Imaging - Preprocessing and Histograms
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is preprocessing?
Manipulations made to the raw digital image data to compensate for physical flaws in image acquisition
Occurs before storage
What kinds of flaws does preprocessing correct?
Physical flaws related to:
1. Elements and circuitry of the image receptor
2. Physical elements and circuitry of the processor
What is point processing?
Adjusting the image brightness and contrast
Involves the creation of a histogram and application of a LUT
What is point processing also known as?
Grayscale processing
What is local processing?
Zooming and magnification (moreso post-processing)
What is geometric processing?
Changing the position or orientation of pixels (rotation)
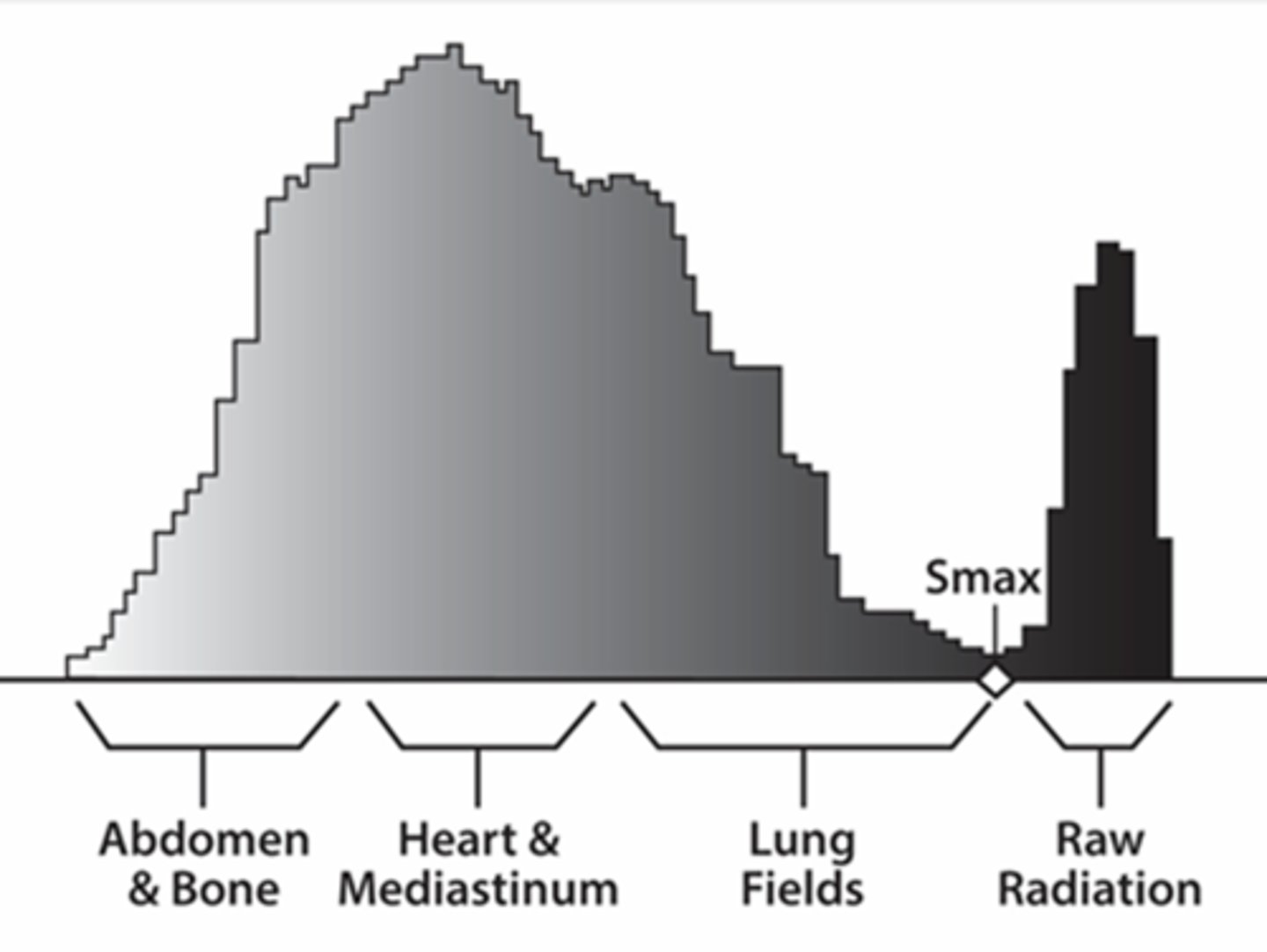
On a histogram of a chest, where would the abdomen, mediastinum, lung tissue, and background be represented?
Abdomen: Left, brighter
Mediastinum: Middle
Lung: Right, darker
Background density is represented by spike to the right
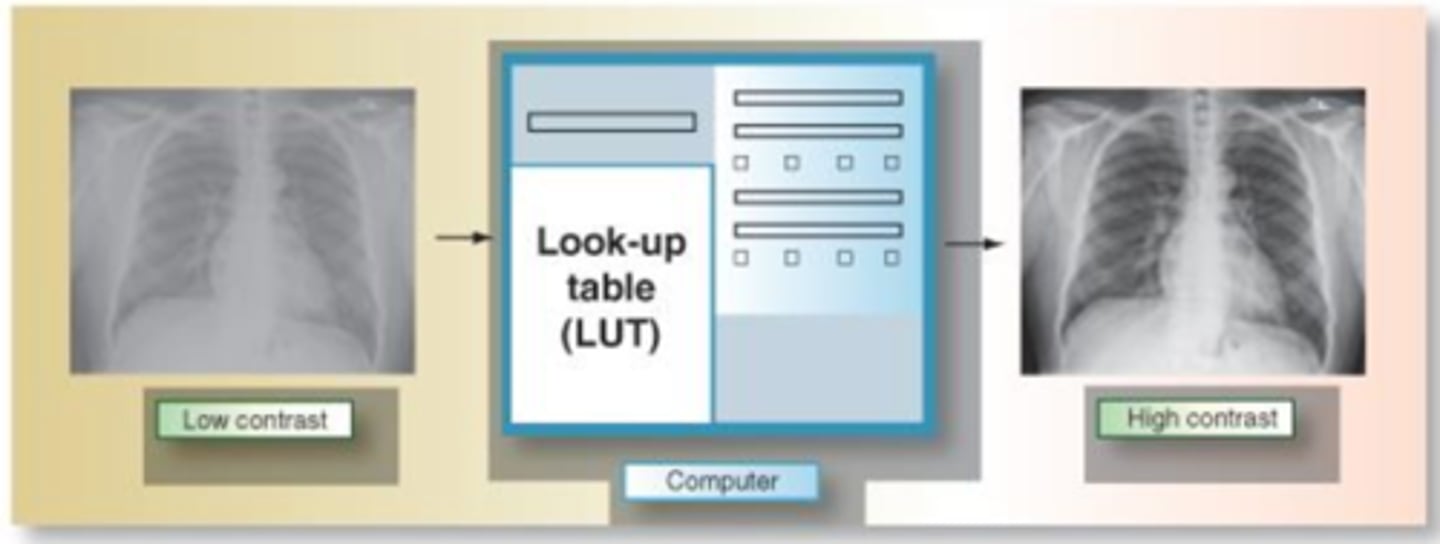
What is the LUT?
