Psychology Midterm 1
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Psychology
scientific study of mental activity and behavior, which depends on processing in the brain
Ontology
the philosophical study of being
your view of reality and to what extent it exists ‘out there’ to be captured through research
Concerned with what is true and real
Psychoanalytic Theory
explains human personality as a series of stages that is formed through inner conflicts
Behaviorism
theory of learning that states all behaviors are learned through conditioned interaction with the environment
Empiricism
conducting psychological research using an objective, evidence-based approach
Science of Learning
research in psychology and other fields that suggests how you can improve your study skills, learning, and academic performance
Critical Thinking
systematically evaluate information to reach conclusions based on the evidence that is presented
Wilhelm Wundt
established the first experimental psychology labratory
Biological
how does your activity in your brain and body give rise to your thoughts, feelings, and actions?
Cognitive
how do your mental activities affect your thoughts, feelings, and actions?
Development
how do you change your life in terms of your thoughts, feelings, and actions?
social and personality
how do social factors and your personal characteristics impact your thoughts, feelings, and actions?
mental and phsyical
what effects your mental and physical health, and how can you develop healthy behaviors?
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
Piaget proposed four major stages of cognitive development, and called them (1) sensorimotor intelligence, (2) preoperational thinking, (3) concrete operational thinking, and (4) formal operational thinking
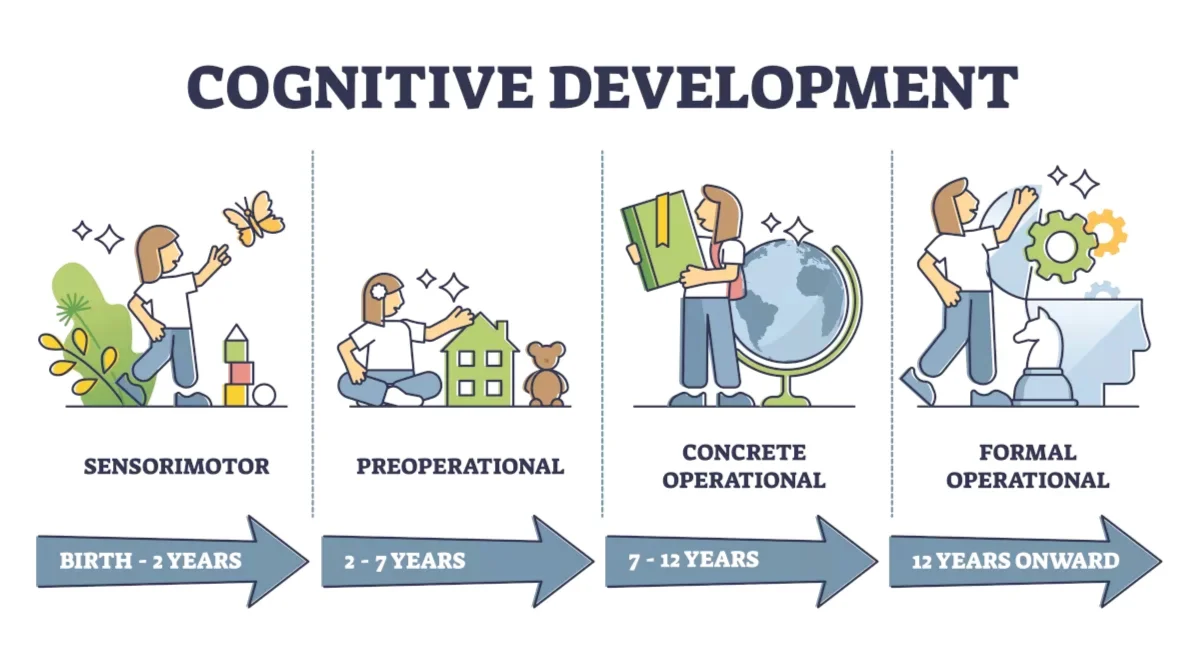
Diversity
characteristics that make us seem different from one another in specific situations
Culture
the beliefs, values, rules, and customs within a group who share a common language and environment (diff. cultures lead to diff. answers in psychological testing)
Ethics
accepted standards of right and wrong
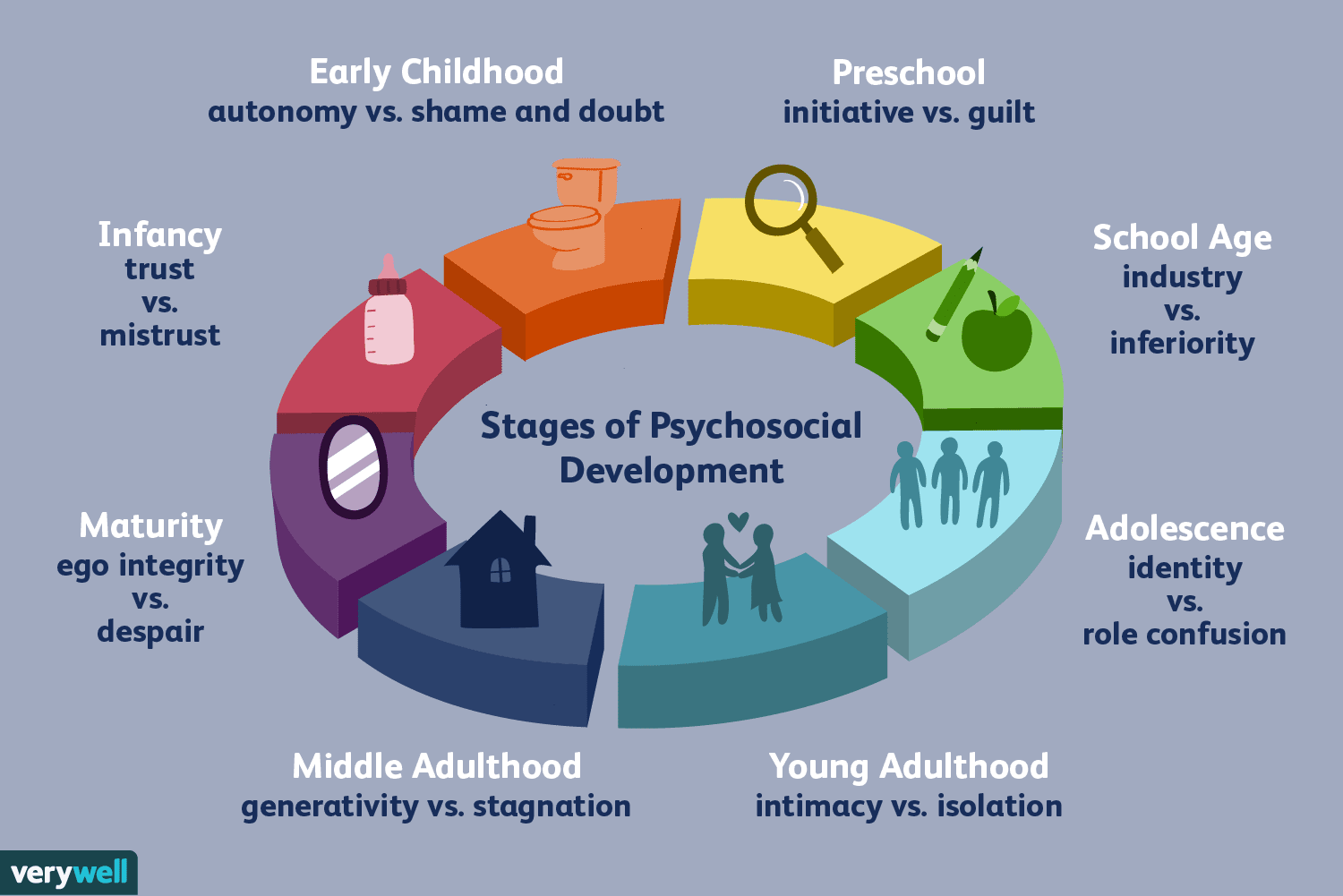
Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development
Stages arise as individuals grow and face new decisions and turning points during childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Each stage is defined by two opposing psychological tendencies – one positive/syntactic and negative/dystonic
Institutional Review Boards (IRBs)
reviews all proposed research to ensure that it meets four ethical standards: privacy, informed consent, confidentiality, and protection from harm
Scientific Method
systematic, empirical approach that psychologists use to achieve these 3 goals: Formulate a theory, develop a testable hypothesis, and test with a research method
Theory
