lab practical 1 (tissues/skin/bone histology)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
epithelial tissue
refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior and interior surfaces of the body, line internal cavities and passageways, and form certain glands, supports gas exchange, surface movement of substances and absorption; appears like thousands of cells squished into layers
skin, lining of organs, sweat glands
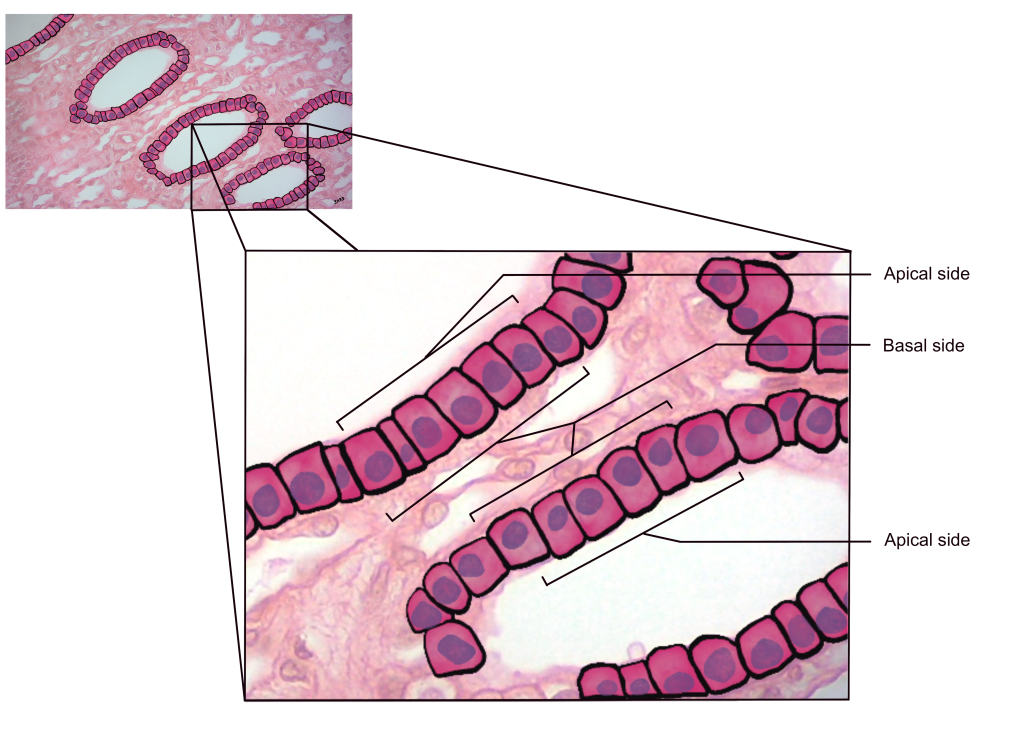
apical surface
an upper free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ
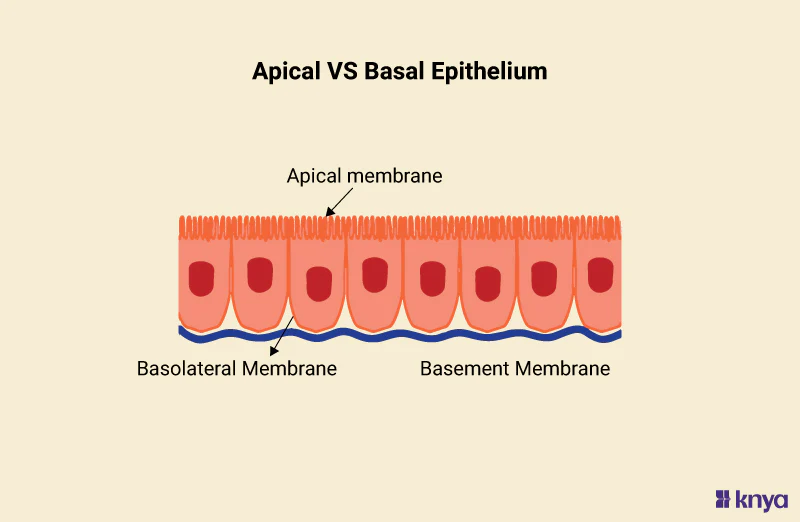
basement membrane / basal surface
layer between epithelium and underlying connective tissue; where epithelial cells are attached
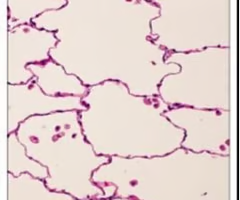
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells
allows easy passage of materials by diffusion and filtration; secretes lubricating substances
located in kidney, glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels
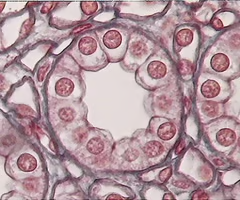
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped cells
secretion and absorption
located in ducts and secretory portions of small glands, kidney tubules, ovary surface
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of tall column shaped cells
absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes and other substances
