LE: Examination and Clinical Diagnosis
1/249
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
What is the difference between sports medicine and regular medicine?
Time
What is the sports medicine team?
Who is on the sports medicine team?
What are their roles?
What is the AT role?
Anybody who would need to work on/with the athlete
AT, Team Physician, Psychologist, etc.
The AT role is to be the link between all sports medicine team.
SOAP Notes
Subjective - symptoms
Objective - signs
Assessment - determination of injury
Plan - keep the athlete motivated and engaged
Long Bone
Epiphysis - end of the long bone
Diaphysis - shaft of the long bone
Metaphysis - flare of the bone
Physis - growth plate
Periosteum - covering of the bone
Traction Epiphysis
Where a tendon applies force (knee)
Pressure Epiphysis
At the end of long bones
Open Fracture
A fracture that also has any break in the skin
Closed Fracture
A fracture where the skin does not have a break
What are the different types of fractures? (12)
Transverse - straight through the bone
Greenstick - incomplete fracture
Oblique - diagonally across the bone
Spiral - fracture line wraps around the bone
Spiral Oblique - fracture line is at an oblique angle and wraps around the shaft of the bone
Impacted/Compound - jamming and shattering at the fracture site
Comminuted - several separate bone fragments
Line/Stress - incomplete fracture involving a crack in the bone without displacement
Avulsion - an attached ligament or tendon pulls away a bone fragment
Chondral / Osteochondral - articular cartilage or the articular cartilage and the underlying bone
Epiphyseal - involves the epiphyseal plate
Intraarticular - fracture that enters the joint space
Ways to identify a fracture?
Observe it happen
Tap test/ Percussion test
Palpation
Tuning fork
Ultrasound
Athlete feels it
Typical Bone Fractures
Greenstick
Spiral
Comminuted
Transverse
Compound
Articular or Hyaline Cartilage
Covers the ends of the bones
Fibrocartilage
Shoulders, knees, vertebrae
Meniscus, labrum
5 Open Wounds
Abrasion - scraping
Laceration - tearing with irregular wound margins
Incision - a cut with smooth, straight wound margins
Puncture - penetration of the skin
Avulsion - a pulling away of the tissue
3 Closed Soft Tissue Wounds
Contusion - a bruise
Strain - stretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon
Sprain - stretching or tearing of a ligament
Dislocation
Complete separation of the joint capsule
Subluxation
Incomplete separation of the joint capsule
Injury Cycle
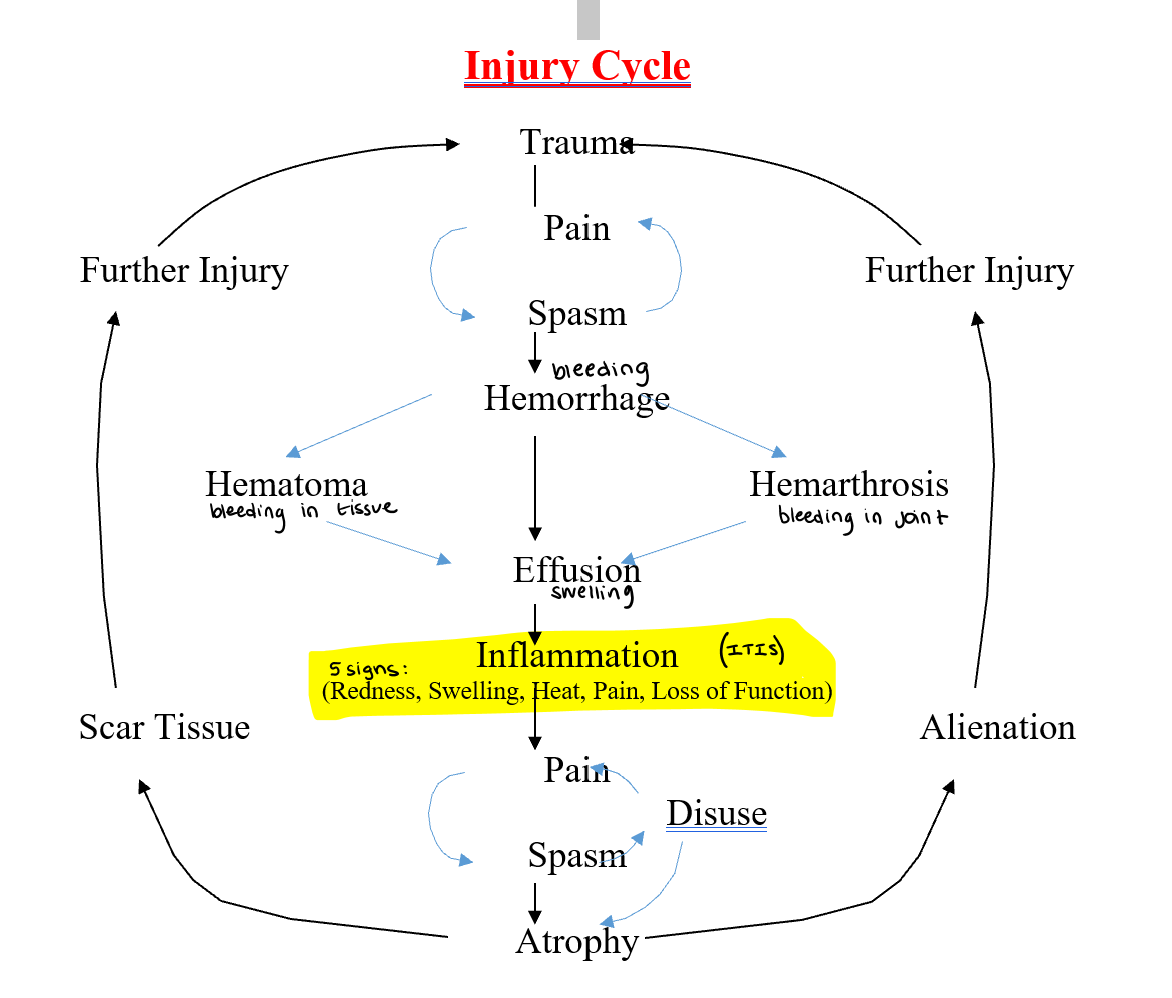
5 Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Pain
Loss of function
R.I.C.E
Rest - Non weight bearing, slow down activity
Ice - 15 - 20 minutes (depends on location), while the injury is still producing heat
Compression - Trying to remove the swelling
Elevation - helps with removing the swelling