explanation of how some mental process or behavior occurs
Hypothesis
specific, testable prediction about what should be observed if a theory is correct
Descriptive Reasearch Methods
describe what is occurring (ex. case studies, observational study, and self-reports)
Correlational Research Methods
test the relationship between variables
Experimental Research Methods
investigate cause of outcome
Case Studies
allow in-depth investigation of one or few people
Observation Study
watch what participants do in a natural environment
Self-Reports
gather information directly from participants
Replication
verify results of a study by doing it again
Descripitive Methods
research methods that provide a systematic and objective snapshot of what is occurring at a certain point in time
Hawthorne Effect
alteration of behavior by the subjects of a study due to their awareness of being observed
Correlational Methods
examine a naturally occurring relationship between 2 factors without alteration
Experimental Methods
determine whether causality exists between variables or to explain why a phenomenon occurs
Independent Variable
manipulated and under the experimenter’s control
Dependent Variable
the effect of the independent variable on a second variable
Operational Definitions
objective and systematic defintions of a word
Control Group
baseline with no change
Experimental Group
manipulated
Random Sample
each member of a population has an equal chance of being chosen to participate in research— random assignment to place participants in control v. experimental group
What is Psychology?
Mind is made up of all mental activity that lets us experience the world; behavior is all the actions resulting from sensing and interpreting information
What makes something “Mental”?
mental, behavioral, and brain are all the same, it just depends on how you look at it
psychology has taken advantage of splitting things into mental v. nonmental
the behavior of acting emotional is emotion (nonmental)
What about clinical psychology? How does it fit?
science + research = therapy
study human behavior in therapy
Can we have a science of human activity? Should we?
prediction through science
ability to influence and control
if people are doing the science, how do we explain their scientific behavior?
PERENNIAL THEME- hall of mirrors problem
Hall of Mirrors Problem
A situation where it's difficult to distinguish between reality and perception due to multiple conflicting perspectives reflected back at you
What is Psychology? (Lecture)
Empirical extension of philosophy
A mostly secular group of predominantly white, European, 20th century, alleged experts in human functioning
The behavior of people who call themselves psychologists
Somewhere in between sociology and neuroscience
A divide field of study (e.g., developmental, social, cognitive, clinical, etc.)