Series of mathematical equations that are used for postprocessing in radiography
Used as a reference to evaluate raw image data and make corrections to it
What is automatic rescaling?
Software automatically adjusting image's grayscale levels based off of histogram analysis in order to produce a normal-appearing radiograph for that view
What is a threshold algorithm?
Computer's method of finding S-min and S-max depending on the number of pixels in each level of gray, defining the region of useful data
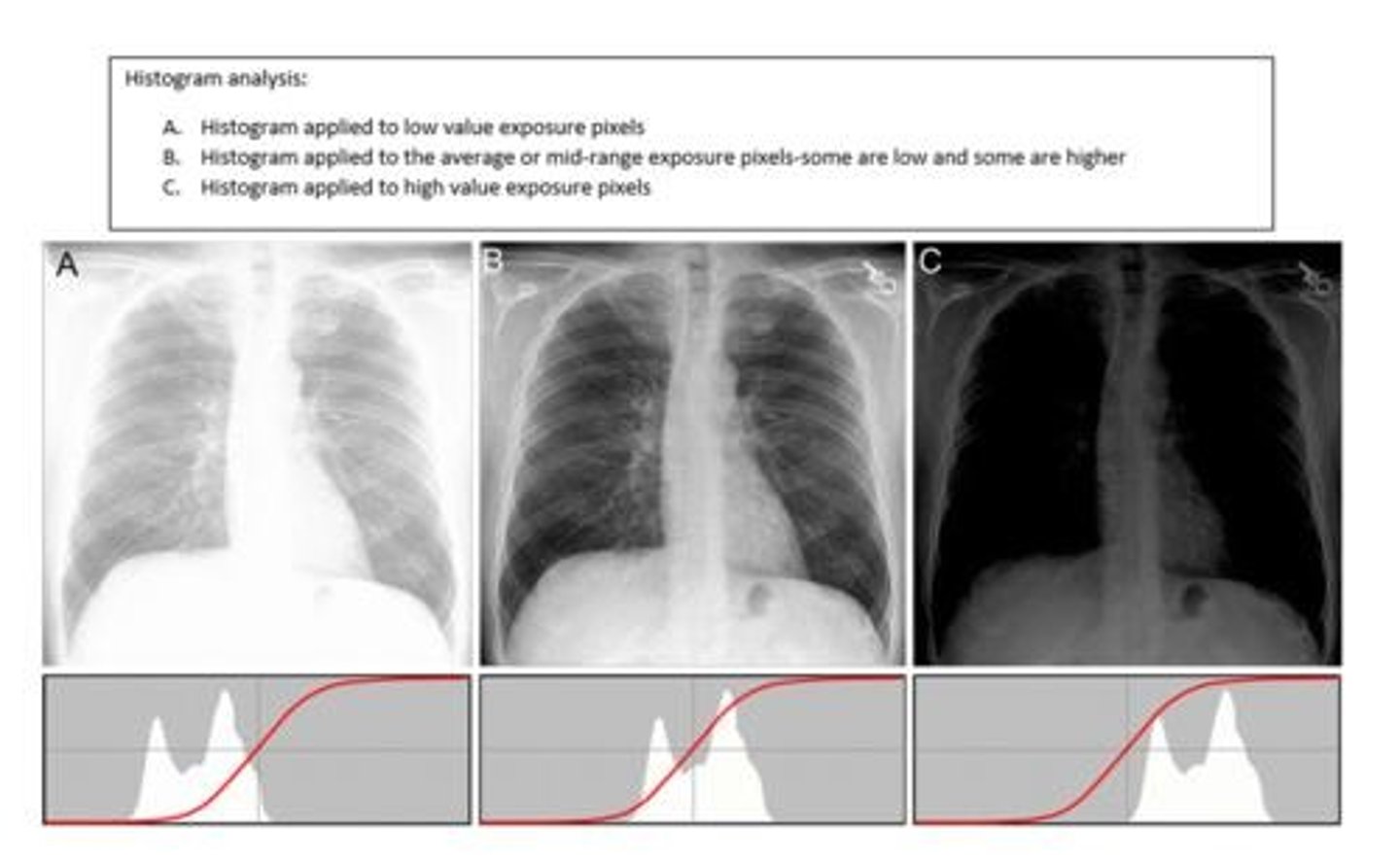
What is histogram analysis?
A histogram of the image taken is generated and then compared to an ideal histogram based off of the LUT for that view
Occurs before edge detecting and rescaling
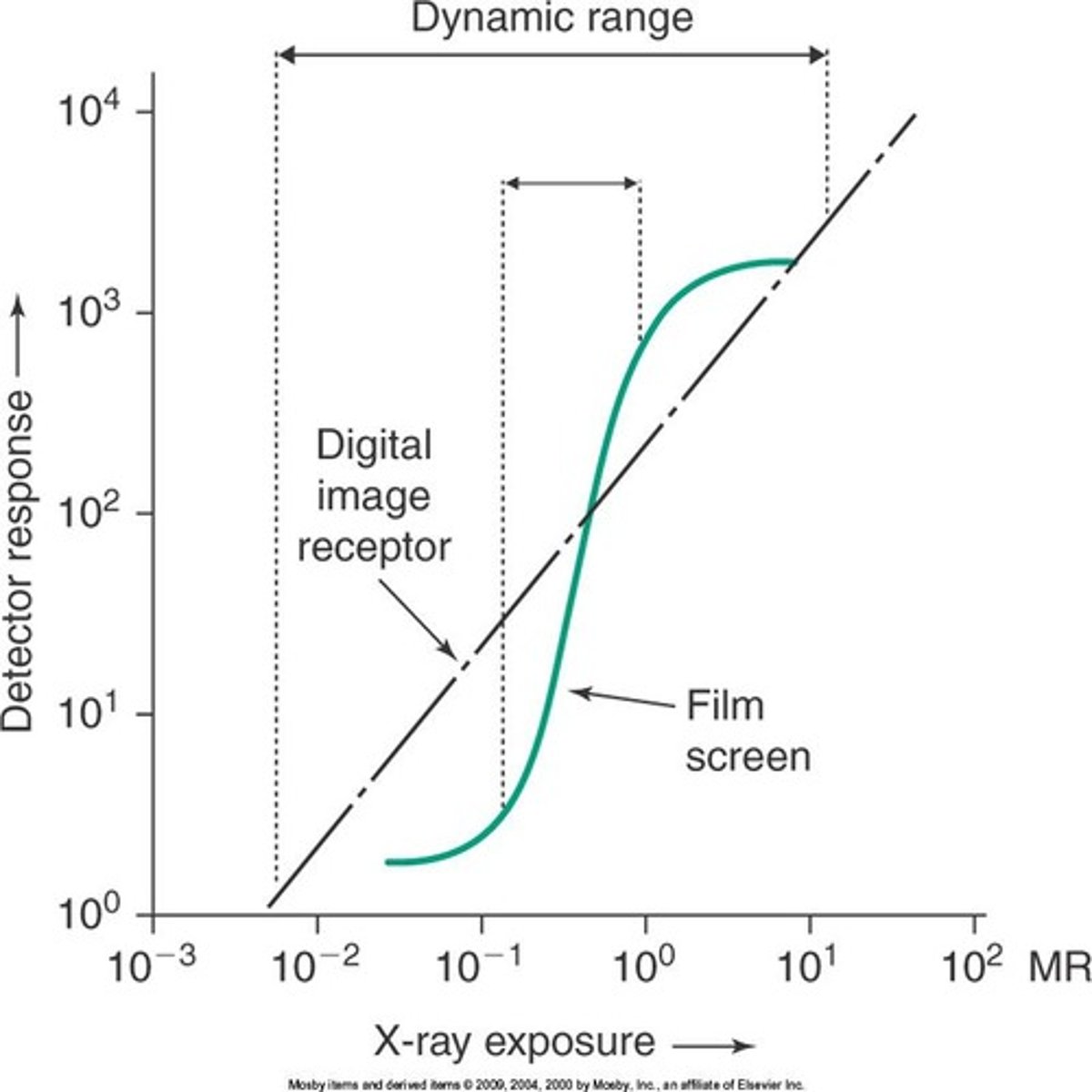
Characteristic curve