nonciliated types lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), gallbladder and excretory ducts of some glands
ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
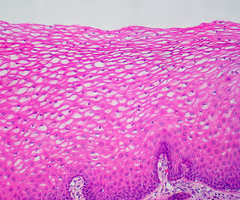
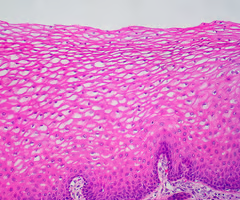
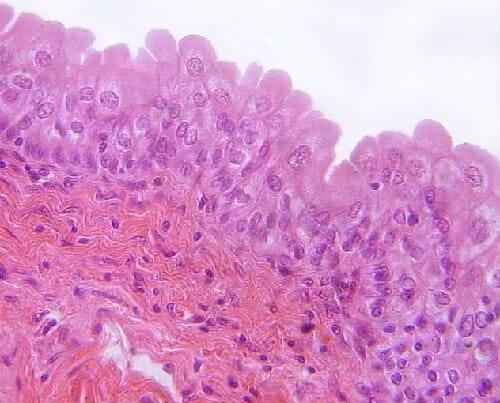
stratified squamous epithelium
multiple layers of flat cells
protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
nonkeratinized type forms the moist lining of the esophagus, mouth and vagina
keratinized type forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane
stratified cuboidal epithelium
two or more layers of cube shaped cells
protection
located largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands and salivary glands
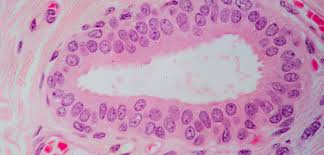
stratified columnar epithelium
two or more layers of column like cells
protection and secretion
rare in the body; small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands (salivary esophageal)
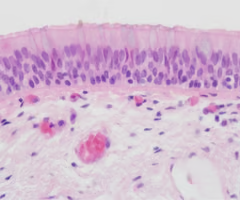
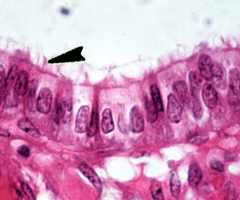
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of cells that appears to be made up of multiple layers of cells; each cell may have different heights/nucleus positions
secretes substances, particularly mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
ciliated variety lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract; males sperm carrying duct