A dying field of study? Will it all ultimately be about the brain?
What do Psychologists do?
research (academic and otherwise)
teaching
therapy
consultation
assessment/testing
Nervous System
a network of billions of cells in your brain and body
receives sensory input through sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell
process info in the brain by paying attention to it, perceiving it, and remembering it
responds to info by acting on it
Central Nervous System (CNS)
nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the nerve cells outside of the brain and spinal cord
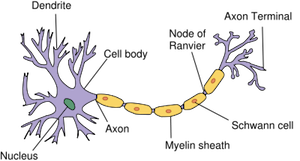
Neurons
small units that make up divisions of the nervous system
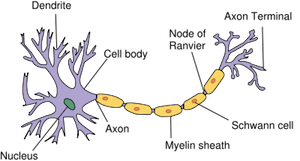
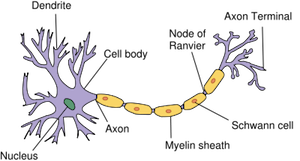
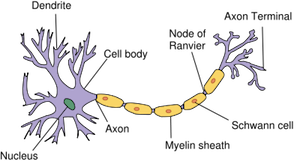
Dendrites
Branch-like extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons. They play a crucial role in transmitting information to the cell body for further processing.
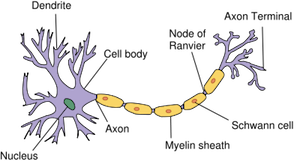
Cell Body
where info received from thousands of neurons is collected and interpreted (combined)—responsible for processing and integrating information received from dendrites and sending signals down the axon.
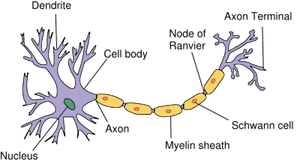
Axon
long, slender projection of a neuron that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons
Terminal Buttons
the end of the axon— responsible for releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap.
Synapse
A junction between two neurons, where electrical or chemical signals are transmitted. It allows for communication and information transfer in the nervous system.
the gap between terminal buttons sending neurons and dendrites receiving neurons
Transmission Phase
neural communication begins when there is enough stimulation in the presynaptic neuron to create an action potential
the action potential travels down the axon to the terminal buttons and causes neurotransmitters to be released from the terminal buttons at the end of the axon