Representation of the response of a screen film radiograph to exposure on a histogram
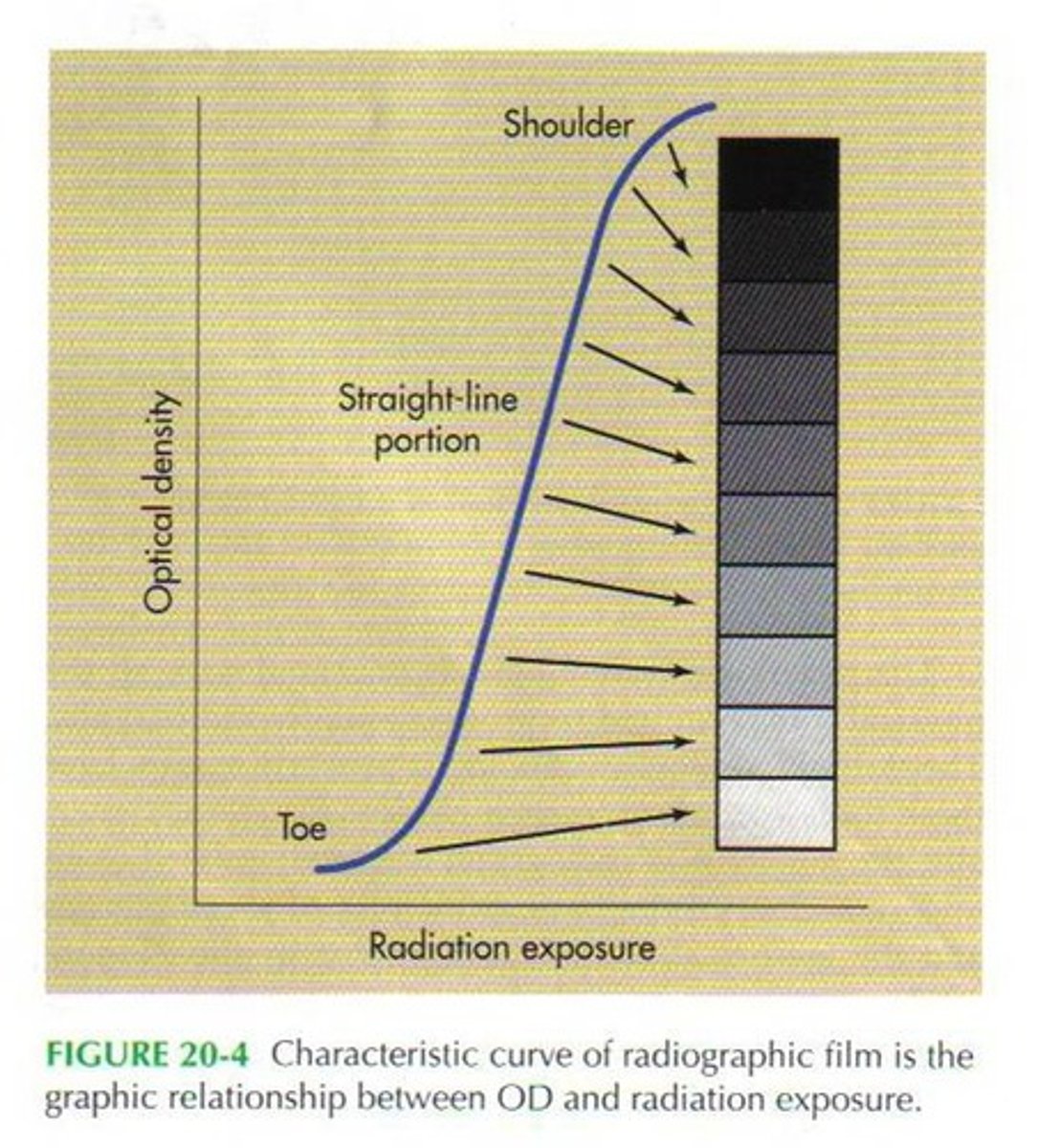
What is the difference between characteristic curve when using film versus when using digital?
Film: curve was steeper and narrower, could not recognize exposure that was too low or too high, smaller dynamic range
Digital: a straight line instead of a curve (because digital is much more sensitive and efficient), wider dynamic range
What causes histogram errors?
Anything that presents a great variation from the normal anatomy can throw off histogram analysis (prosthetic, lead, etc.)
May result in large spikes in histogram, which will throw off Smin
Not directly related to technique
What is dark masking?
Puts a dark area behind image
What is image reversal?
