Unit 15: Atomic Physics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Define Radioactivity
The process in which an unstable atomic nucleus spontaneously emits radiation to become stable.
Define Atom
It is the fundamental and basic unit of an element.
Nuclide Notation
Mass/Nucleon number: (A) protons + neutrons
Atomic number: (Z) protons
protons = electrons
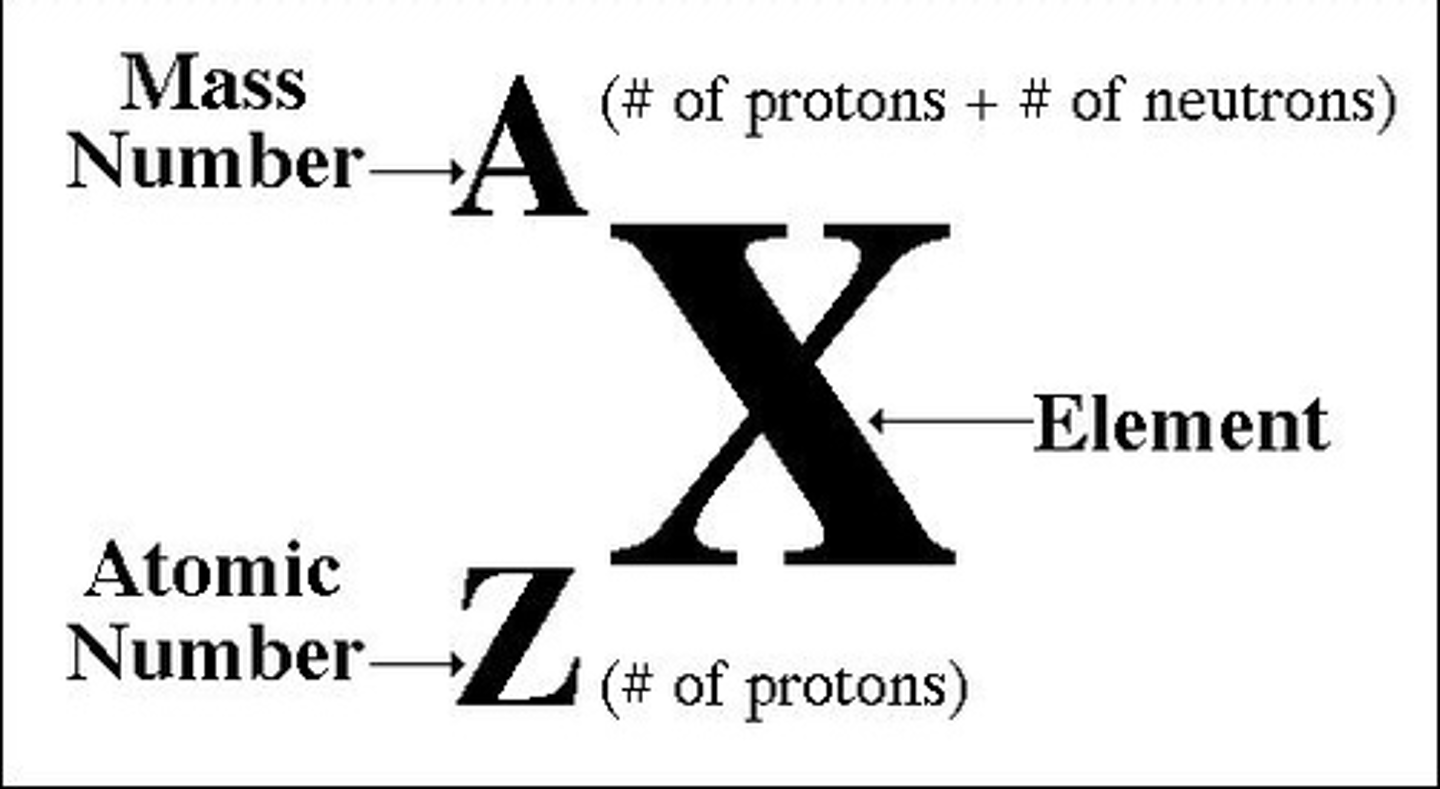
Define Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is background radiation?
The radiation that is present in the environment.
Sun, rock, air, food
What types of radiation would be release when an unstable nucleus becomes stable?
alpha, beta, gamma
Characteristic of Alpha.
