AP Human Geo-Midterm Review
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
Physical Geography
Study of natural processes and distribution of features in the environment
Human Geography
The study of human activities and their relationship to the cultural and physical environments.
Spatial Perspective
Refers to where something occurs
Ecological Perspective
Refers to living things and their environment
Location
A specific point or area on the Earth's surface.
Absolute Location
The exact position of a place on the Earth's surface, usually expressed in coordinates (latitude and longitude).
Meridians
Lines of longitude that run from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Parallels
Lines of latitude that run parallel to the equator.
Latitude
The distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees.
Longitude
The distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees.
Relative Location
The position of a place in relation to other places.
Place
Location on Earth known by its physical and human characteristics
Site
The physical characteristics of a place, including its terrain, soil, and climate.
Situation
The location of a place relative to its surroundings and other places.
Space
the area between two or more things on Earth's surface
Distribution
Studying the way things are arranged within a given space
Density
# of things in a specific area (people, animals, objects)
Pattern
how things are arranged in a particular space
Flow
The movement of people, goods, or information from one location to another.
Environmental Determinism
The theory that the physical environment, especially the climate, shapes human behaviors and societal development.
Possibilism
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment.
Sustainability
The ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Distance Decay
The farther away one thing is from another, the less interaction the two things have
Friction of Distance
The concept that distance creates a barrier to interaction and communication.
Time-space Compression
The process by which the relative distance between places is reduced due to advancements in transportation and communication.
Scale
Refers to the area of the world being studied
Region
An area with certain characteristics that makes it distinct from other areas.
Formal Region
An area defined by official boundaries and uniform characteristics.
Functional Region
An area organized around a node or focal point, characterized by a specific function.
Node
The central point of a functional region.
Perceptual or Vernacular Region
An area defined by people's perceptions and feelings rather than formal boundaries.
Globalization
The process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or operate on an international scale.
World Systems Theory
A theory that emphasizes the world as a complex system of interrelated parts, focusing on the relationships between core, semi-periphery, and periphery countries.
Core
Countries that are economically and politically dominant, often characterized by high levels of wealth and education.
Periphery
Countries that are less developed, often with unstable governments and lower levels of wealth and education.
Semi-periphery
Countries that are in the process of industrializing and have characteristics of both core and periphery countries.
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Quantitative data
info that can be measured numerically.
Qualitative data
interpetations of data sources, often collected through interviews and observations.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
A system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data.
Topography
The arrangement of the natural and artificial physical features of an area.
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact, often through satellite or aerial imagery.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth.
Cartographers
Individuals who create maps.
Absolute Distance
The exact measurement of the space between two points.
Relative Distance
The distance between two places as measured by the time or cost it takes to travel between them.
Absolute Direction
A compass direction such as north, south, east, or west.
Relative Direction
A direction such as left, right, forward, or backward that is based on a person's perspective.
Map Scales
The ratio of a distance on a map to the corresponding distance on the ground.
How does map scale work?
The smaller the scale, the bigger the area
Map Projections
Methods used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map.
Robinson Projection
A map projection that attempts to balance size and shape, providing a visually appealing representation of the world.
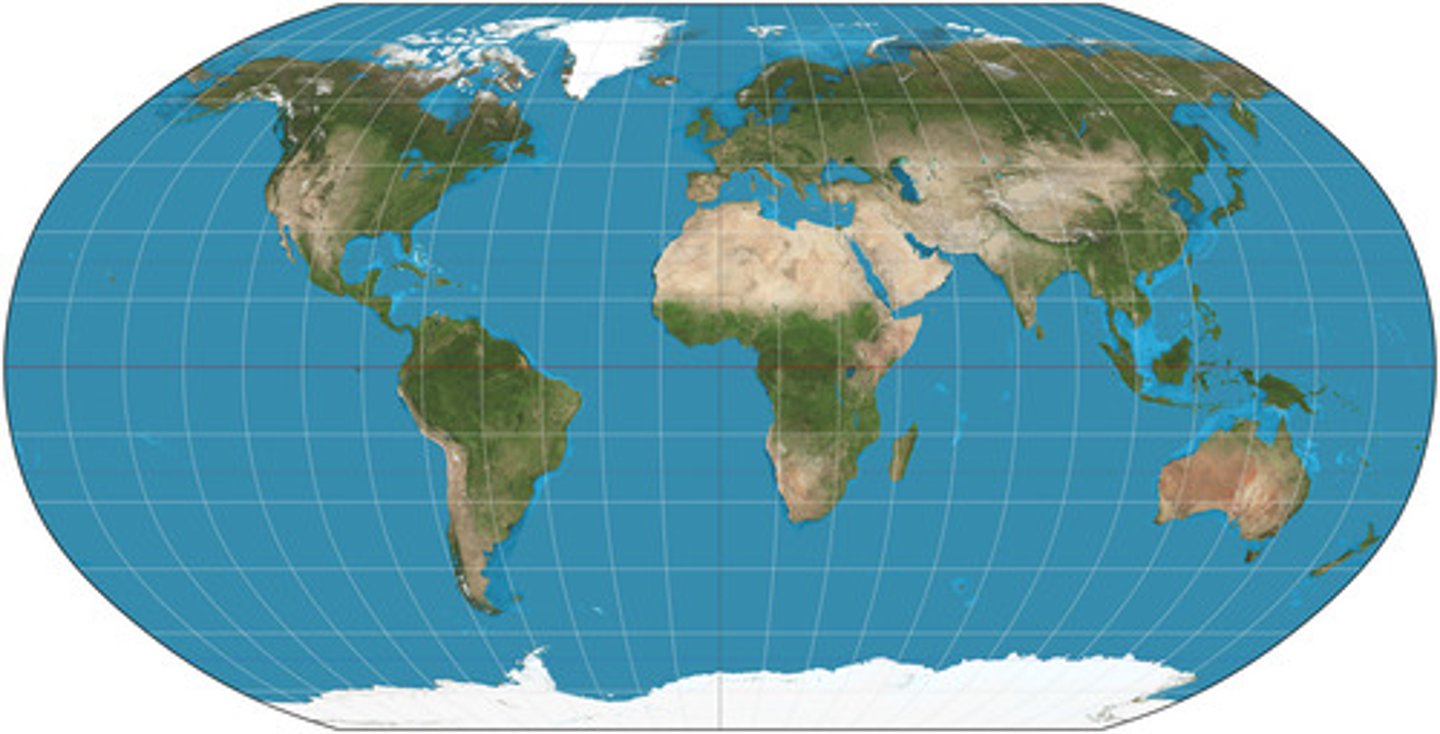
Mercator Projection
A cylindrical map projection that distorts size but preserves shape, commonly used for navigation.