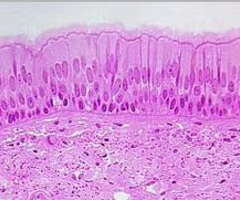
transitional epithelium
Type of stratified epithelium that lines the urinary tract
stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
only in the urinary system: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
connective tissue
binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection, support, and integration of all parts of the body
made up of fibroblasts (connective tissue cells)
bone, fat, cartilage, blood, padding tissue
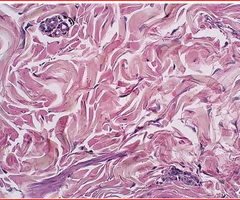
areolar connective tissue (loose)
gel-like matrix with web like fibers
fills the spaces between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and supports organs in the abdominal cavity
underlies most epithelium
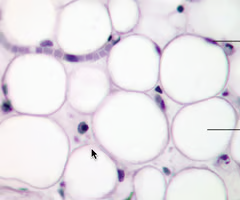
adipose connective tissue (loose)
closely packed adipocytes; acts as storage depts for fat with little cellular matrix
rapid storage mobilization of lipid molecules
cushion and protection
found cushioning around the kidneys and back of the eye
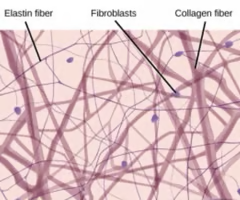
reticular connective tissue (loose)
network of reticular fibers in a typical loose ground substance; mesh-like supportive framework
form a framework for soft internal structures; creates network that supports attachment of other cell types like white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
located in lymphoid organs, lymph nodes, bone marrow and spleen