- nature: helium nuclei
- made up of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
- positive charge +2
- mass: 4
- ionisation: high
- penetration: low
- absorbed by 0.2 mm paper.
range in air: few cm to 10cm

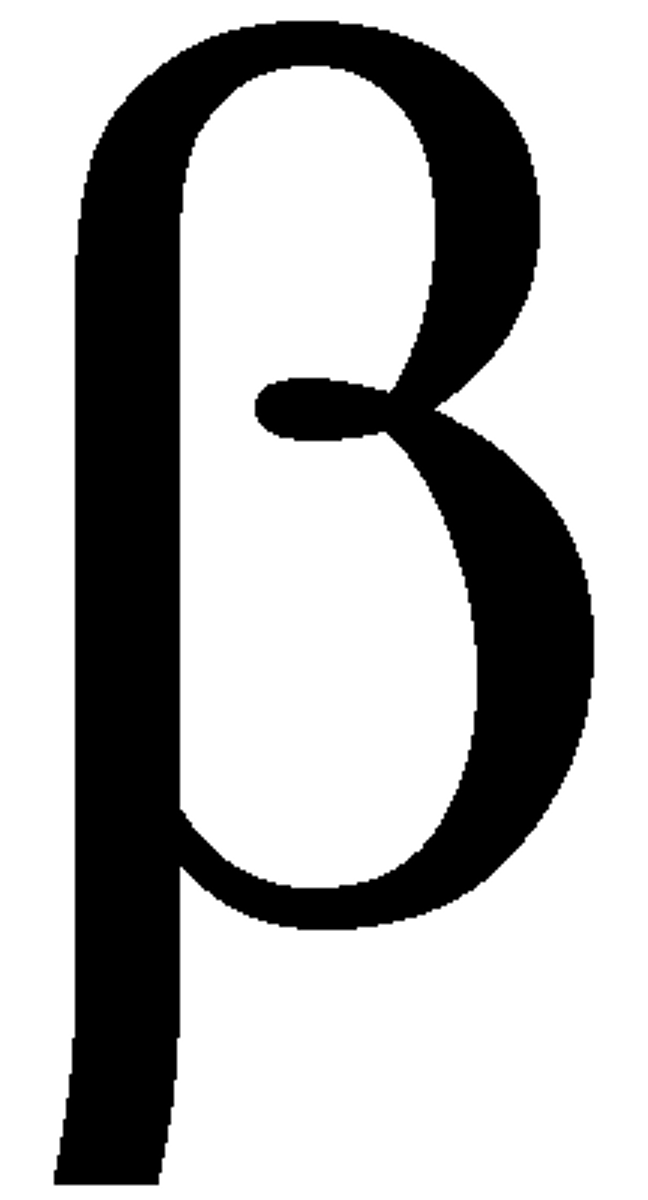
Characteristic of Beta.
- nature: electrons
- charge: -1
- mass: 1/1800
- ionisation: medium
- penetration: medium
- range in air: few m to 10m.
- absorbed by thick/2mm of aluminium.
- more dangerous than alpha as they travel further and can penetrate through the skin.
Characteristic of Gamma.
- nature: electromagnetic waves
- no charge
- no mass
- speed: 3 × 10^8
- ionisation: low
- penetration: high
- infinite range in air
- absorbed by thick/30cm lead or 3m concrete.
