birds basics
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What is the defining feature of birds
Feathers
Purpose of feathers
insulation,
color and selective adaptations
Enables flight
Hypothetical feather evolution
Elongation
Splitting
Fraying and pigmentation
Elongation
Secondary splits, barbs, hooks
HFE elongation 1
Solar reflection
HFE splitting
Enables further elongation and splitting
HFE fraying and pigmentation
Insulation and displays
HFE elongation 2
Flight/balance
HFE secondary splits, barbs , hooks
Lightening and insulation
What are the 4 types of feathers
Contour
Down
Semiplume/filoplume
Flight
Purpose of contour feathers
Cover the body
Purpose of down
Insulation
Purpose of semiplume/filoplume
Monitor flight position
List the 8 feather tracts
capital
Spinal
Ventral
Humeral
Femoral
Rural
Alar
Caudal

1
Capital tracts
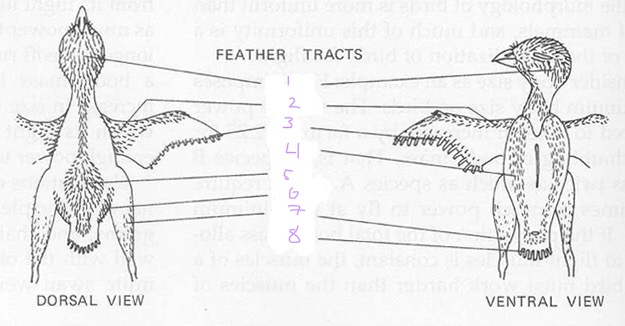
2
Humeral tracts

3
Alar tract
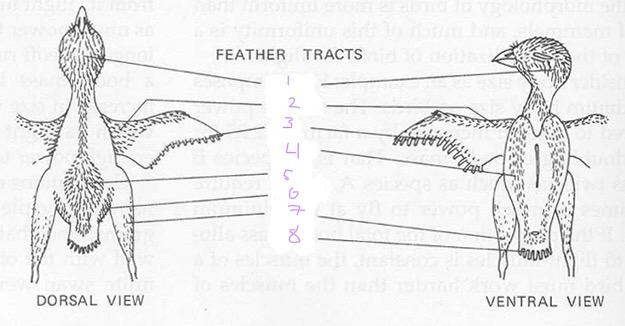
4
Ventral tract
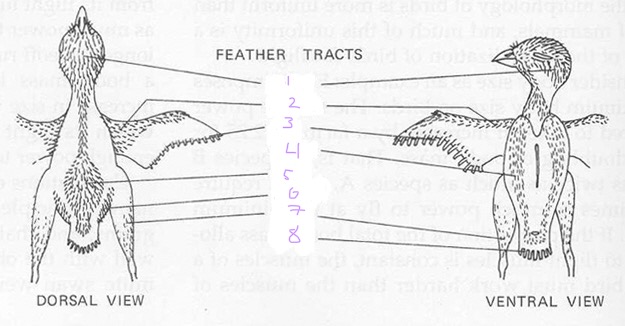
5
Spinal tract
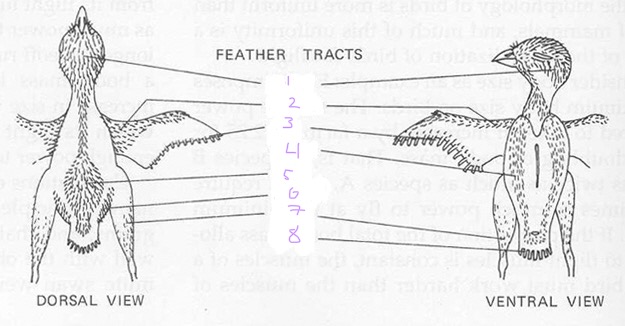
6
Femoral tract
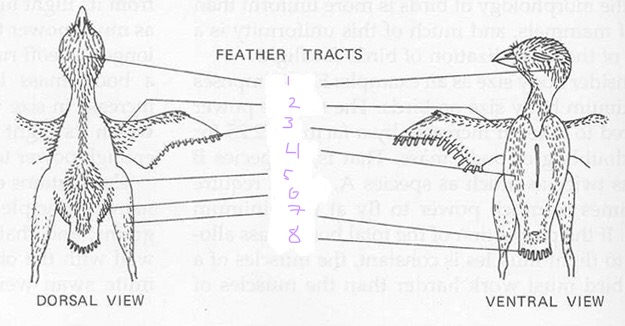
7
Crural tract