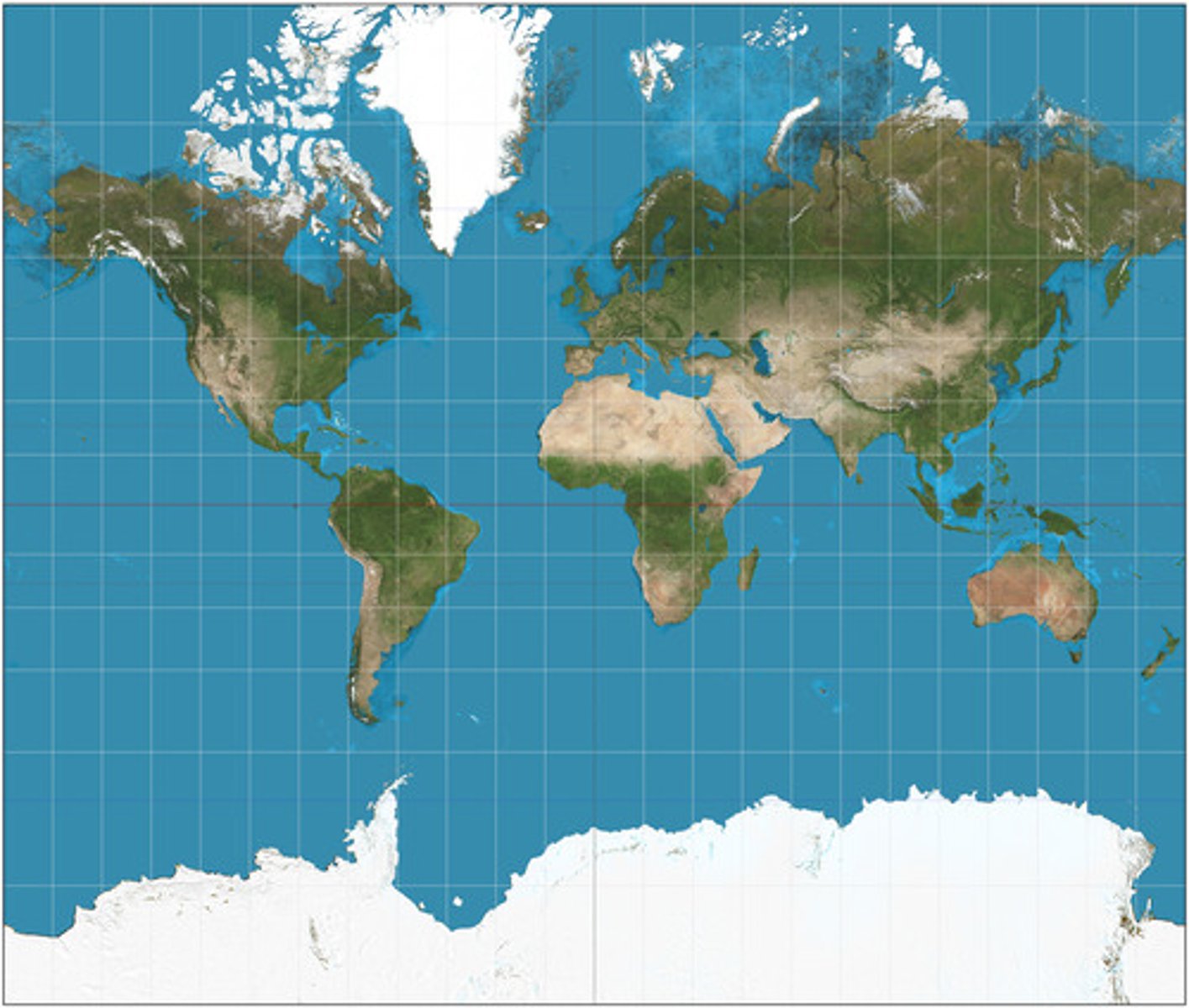
Gall-Peters Projection
A map projection that represents areas in true proportion but distorts shapes, emphasizing the size of developing countries.
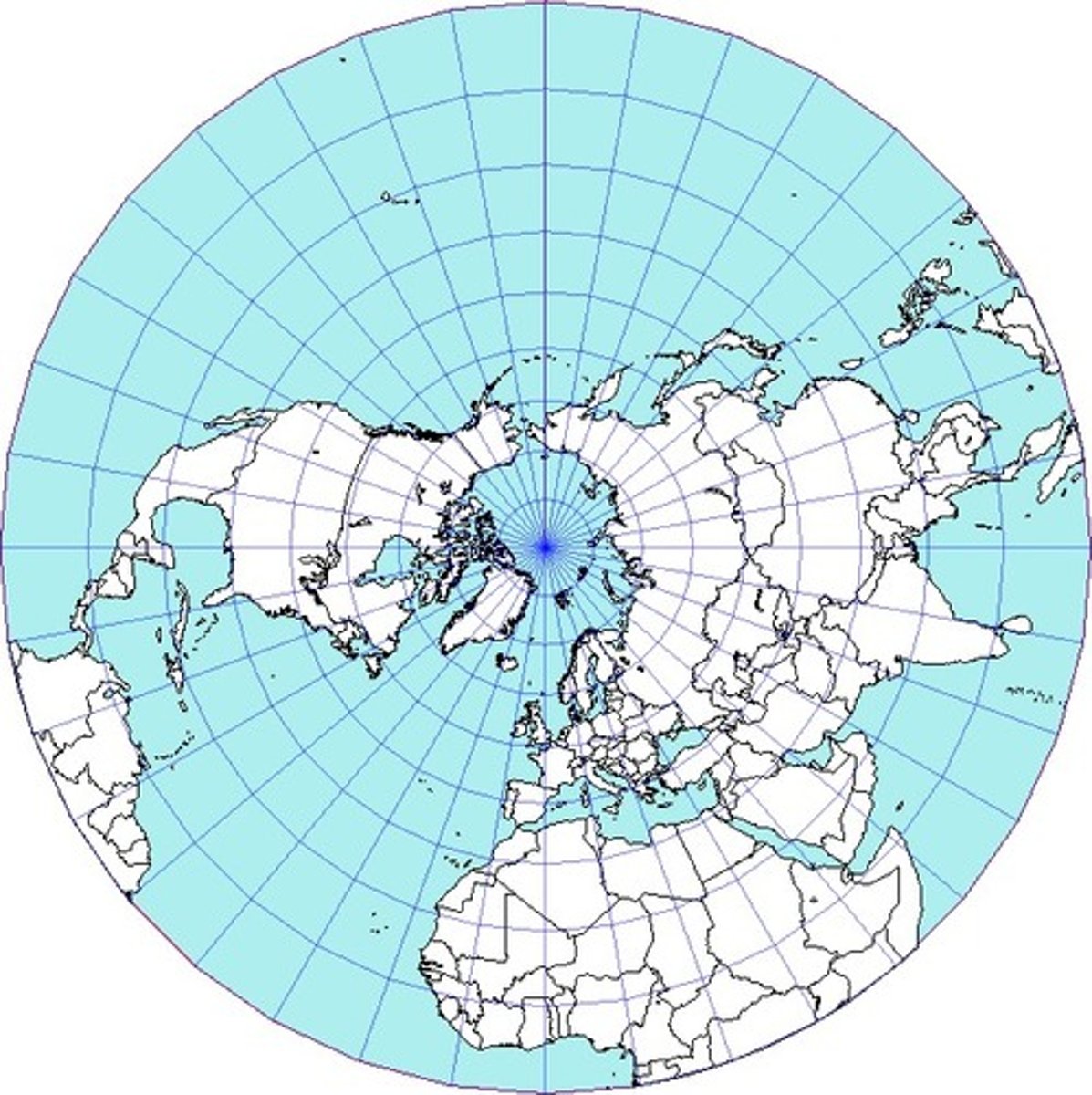
Azimuthal Projection
A map projection that shows the Earth from a specific point, often used for polar regions.