- used to detect leaks in underground water pipes
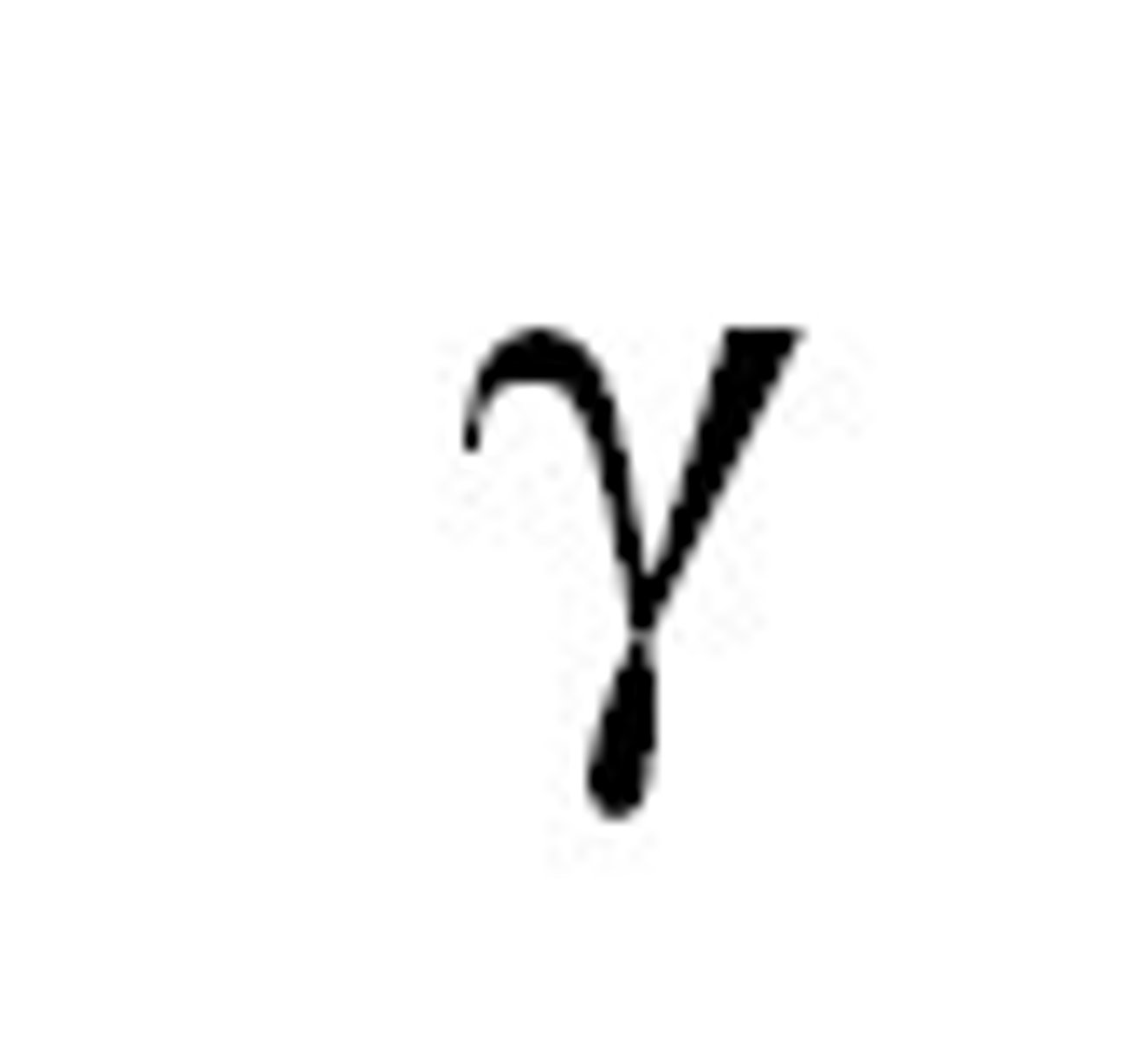
Why this emission and this half-life make y-ray a suitable material for a tracer in medical diagnosis?
- y ray can be detected outside the body.
- needs long enough half life to reach to the target organ.
- gamma has weak ionisation.