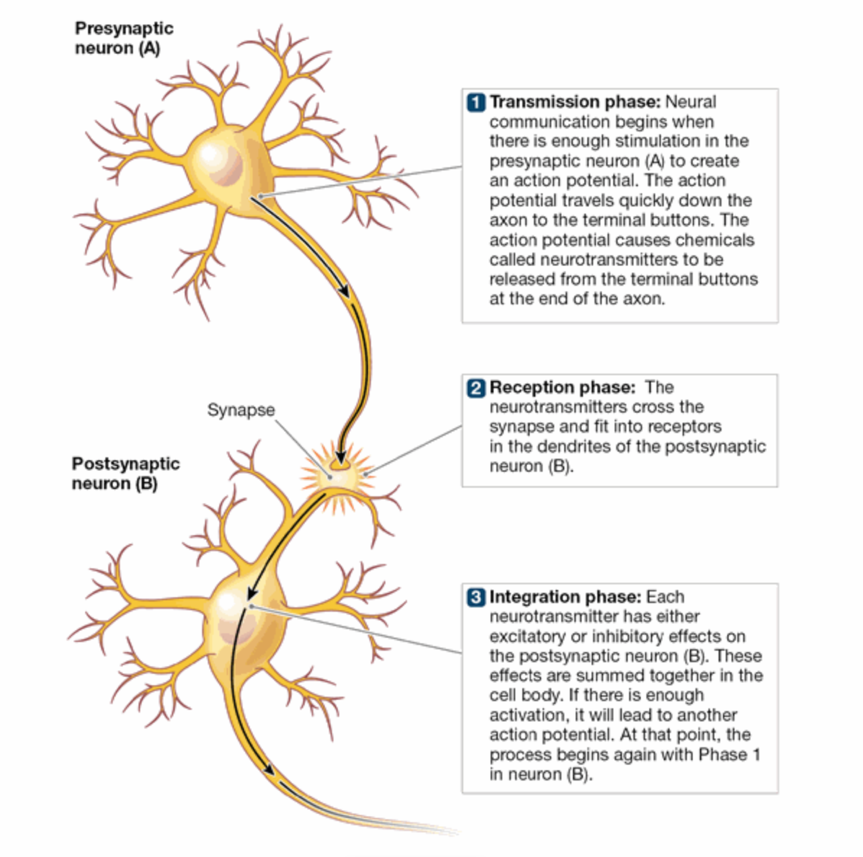
Reception Phase
the neurotransmitters cross the synapse and fit into receptors in the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron
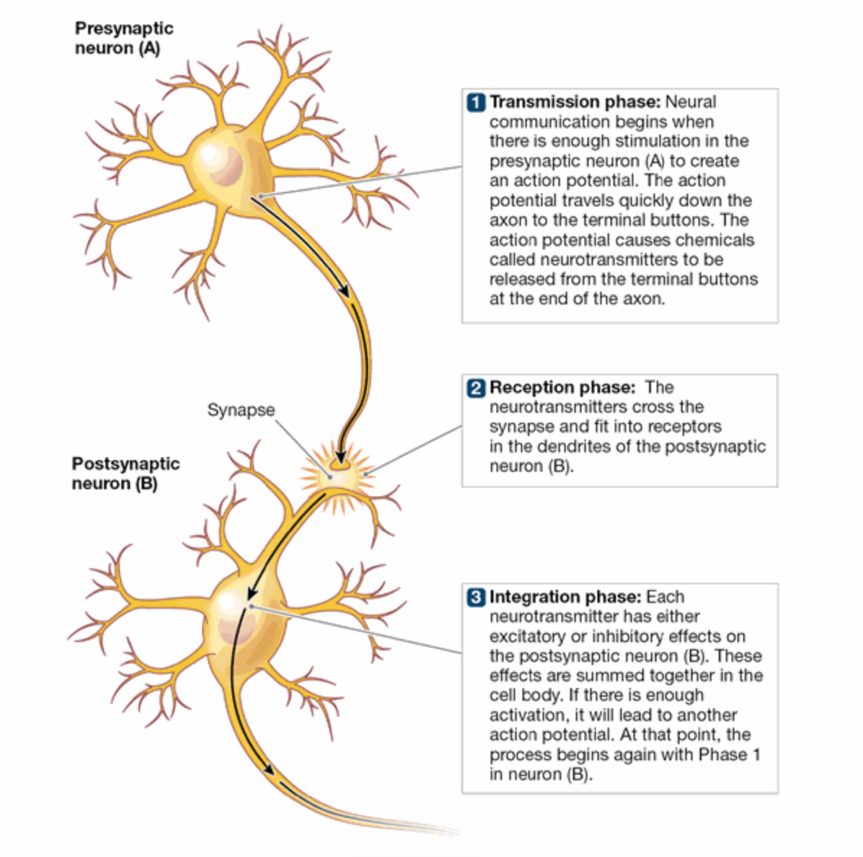
Integration Phase
each neurotransmitter has either excitatory or inhibitory effects on the postsynaptic neuron
these effects are summed together in the cell body
if there is enough activation, it will lead to another action potential
at that point the process begins again
Action Potential
the neural impulse that travels along the axon and then causes the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse
Myelin Sheath
the fatty layer that insulates the axon
allows for faster movement of electrical impulses
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter: motor control over muscles; Attention, memory, learning, sleeping
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter: arousal and alertness
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter: emotional states and impules control; dreaming
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter: reward and motivation; motor control over voluntary movement
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Neurotransmitter: inhibition of action potentials; anxiety reduction; intoxication (through alcohol)
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter: enhancement of action potentials; learning and memory
Endorphins
Neurotransmitter: pain reduction; reward
Hindbrain
Medulla: breathing, heart rate, other survival mechanisms
Pons: sleep, arousal, left-right body movement coordination
Cerebellum: motor learning, coordination, balance
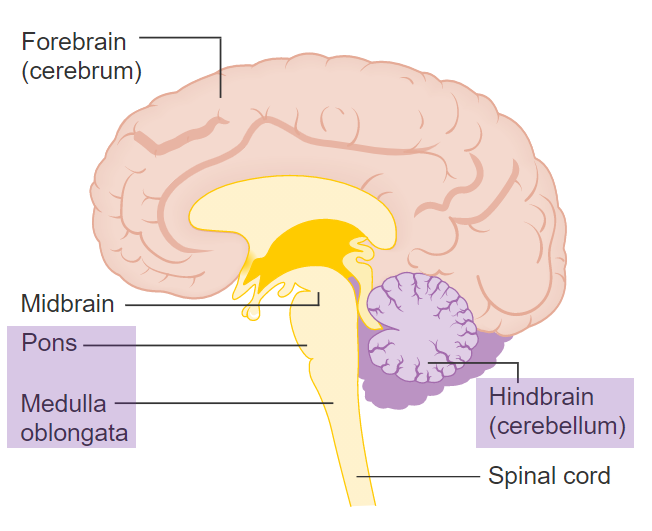
Midbrain
Substantia Nigra: initiation of voluntary motor activity
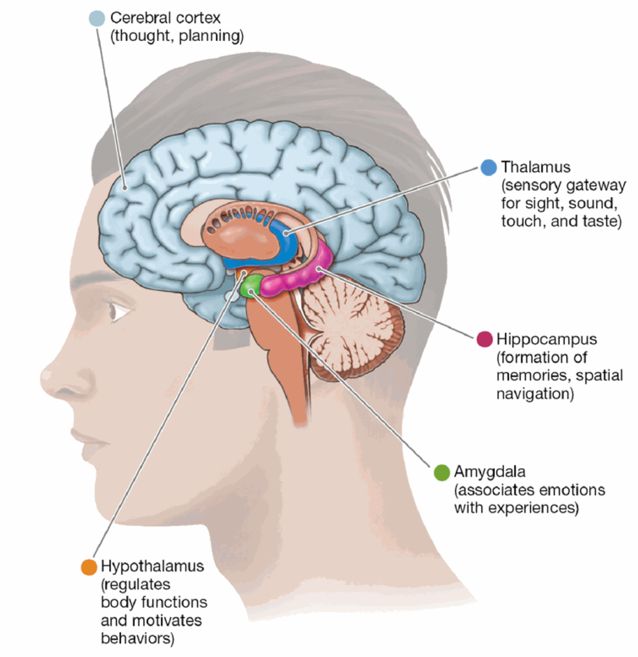
Forebrain (Subcortical Structures)
Thalamus: sensory information (except smell)
Hypothalamus: regulation of body functions (sleep, temp, etc.) and motivation (hunger, thirst, sex, etc.)