Reverses grayscale on image
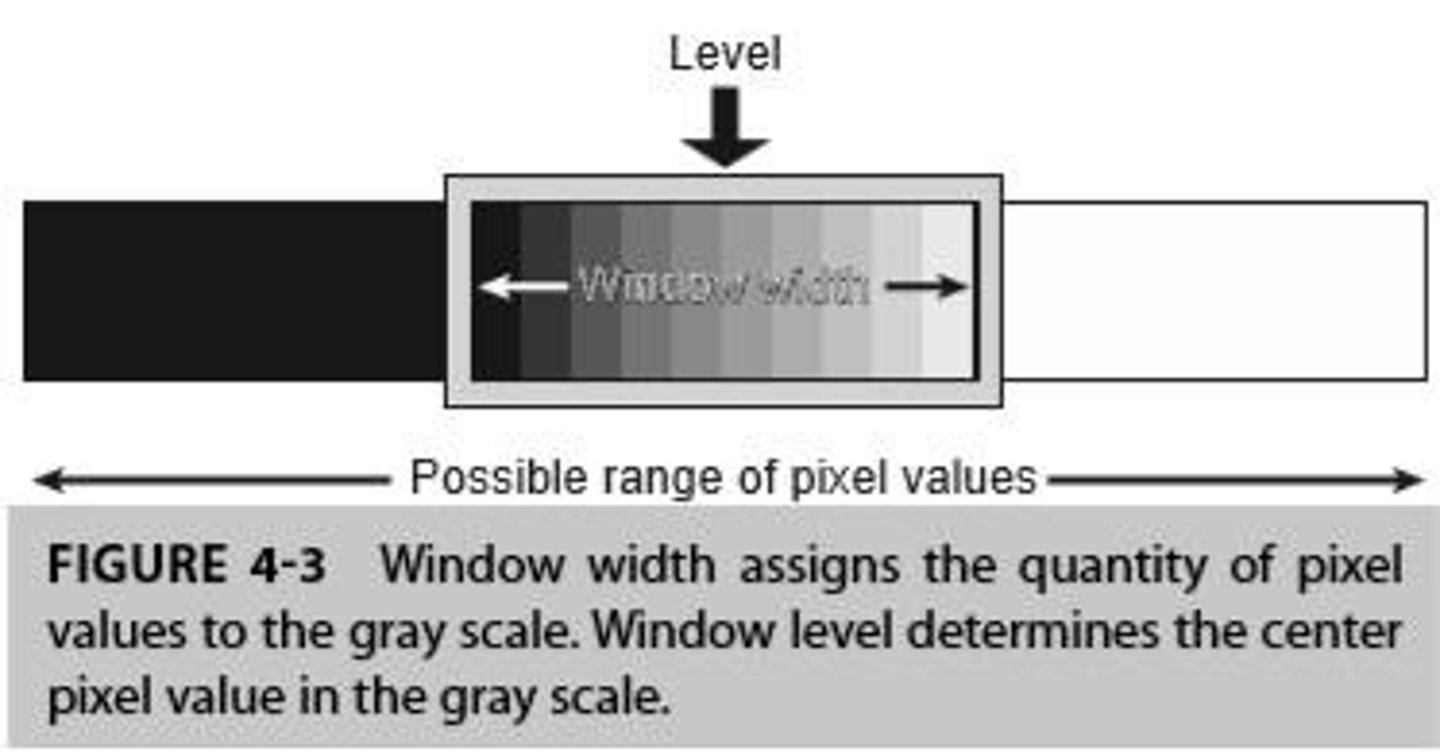
What is window leveling?
Average brightness of an image
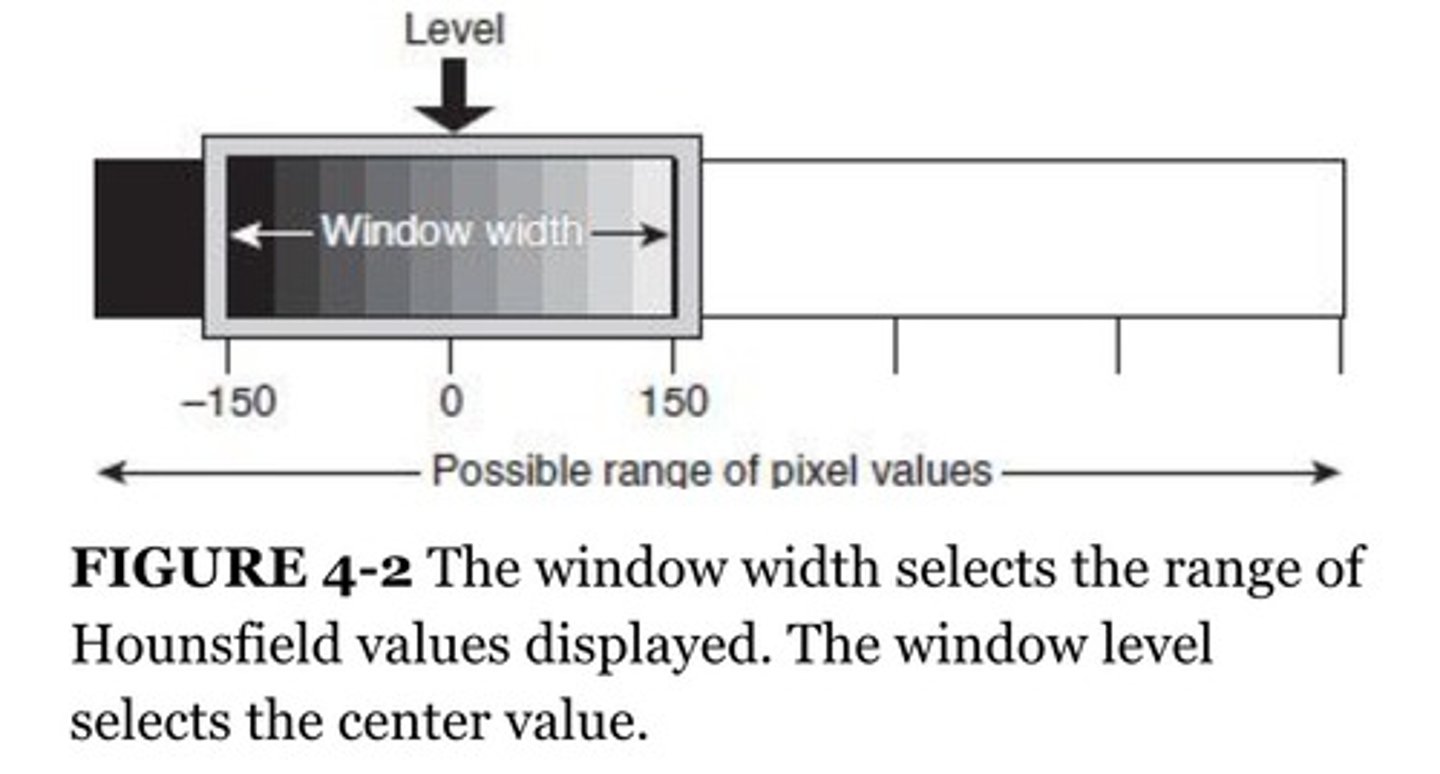
What is another term for window level?
Center (because it refers to the center point of the entire grayscale range)
What is another term for window width?