Reference Maps
Maps that show the location of various features in an area, such as roads, rivers, and boundaries.
Thematic Maps
Maps that focus on a specific theme or subject, such as population density or climate.
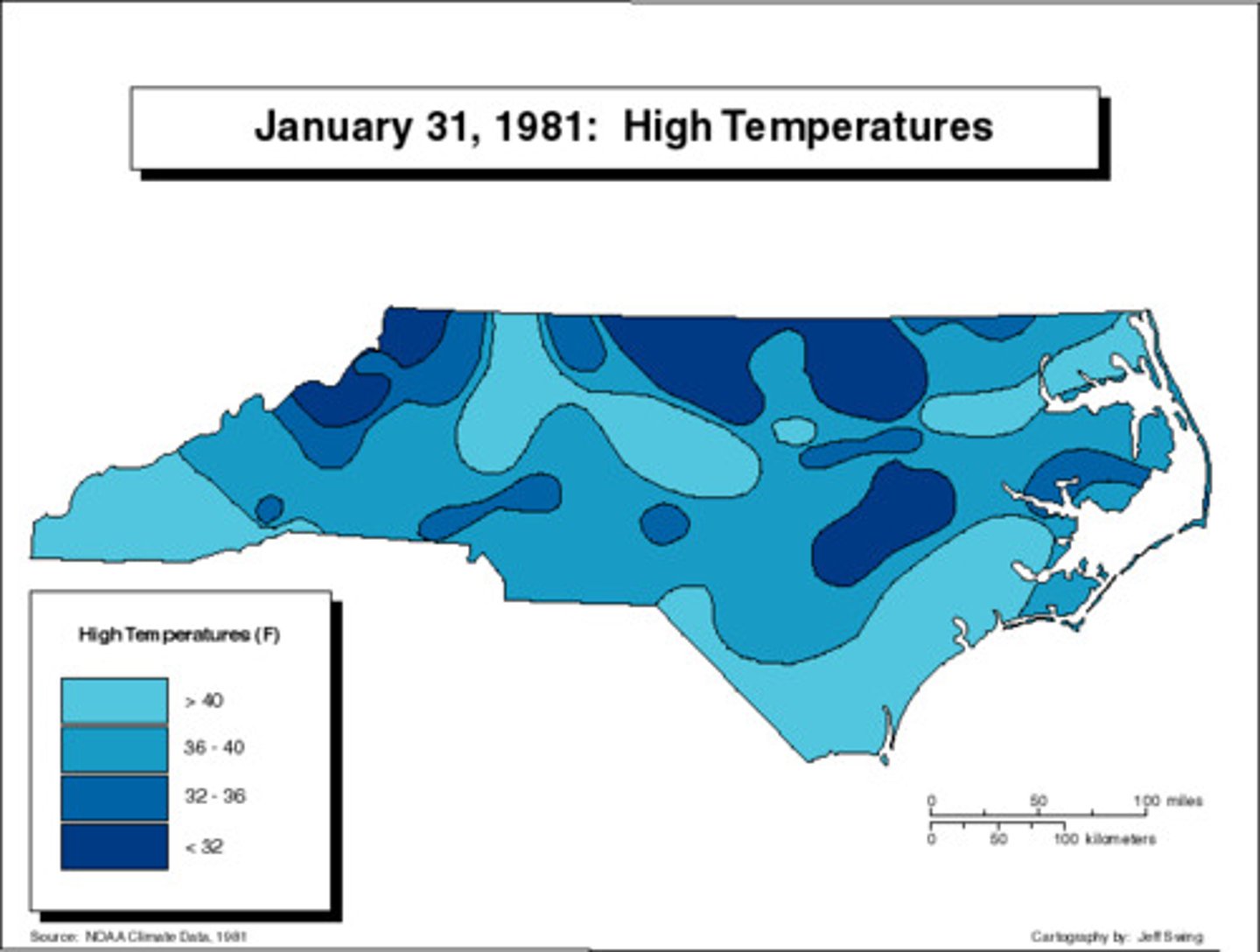
Isoline Maps
Maps that use lines to connect points of equal value, such as elevation or temperature.
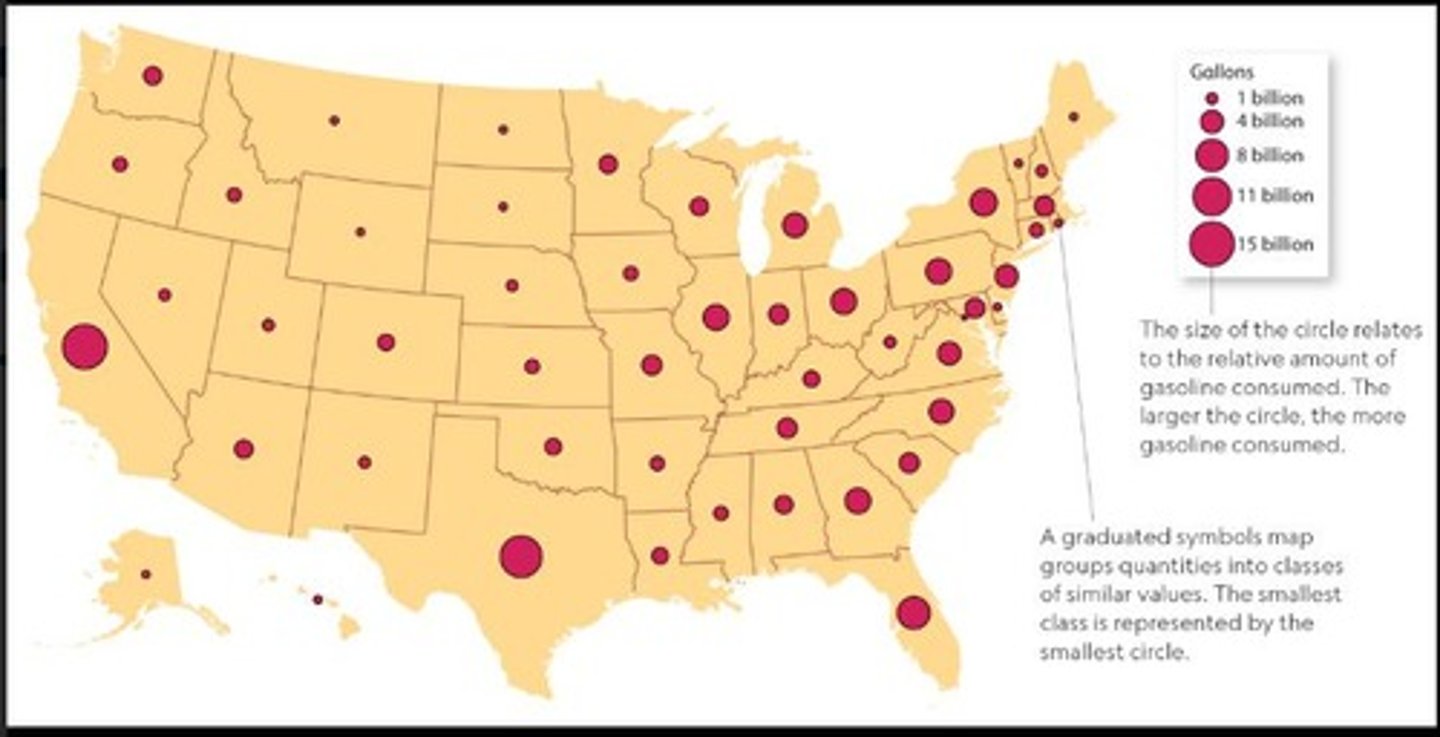
Graduated Symbols Map
A map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent data values, such as population size.