Looks kind of like a cherry blossom tree in most images — reticular fibers are the wood
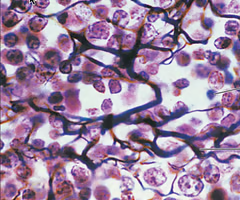
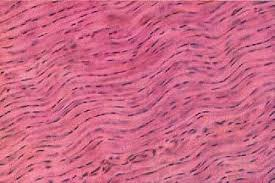
dense regular connective tissue (dense)
fibers are parallel to each other, enhancing tensile strength and resistance to stretching in the direction of the fiber orientations
attaches muscle to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones, withstands great tensile strength when pulling force is applied in ONE direction
makes up / located in tendons, ligaments, and layer under the epidermis
collagen fibers are densely packed and run parallel to each other, creating a "wavy-hair" like pattern.
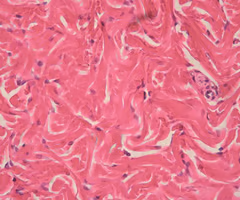
dense irregular connective tissue (dense)
fibers are in randomized directions; increases strength when pulled in multiple directions, less in one direction
able to withstand tension exerted in MANY directions; provides structural strength
dermis of the skin, submucosa of digestive tract; fibrous capsules of organs and of joints
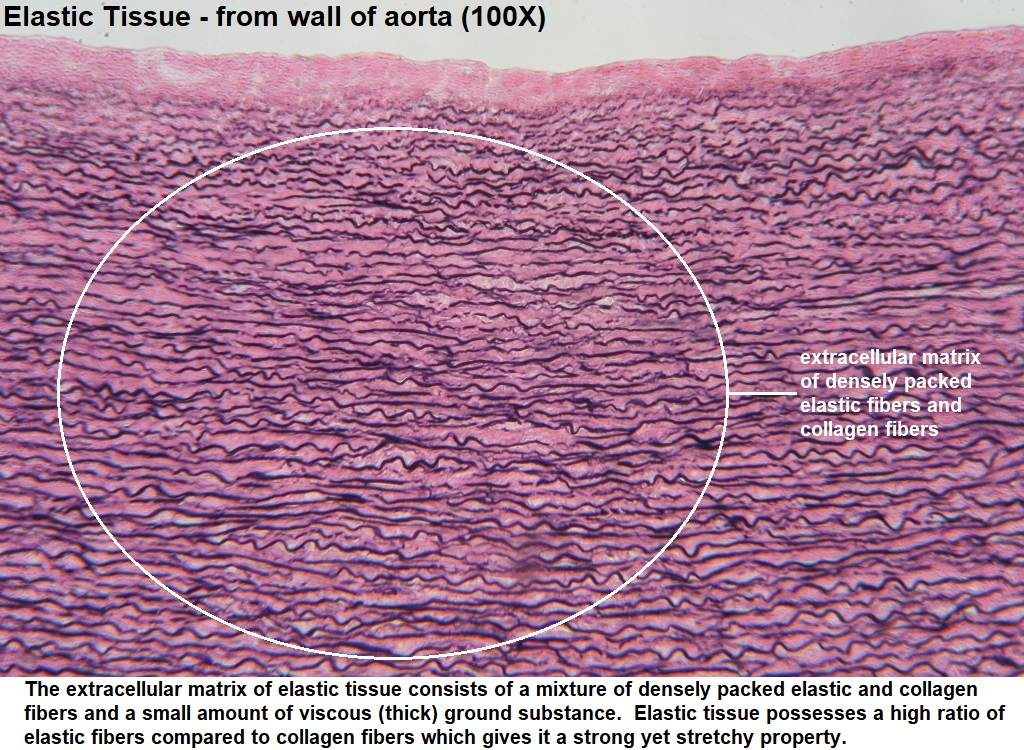
elastic connective tissue (Dense)
stretchy and squiggly appearance; densely packed fibers
allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs
located in walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with vertebral column, within the walls of the bronchial tubes
