Science Term1-2
1/78
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Wire
Allows a path for current flow.
Resistor
An electrical device that resists the flow of electrical current.
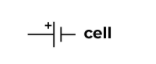
Battery (Single cell)
The power source of a circuit with a single cell.
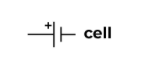
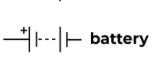
Battery (two cells in a series)
The power source of a circuit with two cells.
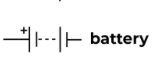
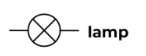
Light Globe
Generates light when current flows through.
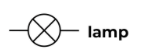
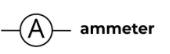
Ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit.
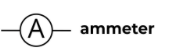
Voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference.
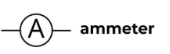

Switch closed
Provides a path for the current to flow when closed.

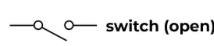
Switch open
Current flow is stopped when the switch is open.
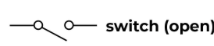
Diode
A component that only allows current to flow in one direction

Ohm's law states that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage/potential difference.
R
Represents resistance and its unit is the ohm (Ω) R= V (voltage) ÷I (current)
V
Is the voltage drop in volts.
I
Is the electric current in ampheres (A).
V= IxR
I= V÷R R=V÷I
Ohm’s law in series
Current through the circuit is always the same.
Voltage through the circuit is divided amongst the components of the circuit.
The total resistance is the sum of the resistance of all the components.
Ohms law in parallel
Current is divided amongst the different branches in the circuit.
◦Voltage across the branches are the same.
Magnets
Magnets attract iron and alloys containing iron. They also attract alloys containing nickel and cobalt.
All magnets, no matter what their shape, have a north pole and a south pole.
Like poles of magnets repel while unlike poles attract.
Permanent magnets retain their magnetism at all times.
Temporary magnets lose their magnetism when removed from other magnets.
Magnetic field
The region in which a magnetic force exists is called a magnetic field.
Resistor
Resistors are used in electric circuits to control the voltage and current. They can have a fixed resistance or can be variable like those in volume controls.
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is used to measure the voltage gain across the terminals of a power supply or voltage drop across parts of an electric circuit.
Random eror
Random error is an error that occurs due to estimation when reading scales, or when the quantity being measured changes randomly.
Systematic error
Systematic error is consistently high or low due to the incorrect use or limitations of equipment.
Systematic errors can be eliminated by knowing how to use the equipment correctly.
Compass
The compass needle sings toward the geographical north pole or the magnetic south pole.
A compass works the way it does because Earth has a magnetic field that looks a lot like the one in a magnet.
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet consisting of a coil of wire and an iron core.
The coil of wire is called a solenoid, when the electric current flows in the coil, a magnetic field is produced.
Without the iron core, a magnetic field would still be created. However, it would not be as strong.
Static Electricity
Static electricity is generated by friction between two insulating materials. When the materials are rubbed together, electrons are removed from atoms within the materials, giving rise to a static electric charge.
Static electric shock
Static electricity occurs more often during the colder seasons because the air is drier, and it’s easier to build up electrons on the skin’s surface.
AC Current (Alternating current)
Electric current flows in two ways as an alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