Cartogram
A map that distorts the size of areas based on a specific variable, such as population.
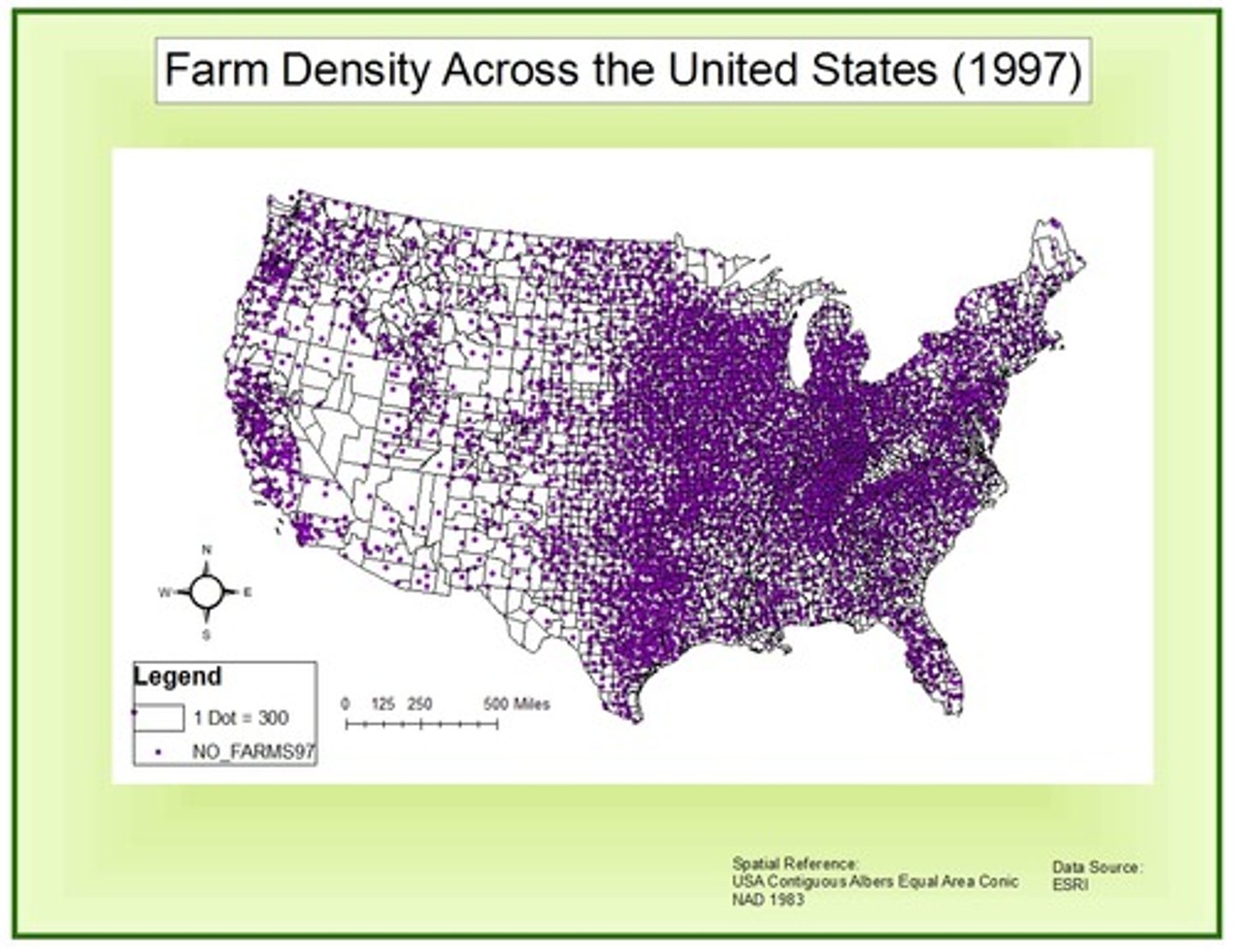
Dot Map
A map that uses dots to represent the presence of a feature or phenomenon in a given area.