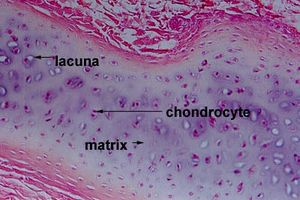
cartilage
connective tissue made up of chondrocytes and empty spaces called lucana
hyaline cartilage
most abundant type of cartilage; short and dispersed collagen fibers
forms moveable joints and embryonic skeleton
found on the ends of long bones, ribs and nose
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers
characterized by a matrix rich in elastic fibers, allowing it to bend and recoil without losing its original shape.
gives rigid support as well as flexibility
found in external construction of the ear
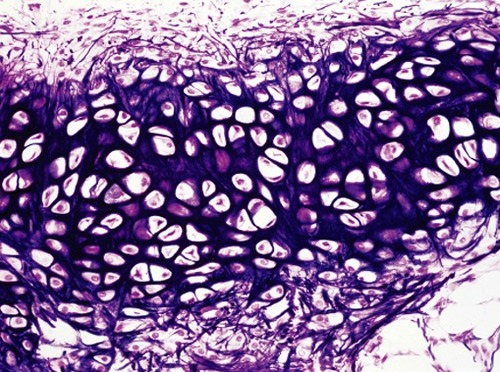
fibrocartilage
tough due to its thick bundles of collagen fibers dispersed through its matrix
act as a cushion within joints
found in menisci in the knee joint and intervertebral discs
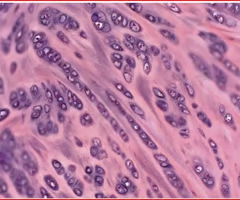
bone
dense, mineralized, hard connective tissue composing the skeleton
two main types: compact (cortical) and spongy (cancellous) bone
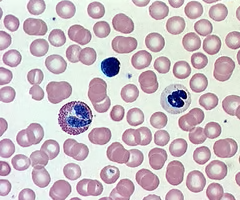
blood connective tissue
fluid extracellular matrix used to transport substances throughout the body filled with blood cells
muscle tissue
excitable, responding to stimulation and contracting / lengthening to provide movement
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
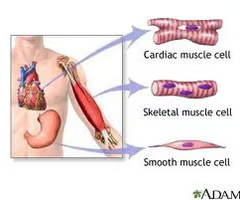
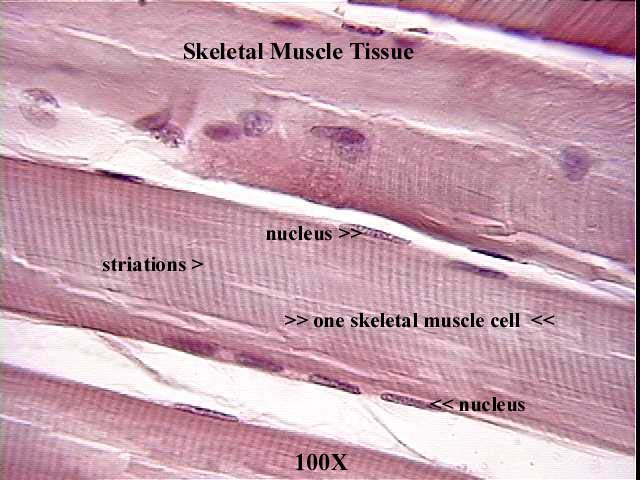
skeletal muscle
muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones; each cell