Sometimes referred to only as window
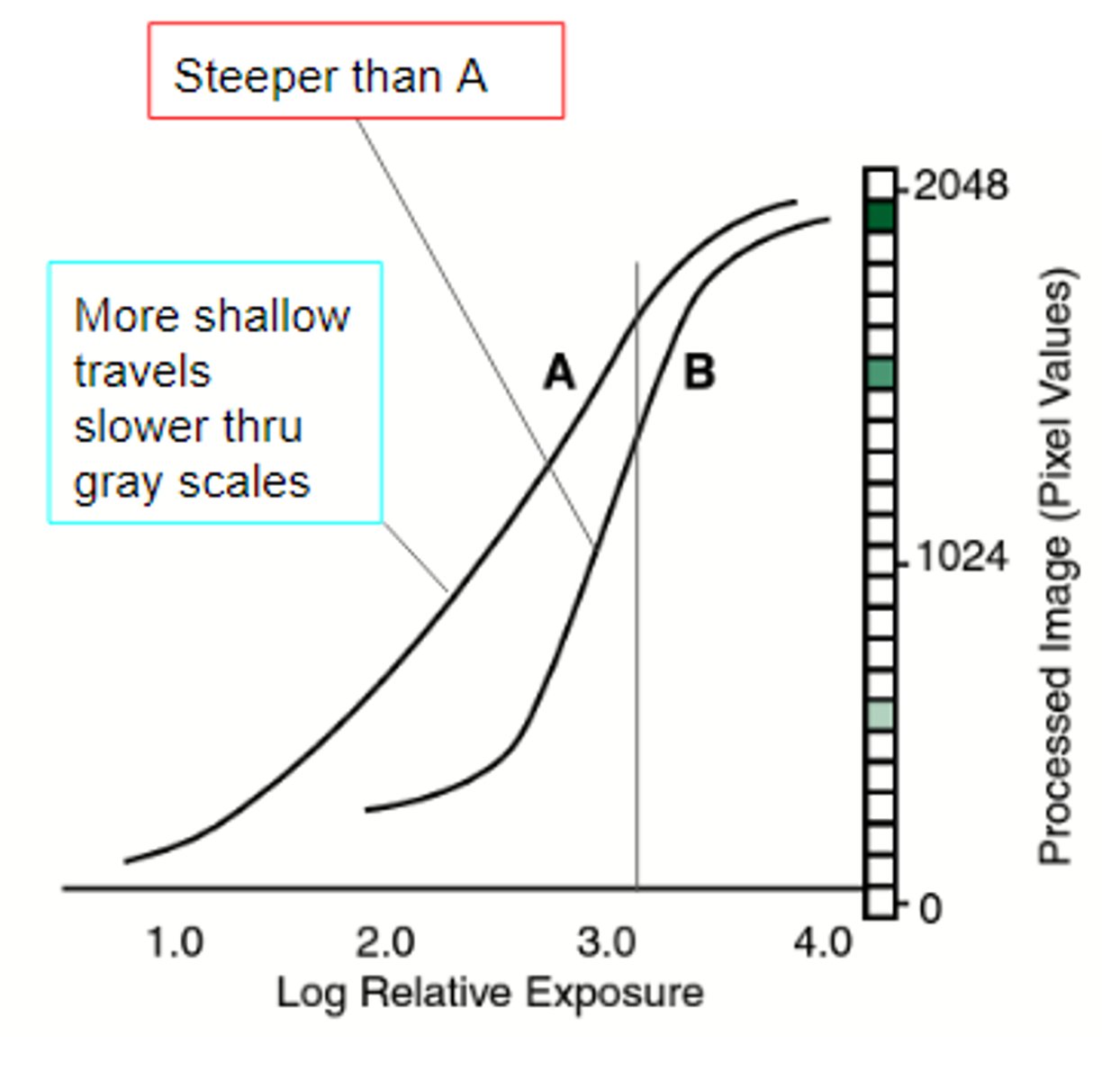
What is a gradient curve?
Line on a histogram that follows the change of densities on an image. Brightness is represented by length from left to right and contrast is represented by steepness. Curve is adjusted to fit ideal contrast during rescaling.
What is gradation?
A gradual passing from one tint or shade to another
What is gradient processing?
When the gradient curve is rescaled to match the gradient curve of the LUT
(rescaled to Qmin and Qmax)
What is smoothing?
Post-processing technique that suppresses visible mottle in an image, reduces noise, and makes edges appear less harsh
Should not be used with severe quantum mottle
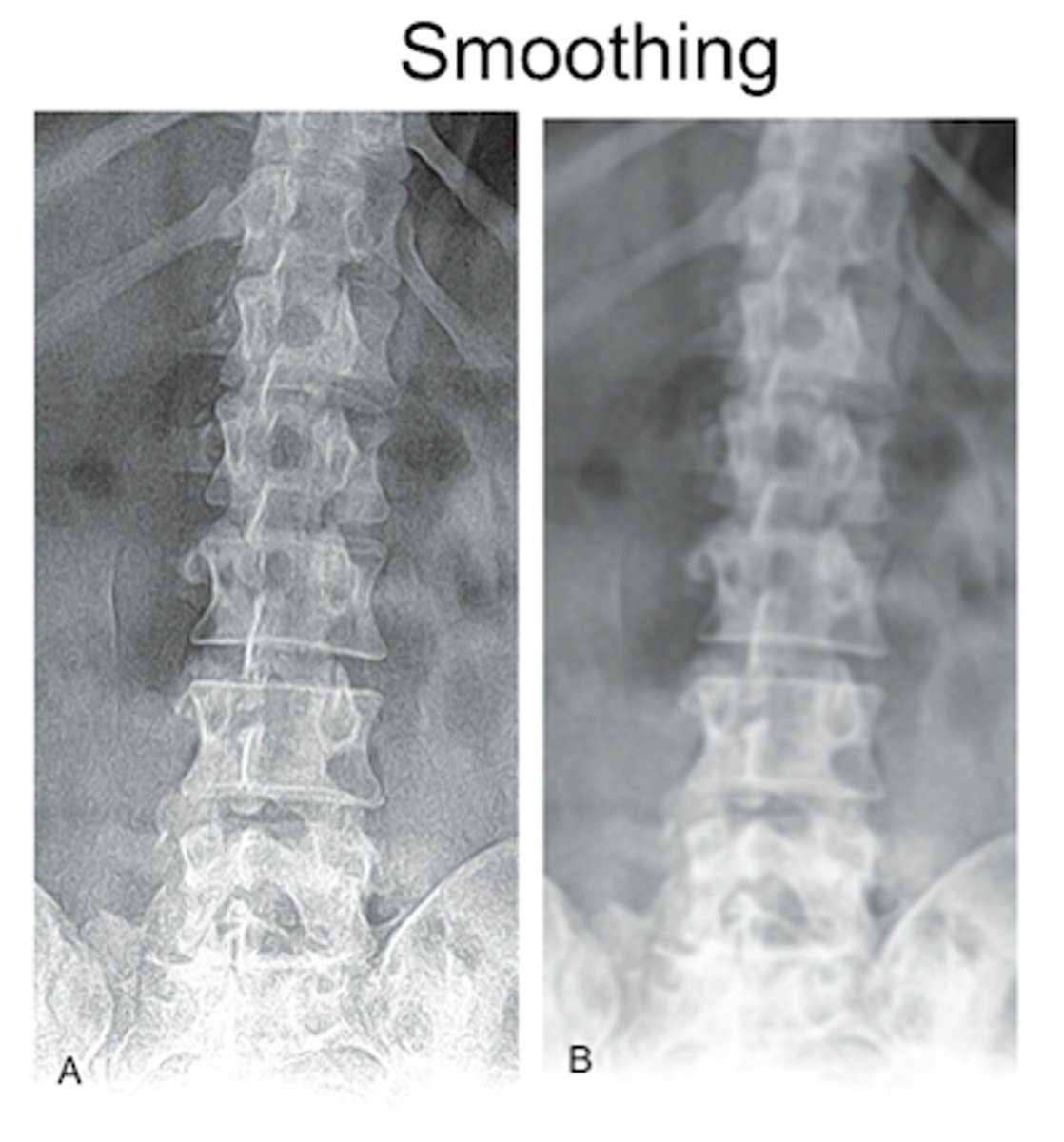
What is the downside to using smoothing?