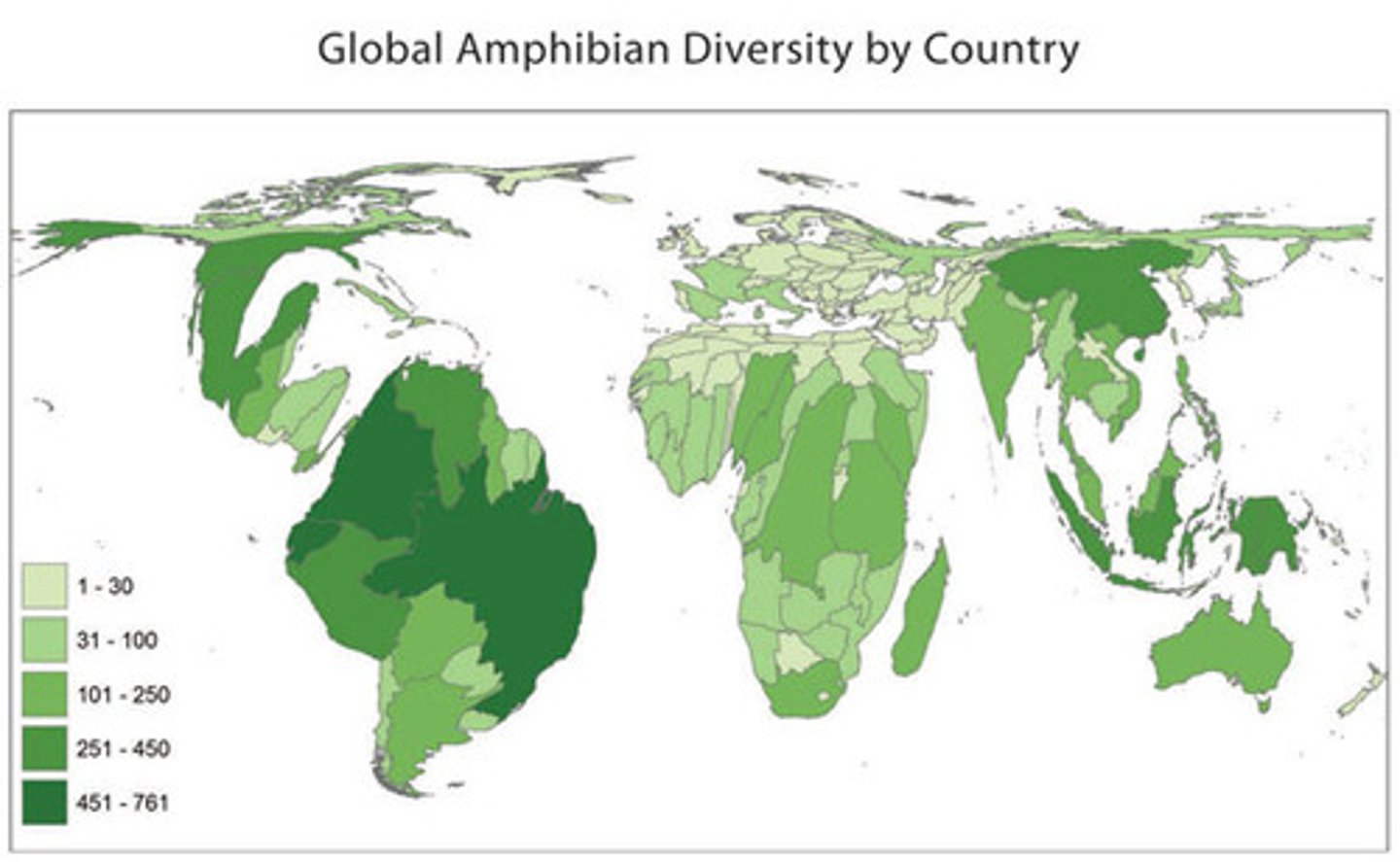
Choropleth Map
A map that uses different shades or colors to represent data values in predefined areas.
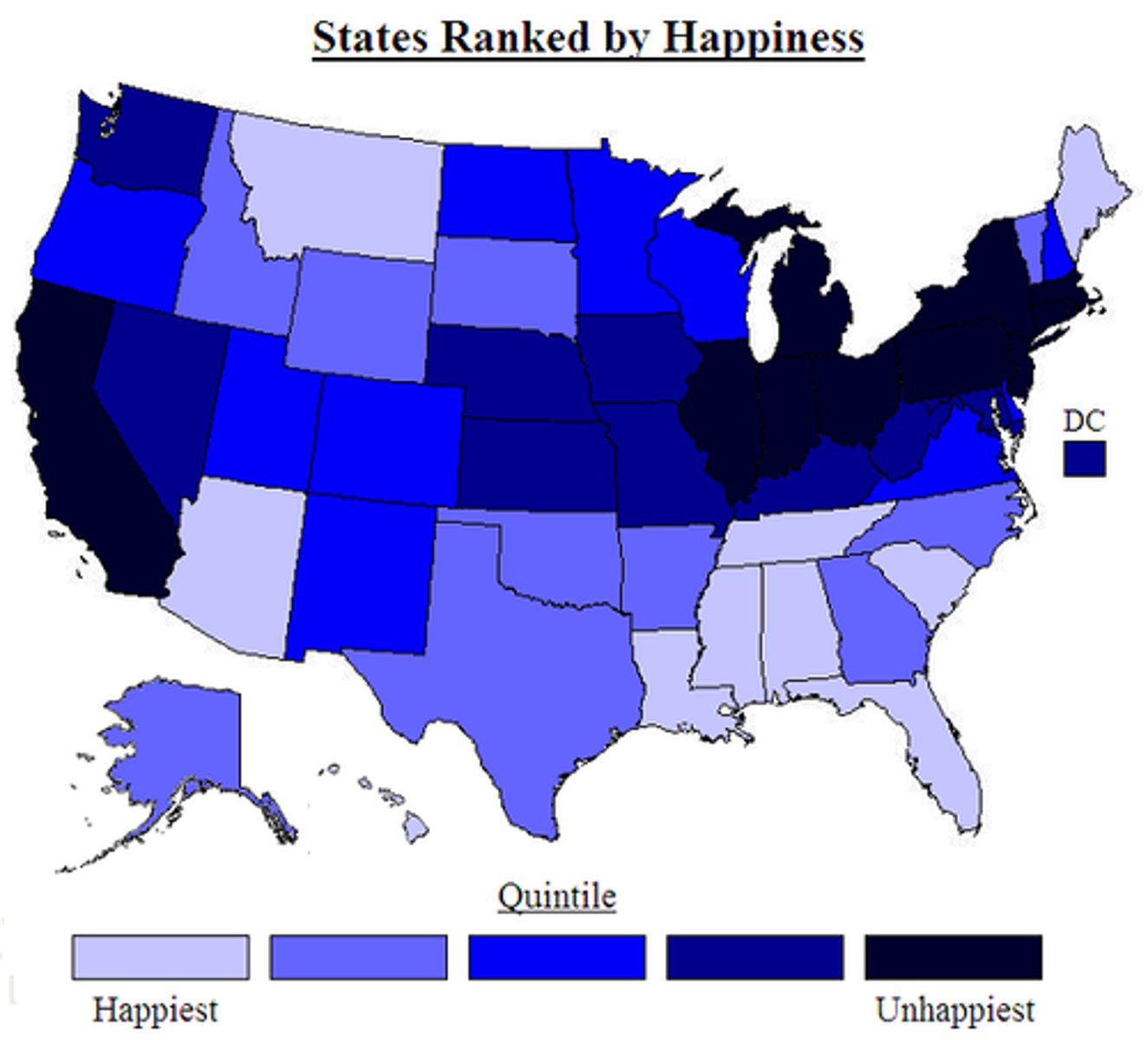
Population Distribution
The way in which people are spread across a given area.
Uniform Population Distribution
A pattern where individuals are evenly spaced across an area.