voluntary
striated
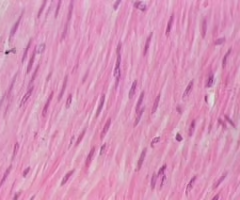
smooth muscle
muscle found inside many internal organs of the body that causes their movement (ex: stomach muscle)
involuntary
smooth
cardiac muscle
muscle tissue found only in the heart
involuntary
striated
intercalated disc
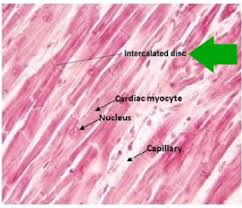
intercalated discs
attachment sites between the transverse lines between cardiac muscle cells (CARDIAC ONLY)
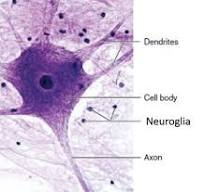
nervous tissue
excitable, allowing the propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different regions of the body
brain
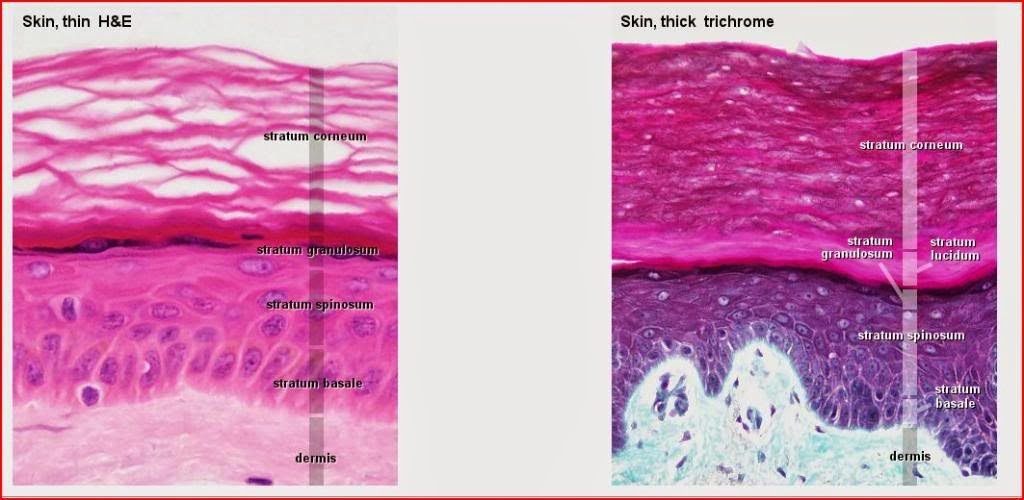
thin skin
covers most of the body
four layers of keratinocytes
contains hair follicles
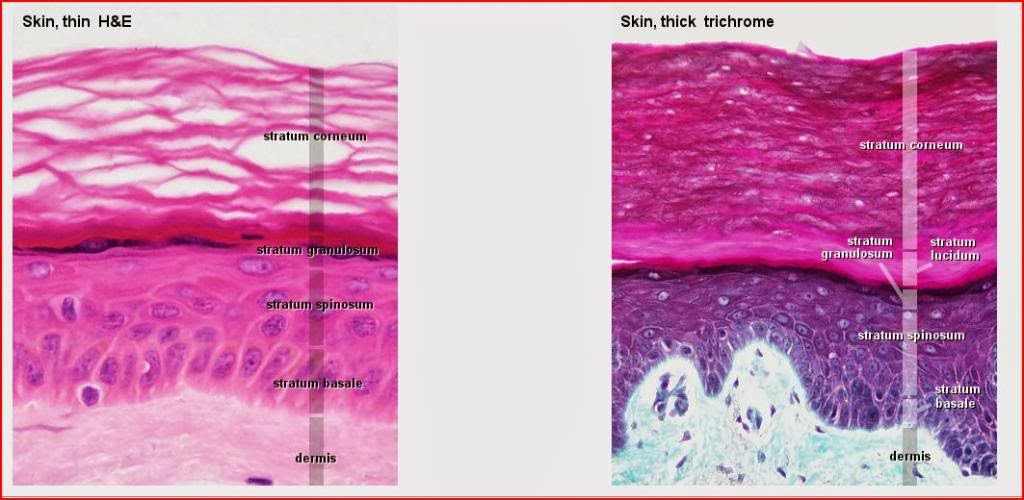
thick skin
covers palms of hands and soles of feet
has five layers of keratinocytes
no hair follicles
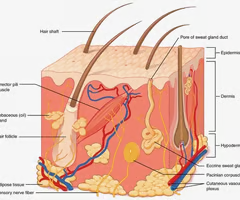
layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis (subcutaneous)
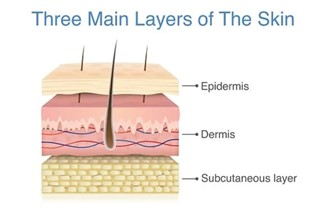
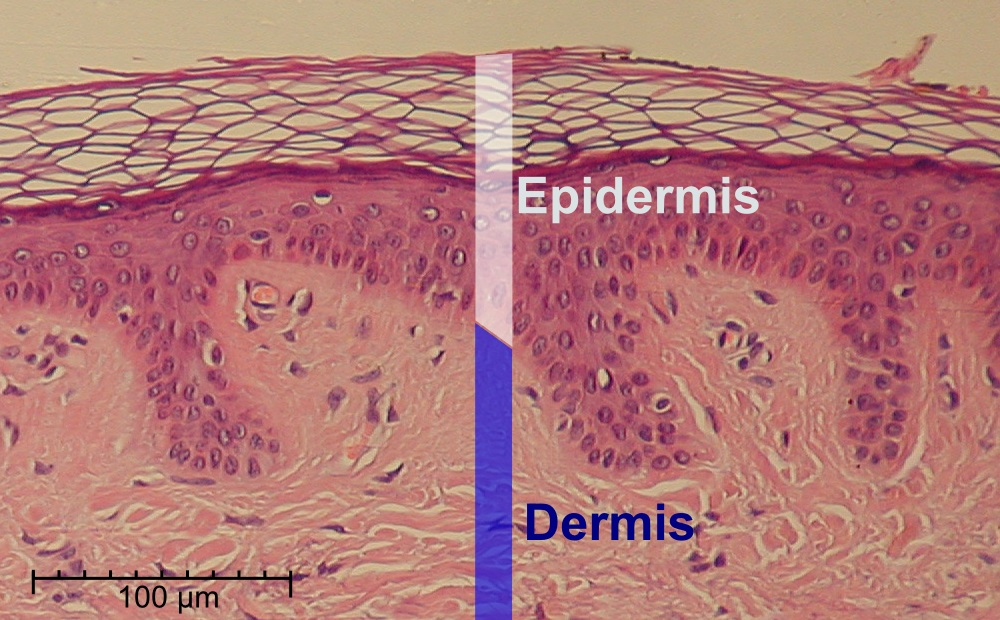
epidermis
composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium; outermost / top layer of the skin
keratin is an intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their hardness and water-resistant properties
keratinocytes is a cell that manufactures and stores the protein keratin