Can cause loss of contrast and detail
What is edge enhancement?
A post-processing technique that improves visibility of small, high-contrast structures

What is the downside to using edge enhancement?
Image noise is slightly increased
Halo effect
What is the Halo effect?
Black line along structure due to too much edge enhancement
What is spatial location domain?
Assigns anatomical structures to x and y coordinates on an image
The image smoothing feature should not be applied to an image which already has a very low ____________
Spatial resolution
For digital radiographs, spatial resolution should be at least __________.
2.5 LP/mm
What controls slope of gray scale curve?
Gradient curve
Narrow window width results in:
Higher contrast
Which domain uses X and Y coordinates?
Spatial location
An algorithm designed to accentuate soft tissue densities will locate the _______ on the histogram.
VOI
Exposure field recognition is normally done as part of _______________.
Histogram analysis
___________ is best described as an attempt by the computer system to make a low-contrast raw digital image appear like a conventional radiograph prior to any post-processing.
Rescaling
Which portion of the histogram corresponds to the lungs in a chest radiograph?
Left portion of the curve (or whatever side is the darker side)
What is an exposure histogram?
Graph showing gray levels in range of exposure
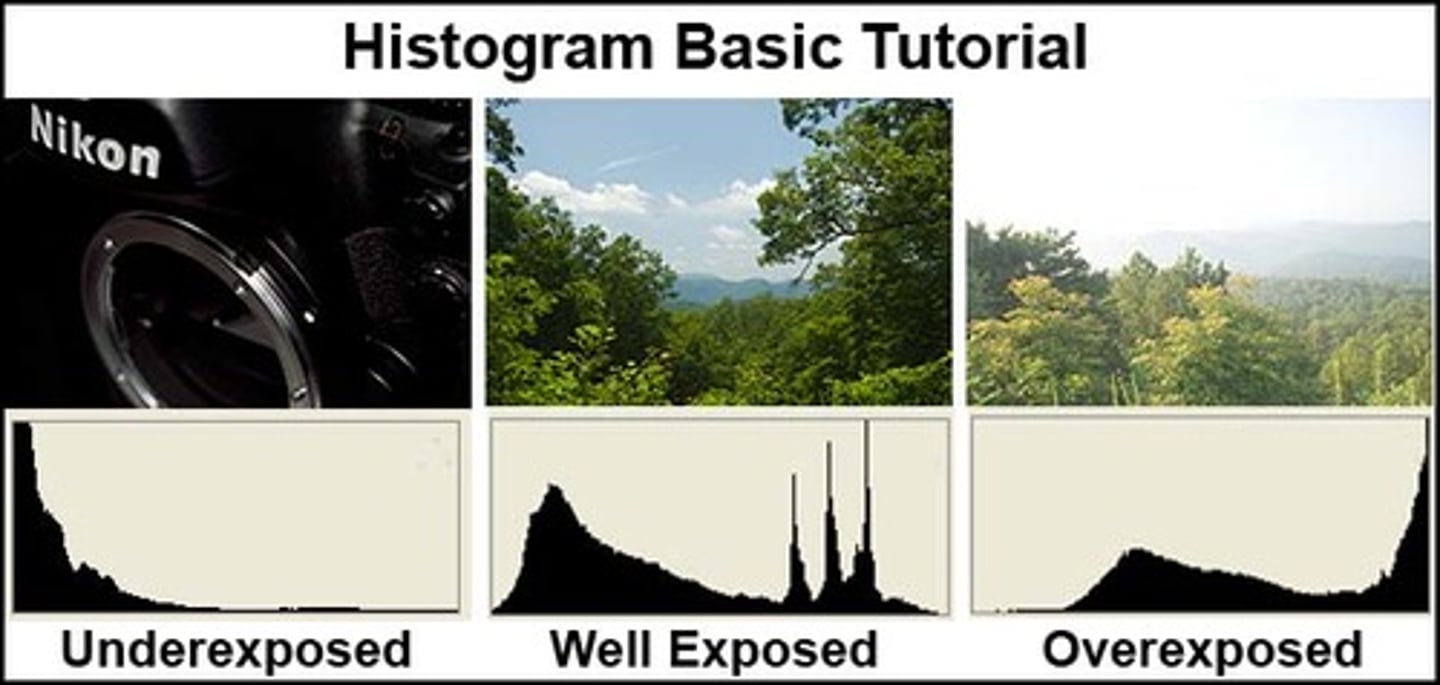
What does X and Y represent on an exposure histogram?
X axis (horizontal) represents tones, Y axis (vertical) represents number of pixel in each tone
What is exposure field recognition?
The system identifies the part of the image that contains actual anatomy and ignores things like background, shields, etc
What is the region of interest?
Area on histogram that has optimal exposure levels
Between Smin and Smax
Contains values of interest (VOI)
What is S-min?
The lowest useful signal (brightest area of anatomy)
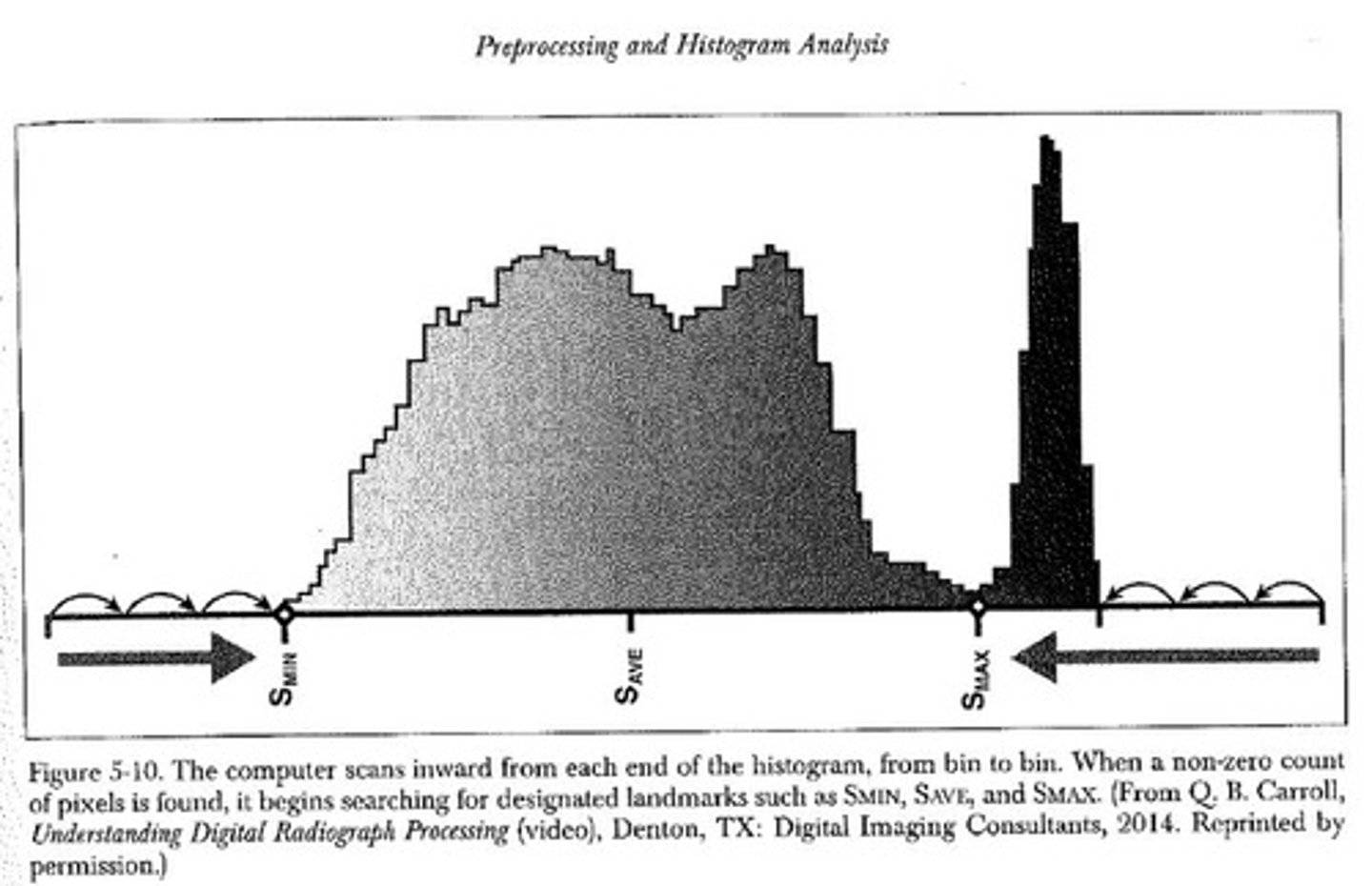
What is s-max?