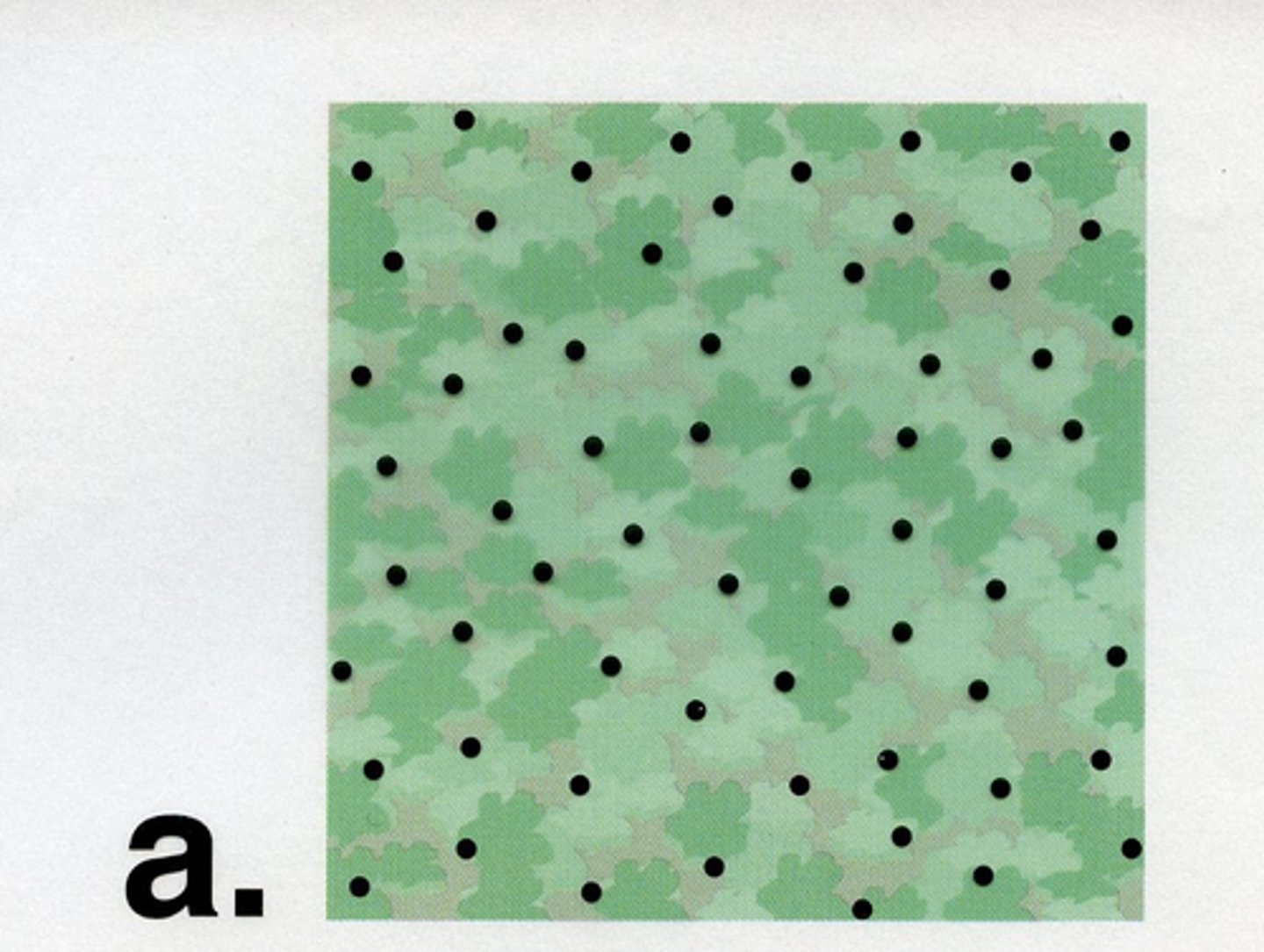
Clustered Population Distribution
A pattern where individuals are grouped closely together.
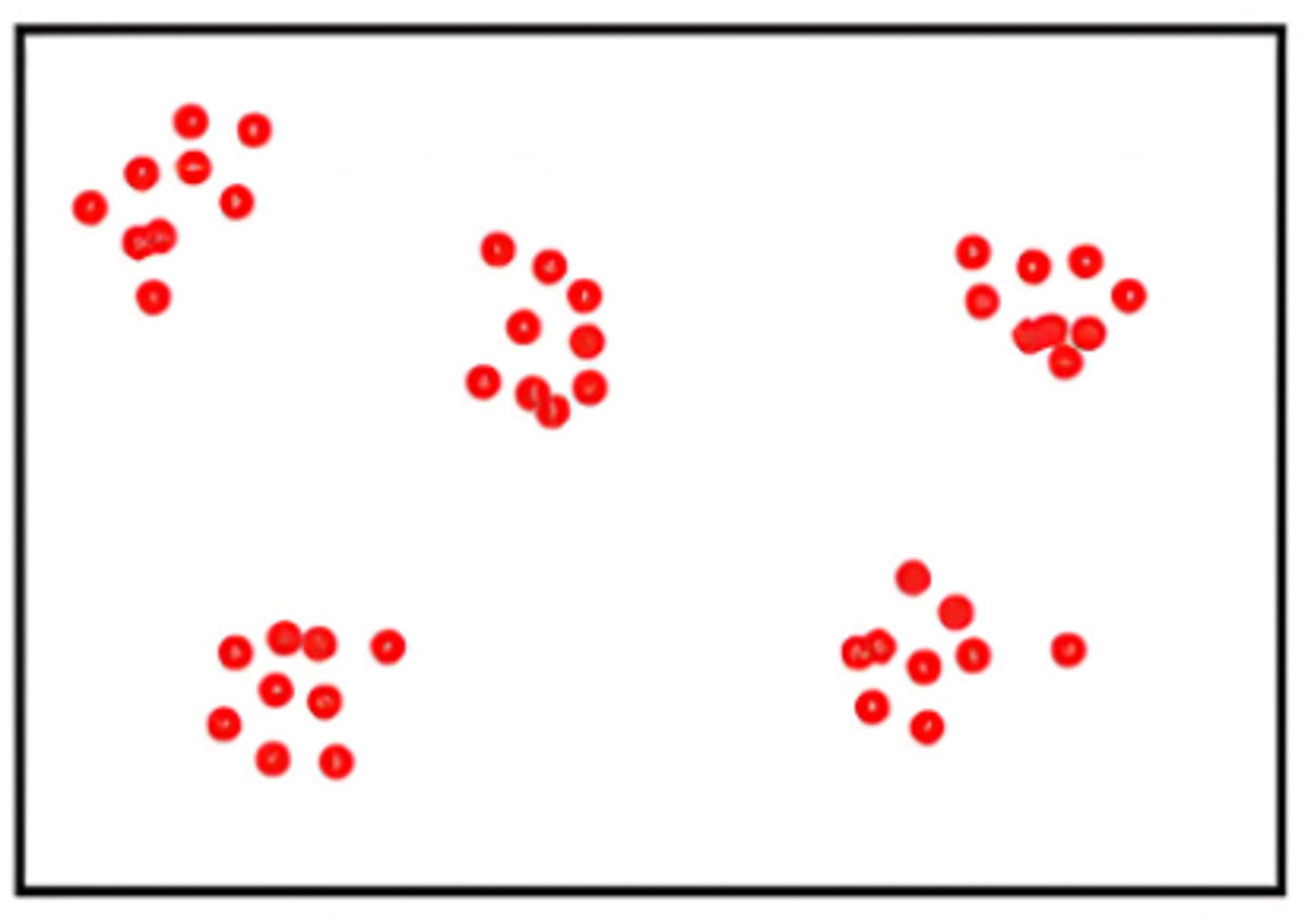
Linear Population Distribution
A pattern where individuals are arranged in a line, often along a resource or transportation route.
