BMET: Electronics- basic electrical components and resistor color codes
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
module 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is a Capacitor? Its symbol?
A device which stores electrical energy. Commonly used for filtering out voltage spikes
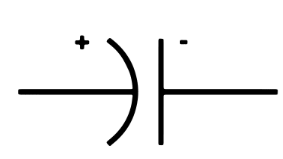
What is this
Capacitor
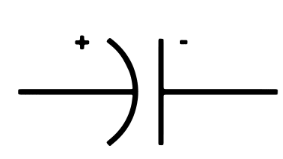
What is this
Capacitor
What is a Diode? Its symbol?
An electrical device that will allow current to pass through itself in one direction only
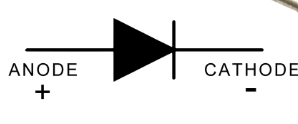
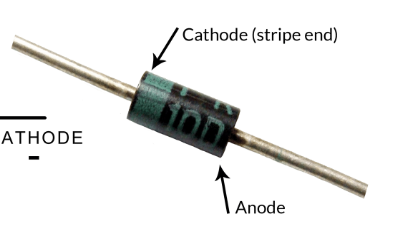
What is this
Diode
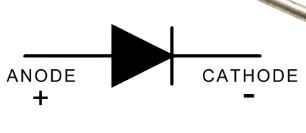
What is this
Diode
What is a Fuse? Its symbol?
A replaceable safety device for an electrical circuit.
When an overload occurs in the circuit, the wire or metal strip melts, breaking the circuit


What is this?
Fuse

What is this
Fuse
What is an IC Circuit?
An electronic circuit which utilizes resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors to perform various types of operations. The two major types are Analog and Digital Integrated Circuits
What is this
IC Circuit
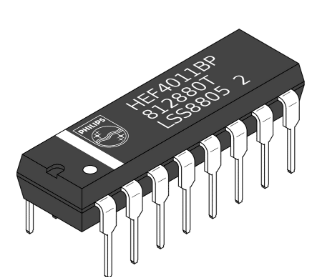
What is this
IC Circuit
What is an Inductor?
A coil of wire wrapped around an iron core

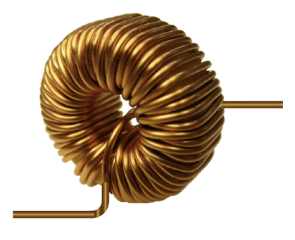
What is this
Inductor

What is this
Inductor
What is a Light Emitting Diode?
A solid-state display device that emits light when a forward-biased current flows through it.
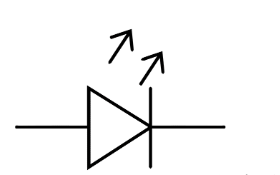

What is this
Light Emitting Diode
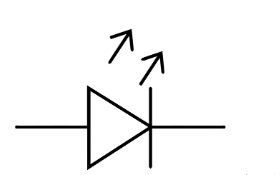
What is this
Light Emitting Diode
What is a Potentiometer?
A variable resistor used as a voltage divider.
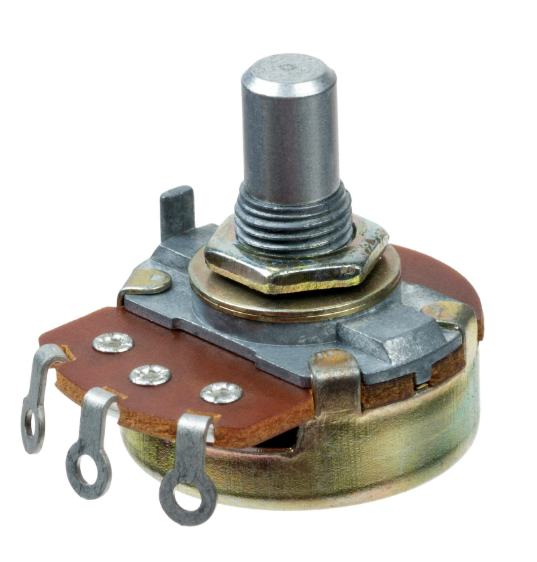