The highest useful signal (darkest area of anatomy)
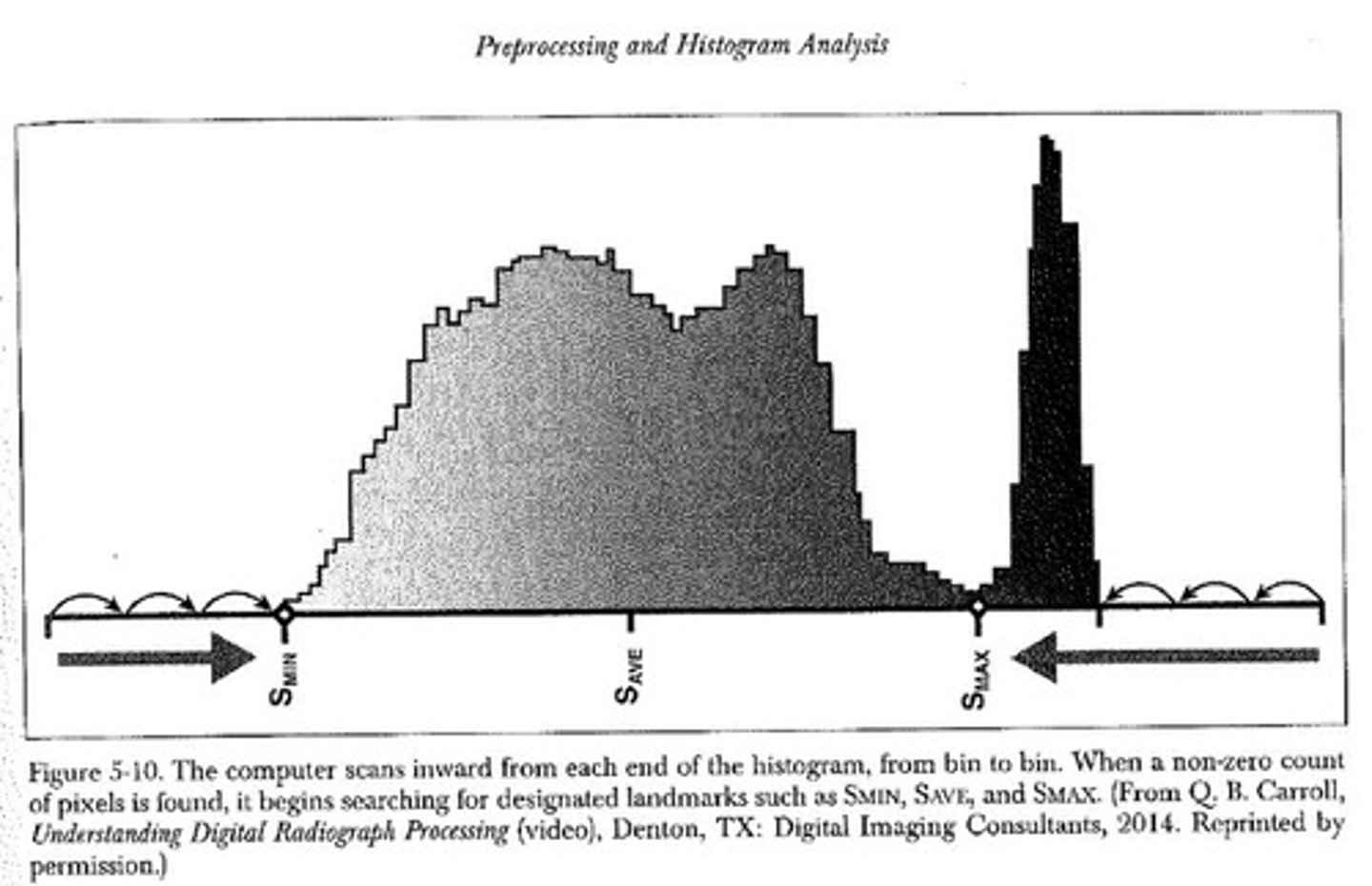
What is the S-ave?
