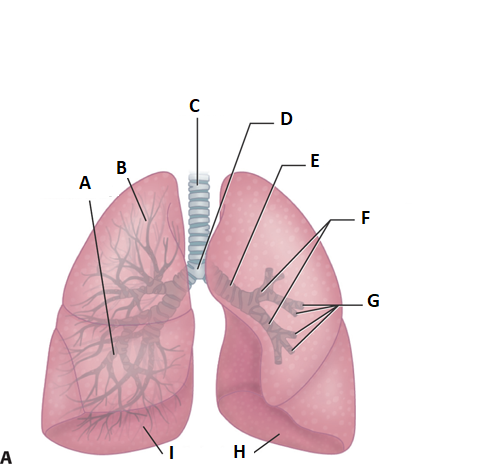
ladel d
carnia
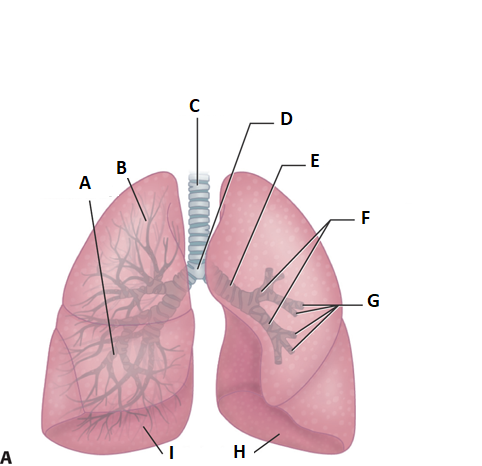
label e
mainstem bronchus
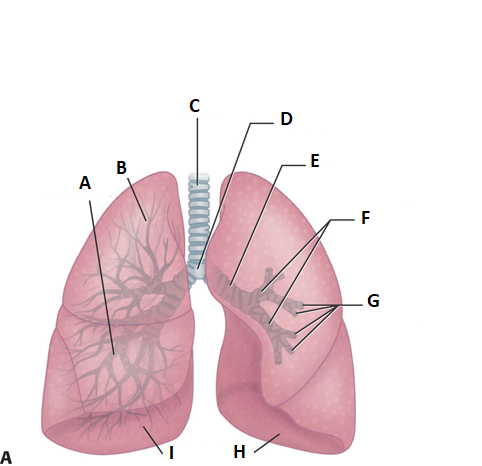
label f
secondary bronchi
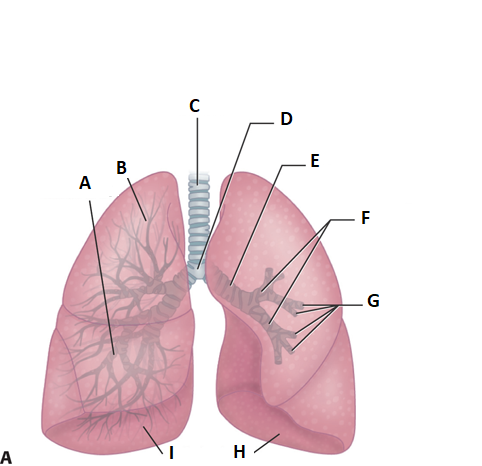
label g
tertiary bronchi
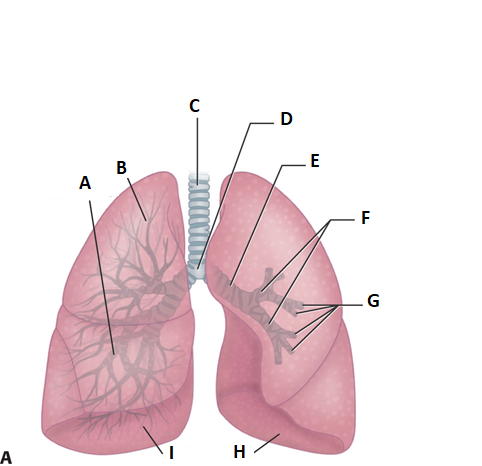
label i and h
inferior lobe
what is the purpose of the plura lining?
it wraps around our lung tissue
What is the outer layer of the pleura called?
parietal
what is the inner layer of the pleurea called?
visceral
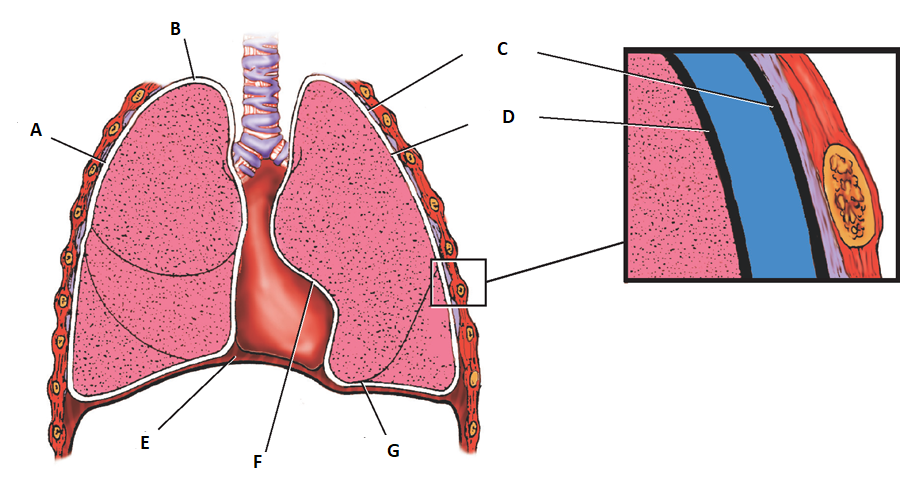
label a
costal pleura
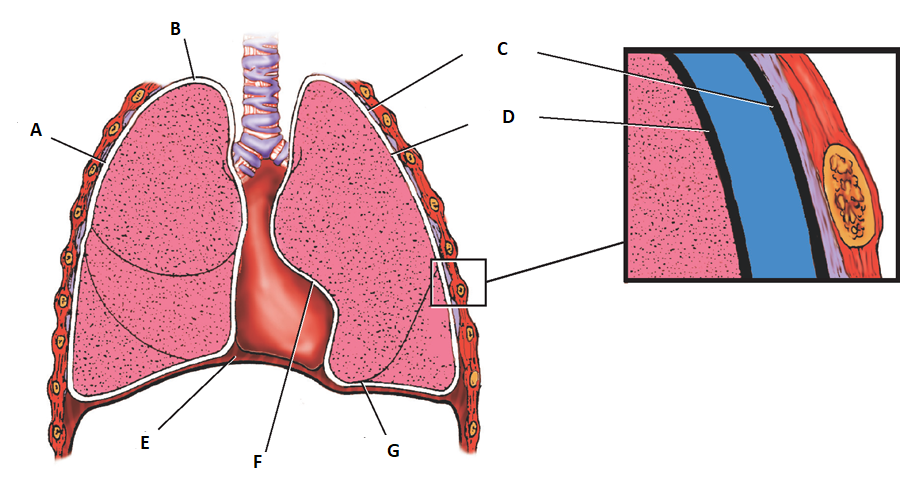
label b
apical pleura