Alpha Decay
When an alpha particle is emitted from a nucleus:
The nucleus loses 2 protons:
- the proton (atomic) number decreases by 2
- the nucleus loses 4 (nucleons)
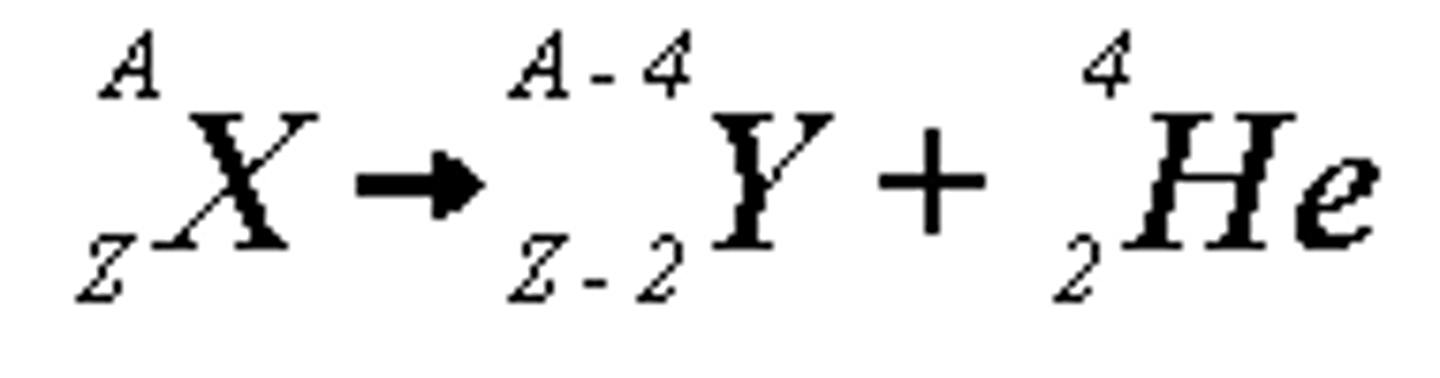
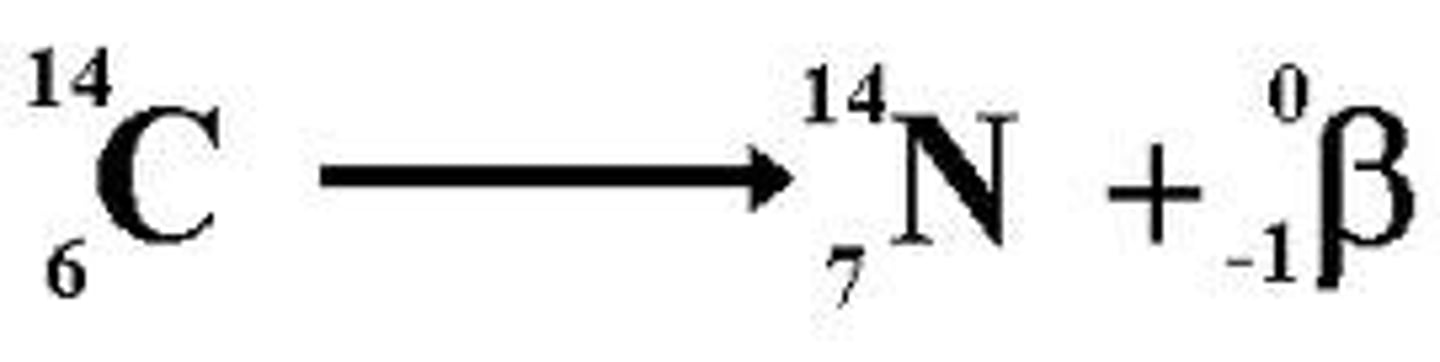
Beta Decay
It is emitted when a neutron in the nucleus suddenly changes into a proton - an electron is created in order to balance the positive charge of the proton.
When a beta particle is emitted from a nucleus:
- the proton (atomic) increases by 1
- the nucleon number doesn't change.
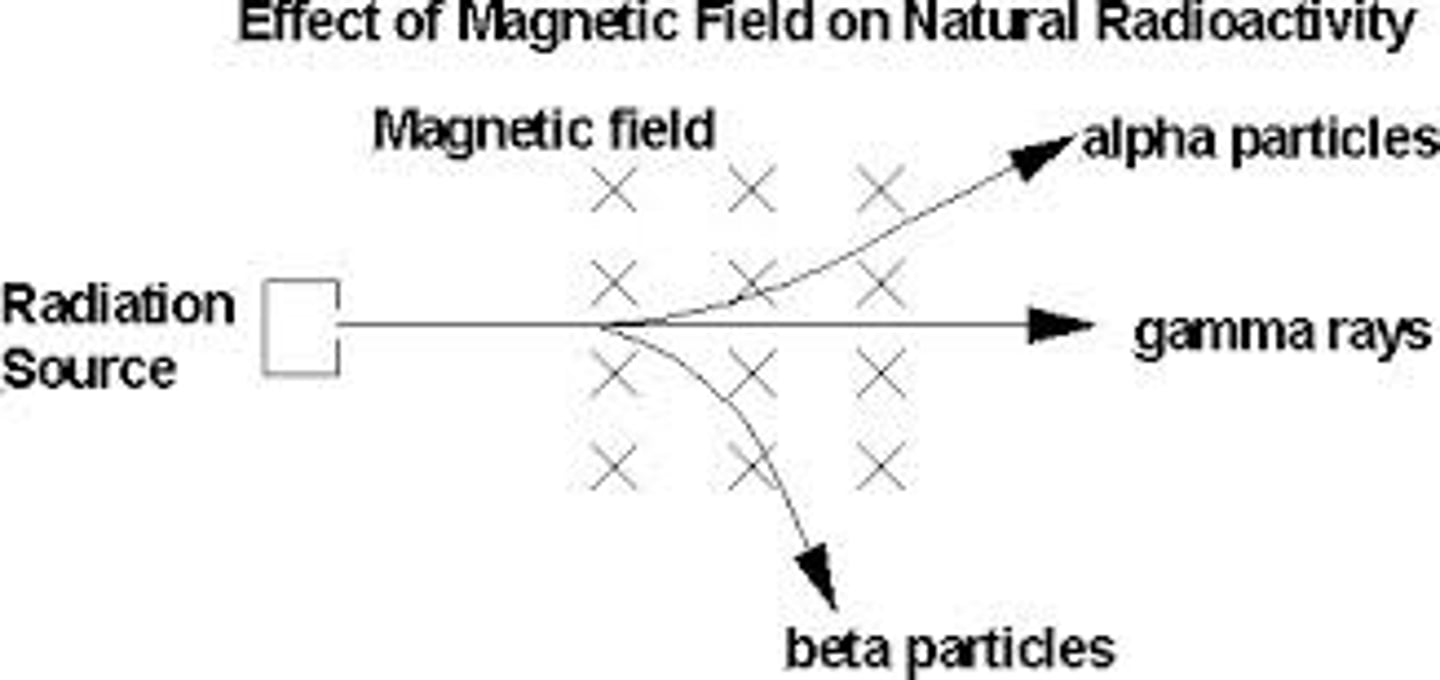
Radiation Deflection
- Alpha and Beta particles are deflected in opposite directions, because they have opposite charge.
- Beta is deflected by more than alpha, because beta particles have a much smaller mass.
- Gamma is not deflected because gamma rays have no charge.
What is Ionising?
The removal or addition of electrons to create an ion.
The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion.
Ionisation can cause chemical changes in materials and can damage/kill living cells.
How do Smoke Detectors work?
The air between the electrodes is ionized by a-particles (split into positive and negative ions), causing a small electric current to flow between them.
When smoke enters the compartment, it absorbs the a-particles which decreases the electrical current between the electrodes. This sudden change triggers the alarm mechanism in the device.
Reasons for using a-particles in smoke detector:
- high ionizing compared to b-particles & gamma rays
- short range in air
- safer to use as it cannot travel out of smoke detectors.