Random Population Distribution
A pattern where individuals are spread without a predictable pattern.
Physical Factors in Human Settlement
Natural features such as climate and landforms that influence where people live.
Climate
The long-term average of weather conditions in a particular area.
Temperate Climate
A climate characterized by mild temperatures and moderate precipitation.
Human Migration
The movement of people from one place to another with the intention of settling temporarily or permanently.
Population Density
The number of people occupying a unit of land
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land.
Arable Land
Land suitable for growing crops.
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely.
Dependency Ratio
The ratio of the dependent population (those not in the labor force) to the working-age population.
Sex Ratio
The ratio of males to females in a population.
Demographics
Statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.
Fertility
The natural capability to produce offspring.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births per 1,000 people in a population per year.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman would have during her lifetime based on current birth rates.
Mortality
The incidence of death in a population.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population per year.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The number of deaths of infants under one year old per 1,000 live births.
Life Expectancy
The average period that a person may expect to live.
Population Pyramids
Graphical representations of the age and sex distribution of a population.
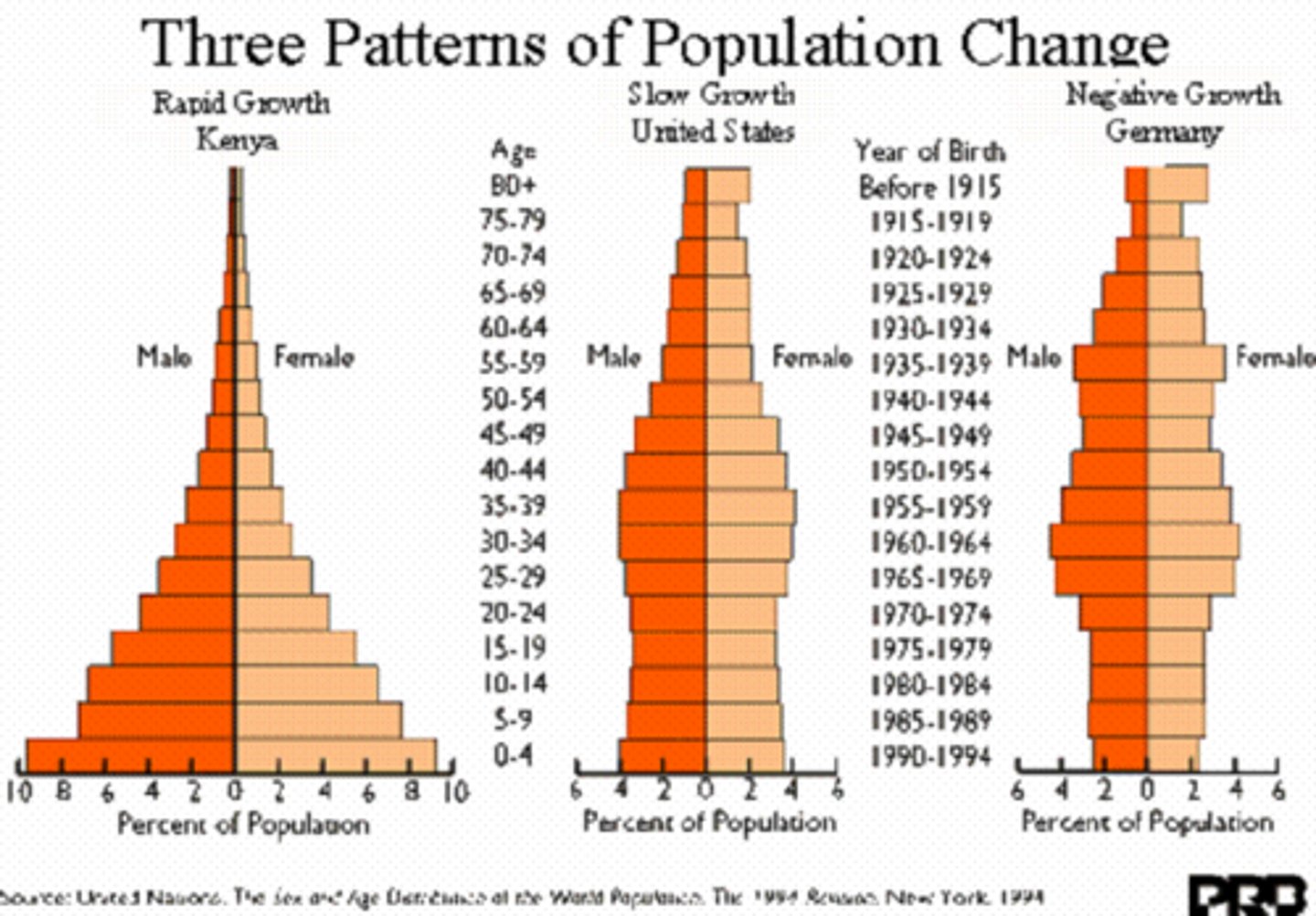
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The difference between the number of live births and the number of deaths in a population.
Doubling Time
The period of time required for a quantity to double in size or value.
Urbanization
The increasing number of people that live in urban areas.
Malthus's Theory of Population Growth
The theory that population growth will outpace food production, leading to famine and conflict.
Overpopulation
A situation where the number of people exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life.
Neo-Malthusian
A modern adaptation of Malthus's theory, emphasizing the need for population control.