Hippocampus: formation of new memories
Amygdala: association of emotions with experiences
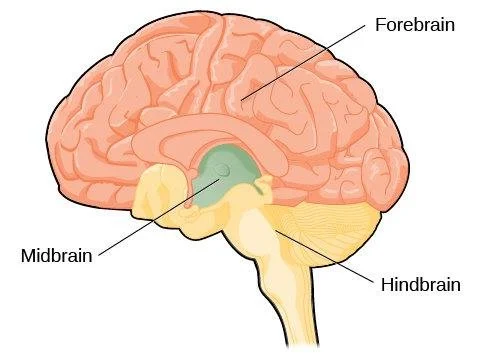
Forebrain (Cortical Structures)
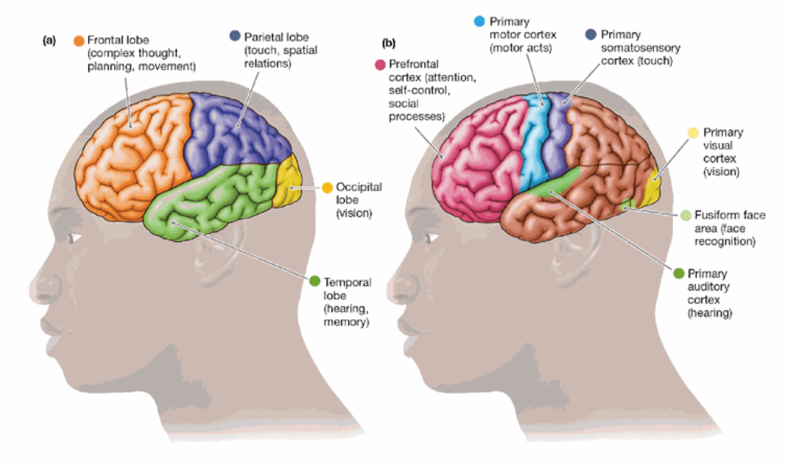
Occipital Lobes: vision
Parietal Lobes: touch, spatial information
Temporal Lobes: hearing, memory
Frontal Lobes: Planning movement, complex thought
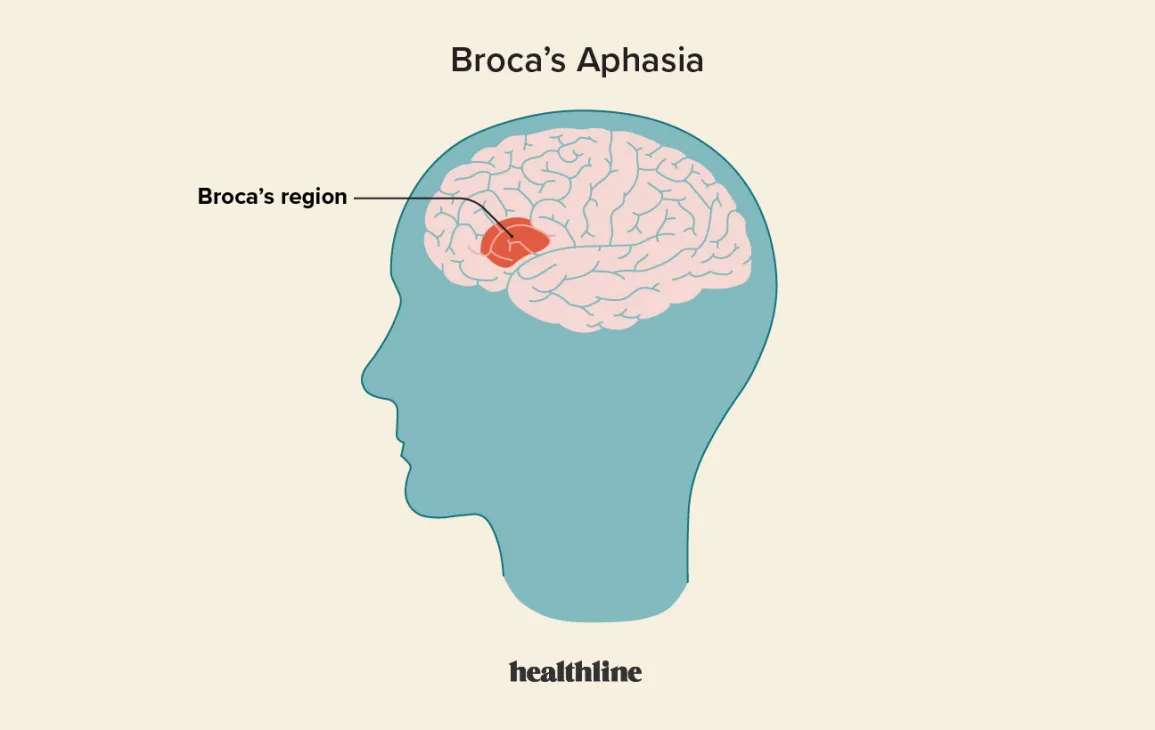
Broca’s Area
a small portion of the left frontal region of the brain; this area is crucial for producing speech
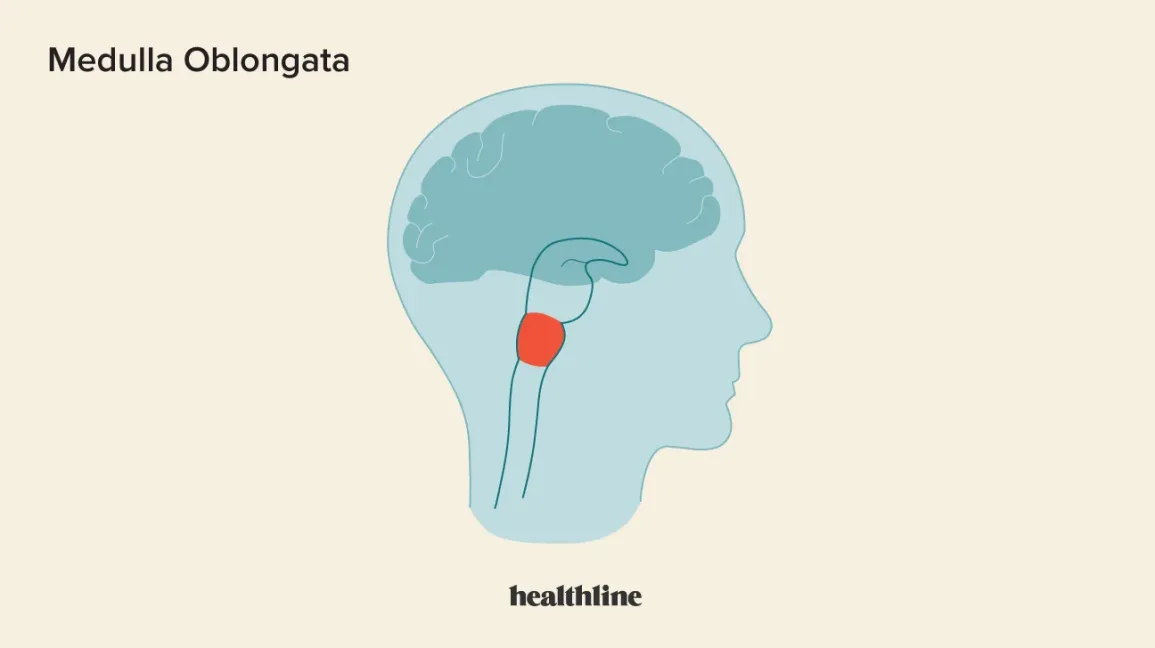
Medulla
controls the basic functions of survival; heart rate, bretaing, swallowing, etc.
Pons
Sleep and arousal; coordinating movements between the left and right sides of the body
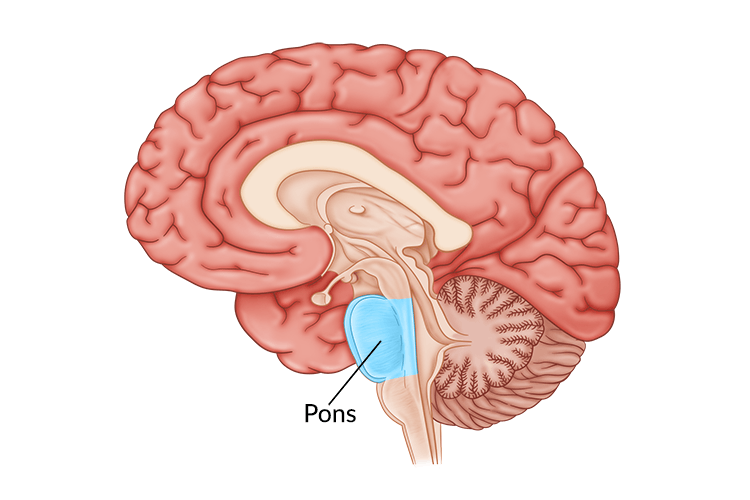
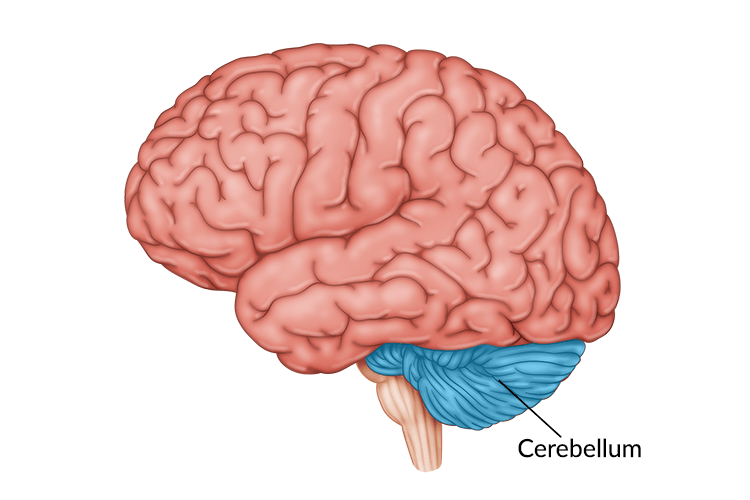
Cerebellum
essential for proper motor functions; motor learning and memory
Thalamus
the gateway to the brain for sight, sound, touch, and taste sensory info before that info reaches the cortex