What is this
Potentiometer
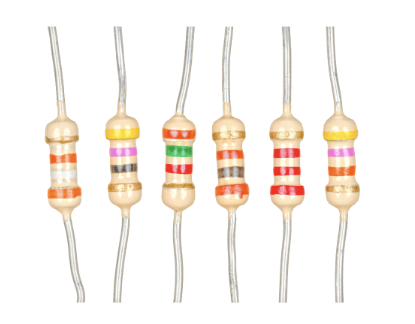
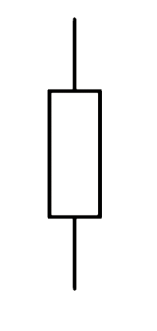
What is a Resistor?
A device usually made of wire or carbon which presents a resistance to current flow
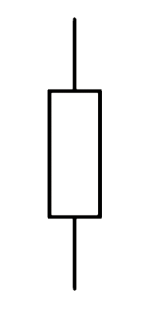
What is this
Resistor
What is this?
Resistor
What is a Switch?
A device which opens or closes electrical pathways in an electrical circuit


What is this?
Switch

What is this?
Switch
What is a transformer?
A device that transfers voltage from one coil to the next through electromagnetic induction. Depending upon the number of windings per coil, a transformer can be designed to step - up or step - down its output voltage from its input voltage.

What is this
Transformer
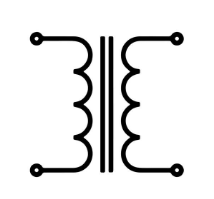
What is this?
Transformer
What is a Transistor?
A device constructed of semi - conductors that is used in circuits to control a larger current by using a smaller current for operation. Its function is the same as a relay
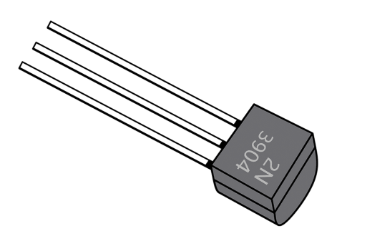
What is this?
Transistor
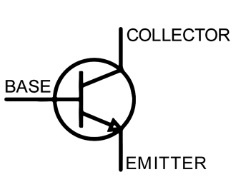
What is this?
Transistor
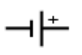
What is this
DC voltage source

What is this
AC voltage source
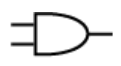
What is this
And Gate
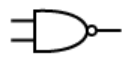
What is this
Nand gate

What is this
Or gate
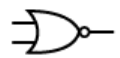
What is this
Nor gate
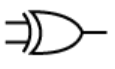
What is this
Xor gate

What is this
Inverter (not gate)
In a banded resistor, what does the 1st band represent?
The first digit of the resistor value
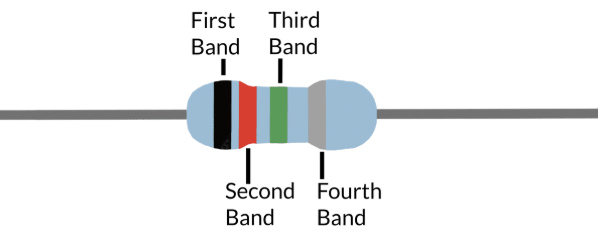
In a banded resistor, what does the 2nd band represent?
The second digit of the resistor value
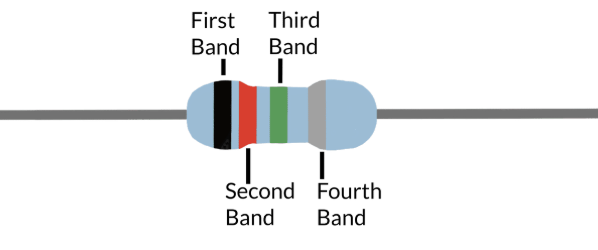
In a banded resistor, what does the 3rd band represent?
the multiplier, which adjusts the decimal place to convert values from megaohms to milliohms and everything in between
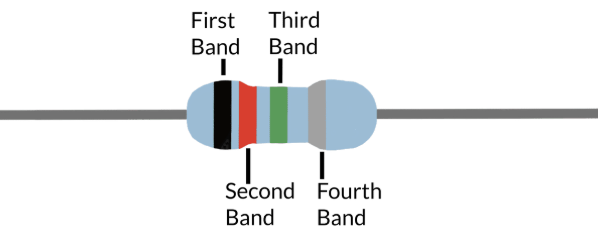
In a banded resistor, what does the 4th band represent?
the tolerance level
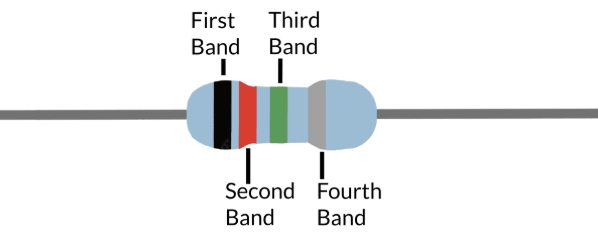
if a banded resistor is missing the 4th band, what is the default tolerance value?
±20%