8
Caudal tract
Where are the primaries on the wing
Outer wing
Where are the secondaries on the wing
Inner wing
How are secondaries numbered
Highest number innermost
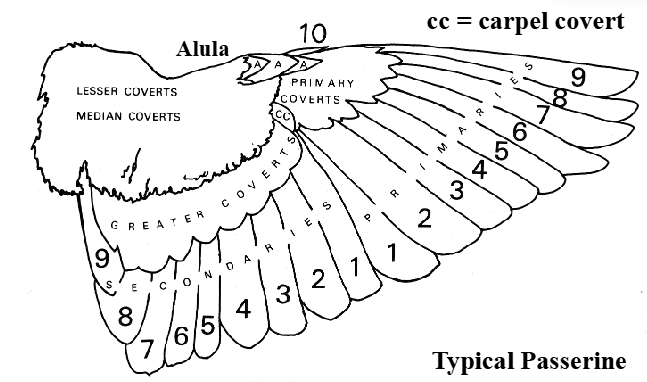
How are primaries numbered
Lowest number innermost
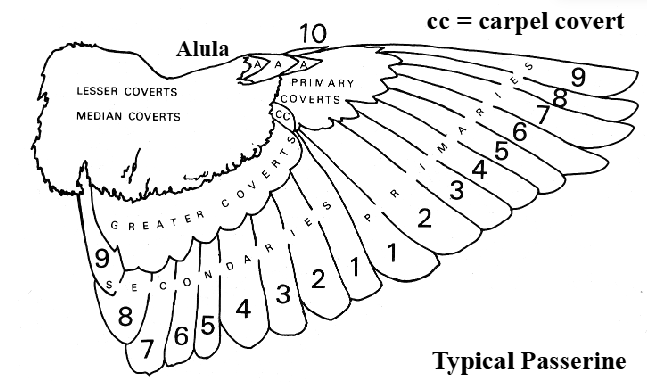
What is the purpose of wing covets
Short feathers to protect primaries and secondaries
How do birds preen and oil
Rub beak on preen gland the rub over feathers
Where is preen gland
Base of tail
How do birds bathe
In water and dust
Some even bathe in mole to kill parasites ticks and fleas
Why do birds moult?
Feathers wear out, mites and parasites, change plumage
3 parts of feather maintenance
Preening
Bathing
Moulting
Why is there variation in moulting patterns
Related to flight dependency
4 times active flapping flight has evolved
Insects
Pterosaurs - extinct
Birds
Bats
3 requirements of active flight
Large wing surfaces
High energy
Very efficient oxygen transport
Wing aspect ratio
Wingspan squared / wing area
What does a low aspect ratio indicate
Short and round wing
Rapid takeoff, higher manouverability
What does a high wing aspect ratio indicate
Long and thin
Good gliders, high speed
What does wing turbulence cause
Stalling at low speeds
How is wing turbulence reduce
Alula
Purpose of alula
Allows hovering when wind is present
What do wing tip slots do
Allow control at lower speeds
What birds have wing tip slots
Large birds that soar
crane, eagles, vultures, buzzards
4 parts of bird respiratory system
Glottis
Trachea
Lungs
Air was
1st inhale
Air moves In through trachea, past lungs into the abdominal and caudal air sacs
1st exhale
Air moves into lung tissue
2nd inhale
Waste air moves into clavicular and cranial air sacs
2nd exhale
Waste air leaves body through trachea
Birds vs mammal lungs
one way air flow
2 breaths in and out over cycle
Air pump and gas exchange separate
Purpose of separate air pump and gas exchange
Allows thinned exchange surface
How much more o2 is removed from air compared to human
25%
Other adaptations for flight
hollow bones
No teeth = light head
Center of gravity in body center
bird evolutionary origin
land dinosaurs (not pterosaurs)
name the link between birds and dinosaurs
archeopteryx
bird classification kingdom
animalia
bird classification phylum
chordata
bird classification class
aves
how many orders of birds are there
27
how many living species of birds are there
10000
flightless birds why
reduced predation risk - flying is energetically expensive
flightless birds evolved from …
flying ancestors
flightless bird orders
struthioniformes (ostrich)
apterygiformes (kiwi)
sphenisciformes (penguin)
waterbirds characteristics
dense plumage
webbed feet
usually waterproof
breed on land
marine waterbird orders
gaviformes (black throated diver)
suliformes ( blue footed booby)
podicipediformes (little grebe)
freshwater waterbird orders
gruiformes (granes and rails)
anseriformes (swans, geese, ducks)
order procellariiformes
pelagic
albatrosses, petrels, shearwaters
live 30-40 years
have a gland in nose to get rid of excess sea salt
birds of prey characteristics
talons and hooks
forwards facing eyes
hunt birds, mammals and others
birds of prey orders
falconiformes = falcons
acciptitriformes = eagles, kites, osprey, vultures
strigiformes = owls
wading birds characteristics
long legs
feed on worms molluscls and other invertebrates
adaptive radiation of bill shape
song birds characteristics
5200 sp
perching birds
incl. thrushes, warblers, sparrows, finches, crows
plumage color purpose
camoflage or sexual signal
bird breeding
eggs in nests
bi-parental care
incubation of eggs
chick development
precocial or altricial
precocial
downy and can thermoregulate and feed themselves
altricial
naked and blind, cannot thermoregulate or feed themselves
social behavior
breeding in colonies
roosting in groups
foraging in groups
migration
seasonal migration north to south
tracked by ringing and gps