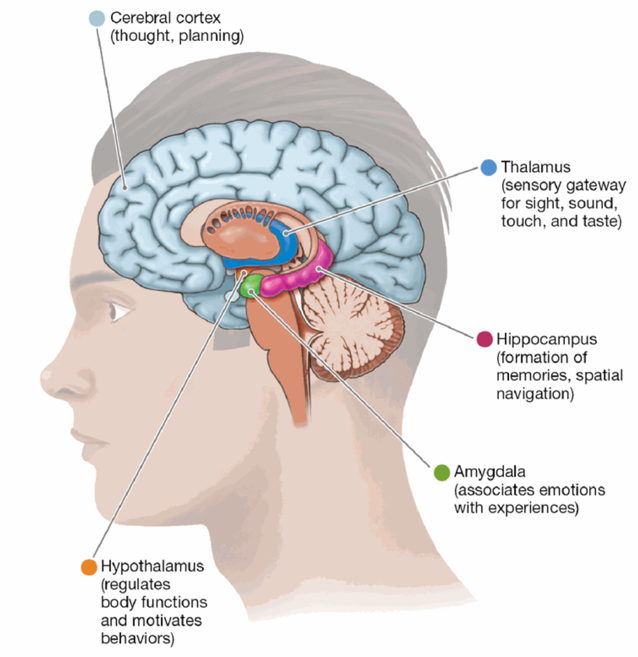
Hypothalamus
regulates bodily functions; basic motivated behaviors
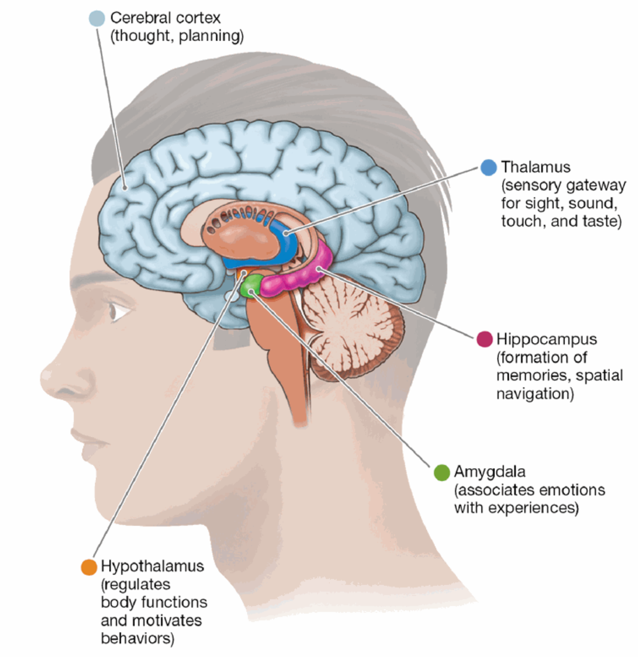
Hippocampus
formation of new memories and with spatial navigation
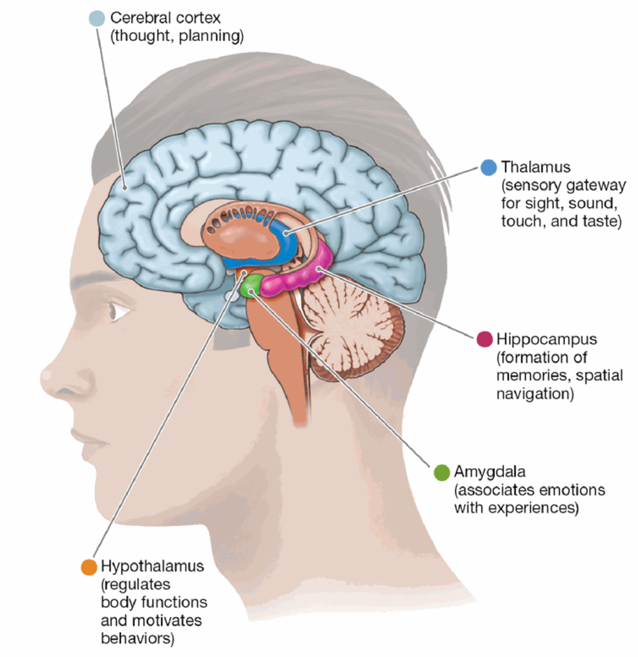
Amygdala
learning to associate things with emotional responses and in processing emotional information
Occipital Lobes
vision
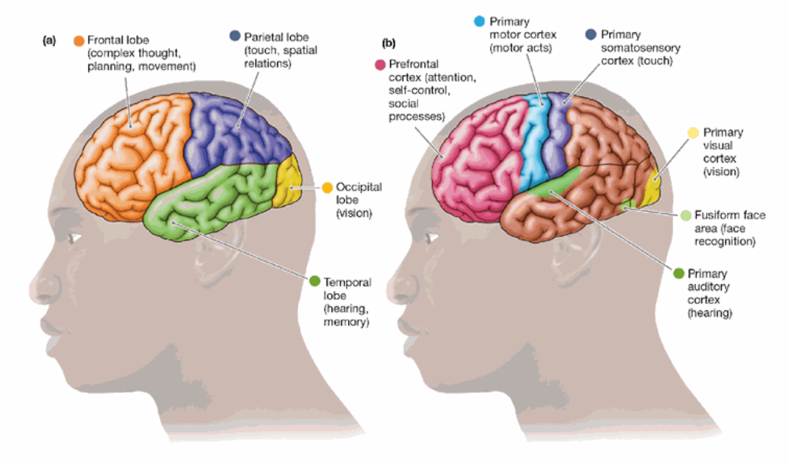
Parietal Lobes
touch
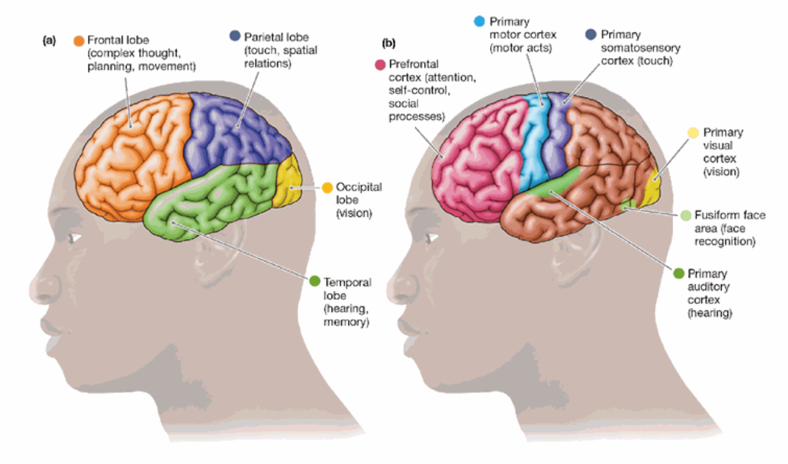
Temporal Lobes
hold the primary auditory cortex (hearing)
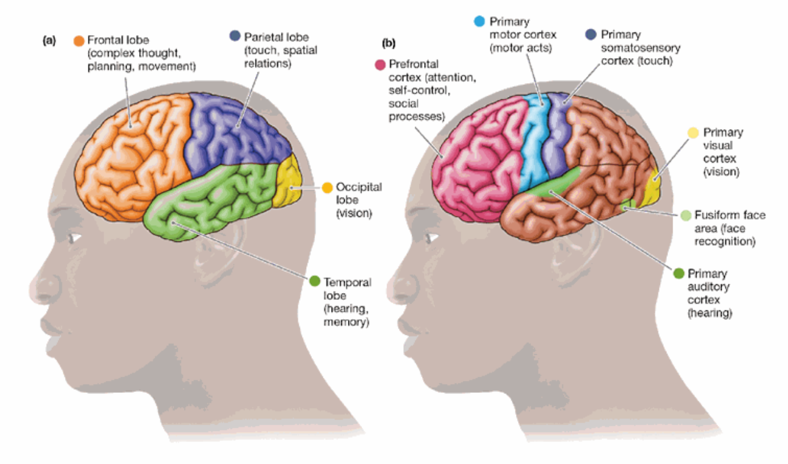
Frontal Lobes
essential for complex thought, planning, and movement
Split Brain
a condition in which the corpus callosum is surgically severed and the two hemispheres of the brain do not receive information directly from each other
epilepsy
Right Hemisphere
better with special relationships and controls left-side body movements
Left Hemisphere
better with language and controls right-side body movements
Left Hemisphere Occipital Lobe