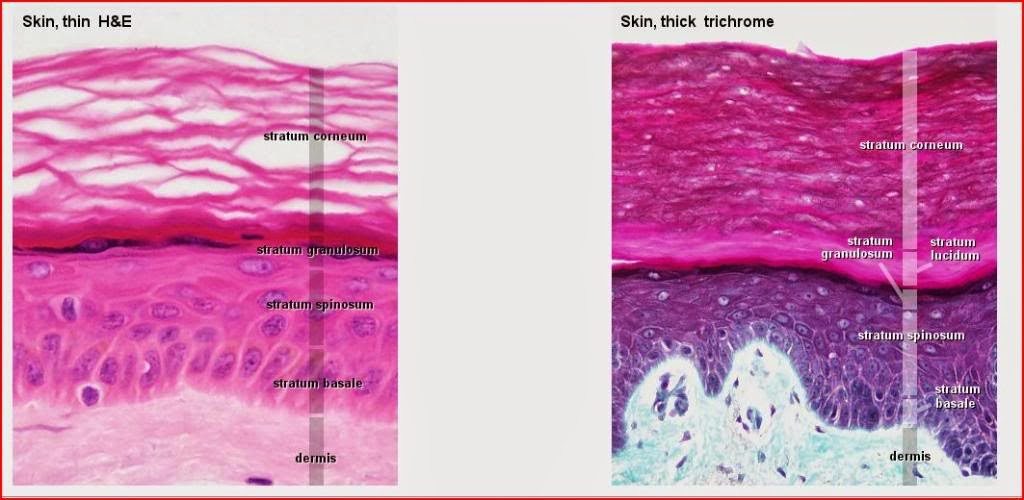
layers of epidermis (superficial to deep)
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum (not in thin skin)
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
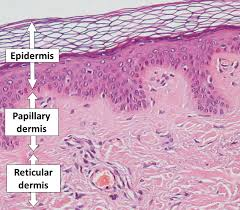
dermis
middle layer of skin; contains blood and lymph vessels, nerves and other structures, such as hair follicles and sweat glands
papillary layer (superficial)
reticular layer (deep)
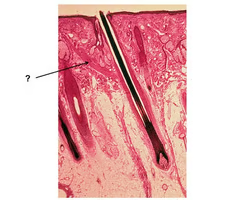
hair follicle histology
surrounded by sebaceous glands
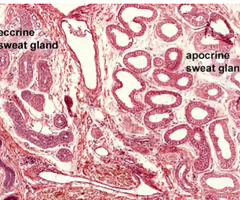
sweat gland histology
apocrine sweat gland (larger than eccrine, like in armpits)
also has more “white” in circle in histology
eccrine sweat gland (sweat)
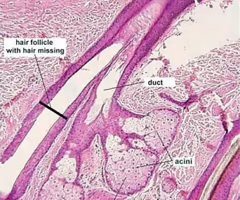
sebaceous glands
exocrine glands in the skin that produce and secrete sebum, an oily substance that lubricates and waterproofs the skin and hair
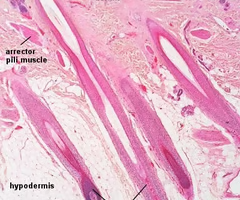
arrector pili muscle
small muscle in the skin attached to hair follicles. When it contracts, it causes the hair to stand on end, a phenomenon known as "goosebumps".
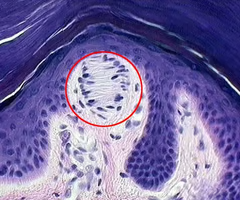
Pacinian corupscle
pressure receptors
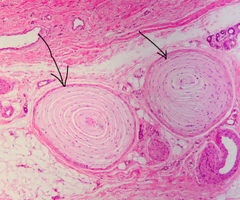
Meissner corpuscle
receptor in the skin that responds to light touch
parts of the skin (helpful overall diagram)
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