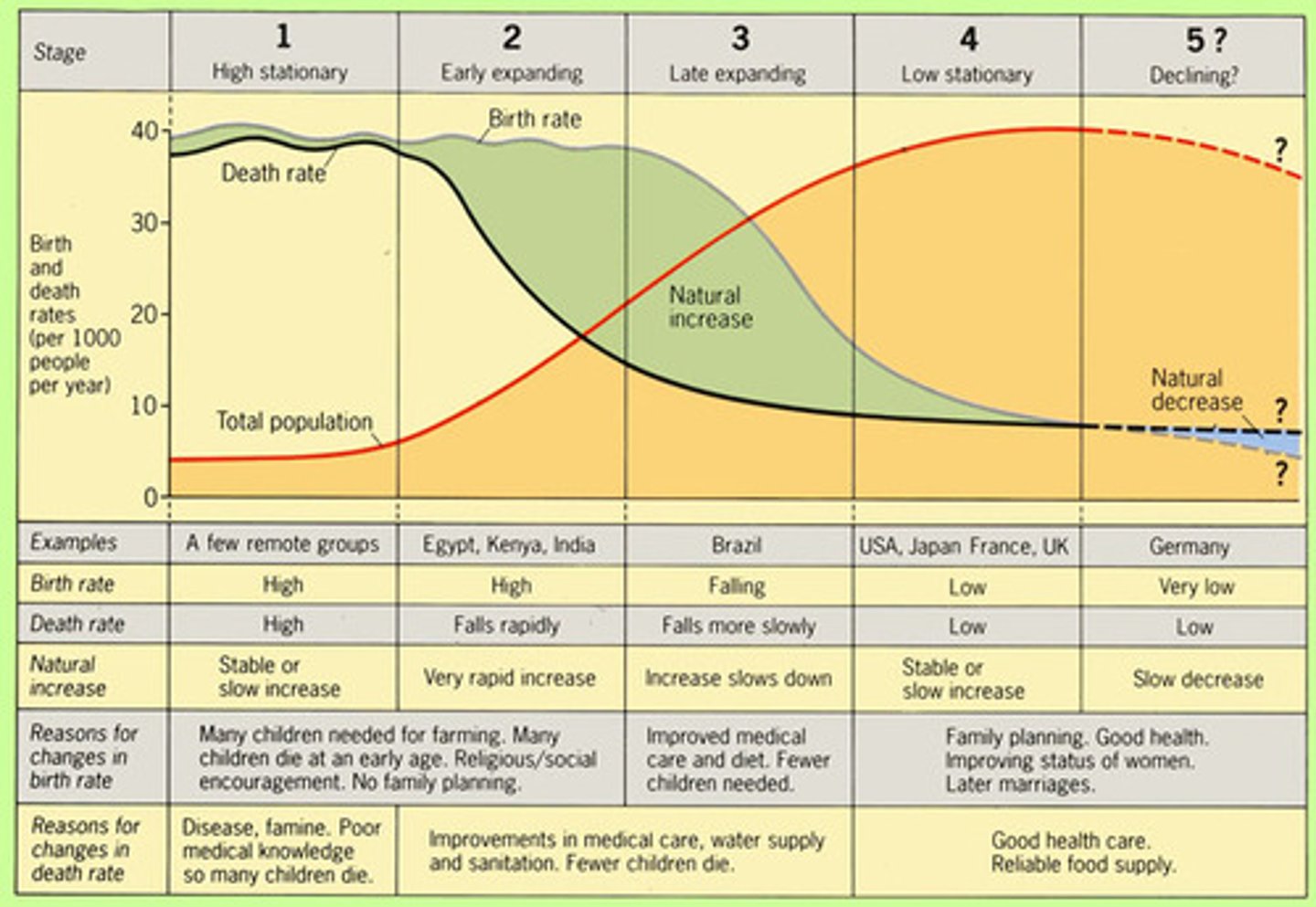
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
A model that describes the stages a country goes through as it transitions from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates.
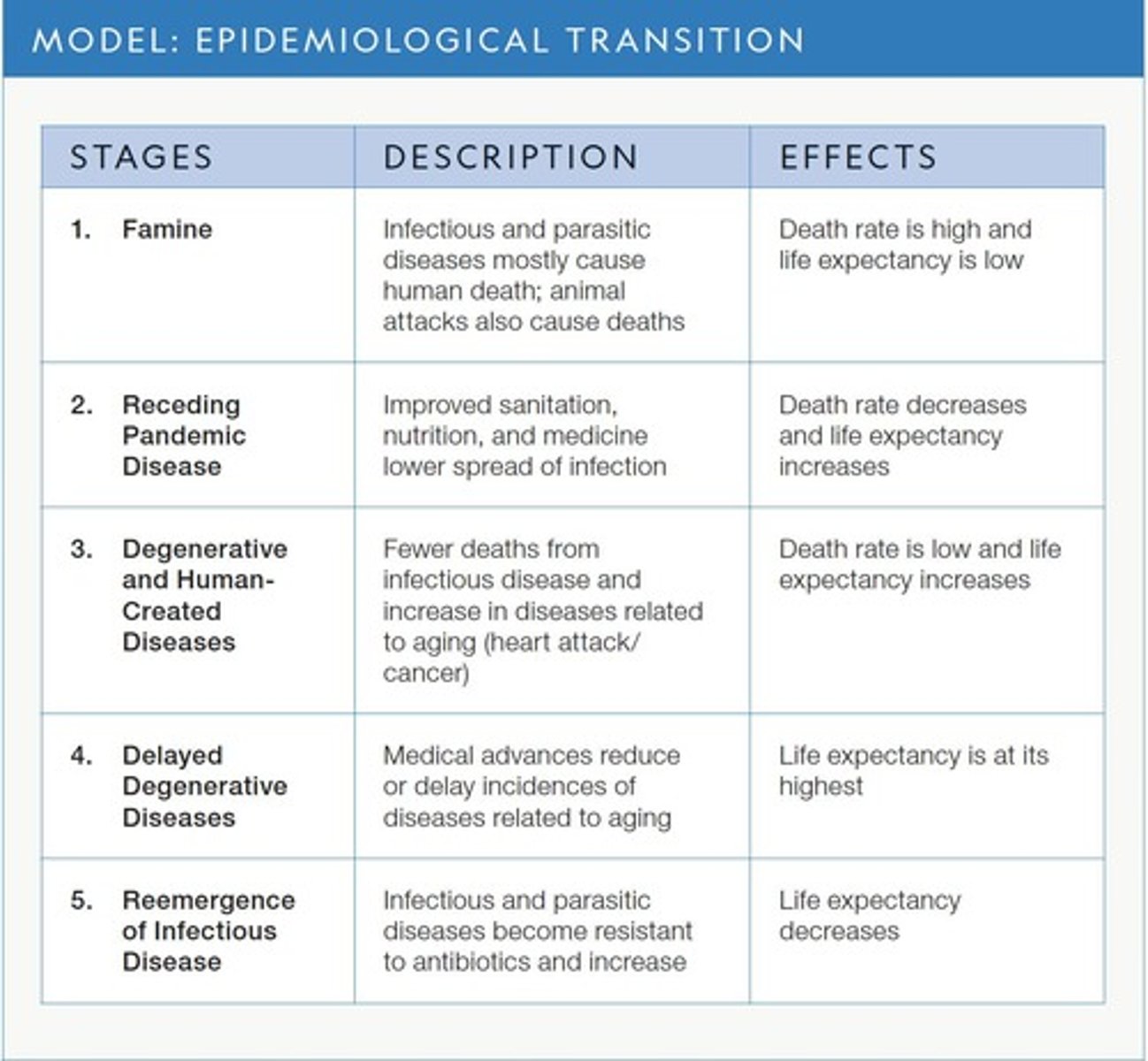
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM)
A model that describes the changes in population health and mortality patterns as a country develops.
Antinatalist
Policies or beliefs that discourage population growth.
Pronatalist
Policies or beliefs that encourage population growth.
Land Degradation
long-term damage to the soil's ability to support life
Mobility
All types of movement from one location to another.