Electrons keep switching directions, going forward and then backwards in AC.
DC Current (Direct current)
Electric current flows in two ways as an alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
In DC, the electrons flow steadily in a single direction.
Physical Change
Change in shape, size, appearance or state.
Chemical Change
When a new substance is created.
Reactants
The original substances in a chemical reaction are called the reactants.
Products
The new substances that are formed during a chemical reaction are called the products.
Word Equations
Reactant + reactant --> product + product
eg. Iron reacts with flourine gas to produce iron flouride.
During a chemical reaction…
During a chemical reaction atoms are rearranged and mass is conserved.
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, the mass of the reactants before the reaction needs to equal the mass of the products after the reaction. This applies to the number of atoms as well. The number of atoms before a reaction need to equal the number of atoms after the reaction.
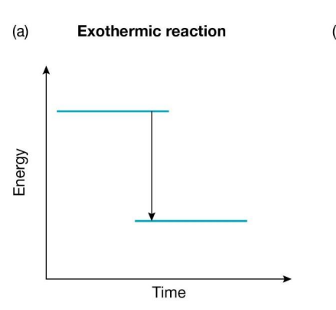
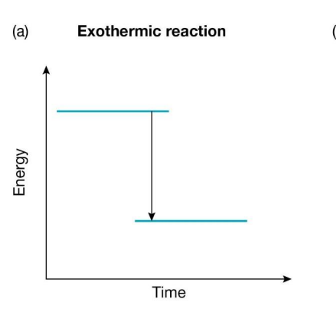
Exothermic Reaction
Chemical reactions that release energy are called exothermic reactions.
The energy released comes from the rearrangement of atoms. There is l
ess energy stored in the chemical bonds in the products than there was in the reactants.
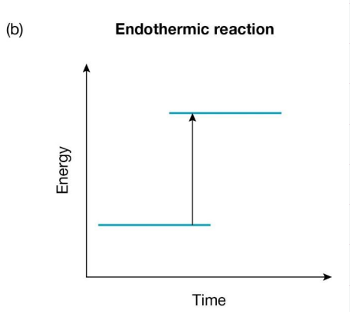
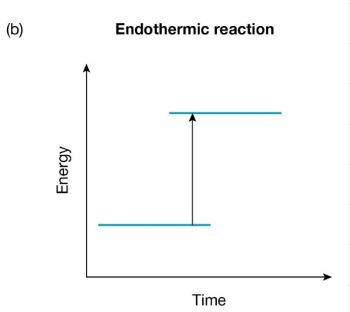
Endothermic Reaction
Chemical reactions in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings are called endothermic reactions.
There is more energy ‘stored’ in the chemical bonds of the products than there was in the reactants.
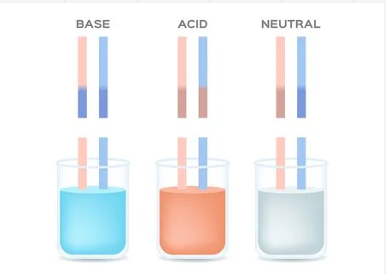
Acids
Sour tasting, corrosive (eats away solid objects), turns litmus paper red, turns bromothymol blue yellow.
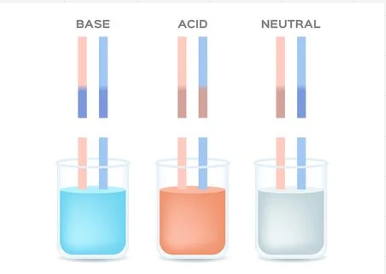
Bases
Bitter tasting, feels soapy or slippery, can be corrosive and breaks down fat. Bases turn litmus paper blue and bromothymol blue a bluish-purple.
Alkali
Bases that can dissolve in water.
Red Cabbage
Red Cabbage is a natural pH indicator.
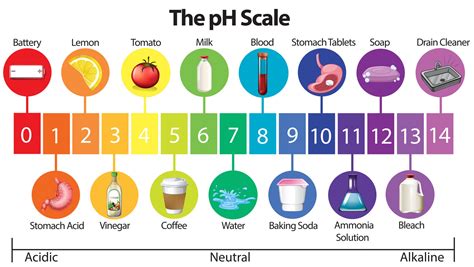
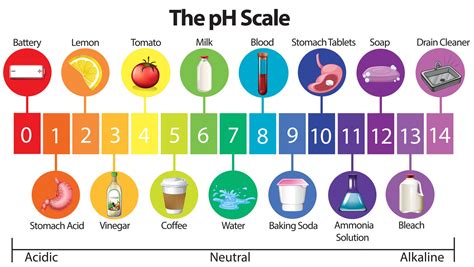
The pH scale
The pH scale ranges from 1-14. <7 is acidic and >7 is basic. At pH 7, a substance is said to be neutral. Acids and bases can be graded from strong to weak. For example, a strong acid has a very low pH (pH 0 or 1) and a strong base has a very high pH (pH 13 or 14).
Universal Indicator
The pH of a substance can be measured using a pH meter or a special indicator called universal indicator. Universal indicator is a mixture of indicators and it changes colour as the strength of an acid or base changes.
Neutralisation Reaction
Acid + base → salt + water, neutralisation a reaction between an acid and a base. A salt and water (a neutral liquid) are the products of this type of reaction. To neutralise something means to stop something from having an effect.
Indigestion
The hydrochloric acid in your stomach helps to break down the food you eat. It is a very strong acid, with a pH of less than 1.5.
Indigestion 2
But if you eat too quickly, or eat too much of the wrong food, the contents of your stomach become even more acidic. You feel a burning sensation because of the corrosive properties of the acid.
Antacid Tablets
Antacid tablets contain weak bases like aluminium hydroxide, magnesium carbonate, and magnesium hydroxide to neutralize stomach acid. Examples of chemical word equations:
hydrochloric acid + aluminium hydroxide → aluminium chloride + water
hydrochloric acid + magnesium hydroxide → magnesium chloride + water
hydrochloric acid + magnesium carbonate → magnesium chloride + water + carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide
One product of this last reaction is carbon dioxide gas. You burp to get the gas out of your stomach.
The Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.