Soft Tissue Management (PEACE and LOVE concept)
Let pain guide your return, incorporate earlier activity, optimal loading
Abduction
Away from midline
Abrasion
Scrap
Acclimatization
Adjusting to conditions
Acute
Of sudden onset
Active Range of Motion
Range of motion provided by the patient
Adduction
Toward the midline
Aerobic
With oxygen
Alienation
Disuse of an injured body part
Anerobic
Without oxygen
Anastamosis
A group of blood vessels
Anatomical Postion
Standing with the arms supinated and to the sides
Antalgic
Painful (gait)
Anterior
Toward the front
Aponerosis
A fascia
Apophysis
A traction epiphysis
Arrythmia
Abnormal heart rythmn
Atrophy
Wasting away of a muscle
Avulsion
Tearing away
Axilla
Arm pit
Bilateral
On both sides
Bursa
A fluid filled sac
Chondro
Cartilage
Chronic
Injury over time
Circumduction
Circular range of motion
Concentric
Muscle contraction with muscle shortening
Congenital
Present since birth
Contusion
A bruise
Coxa
Hip
Crepitus
Creaking or grinding
Crus
Lower leg
Cubitus
Elbow
Cyanosis
Bluish skin from lack of oxygen
Deformity
Abnormal anatomy
Diagnosis
A doctor’s opinion of an injury
Diaphysis
The shaft of the bone
Dislocation
Disruption of the joint capsule
Distal
Further from the body
Dorsal
Back
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the foot toward the shin
Eccentric
Muscular contraction with muscle lengthening
Ecchymosis
Bruising and discoloration
Edema
Swelling
Effusion
Swelling
Endurance
Resisted range of motion over several repetitions
Epiphysis
The end of long bones
Epistaxis
Nosebleed
Eversion
Rolling of the ankle to the medial side
Extension
Increasing the angle of a joint
External Rotation
Rotaion of motion away from the midline
Etiology
Cause of an injury
Fascia
Broad, strong connective tissue
Flexibility
Ability to go through a full range of motion
Flexion
Decrease in the joint angle
Gait
Walking pattern
Genu
Knee
Hallux
Big Toe
Hemarthorsis
Bleeding in the joint
Hematome
Bleeding in the tissueHe
Hemmorrhage
Bleeding
Homeostasis
The body’s desire to maintain equilibrium
Horizontal Abduction
Movement away from the midline in the horizontal plane
Horizontal Adduction
Movement toward the body in the horizontal plane
Hyper
Excessive
Hypertrophy
Increase in size
Hypo
Low or beneath
Idiopathic
Of unknown origin
Incontinence
Inability to control bowel or bladder
Infection
The invasion of the body by a foreign substrance
Inferior
LowerIn
Inflammation
The body’s response to irritation
Inversion
Ankle movement to the lateral side
Internal Rotation
Rotation towards the midline
Isokinatic
Movement with accommodating resistance
Isometric
Strength training with no joint movement
Isotonic
Strength training with movement
-itis
Inflammation
Kyphosis
Abnormal curvature of the thoracic spine (hunch back)
Lateral
Towards the ouside
Laxity
Increases movement in a joint