processes right visual field information
Right Hemisphere Occipital Lobe
processes left visual field information
Somatic Nervous System
subdivision of the PNS; transmits sensory signals and motor signals back and forth between the CNS and the skin, muscles, and joints
Autonomic Nervous System
subdivision of the PNS; transmits sensory signals and motor signals back and forth between the CNS and the body’s glands and internal organs
Endocrine System
a communication network that influences many aspects of your body; influences mental activity and behavior
Hormones
the chemicals that are released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands
Natural Selection
the basis of evolution; those who inherit characteristics that help them adapt to their particular environments have an advantage over those who do not
Genes
units of hereditary that help determine an offspring’s characteristics
Monozygotic Twins
Identical
Dizygotic Twins
Fraternal
Plasticity
a property of the brain that causes it to change as a result of experience or injury
The Common View of Nature v. Nurture
Nature = everything you are born with as a result of natural selection/evolution
Nurture = those aspects of human psychology/behavior that are “natural”/inevitable
Nurture is social/psychological while Nature is biological
the effects of nature and nurture can be separated through scientific studies (e.g., identical twins raised together versus those raised apart)
An Alternative (more correct) View of Nature v. Nurture
Nurnature/Nanature
Nurture —> Nature —> Nurture —> Nature
Nature is always nurtured (e.g., cells learn in environments)
Nurture always requires nature (e.g., how we learn from our environment depends on our ‘nature’/biology)
Distinction is bogus
Why does “Nature v. Nurture” Persist?
The Blame/Compassion Game: we talk about aspects of human behavior we don’t like, by dividing them into
“Biological”- not our fault; inevitable
“Psychological”- our fault; a personal flaw or weakness
“Environmental”- a compromise— maybe we can do something about it