Average of S-min and S-max
Where exposure indicator comes from
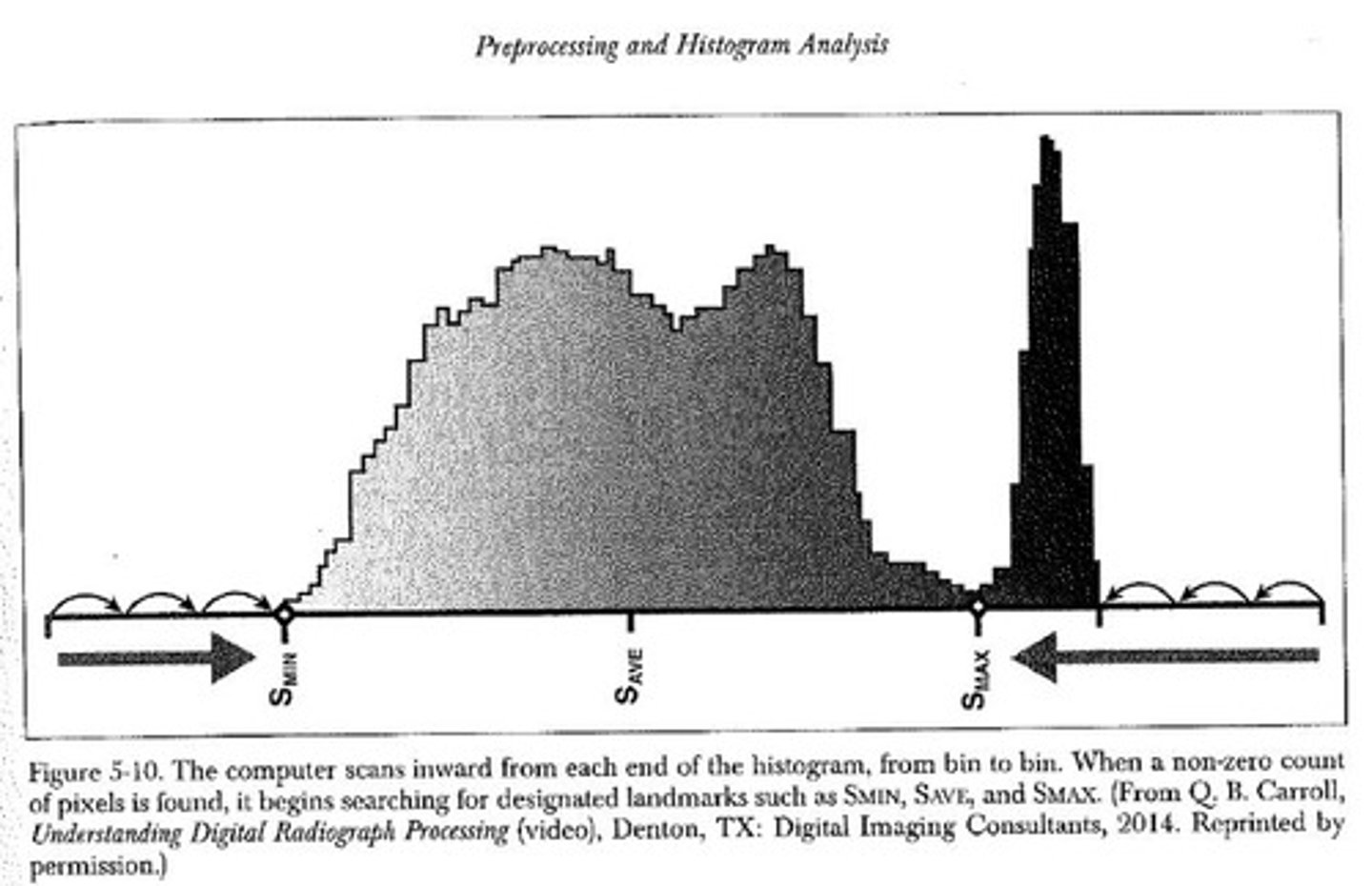
What are values of interest (VOI)?
Range of densities that a computer algorithm selects in order to accentuate particular anatomy
Within region of interest
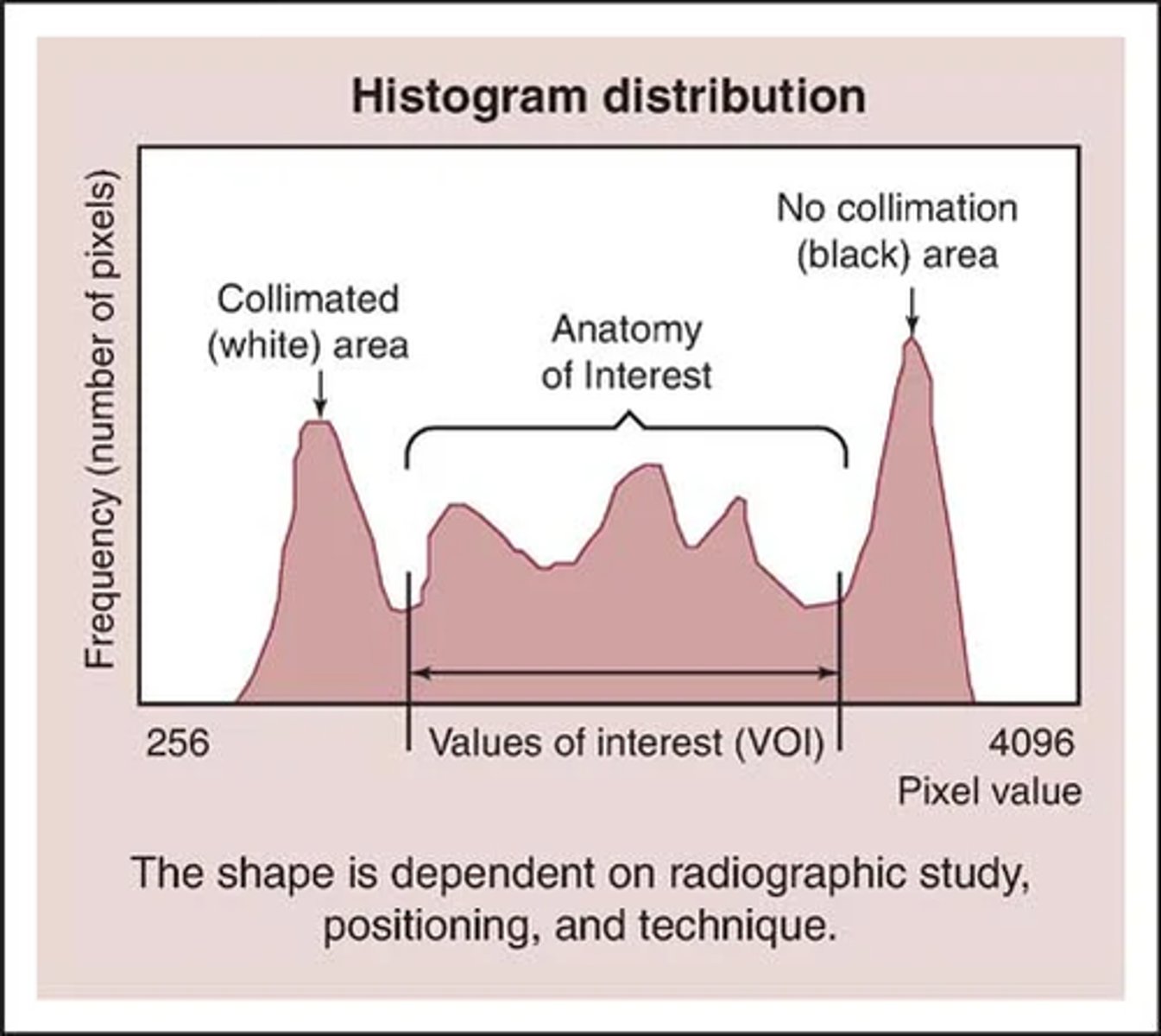
How does a raw digital image appear?
It appears washed out and with low contrast
(Many shades of gray due to digital's linear exposure response)
What is an exposure field recognition?
Process in which computer distinguishes the raw data that is representative of anatomy within the exposure field from that which is outside of the exposure field so that proper automatic rescaling can occur
What are annotations?
Digitally labeling images during postprocessing (adding markers, position/projection, time, etc)
What is image stitching?
Multiple images are attached to one another to form one image
What is window width?
Contrast of an image or length of the grayscale
What does a steeper gradient curve mean?
The image has higher contrast, shorter gray scale
Still learning (51)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!