When a-particles are fired at a thin metal (gold) foil:
◦ Majority of them go straight through.
- the atom is mainly empty space.
◦ Some are deflected at small angles (upwards)
- the positive a-particles are repelled by the positive nucleus.
◦ A very small number are deflected straight back.
- the nucleus is concentrated at the centre.
What does the scattering of a-particles show?
Most of the atom is empty space with the nucleus being concentrated at the centre.
Helium-45 has a half-life of 25.0 minutes. How many minutes would it take for a 10.0mg sample to decay and have only 1.25mg of it remain?
1)
10 → 5 → 2.5 → 1.25mg
3 half-life
2)
25 × 3 = 75 minutes
final answer
= 4500 seconds
The half-life of Helium-23 is 3 minutes. How much of a 2.0g sample would remain after 15 minutes? Suppose you would want to buy, and it required 18 minutes for it to reach you. How much should you order if you need to use 0.1g of this sample?
First Part
1)
15 ÷ 3 = 5 half life
2)
2 → 1 → 0.5 → 0.25 → 0.125 → 0.0625g
Second Part
3)
18 ÷ 3 = 6 half-life
4)
0.1 → 0.2 → 0.4 → 0.8 → 1.6 → 3.2 → 6.4g
final answer
= 6.4g
Which material is best to prevent the escape of most radioactive emissions?
Lead
Why are some radioactive sources made from Lead?
The lead's density and the large number of electrons allow the lead to scatter and absorb all of the radiation.
How radioactive substances should be handled, used and stored?
- use tongs.
- minimise exposure by time and distance.
- use lead screening between the material and people.
- store in a lead cylinder.
- must be disposed of securely.