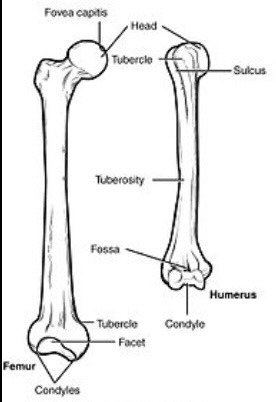
parts of the bone
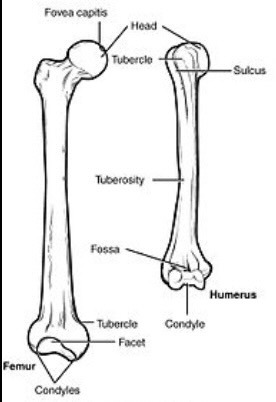
fossa
shallow, basin like and elongated depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
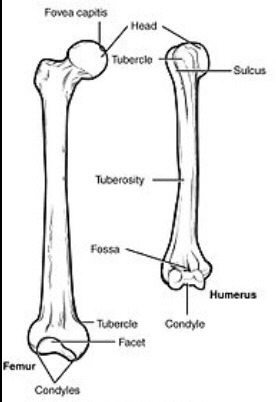
fovea
small pit in the bone
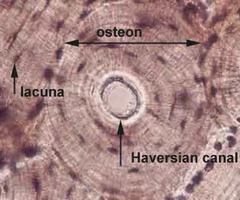
bone histology
matrix is dense and contains calcium, salts and collagen
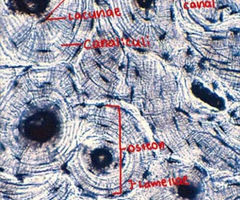
bone histology image overview
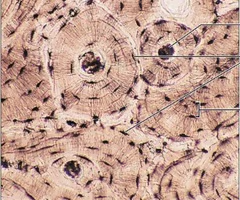
osteon histology
whole thing essentially
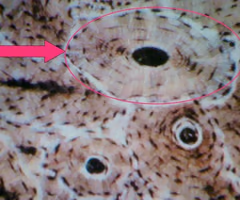
osteocytes histology
bone cells
black dots within the osteon
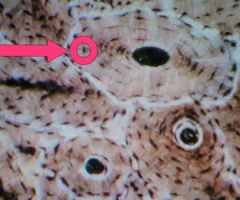
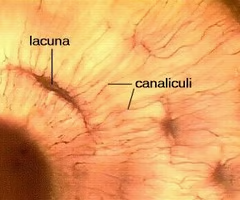
lacunae histology
small spaces or cavities within the bone matrix that house osteocytes
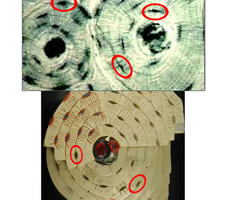
lamellae histology
lamellae form concentric rings around a central canal
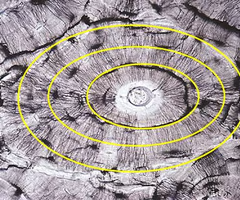
canaliculi histology
microscopic channels found within bone tissue that connect lacunae, which house osteocytes, to each other and to the Haversian canals
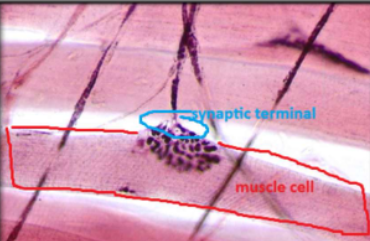
motor nerve ending
found at neuromuscular junction
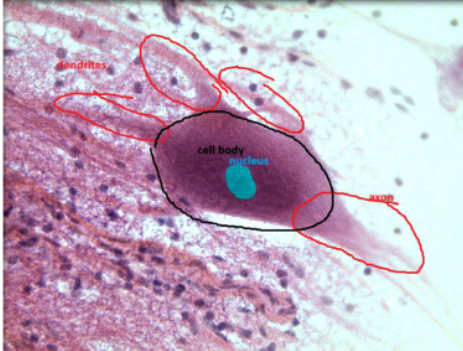
neuron smear
found in central nervous system
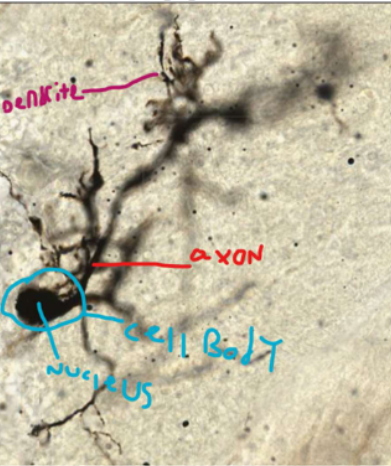
Purkinje cells
cerebellum
nerve cross section
found in peripheral nerves